20db0c5ef1c3312f8492168548921668.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Cotton Modeling to Assess Climate Change and Crop Management V. R. Reddy 1 and K. R. Reddy 2 1 USDA-ARS, Crop Systems and Global Change Laboratory, BARC-West, Beltsville, MD 20705, USA 2 Department of Plant and Soil Sciences, Mississippi State University, Mississippi State, MS 39762, USA December 2005
Cotton Modeling to Assess Climate Change and Crop Management V. R. Reddy 1 and K. R. Reddy 2 1 USDA-ARS, Crop Systems and Global Change Laboratory, BARC-West, Beltsville, MD 20705, USA 2 Department of Plant and Soil Sciences, Mississippi State University, Mississippi State, MS 39762, USA December 2005
 Why Do We Need Models? Ø Provide quantitative description and understanding of biological problems. Ø Help pinpoint knowledge gaps. Ø Design critical experiments. Ø Synthesize knowledge about different components of a system. Ø Summarize data. Ø Transfer research results to users.
Why Do We Need Models? Ø Provide quantitative description and understanding of biological problems. Ø Help pinpoint knowledge gaps. Ø Design critical experiments. Ø Synthesize knowledge about different components of a system. Ø Summarize data. Ø Transfer research results to users.
 Demand for Models Ø Farm management (e. g. planting, irrigation, fertilization and harvest scheduling). Ø Resource management (e. g. several Govt. agencies and private comp. use). Ø Policy analysis. Ø Production forecasts (e. g. global, regional and local forecasts). Ø Research and development (e. g. research priorities and guide fund allocations). Ø Turning information into knowledge (e. g. information overflow in every area including agricultural research).
Demand for Models Ø Farm management (e. g. planting, irrigation, fertilization and harvest scheduling). Ø Resource management (e. g. several Govt. agencies and private comp. use). Ø Policy analysis. Ø Production forecasts (e. g. global, regional and local forecasts). Ø Research and development (e. g. research priorities and guide fund allocations). Ø Turning information into knowledge (e. g. information overflow in every area including agricultural research).
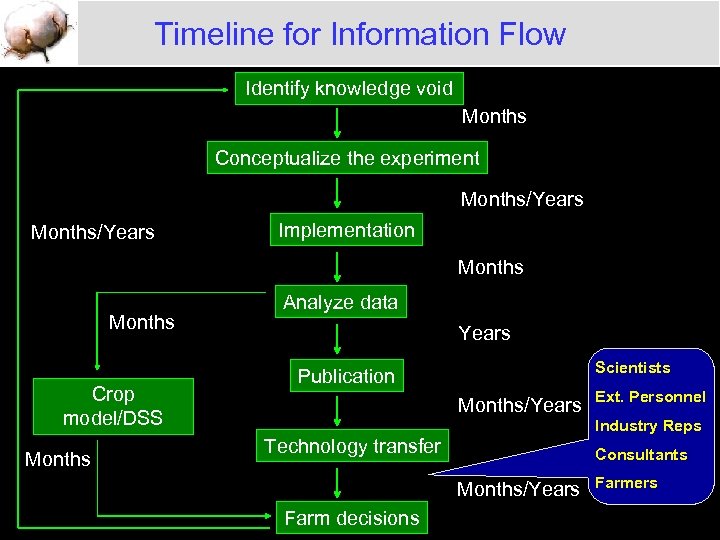 Timeline for Information Flow Identify knowledge void Months Conceptualize the experiment Months/Years Implementation Months Crop model/DSS Months Analyze data Years Scientists Publication Months/Years Ext. Personnel Industry Reps Technology transfer Consultants Months/Years Farm decisions Farmers
Timeline for Information Flow Identify knowledge void Months Conceptualize the experiment Months/Years Implementation Months Crop model/DSS Months Analyze data Years Scientists Publication Months/Years Ext. Personnel Industry Reps Technology transfer Consultants Months/Years Farm decisions Farmers
 SPAR – Database for Modeling
SPAR – Database for Modeling
 SPAR – Database for Modeling
SPAR – Database for Modeling
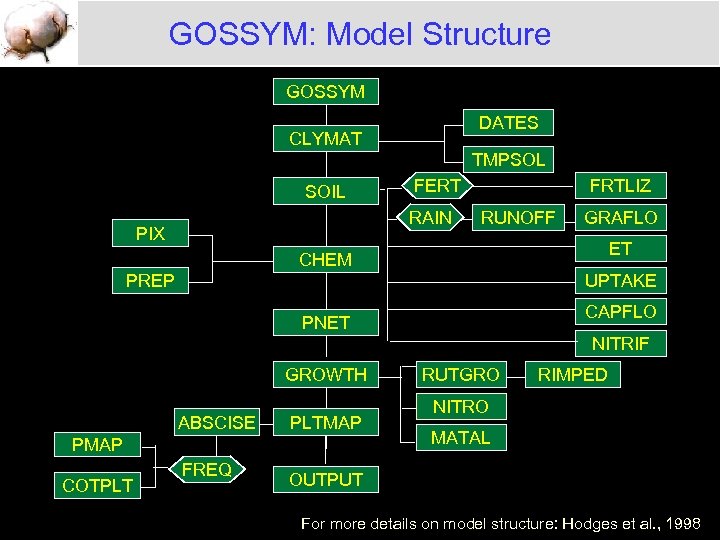 GOSSYM: Model Structure GOSSYM DATES CLYMAT TMPSOL SOIL FERT RAIN PIX FRTLIZ RUNOFF GRAFLO ET CHEM PREP UPTAKE CAPFLO PNET NITRIF GROWTH ABSCISE PLTMAP PMAP COTPLT FREQ RUTGRO RIMPED NITRO MATAL OUTPUT For more details on model structure: Hodges et al. , 1998
GOSSYM: Model Structure GOSSYM DATES CLYMAT TMPSOL SOIL FERT RAIN PIX FRTLIZ RUNOFF GRAFLO ET CHEM PREP UPTAKE CAPFLO PNET NITRIF GROWTH ABSCISE PLTMAP PMAP COTPLT FREQ RUTGRO RIMPED NITRO MATAL OUTPUT For more details on model structure: Hodges et al. , 1998
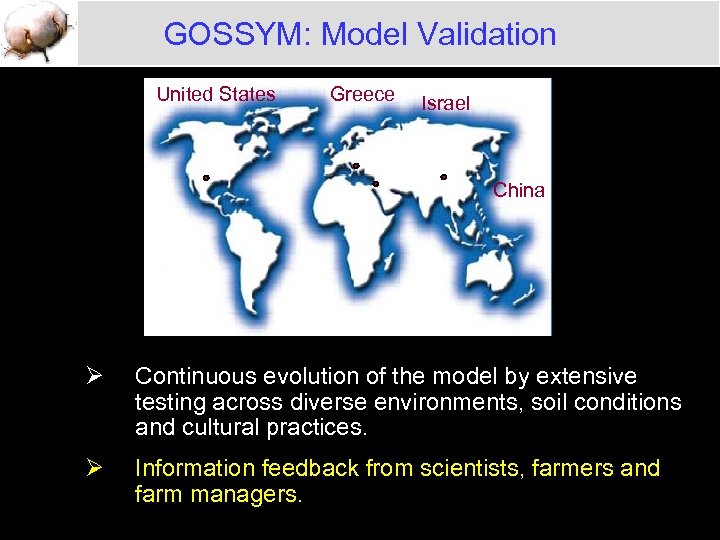 GOSSYM: Model Validation United States Greece Israel China Ø Continuous evolution of the model by extensive testing across diverse environments, soil conditions and cultural practices. Ø Information feedback from scientists, farmers and farm managers.
GOSSYM: Model Validation United States Greece Israel China Ø Continuous evolution of the model by extensive testing across diverse environments, soil conditions and cultural practices. Ø Information feedback from scientists, farmers and farm managers.
 Climate Change Effects
Climate Change Effects
 Climate Change – Cotton Yield Extreme Years Lint yield
Climate Change – Cotton Yield Extreme Years Lint yield
 Tillage and Erosion Studies Ø GOSSYM was used to evaluate the effects of erosion and erosion-related activities on lint yields. Ø GOSSYM was also used to investigate the effects of simulated tillage and wheel traffic on growth and yield.
Tillage and Erosion Studies Ø GOSSYM was used to evaluate the effects of erosion and erosion-related activities on lint yields. Ø GOSSYM was also used to investigate the effects of simulated tillage and wheel traffic on growth and yield.
 Insect Damage Assessment Ø Rb. WHIMS: Rule-based Wholistic Insect Management System. Ø Provides information to the user for determining pesticide management strategies. Ø Recommendations include: extent of pest control, timing of pesticide application/no application and when to observe the field for future management strategies.
Insect Damage Assessment Ø Rb. WHIMS: Rule-based Wholistic Insect Management System. Ø Provides information to the user for determining pesticide management strategies. Ø Recommendations include: extent of pest control, timing of pesticide application/no application and when to observe the field for future management strategies.
 Genetics Improvement Research Ø GOSSYM – a tool to predict the effect and economic benefit of various genetic combinations. Ø Photosynthesis was found to be the limiting factor in the okra leaf-type cottons which have more number of bolls/plant and less lint yield than normal leaf-type cottons.
Genetics Improvement Research Ø GOSSYM – a tool to predict the effect and economic benefit of various genetic combinations. Ø Photosynthesis was found to be the limiting factor in the okra leaf-type cottons which have more number of bolls/plant and less lint yield than normal leaf-type cottons.
 GOSSYM: Educational Applications Ø As a tool for learning: principles of crop and soil management. Ø As a classroom teaching tool: graphically presents the changes in plant growth and development. Ø Educating farm managers to improve their crop productivity. Ø Assist crop consultants in the decision making process. Ø 22 (15 Ph. D and 7 MS) theses on GOSSYM were accepted since 1979 at MSU. Ø GOSSYM served as a template to other crop models (melons, soybean, corn, wheat, rice and potato) at USDA.
GOSSYM: Educational Applications Ø As a tool for learning: principles of crop and soil management. Ø As a classroom teaching tool: graphically presents the changes in plant growth and development. Ø Educating farm managers to improve their crop productivity. Ø Assist crop consultants in the decision making process. Ø 22 (15 Ph. D and 7 MS) theses on GOSSYM were accepted since 1979 at MSU. Ø GOSSYM served as a template to other crop models (melons, soybean, corn, wheat, rice and potato) at USDA.
 GOSSYM: Model Applications Field Scale
GOSSYM: Model Applications Field Scale
 Pre-season and In-season Decisions Ø Timely decisions can be taken by predictions with GOSSYM. Ø Helps in decision-making regarding leasing of farms. Ø Estimations before hand – fertilization and irrigation costs. Ø GOSSYM – for determining crop termination, nitrogen application, irrigation management.
Pre-season and In-season Decisions Ø Timely decisions can be taken by predictions with GOSSYM. Ø Helps in decision-making regarding leasing of farms. Ø Estimations before hand – fertilization and irrigation costs. Ø GOSSYM – for determining crop termination, nitrogen application, irrigation management.
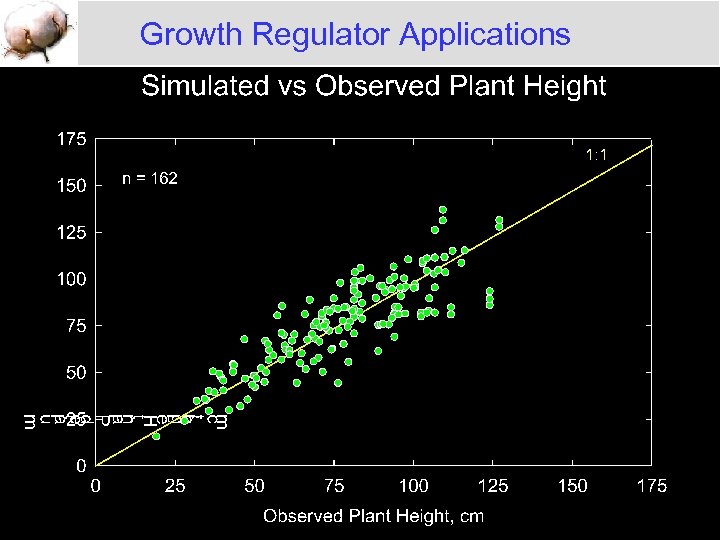 Growth Regulator Applications
Growth Regulator Applications
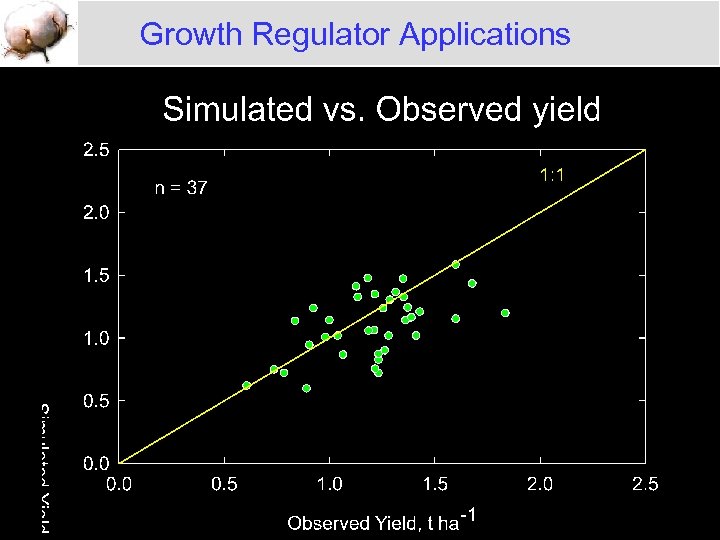 Growth Regulator Applications
Growth Regulator Applications
 GOSSYM: Reap Profits Farmer Plots GOSSYM Plots Ø In another study, GOSSYM plots had a profit of $100 - $350 ha-1 (Mc. Kinion et al. , 1989). Ø GOSSYM plots had a profit of $80 ha-1 than farmer plots (Ladewig and Powell, 1992).
GOSSYM: Reap Profits Farmer Plots GOSSYM Plots Ø In another study, GOSSYM plots had a profit of $100 - $350 ha-1 (Mc. Kinion et al. , 1989). Ø GOSSYM plots had a profit of $80 ha-1 than farmer plots (Ladewig and Powell, 1992).
 GOSSYM Deficiencies and Future Development Needs
GOSSYM Deficiencies and Future Development Needs
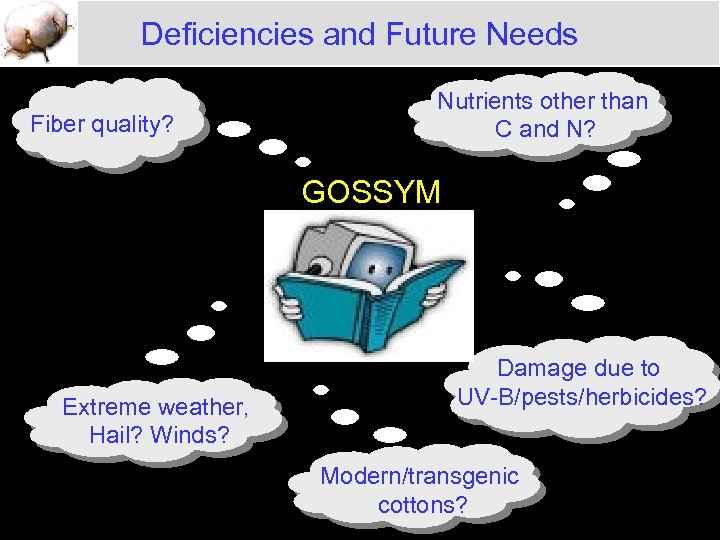 Deficiencies and Future Needs Fiber quality? Nutrients other than C and N? GOSSYM Extreme weather, Hail? Winds? Damage due to UV-B/pests/herbicides? Modern/transgenic cottons?
Deficiencies and Future Needs Fiber quality? Nutrients other than C and N? GOSSYM Extreme weather, Hail? Winds? Damage due to UV-B/pests/herbicides? Modern/transgenic cottons?
 Shall We Discuss! Thank You
Shall We Discuss! Thank You


