2d55395389c7fad631bfd1bbd1e7fe07.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Cost of Producing Information Chapter 1
Cost of Producing Information Chapter 1
 Contents • This presentation covers the cost of: – Hardware – Software – Consumables – Personnel
Contents • This presentation covers the cost of: – Hardware – Software – Consumables – Personnel
 Introduction • An infinite amount of time ago an unknown amount of mass collected together. . . • 13. 73 Billion years ago the universe as we know it was created. . . give or take about 120 million years. . • A few years later people emerged. . .
Introduction • An infinite amount of time ago an unknown amount of mass collected together. . . • 13. 73 Billion years ago the universe as we know it was created. . . give or take about 120 million years. . • A few years later people emerged. . .
 Introduction • But unlike the universe and all that is within it which suddenly appeared (be it by one massive fluke or some greater power). . . • Information doesn’t magically appear. • It is gathered, processed and re-emerges as new information. . . but at a cost.
Introduction • But unlike the universe and all that is within it which suddenly appeared (be it by one massive fluke or some greater power). . . • Information doesn’t magically appear. • It is gathered, processed and re-emerges as new information. . . but at a cost.
 Hardware • Hardware can be used to collect, process, output and store information. • Although expensive to initially purchase, the cost is often spread: – Hardware can last a long time – Hardware can be used for multiple tasks
Hardware • Hardware can be used to collect, process, output and store information. • Although expensive to initially purchase, the cost is often spread: – Hardware can last a long time – Hardware can be used for multiple tasks
 Hardware • Further costs might include repair, maintenance and upgrading. • Some organisations take out maintenance contracts to lower the costs. . . • Some smaller companies may even rent hardware. . . if it breaks down they don’t have to worry about replacing it at a cost!
Hardware • Further costs might include repair, maintenance and upgrading. • Some organisations take out maintenance contracts to lower the costs. . . • Some smaller companies may even rent hardware. . . if it breaks down they don’t have to worry about replacing it at a cost!
 Hardware • As more and more information is collected storage space becomes an issue and further upgrading my be required. • This means spending more money on upgrading current hardware and also later on when backup/archive storage facilities need updating.
Hardware • As more and more information is collected storage space becomes an issue and further upgrading my be required. • This means spending more money on upgrading current hardware and also later on when backup/archive storage facilities need updating.
 Software • Software is seldom free. • There are lots of free applications available however they may not have all of the functionality that custom software applications may have. • More often than not, site licences are required to help lower costs. . . for example Microsoft Windows can be purchased using a site licence. . . lots of schools will do this.
Software • Software is seldom free. • There are lots of free applications available however they may not have all of the functionality that custom software applications may have. • More often than not, site licences are required to help lower costs. . . for example Microsoft Windows can be purchased using a site licence. . . lots of schools will do this.
 Software • Training staff in how to use new software may also need to be considered. • Technical support may also cost extra. – This can come from either the software manufactures or in house teams. • Over time, software may not be able to carry out all of the tasks required of the user/company. Future upgrades will cost money.
Software • Training staff in how to use new software may also need to be considered. • Technical support may also cost extra. – This can come from either the software manufactures or in house teams. • Over time, software may not be able to carry out all of the tasks required of the user/company. Future upgrades will cost money.
 Consumables • Consumables are anything that get used up. • For example: – Paper – Printer Ink – Stationary items
Consumables • Consumables are anything that get used up. • For example: – Paper – Printer Ink – Stationary items
 Personnel • Personnel are often the most expensive part of a company. • Different personnel may be required to do different jobs with information: – Some might collect, some might analyse and some might output information.
Personnel • Personnel are often the most expensive part of a company. • Different personnel may be required to do different jobs with information: – Some might collect, some might analyse and some might output information.
 Personnel • When new members of staff begin working they may need extra time to complete jobs as they get used to working with new systems. • This ‘bedding in’ time needs to be worked into the costs of the company. • On top of training costs, companies may need to cover the staff whilst they are away.
Personnel • When new members of staff begin working they may need extra time to complete jobs as they get used to working with new systems. • This ‘bedding in’ time needs to be worked into the costs of the company. • On top of training costs, companies may need to cover the staff whilst they are away.
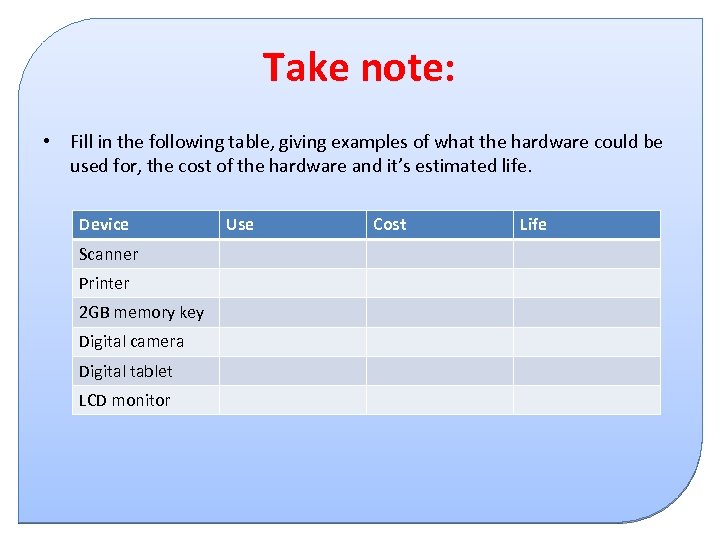 Take note: • Fill in the following table, giving examples of what the hardware could be used for, the cost of the hardware and it’s estimated life. Device Scanner Printer 2 GB memory key Digital camera Digital tablet LCD monitor Use Cost Life
Take note: • Fill in the following table, giving examples of what the hardware could be used for, the cost of the hardware and it’s estimated life. Device Scanner Printer 2 GB memory key Digital camera Digital tablet LCD monitor Use Cost Life
 Take note: • Investigate the cost of training courses for pieces of software such as: – Adobe Photo. Shop – Adobe Flash – Microsoft Access – Visual. Net
Take note: • Investigate the cost of training courses for pieces of software such as: – Adobe Photo. Shop – Adobe Flash – Microsoft Access – Visual. Net
 Take note: • Imagine that you are producing a leaflet for a new vegetable delivery service. • Using the four costs discussed, list all the expenditure associated with producing a leaflet and give a cost to each item.
Take note: • Imagine that you are producing a leaflet for a new vegetable delivery service. • Using the four costs discussed, list all the expenditure associated with producing a leaflet and give a cost to each item.
 Take note: • Describe the hardware items required to collect and input data required for a fashion magazine. • Explain why an organisation might need to upgrade the software it uses to produce information. • Explain the personnel costs incurred by an organisation that produces a leaflet completely from scratch.
Take note: • Describe the hardware items required to collect and input data required for a fashion magazine. • Explain why an organisation might need to upgrade the software it uses to produce information. • Explain the personnel costs incurred by an organisation that produces a leaflet completely from scratch.


