996375d19be0a0ad684444f6220f6aba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Costs of a Food service Operation
Costs of a Food service Operation
 Expenses Labor Total cost of labor employed in the establishment.
Expenses Labor Total cost of labor employed in the establishment.
 Expenses Overhead Controllable Expenses Food, Labor, Supplies Non Controllable Expenses Rent, Utilities, Advertising, Insurance
Expenses Overhead Controllable Expenses Food, Labor, Supplies Non Controllable Expenses Rent, Utilities, Advertising, Insurance
 Expenses Food Cost To control Food cost, standards must be implemented Quality Quantity Portion size Yield The most important standards are the recipes
Expenses Food Cost To control Food cost, standards must be implemented Quality Quantity Portion size Yield The most important standards are the recipes
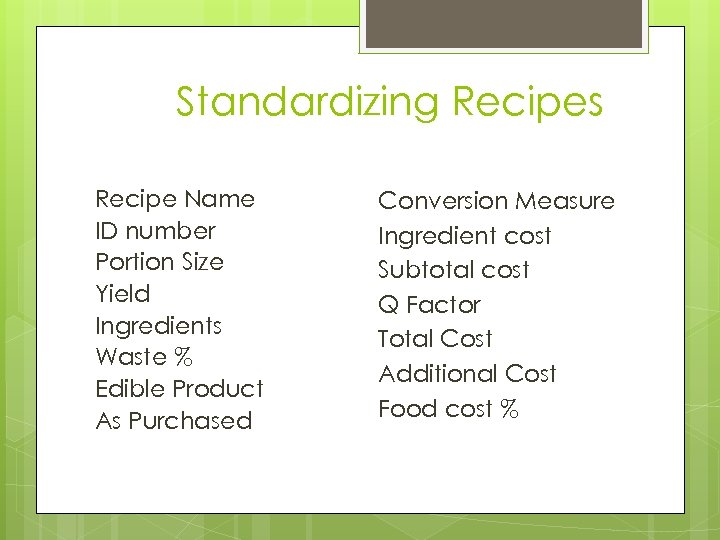 Standardizing Recipes Recipe Name ID number Portion Size Yield Ingredients Waste % Edible Product As Purchased Conversion Measure Ingredient cost Subtotal cost Q Factor Total Cost Additional Cost Food cost %
Standardizing Recipes Recipe Name ID number Portion Size Yield Ingredients Waste % Edible Product As Purchased Conversion Measure Ingredient cost Subtotal cost Q Factor Total Cost Additional Cost Food cost %
 Portions The number of servings that one preparation of the recipe produces. Portions are needed to determine the portion cost For Example Recipe Cost = 12. 90 Portions = 10 12. 90 / 10 = $1. 29 portion cost
Portions The number of servings that one preparation of the recipe produces. Portions are needed to determine the portion cost For Example Recipe Cost = 12. 90 Portions = 10 12. 90 / 10 = $1. 29 portion cost
 Example A Recipe for Chicken Pot Pie makes 10 cups. A portion in considered 1 cup. How many portions are there? 10 / 1 = 10
Example A Recipe for Chicken Pot Pie makes 10 cups. A portion in considered 1 cup. How many portions are there? 10 / 1 = 10
 Example SOUP Recipe Yield 2 gallons Serving size 8 oz How many Portions are there?
Example SOUP Recipe Yield 2 gallons Serving size 8 oz How many Portions are there?
 Yeild % EP/AP = Yield % Edible Portion / As Purchased = Yield %
Yeild % EP/AP = Yield % Edible Portion / As Purchased = Yield %
 Yield % Sample You can find yield % by performing a cut test. A 50# Bag of carrots is purchased After Peeling and dicing, 45# remains What is the Yield %?
Yield % Sample You can find yield % by performing a cut test. A 50# Bag of carrots is purchased After Peeling and dicing, 45# remains What is the Yield %?
 Yield % 45/50 = 90%
Yield % 45/50 = 90%
 Using Yield % Whole carrots cost $1. 00 per pound. How much do peeled carrots cost? Take the original cost and divide by yield % to get the true cost. 1. 00 /. 90 = $1. 11/lb
Using Yield % Whole carrots cost $1. 00 per pound. How much do peeled carrots cost? Take the original cost and divide by yield % to get the true cost. 1. 00 /. 90 = $1. 11/lb
 One more… Red snapper has a yield of 30%. Red Snapper fillets cost $12. 99/lb and the whole fish cost 3. 50/lb. How should you purchase your snapper?
One more… Red snapper has a yield of 30%. Red Snapper fillets cost $12. 99/lb and the whole fish cost 3. 50/lb. How should you purchase your snapper?
 How much should I buy? Ep/ap = yield% Ap = ep/yield %
How much should I buy? Ep/ap = yield% Ap = ep/yield %
 Example A recipe calls for 5 lbs of diced pumpkin. Pumpkin has a yield of 60%. How much should you buy? 5 /. 60 = 8. 33 lbs
Example A recipe calls for 5 lbs of diced pumpkin. Pumpkin has a yield of 60%. How much should you buy? 5 /. 60 = 8. 33 lbs
 One More You have a banquet for 100 people. They will be eating roast beef and each guest will be an ½ lb or 8 oz portion. The only issue is, when you roast the beef, it shrinks 20% which means the yield is 80%. How much beef should you purchase?
One More You have a banquet for 100 people. They will be eating roast beef and each guest will be an ½ lb or 8 oz portion. The only issue is, when you roast the beef, it shrinks 20% which means the yield is 80%. How much beef should you purchase?
 Food Cost Expressed as a percentage Cost of food / sales price Cost of food = $2. 00 Sales Price = $6. 00 Food cost = 33%
Food Cost Expressed as a percentage Cost of food / sales price Cost of food = $2. 00 Sales Price = $6. 00 Food cost = 33%
 Example Chicken Parm $9. 99 8 oz chicken breast 2 oz sauce 1 slice cheese 12 oz pasta Fresh basil (garnish) 1. 50. 25. 40. 55. 05 What is the food cost? ? ?
Example Chicken Parm $9. 99 8 oz chicken breast 2 oz sauce 1 slice cheese 12 oz pasta Fresh basil (garnish) 1. 50. 25. 40. 55. 05 What is the food cost? ? ?
 Food Cost % BLT 2 pieces of bread Bacon Lettuce Tomato You . 15. 60. 25 would like a 30% food cost, how much can you sell the BLT for?
Food Cost % BLT 2 pieces of bread Bacon Lettuce Tomato You . 15. 60. 25 would like a 30% food cost, how much can you sell the BLT for?
 Determining Sales Price Desired food cost % Direct competition Labor intensity Demand (popularity)
Determining Sales Price Desired food cost % Direct competition Labor intensity Demand (popularity)
 Formulas to know YIELD % = EP / AP EP = Starting weight – waste AP = EP/Yield % Food cost % = cost of product / sales price Portion Cost = Total Cost of Recipe / servings
Formulas to know YIELD % = EP / AP EP = Starting weight – waste AP = EP/Yield % Food cost % = cost of product / sales price Portion Cost = Total Cost of Recipe / servings
 Portion Cost Example Clam Chowder costs $22. 00 per gallon to make. There are 16 servings at 8 oz per serving. What is the cost of 1 serving?
Portion Cost Example Clam Chowder costs $22. 00 per gallon to make. There are 16 servings at 8 oz per serving. What is the cost of 1 serving?
 Classwork / Homework Standardize your recipes – put them in easy to use formats Using the price sheet, fill out recipe cost form for all 6 recipes to determine sales price Create your menu Turn in all 13 pages next week
Classwork / Homework Standardize your recipes – put them in easy to use formats Using the price sheet, fill out recipe cost form for all 6 recipes to determine sales price Create your menu Turn in all 13 pages next week


