bd4b4d8bb2e53f8c467015e92324cc69.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Country Progress Report LAO PDR The ninth Technical Advisory Group and National TB Programme Managers meeting for TB control in the Western Pacific Region Manila, Philippines 9 -12 December 2014
Country Progress Report LAO PDR The ninth Technical Advisory Group and National TB Programme Managers meeting for TB control in the Western Pacific Region Manila, Philippines 9 -12 December 2014
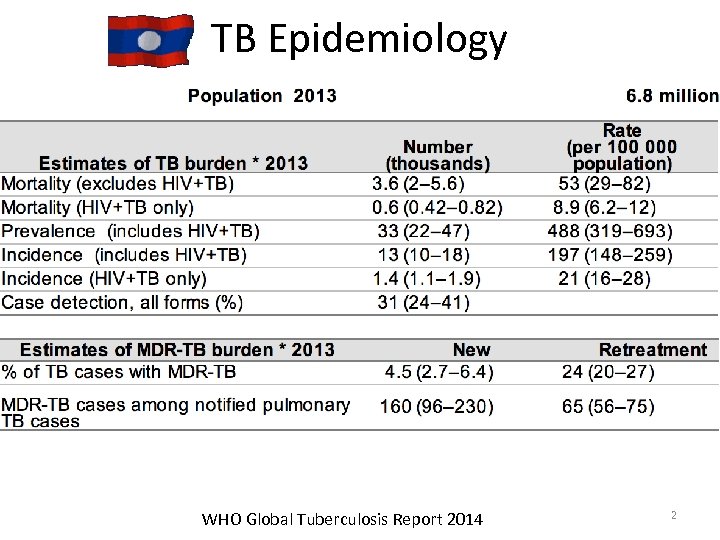 TB Epidemiology WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2014 2
TB Epidemiology WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2014 2
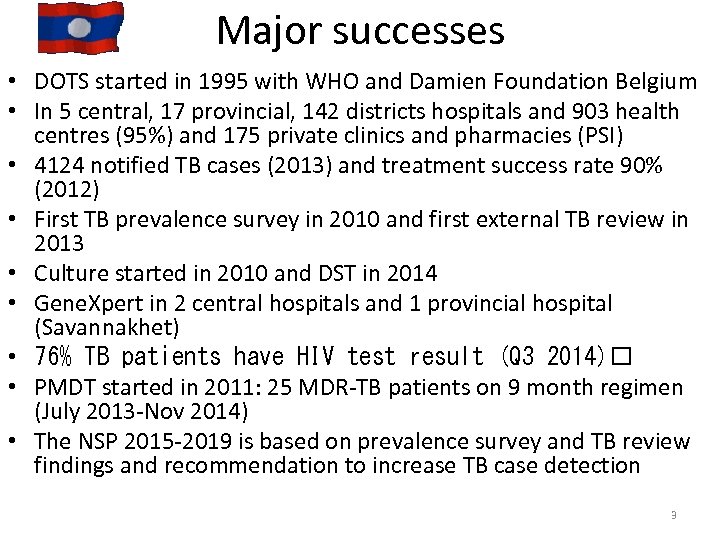 Major successes • DOTS started in 1995 with WHO and Damien Foundation Belgium • In 5 central, 17 provincial, 142 districts hospitals and 903 health centres (95%) and 175 private clinics and pharmacies (PSI) • 4124 notified TB cases (2013) and treatment success rate 90% (2012) • First TB prevalence survey in 2010 and first external TB review in 2013 • Culture started in 2010 and DST in 2014 • Gene. Xpert in 2 central hospitals and 1 provincial hospital (Savannakhet) • 76% TB patients have HIV test result (Q 3 2014) • PMDT started in 2011: 25 MDR-TB patients on 9 month regimen (July 2013 -Nov 2014) • The NSP 2015 -2019 is based on prevalence survey and TB review findings and recommendation to increase TB case detection 3
Major successes • DOTS started in 1995 with WHO and Damien Foundation Belgium • In 5 central, 17 provincial, 142 districts hospitals and 903 health centres (95%) and 175 private clinics and pharmacies (PSI) • 4124 notified TB cases (2013) and treatment success rate 90% (2012) • First TB prevalence survey in 2010 and first external TB review in 2013 • Culture started in 2010 and DST in 2014 • Gene. Xpert in 2 central hospitals and 1 provincial hospital (Savannakhet) • 76% TB patients have HIV test result (Q 3 2014) • PMDT started in 2011: 25 MDR-TB patients on 9 month regimen (July 2013 -Nov 2014) • The NSP 2015 -2019 is based on prevalence survey and TB review findings and recommendation to increase TB case detection 3
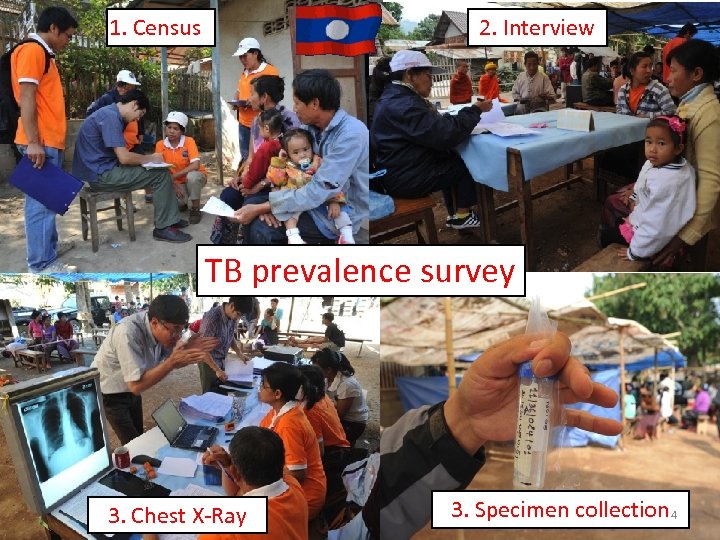 1. Census 2. Interview TB prevalence survey 3. Chest X-Ray 3. Specimen collection 4
1. Census 2. Interview TB prevalence survey 3. Chest X-Ray 3. Specimen collection 4
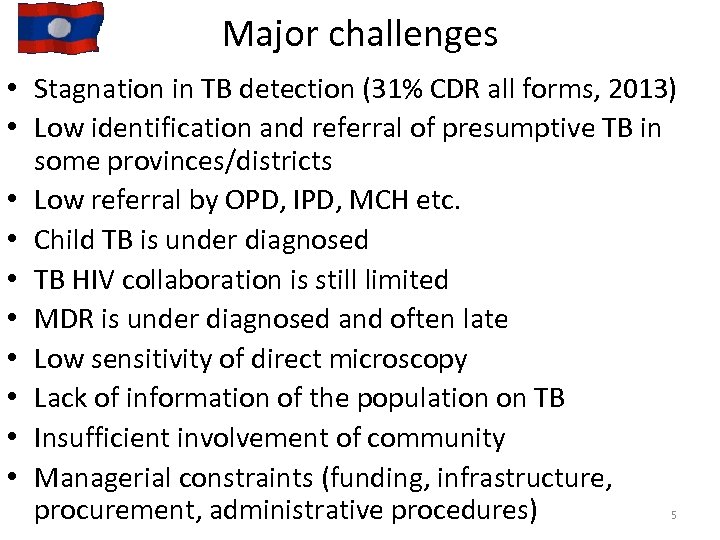 Major challenges • Stagnation in TB detection (31% CDR all forms, 2013) • Low identification and referral of presumptive TB in some provinces/districts • Low referral by OPD, IPD, MCH etc. • Child TB is under diagnosed • TB HIV collaboration is still limited • MDR is under diagnosed and often late • Low sensitivity of direct microscopy • Lack of information of the population on TB • Insufficient involvement of community • Managerial constraints (funding, infrastructure, procurement, administrative procedures) 5
Major challenges • Stagnation in TB detection (31% CDR all forms, 2013) • Low identification and referral of presumptive TB in some provinces/districts • Low referral by OPD, IPD, MCH etc. • Child TB is under diagnosed • TB HIV collaboration is still limited • MDR is under diagnosed and often late • Low sensitivity of direct microscopy • Lack of information of the population on TB • Insufficient involvement of community • Managerial constraints (funding, infrastructure, procurement, administrative procedures) 5
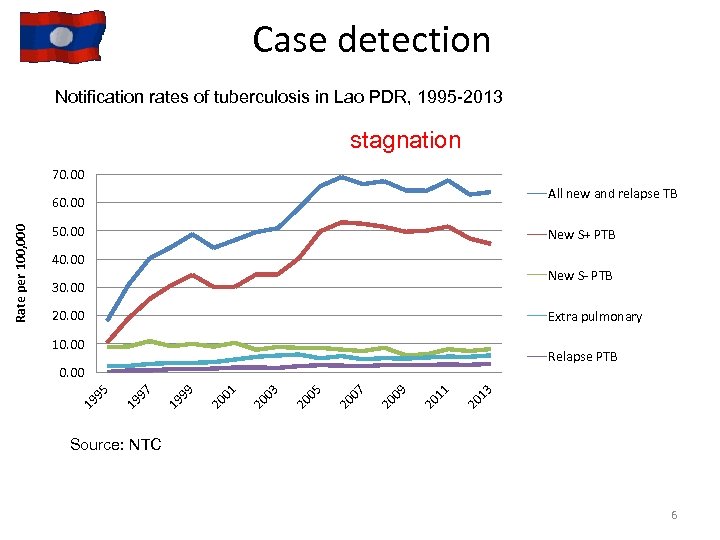 Case detection Notification rates of tuberculosis in Lao PDR, 1995 -2013 stagnation 70. 00 All new and relapse TB 50. 00 New S+ PTB 40. 00 New S- PTB 30. 00 20. 00 Extra pulmonary 10. 00 Relapse PTB 13 20 11 20 09 20 07 20 05 20 03 20 01 20 99 19 97 19 95 0. 00 19 Rate per 100, 000 60. 00 Source: NTC 6
Case detection Notification rates of tuberculosis in Lao PDR, 1995 -2013 stagnation 70. 00 All new and relapse TB 50. 00 New S+ PTB 40. 00 New S- PTB 30. 00 20. 00 Extra pulmonary 10. 00 Relapse PTB 13 20 11 20 09 20 07 20 05 20 03 20 01 20 99 19 97 19 95 0. 00 19 Rate per 100, 000 60. 00 Source: NTC 6
 National TB Strategic Plan 2015 -2019 • Aligned with National Health Sector Plan • Budgeted • Funded mostly by Global Fund (NFM request for 2015 -2017) and other partners (WHO, DFB, USAID): • LAO PDR NTP will be member of the Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance Vision: zero deaths, disease and suffering due to TB Goal: To reduce TB burden and to reach the targets of WHO Post-2015 Global Tuberculosis Strategy (adopted by 67 th World Health Assembly 2014 on 19 May 2014) Specific target: Increase TB case detection rate (CDR) from 31% in 2013 to 70% in 2019 Objectives: • Integrated patient centred TB care and prevention • Strengthening TB-HIV collaborative activities • Managing drug resistant tuberculosis (PMDT) • Improved management 7
National TB Strategic Plan 2015 -2019 • Aligned with National Health Sector Plan • Budgeted • Funded mostly by Global Fund (NFM request for 2015 -2017) and other partners (WHO, DFB, USAID): • LAO PDR NTP will be member of the Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance Vision: zero deaths, disease and suffering due to TB Goal: To reduce TB burden and to reach the targets of WHO Post-2015 Global Tuberculosis Strategy (adopted by 67 th World Health Assembly 2014 on 19 May 2014) Specific target: Increase TB case detection rate (CDR) from 31% in 2013 to 70% in 2019 Objectives: • Integrated patient centred TB care and prevention • Strengthening TB-HIV collaborative activities • Managing drug resistant tuberculosis (PMDT) • Improved management 7
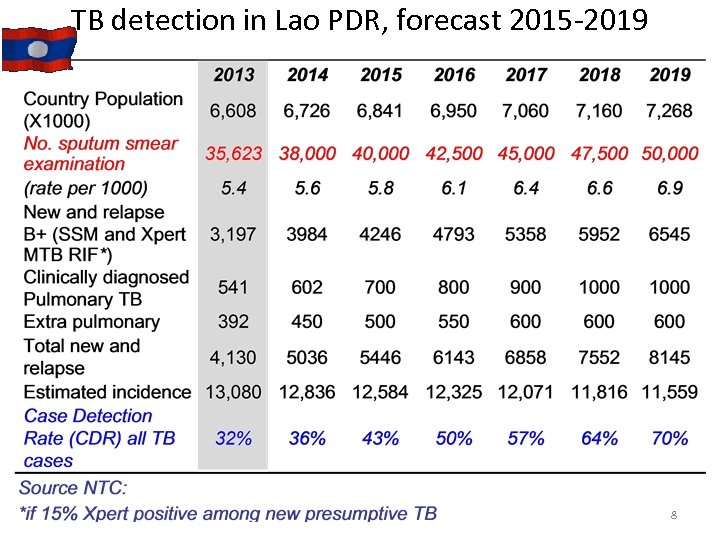 TB detection in Lao PDR, forecast 2015 -2019 8
TB detection in Lao PDR, forecast 2015 -2019 8
 Laboratory strengthening • LED: not significant advantage compared to ZN in Lao context of low work load • Xpert MTB/RIF: 30% yield compared to microscopy (as a first test, NRL April-Nov 2014) • Gene. Xpert scaling-up: cumulative 10 in 2014 (being procured), 15 in 2015, 20 in 2016 • EQA microscopy since 2004, • QA Culture and DST with KIT as SRL • Laboratory information management system • TA partners: WHO, Stop TB partnership, KIT, Merieux Foundation 9
Laboratory strengthening • LED: not significant advantage compared to ZN in Lao context of low work load • Xpert MTB/RIF: 30% yield compared to microscopy (as a first test, NRL April-Nov 2014) • Gene. Xpert scaling-up: cumulative 10 in 2014 (being procured), 15 in 2015, 20 in 2016 • EQA microscopy since 2004, • QA Culture and DST with KIT as SRL • Laboratory information management system • TA partners: WHO, Stop TB partnership, KIT, Merieux Foundation 9
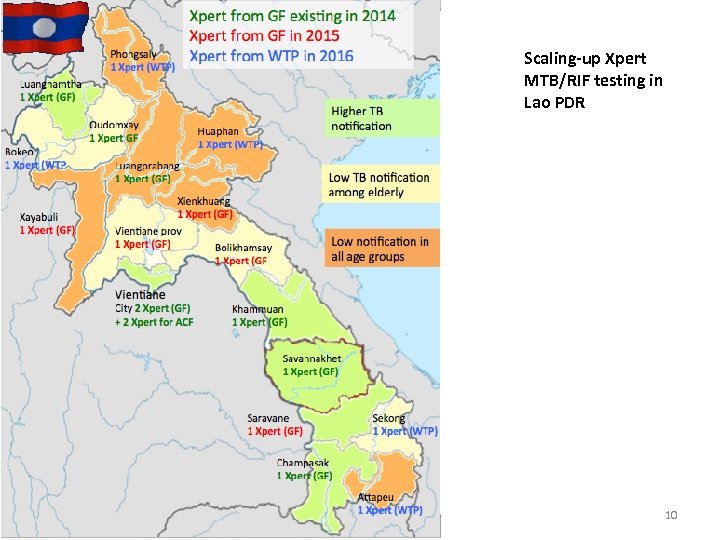 Scaling-up Xpert MTB/RIF testing in Lao PDR 10
Scaling-up Xpert MTB/RIF testing in Lao PDR 10
 Reach the unreached: intensive case finding • Engaging all health providers in public (OPDs, IPDs, MCH, ANC etc. and private sector) at all levels of the PHC • ICF among house hold TB contacts including children, PLWH, prisoners, mine workers, mobile population, factories, patient with diabetes and other co-morbidities, • ACF mobile camps in high prevalence areas (with CXR and Gene. Xpert) • Diagnosis and treatment of child-TB • Identify and refer all presumptive TB patients to the TB unit or to the TB laboratory • Support health centres (training, supervision, budget for transportation of specimens) • Advocate to local authority, chiefs of villages, village health committees to involve in TB control activities • Use NGOs/CBOs (LYU, LOPHA, MAAP, PEDA, PSI) 11
Reach the unreached: intensive case finding • Engaging all health providers in public (OPDs, IPDs, MCH, ANC etc. and private sector) at all levels of the PHC • ICF among house hold TB contacts including children, PLWH, prisoners, mine workers, mobile population, factories, patient with diabetes and other co-morbidities, • ACF mobile camps in high prevalence areas (with CXR and Gene. Xpert) • Diagnosis and treatment of child-TB • Identify and refer all presumptive TB patients to the TB unit or to the TB laboratory • Support health centres (training, supervision, budget for transportation of specimens) • Advocate to local authority, chiefs of villages, village health committees to involve in TB control activities • Use NGOs/CBOs (LYU, LOPHA, MAAP, PEDA, PSI) 11
 Patient centred care: involvement of patients and civil society • All stakeholders, public sector, donors, partners, NGOs/CBOs, key affected population and patients representatives provided their input in situation analysis, NSP elaboration and country dialogue (workshops) • TB technical working group (TWG) includes NGOs/CBOs and partners • NGOs/CBOs conduct joint need assessment surveys with local authorities to identify at risk population and explore gaps and barriers in accessing TB services • NGOs/CBOs mobilize village health committees, chiefs of villages and villagers for TB case detection and sending patients/specimens in relation with the health centres and to participate in ACF campaigns • NTP supports specimen transportation from health centres to TB laboratory 12
Patient centred care: involvement of patients and civil society • All stakeholders, public sector, donors, partners, NGOs/CBOs, key affected population and patients representatives provided their input in situation analysis, NSP elaboration and country dialogue (workshops) • TB technical working group (TWG) includes NGOs/CBOs and partners • NGOs/CBOs conduct joint need assessment surveys with local authorities to identify at risk population and explore gaps and barriers in accessing TB services • NGOs/CBOs mobilize village health committees, chiefs of villages and villagers for TB case detection and sending patients/specimens in relation with the health centres and to participate in ACF campaigns • NTP supports specimen transportation from health centres to TB laboratory 12
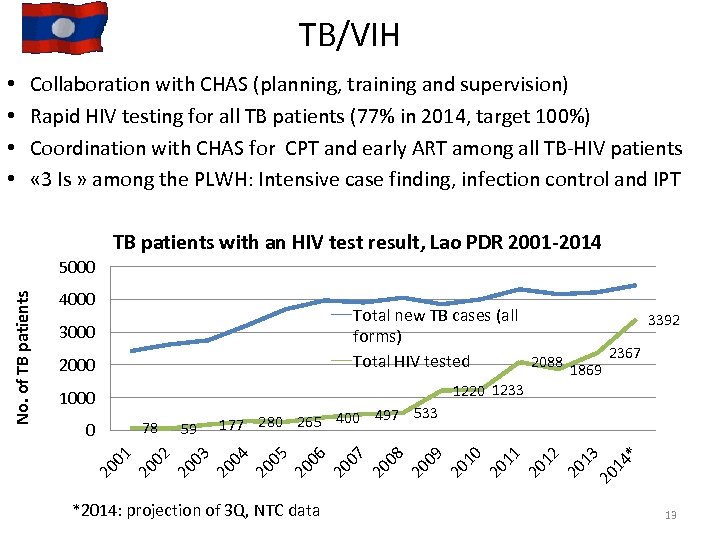 TB/VIH • • Collaboration with CHAS (planning, training and supervision) Rapid HIV testing for all TB patients (77% in 2014, target 100%) Coordination with CHAS for CPT and early ART among all TB-HIV patients « 3 Is » among the PLWH: Intensive case finding, infection control and IPT TB patients with an HIV test result, Lao PDR 2001 -2014 4000 Total new TB cases (all 3392 forms) 2367 Total HIV tested 2088 1869 3000 2000 1220 1233 1000 *2014: projection of 3 Q, NTC data * 14 20 13 20 12 20 11 20 10 20 09 20 08 20 07 20 06 20 05 20 20 20 03 59 02 20 01 497 533 177 280 265 400 04 78 0 20 No. of TB patients 5000 13
TB/VIH • • Collaboration with CHAS (planning, training and supervision) Rapid HIV testing for all TB patients (77% in 2014, target 100%) Coordination with CHAS for CPT and early ART among all TB-HIV patients « 3 Is » among the PLWH: Intensive case finding, infection control and IPT TB patients with an HIV test result, Lao PDR 2001 -2014 4000 Total new TB cases (all 3392 forms) 2367 Total HIV tested 2088 1869 3000 2000 1220 1233 1000 *2014: projection of 3 Q, NTC data * 14 20 13 20 12 20 11 20 10 20 09 20 08 20 07 20 06 20 05 20 20 20 03 59 02 20 01 497 533 177 280 265 400 04 78 0 20 No. of TB patients 5000 13
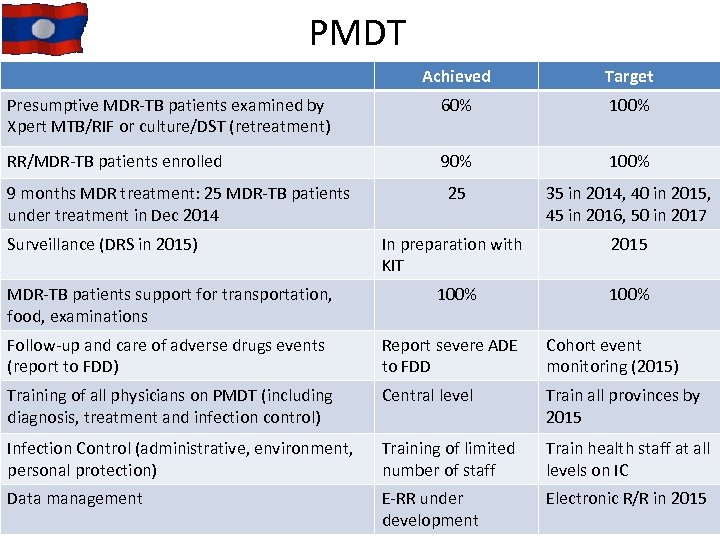 PMDT Achieved Target Presumptive MDR-TB patients examined by Xpert MTB/RIF or culture/DST (retreatment) 60% 100% RR/MDR-TB patients enrolled 90% 100% 25 35 in 2014, 40 in 2015, 45 in 2016, 50 in 2017 In preparation with KIT 2015 MDR-TB patients support for transportation, food, examinations 100% Follow-up and care of adverse drugs events (report to FDD) Report severe ADE to FDD Cohort event monitoring (2015) Training of all physicians on PMDT (including diagnosis, treatment and infection control) Central level Train all provinces by 2015 Infection Control (administrative, environment, personal protection) Training of limited number of staff Train health staff at all levels on IC Data management E-RR under development Electronic R/R in 2015 9 months MDR treatment: 25 MDR-TB patients under treatment in Dec 2014 Surveillance (DRS in 2015) 14
PMDT Achieved Target Presumptive MDR-TB patients examined by Xpert MTB/RIF or culture/DST (retreatment) 60% 100% RR/MDR-TB patients enrolled 90% 100% 25 35 in 2014, 40 in 2015, 45 in 2016, 50 in 2017 In preparation with KIT 2015 MDR-TB patients support for transportation, food, examinations 100% Follow-up and care of adverse drugs events (report to FDD) Report severe ADE to FDD Cohort event monitoring (2015) Training of all physicians on PMDT (including diagnosis, treatment and infection control) Central level Train all provinces by 2015 Infection Control (administrative, environment, personal protection) Training of limited number of staff Train health staff at all levels on IC Data management E-RR under development Electronic R/R in 2015 9 months MDR treatment: 25 MDR-TB patients under treatment in Dec 2014 Surveillance (DRS in 2015) 14
 Surveillance • Quality of surveillance system: EQA microscopy established since 2004 • QA culture and DST with KIT • DRS to be conducted in 2015 • New case definition rolled out in new national TB guidelines 3 rd edition (2014) • e-R&R: under development for MDR-TB • Analysis and usage of data at national and sub-national levels: briefing and debriefing meeting of NTP supervisors • LAO PDR NTP will become member of the Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance (cross-border information and collaboration on TB control) 15
Surveillance • Quality of surveillance system: EQA microscopy established since 2004 • QA culture and DST with KIT • DRS to be conducted in 2015 • New case definition rolled out in new national TB guidelines 3 rd edition (2014) • e-R&R: under development for MDR-TB • Analysis and usage of data at national and sub-national levels: briefing and debriefing meeting of NTP supervisors • LAO PDR NTP will become member of the Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance (cross-border information and collaboration on TB control) 15
 Policies and supportive systems • TB care financing and social protection: – social protection is limited to only 10 -15% of the population • Strengthening notification mechanism: – Training all physicians and nurses in TB wards, OPD, IPD in public and private hospitals, in health centres, village health volunteers (VHV) and village health workers (VHW), private clinics and pharmacists – paper based RR system to be upgraded to electronic RR • Drug regulations: – No change since drug regulation meeting in March 2014 16
Policies and supportive systems • TB care financing and social protection: – social protection is limited to only 10 -15% of the population • Strengthening notification mechanism: – Training all physicians and nurses in TB wards, OPD, IPD in public and private hospitals, in health centres, village health volunteers (VHV) and village health workers (VHW), private clinics and pharmacists – paper based RR system to be upgraded to electronic RR • Drug regulations: – No change since drug regulation meeting in March 2014 16
 Management • • Supervising all levels (central, province, district hospitals and health centre) and visit TB patients Improving communication, reporting and feed back (web based R/R) Train staff of all levels on administration, finances and reporting Ensure procurement, maintenance, logistic and storage 17
Management • • Supervising all levels (central, province, district hospitals and health centre) and visit TB patients Improving communication, reporting and feed back (web based R/R) Train staff of all levels on administration, finances and reporting Ensure procurement, maintenance, logistic and storage 17
 Partners 18
Partners 18
 Thank you 19
Thank you 19


