Countable and Uncountable Nouns.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Countable and Uncountable Nouns
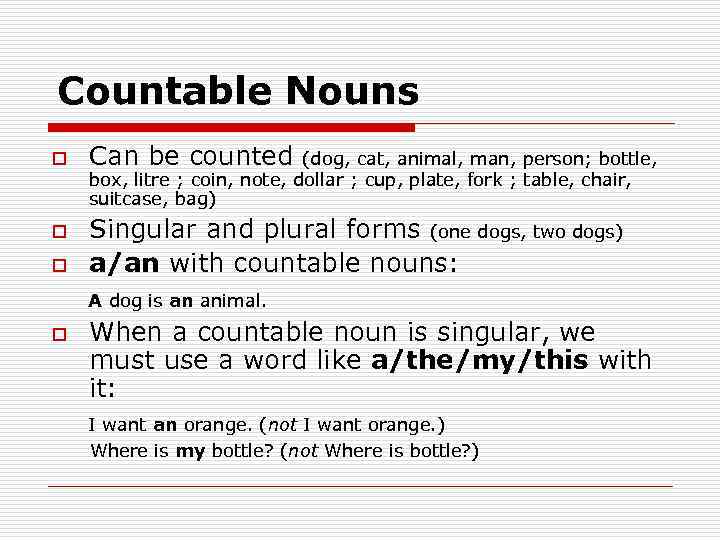
Countable Nouns o Can be counted (dog, cat, animal, man, person; bottle, box, litre ; coin, note, dollar ; cup, plate, fork ; table, chair, suitcase, bag) Singular and plural forms (one dogs, two dogs) o a/an with countable nouns: A dog is an animal. o When a countable noun is singular, we must use a word like a/the/my/this with it: I want an orange. (not I want orange. ) o Where is my bottle? (not Where is bottle? )

Countable Nouns When a countable noun is plural, we can use it alone: I like oranges. Bottles can break. o

Uncountable Nouns o o § § § Cannot be counted Cannot be divided into separate elements. Examples: music, art, love, happiness advice, information, news furniture, luggage rice, sugar, butter, water electricity, gas, power money, currency

Uncountable Nouns o § § We usually treat uncountable nouns as singular. We use a singular verb. For example: This news is very important. Your luggage looks heavy.

Uncountable Nouns o § § § We do not usually use the indefinite article a/an with uncountable nouns. We cannot say "an information" or "a music". But we can say a something of: a piece of news a bottle of water a grain of rice
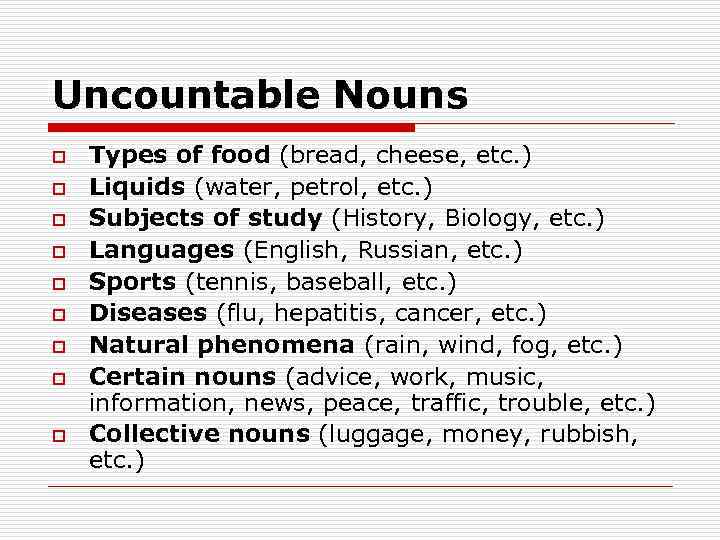
Uncountable Nouns o o o o o Types of food (bread, cheese, etc. ) Liquids (water, petrol, etc. ) Subjects of study (History, Biology, etc. ) Languages (English, Russian, etc. ) Sports (tennis, baseball, etc. ) Diseases (flu, hepatitis, cancer, etc. ) Natural phenomena (rain, wind, fog, etc. ) Certain nouns (advice, work, music, information, news, peace, traffic, trouble, etc. ) Collective nouns (luggage, money, rubbish, etc. )
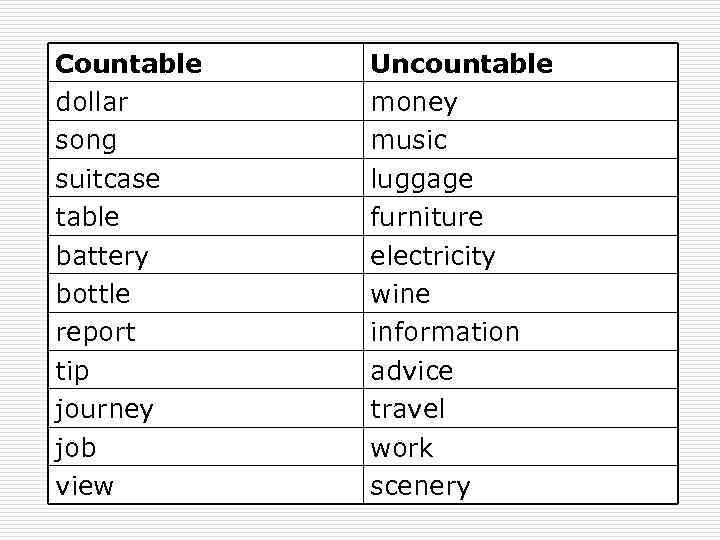
Countable dollar song suitcase table battery bottle report tip journey job view Uncountable money music luggage furniture electricity wine information advice travel work scenery

Some/Any/No

Some/Any/No o Some = a little, a few or a small number of amount Any = one, some or all No = not any… +, ? (to make an offer, a request, or when we expect a positive answer) -, ? , + -
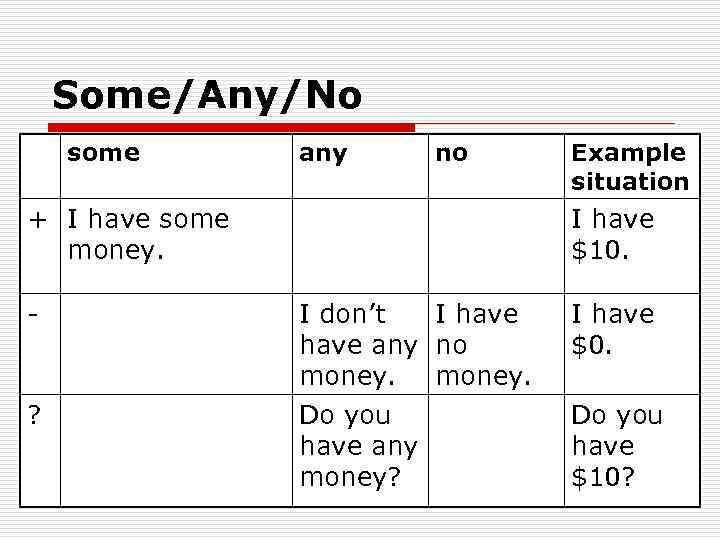
Some/Any/No some any no + I have some money. - ? Example situation I have $10. I don’t I have any no money. Do you have any money? I have $0. Do you have $10?
Much/Many

Much/Many Much is used with uncountable nouns: There isn’t much milk in the bottle. o Many is used with plural countable nouns: Do you know many people? o

Much/Many o How much and how many are used in questions. How much + uncountable noun → amount How much money have you got? § How many + countable noun → number How many photographs did you take? §

(A) few/(A) little

(A) few/(A) little Few (=not many, almost none) + plural countable noun There were few people in the park. It was nearly empty. o A few (=some but not many) + plural countable noun We’re going away for a few days. o

(A) few/(A) little A few is a positive idea: I’ve got a few friends, so I’m not lonely. (=some but not many friends) o Few is a negative idea: I’m sad and lonely. I’ve got few friends. (=nearly no friends) o

(A) few/(A) little Little (=nearly no… or nearly nothing) + uncountable noun There was little food in the fridge. It was nearly empty. o A little (=some but not much) + uncountable noun I speak a little Spanish. (=some Spanish but not much) o

(A) few/(A) little A little is a positive idea: They have a little money so they’re not poor. (=some but not much money) o Little is a negative idea: They have little money. They are very poor. (=nearly no money) o

Comparative/ Superlative Form

Comparative Form Comparative form + than (comparing two people, things, places, etc. ) I am taller than you. o

Comparative Form o Short adjectives (1 syllable) → -er Old → older Nice → nicer § Spelling: big → bigger hot → hotter § But good/well → better bad → worse far → further

Comparative Form -y adjectives (2 syllables) easy/heavy etc. → -ier easy → easier heavy →heavier o Long adjectives (2/3/4 syllables) modern (=MOD-ERN)/expensive (=EX-PENS-IVE) etc. → more… polite → more polite interesting → more interesting o

Comparative Form o Clever, common, cruel, friendly, gentle, narrow, pleasant, polite, shallow, simple, stupid, quiet → er/more gentle – gentler/more gentle

Superlative Form The + superlative form + of/in (comparing a person, thing or place with the whole group they belong to; use in to talk about places) He is the tallest of his friends. o Lugansk is the most beautiful city in Europe.

Superlative Form 1/2 syllables adjectives → -(e)st the tallest (of/in) o 3 or more syllables adjectives → most beautiful – the most beautiful o Clever, common, cruel, friendly, gentle, narrow, pleasant, polite, shallow, simple, stupid, quiet → -est/more o simple - the simplest/the most simple

Superlative Form 1 -syllable adjectives ending in –e take –st nice – nicest o 2 -syllable adjectives ending in –y turn the –y into i and then take –est funny – funniest o Adjectives ending in a stressed vowel between two consonants double the final consonant and take –est big - biggest o
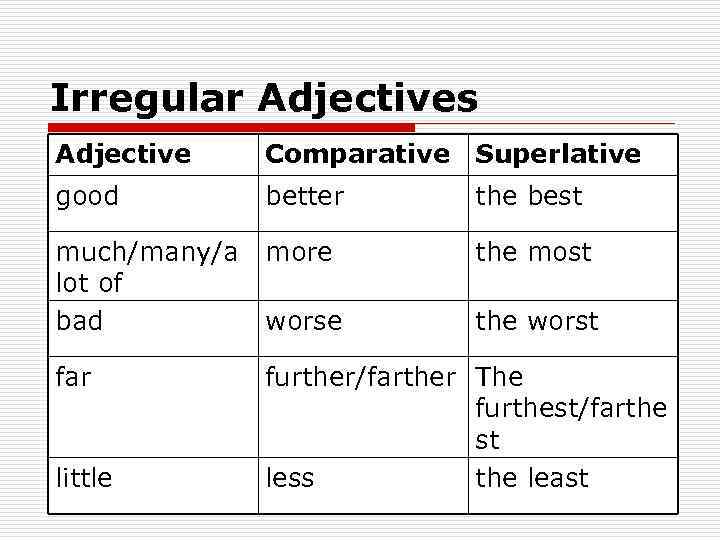
Irregular Adjectives Adjective Comparative Superlative good better much/many/a more lot of bad worse far little the best the most the worst further/farther The furthest/farthe st less the least

Expressing Preference

Expressing Preference prefer + -ing form/noun I prefer living on my own. o

Expressing Preference o Would prefer + to –inf + rather than + inf without to I would prefer to stay at home rather than go to school

Expressing Preference o Would rather + inf without to + than + inf without to I would rather buy a car than go to work by bus
Countable and Uncountable Nouns.ppt