e41b16c697d46a84361fd90fafd4bf8a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Cost Management in Academic Libraries Roswitha Poll University and Regional Library Münster • "It is an unusual business that cannot say how much it costs to deliver any of its products; and I do not believe we will continue to get away with it. " • (J. Stephen Town) ULB MÜNSTER

Reasons for Cost Management • General demand for transparency of costs • Justification of expenditure • Dwindling resources • Rising prices • New tasks and products in libraries • • Allocation of resources Outsourcing, insourcing Enlarging, reducing, introducing services Service-level agreements ULB MÜNSTER

• What we could answer exactly The price of every document acquired or of one PC bought • What we cannot answer How much for one issue? Or for one reference question answered? How much does a student of philosophy cost per year? ULB MÜNSTER

What we count by now • Income (from different sources) • Expenditure – – on collection building and maintenance on automation on the operating of the library on staff The new International Standard for Library Statistics (ISO FDIS 2789) contains many differentiations as to expenses, especially with regard to electronic media But it is all "expenses", and that means items that ULB MÜNSTER appear on bills or staff payrolls

"Costs" are another thing The consumption of resources to acquire, produce or maintain goods or services within a defined period The recources consumed for one product • can originate in different departments of the library (document delivery) • can occur outside the library (central heating) • even outside the institution (regional office for staff payrolls) • can stretch over several years (depreciation) ULB MÜNSTER

Occasions for analyzing costs • Outsourcing services (binding) • Buying products (cataloguing) • Introducing new services (document delivery) ULB MÜNSTER

Project: Cost Management for University Libraries • Funds Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft • Partners Univ. and Regional Lib. Münster (chairing) Univ. and Regional Lib. Düsseldorf Univ. Lib. Paderborn • Time 4/1997 – 7/1999 • Method Activity-based cost accounting • Product Handbook and Software Ceynowa, Klaus / Coners, André: Kostenmanagement für Hochschulbibliotheken. Frankfurt a. M. : Klostermann 1999. ULB MÜNSTER
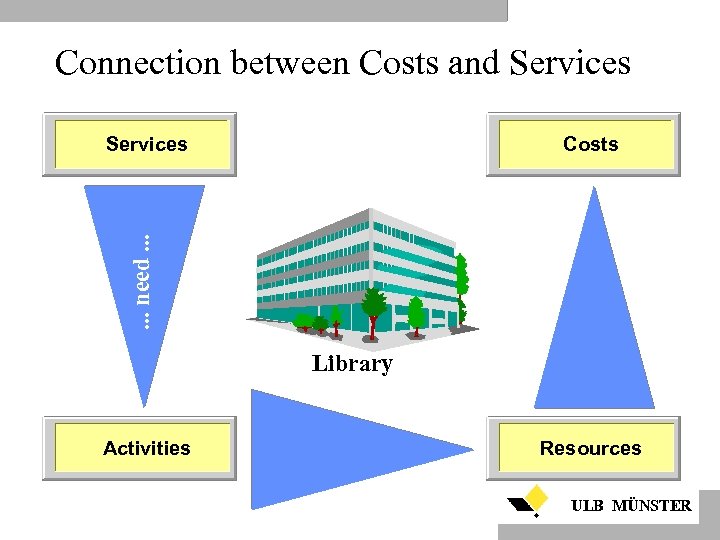
Connection between Costs and Services Costs . . . need. . . Cause. . . Services Library Activities Resources . . . Consume. . . ULB MÜNSTER

Cost Analysis in Public Service Institutions • Products are nonmaterial • Capacity costs are predominant • Many costs are fixed Library ULB MÜNSTER

Cost Analysis in Libraries • Problems – Availability of Data – Standards for Depreciation – Staff Costs: Real or Standardized Costs? ULB MÜNSTER
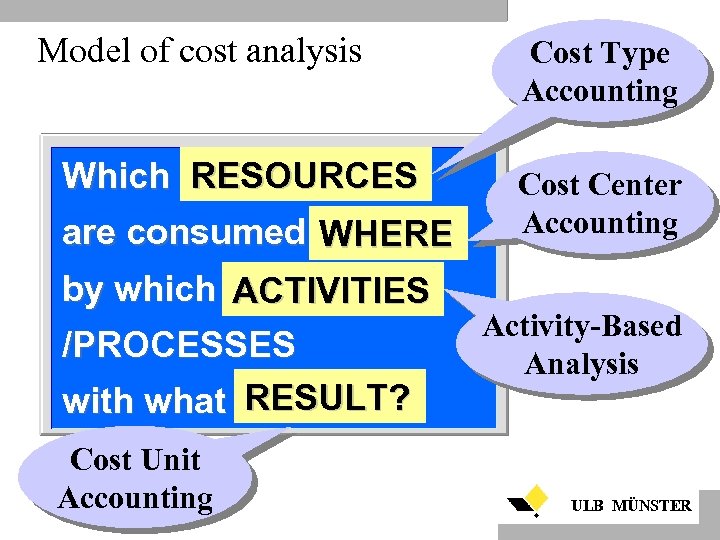
Model of cost analysis RESOURCES Which RESOURCES are consumed WHERE by which ACTIVITIES /PROCESSES RESULT? with what RESULT? Cost Unit Accounting Cost Type Accounting Cost Center Accounting Activity-Based Analysis ULB MÜNSTER
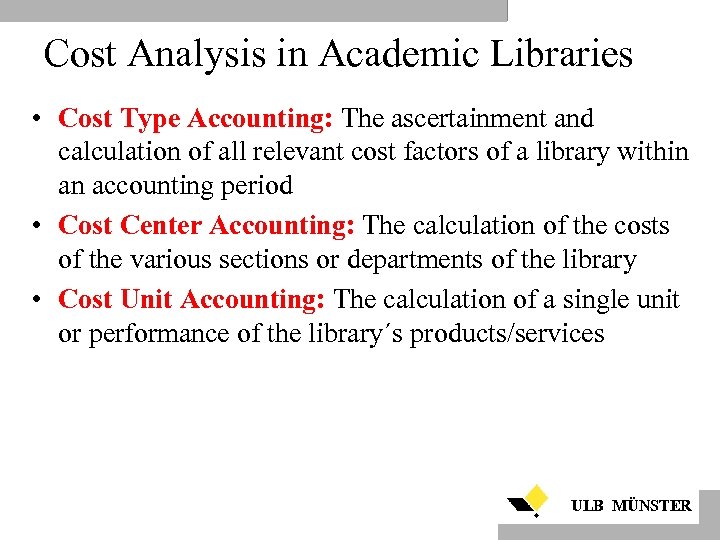
Cost Analysis in Academic Libraries • Cost Type Accounting: The ascertainment and calculation of all relevant cost factors of a library within an accounting period • Cost Center Accounting: The calculation of the costs of the various sections or departments of the library • Cost Unit Accounting: The calculation of a single unit or performance of the library´s products/services ULB MÜNSTER
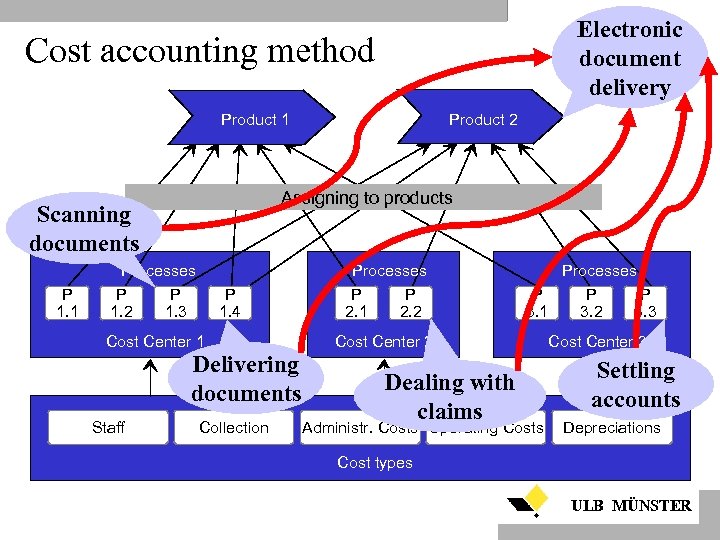
Electronic document delivery Cost accounting method Product 1 Assigning to products Scanning documents P 1. 1 Processes P P 1. 2 1. 3 P 1. 4 Cost Center 1 Delivering documents Staff Product 2 Collection Processes P P 2. 1 2. 2 Processes P P P 3. 1 3. 2 3. 3 Cost Center 2 Dealing with claims Administr. Costs Operating Costs Cost Center 3 Settling accounts Depreciations Cost types ULB MÜNSTER
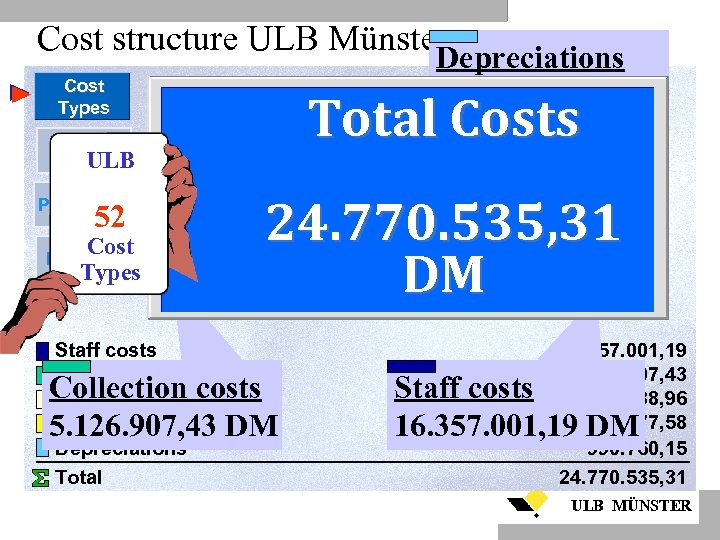
Cost structure ULB Münster Depreciations Operating costs Adminstr. Costs Cost Types Cost Centers ULB Processes 52 5% Cost Types Products Staff costs Collection costs Administration Costs Operating Costs Depreciations Total 990. 760, 15 1. 384. 577, 58 DM 911. 288, 96 DM Total Costs 4% 21 % 4% 66 % 24. 770. 535, 31 DM Collection costs 5. 126. 907, 43 DM 16. 357. 001, 19 5. 126. 907, 43 911. 288, 96 1. 384. 577, 58 990. 760, 15 24. 770. 535, 31 Staff costs 16. 357. 001, 19 DM ULB MÜNSTER
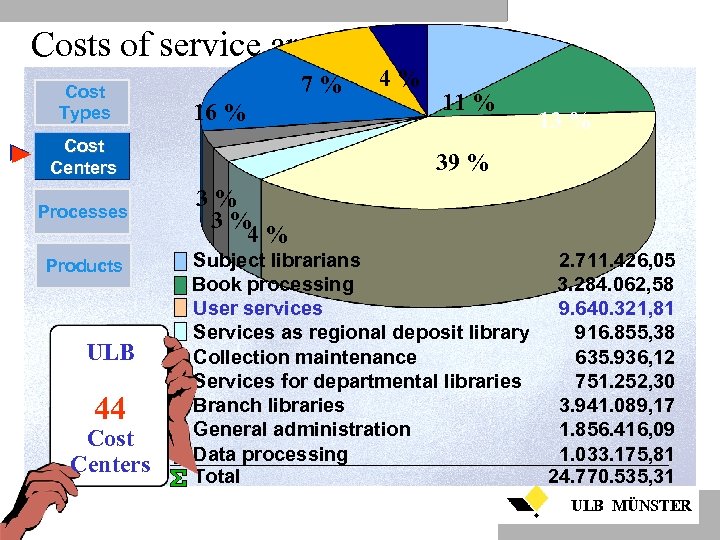
Costs of service areas Cost Types 7% 16 % Cost Centers Processes Products ULB 44 Cost Centers 4% 11 % 13 % 39 % 3% 3% 4% Subject librarians 2. 711. 426, 05 Book processing 3. 284. 062, 58 User services 9. 640. 321, 81 Services as regional deposit library 916. 855, 38 Collection maintenance 635. 936, 12 Services for departmental libraries 751. 252, 30 Branch libraries 3. 941. 089, 17 General administration 1. 856. 416, 09 Data processing 1. 033. 175, 81 Total 24. 770. 535, 31 ULB MÜNSTER
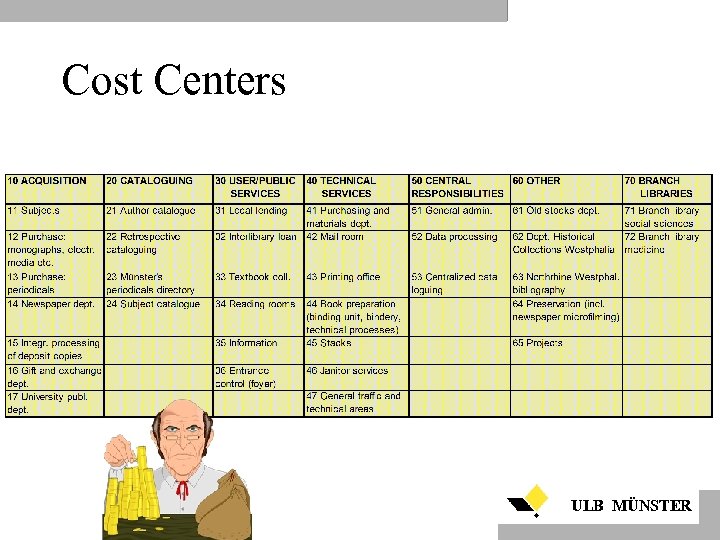
Cost Centers ULB MÜNSTER
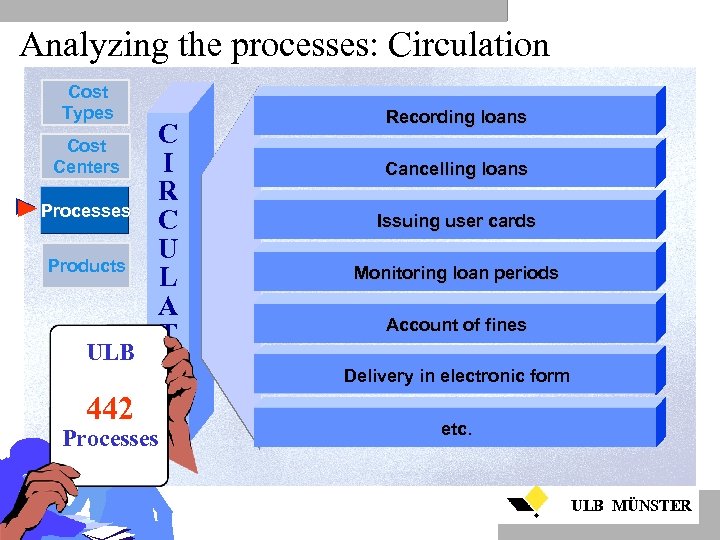
Analyzing the processes: Circulation Cost Types Recording loans Cost Centers Cancelling loans C I R Processes C U Products L A T ULB I O 442 N Processes Issuing user cards Monitoring loan periods Account of fines Delivery in electronic form etc. ULB MÜNSTER
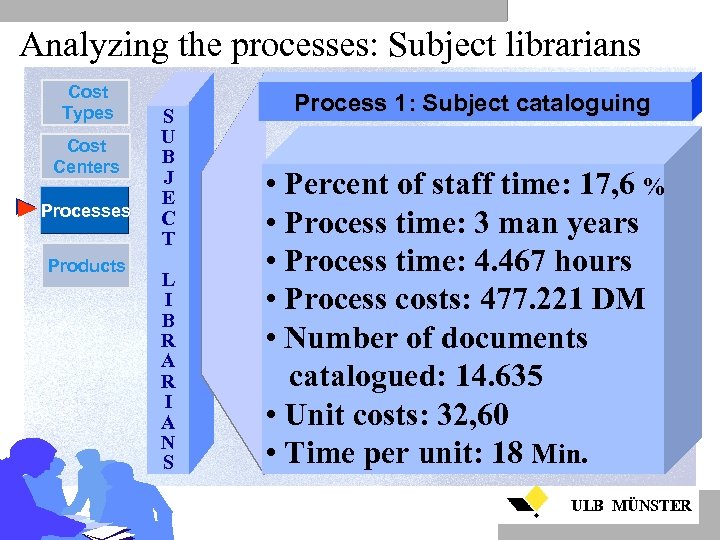
Analyzing the processes: Subject librarians Cost Types Cost Centers Processes Products S U B J E C T L I B R A R I A N S Process 1: Subject cataloguing • Percent of staff time: 17, 6 % • Process time: 3 man years • Process time: 4. 467 hours • Process costs: 477. 221 DM • Number of documents catalogued: 14. 635 • Unit costs: 32, 60 • Time per unit: 18 Min. ULB MÜNSTER
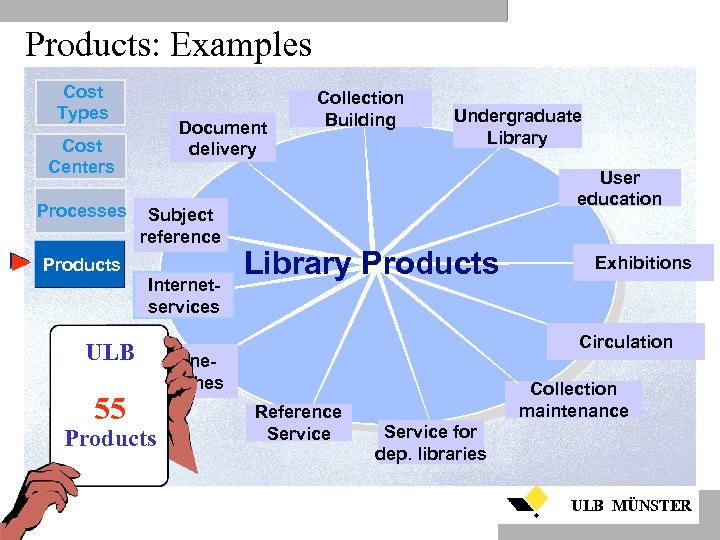
Products: Examples Cost Types Document delivery Cost Centers Processes Products ULB 55 Subject reference Internetservices Collection Building Undergraduate Library User education Library Products Circulation Onlinesearches Products Exhibitions Reference Service Collection maintenance Service for dep. libraries ULB MÜNSTER
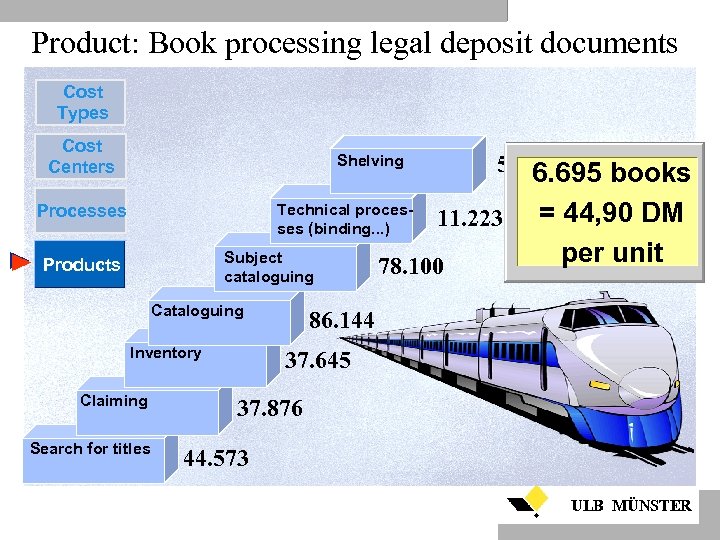
Product: Book processing legal deposit documents Cost Types Cost Centers 5. 308 6. 695 books Shelving Processes Technical processes (binding. . . ) Subject cataloguing Products Cataloguing Inventory Claiming Search for titles 11. 223 78. 100 = 44, 90 DM Total: per unit 300. 869 DM 86. 144 37. 645 37. 876 44. 573 ULB MÜNSTER
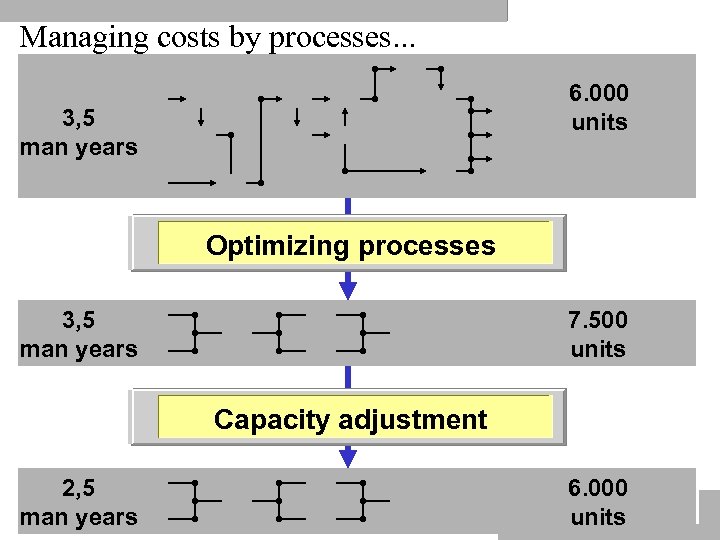
Managing costs by processes. . . 6. 000 units 3, 5 man years Optimizing processes 3, 5 man years 7. 500 units Capacity adjustment 2, 5 man years 6. 000 ULB MÜNSTER units
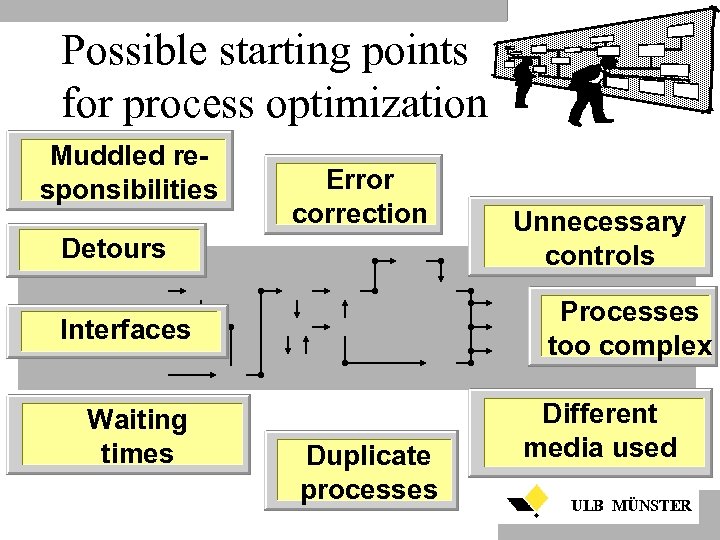
Possible starting points for process optimization Muddled responsibilities Error correction Detours Processes too complex Interfaces Waiting times Unnecessary controls Duplicate processes Different media used ULB MÜNSTER
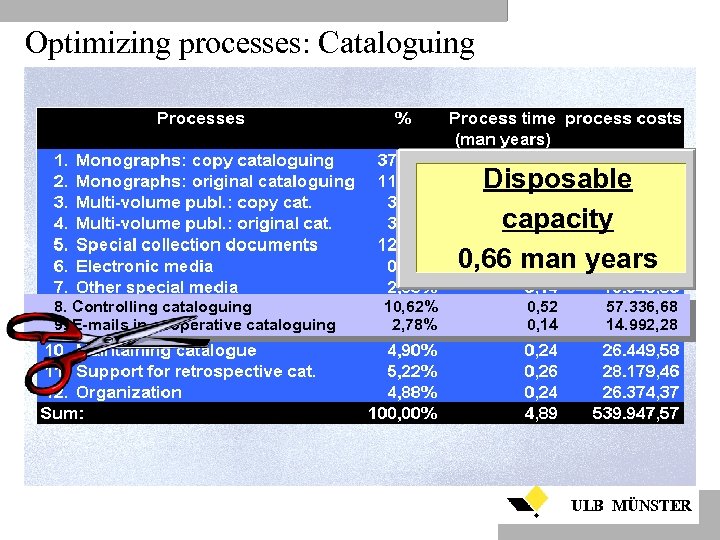
Optimizing processes: Cataloguing Disposable capacity 0, 66 man years 8. Controlling cataloguing 9. E-mails in cooperative cataloguing 10, 62% 2, 78% 0, 52 0, 14 57. 336, 68 14. 992, 28 ULB MÜNSTER
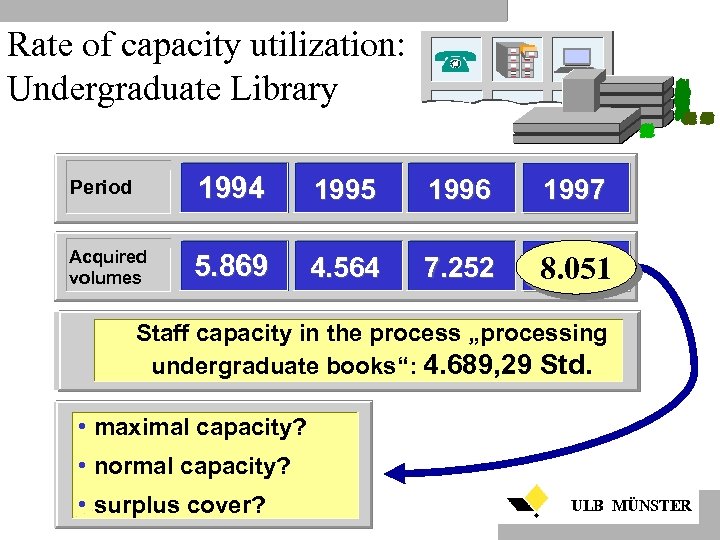
Rate of capacity utilization: Undergraduate Library Period 1994 1995 1996 1997 Acquired volumes 5. 869 4. 564 7. 252 8. 051 Staff capacity in the process „processing undergraduate books“: 4. 689, 29 Std. • maximal capacity? • normal capacity? • surplus cover? ULB MÜNSTER

Optimizing processes results in. . . • Gain in productivity without higher costs • Cost reduction without loss in productivity To produce more/better with lower costs = Efficiency ULB MÜNSTER

The use for management decisions • to justify claims for resources (e. g. service level agreements) • to estimate costs – For new or enlarged services – Gained by reduction or deletion of services – For taking fees • benchmarking • decisions on outsourcing • process optimization, especially to adapt capacity costs to output • comparing cost-efficiency and quality ULB MÜNSTER
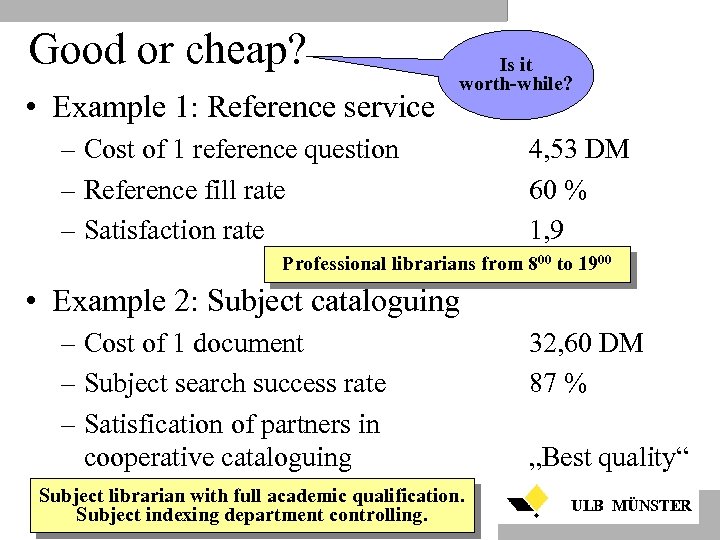
Good or cheap? • Example 1: Reference service Is it worth-while? – Cost of 1 reference question – Reference fill rate – Satisfaction rate 4, 53 DM 60 % 1, 9 Professional librarians from 800 to 1900 • Example 2: Subject cataloguing – Cost of 1 document – Subject search success rate – Satisfication of partners in cooperative cataloguing Subject librarian with full academic qualification. Subject indexing department controlling. 32, 60 DM 87 % „Best quality“ ULB MÜNSTER

The price spoils the pleasure (French proverb) . . . if money go before, all ways do lie open (Shakespeare) Penny and penny laid up will be many (English proverb) ULB MÜNSTER

ULB MÜNSTER
e41b16c697d46a84361fd90fafd4bf8a.ppt