692e9f4b3faacdc750b835cf64811991.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Cost Control Automation (Executive Overview) Robert Walcutt Grueser, PMP ROBERT WALCUTT & ASSOCIATES Santiago, Chile October 2014

Why focus on controlling costs? Beyond the obvious need to meet an established budget, a cost deviation in a project can: • Indicate planning errors • Result from problems in execution • Be caused by unidentified risks • Forecast more serious problems in the future And all of these require corrective actions.

Why automate cost control? Some of the benefits of automation include: + + Reducing errors Improving efficiency Data always up-to-date Obtaining a global vision (through the integration of various data sources) + Tracking the performance of groups of activities, vendors, and contracts + Generating reports as and when needed = Improving project and program management

Activities Required to Control Costs There are 4 key activities required to control costs: • Establish a budget and permitted deviation for each task • Collect data on costs incurred • Compare costs with planned expenses • Generate cost reports The first of these is a process input, but the last three can easily be automated.
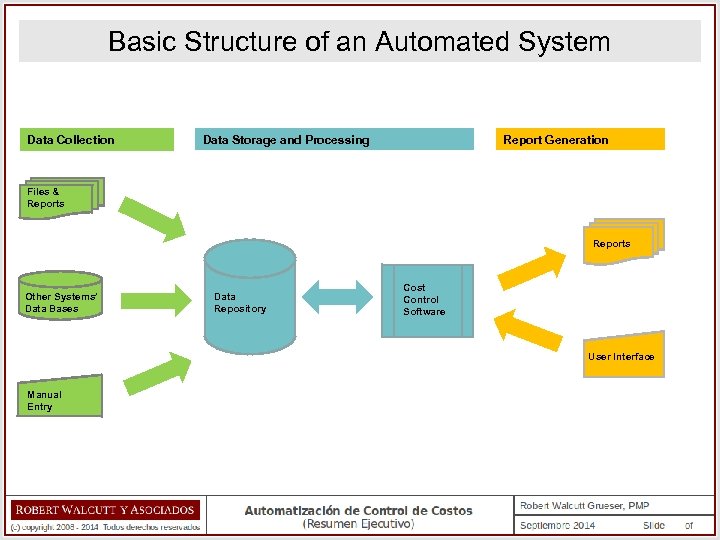
Basic Structure of an Automated System Data Collection Data Storage and Processing Report Generation Files & Reports Other Systems’ Data Bases Data Repository Cost Control Software User Interface Manual Entry
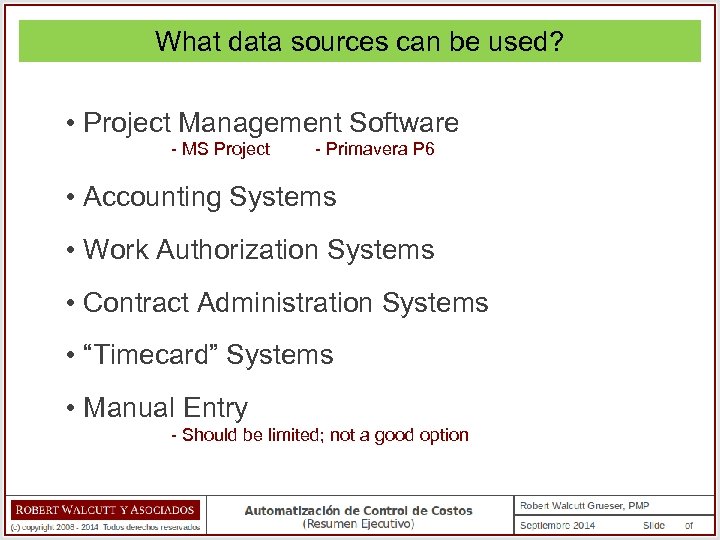
What data sources can be used? • Project Management Software - MS Project - Primavera P 6 • Accounting Systems • Work Authorization Systems • Contract Administration Systems • “Timecard” Systems • Manual Entry - Should be limited; not a good option

What gets stored in the data base? The principal data tables (groups) are: • Programs, Projects, Tasks • Activity Categories / Control Accounts • Planned Budget and Permitted Deviations • Authorized Budget Modifications • Vendors and Contracts • Responsible Parties / “Owners” • Costs Incurred

How are costs organized? The basic organizational relationship is: Program ← Project(s) ← Task(s) ← Cost(s) But costs can also be grouped by: • Contract • Vendor • “Owner” • Activity Category • Control Account • and others Which permits generating performance reports focused on any of these.
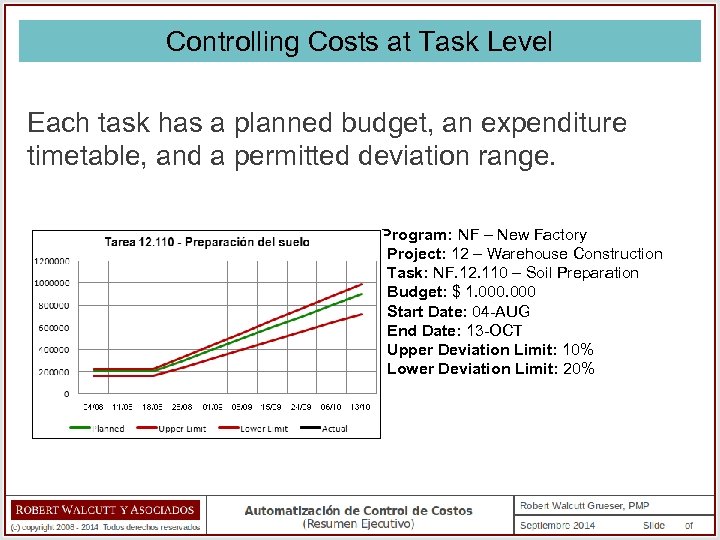
Controlling Costs at Task Level Each task has a planned budget, an expenditure timetable, and a permitted deviation range. Program: NF – New Factory Project: 12 – Warehouse Construction Task: NF. 12. 110 – Soil Preparation Budget: $ 1. 000 Start Date: 04 -AUG End Date: 13 -OCT Upper Deviation Limit: 10% Lower Deviation Limit: 20%
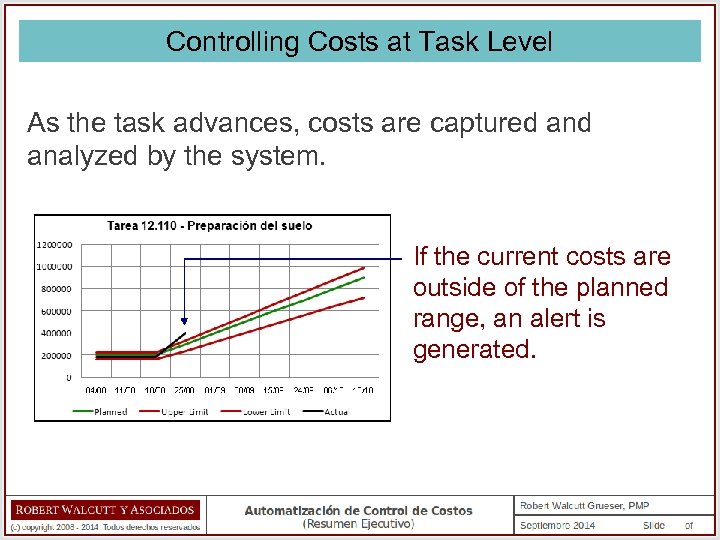
Controlling Costs at Task Level As the task advances, costs are captured analyzed by the system. If the current costs are outside of the planned range, an alert is generated.

Controlling Costs at Task Level This will allow the identification of a task (project or program) that has not yet exceeded it’s total budget – but is incurring costs more rapidly than planned. And that in turn allows forecasting with anticipation that it is possible that the task (project or program) is going to exceed it’s budget….
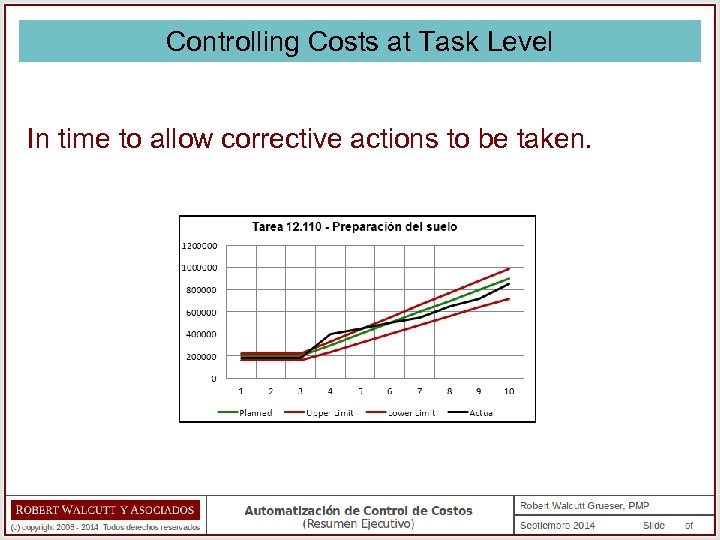
Controlling Costs at Task Level In time to allow corrective actions to be taken.
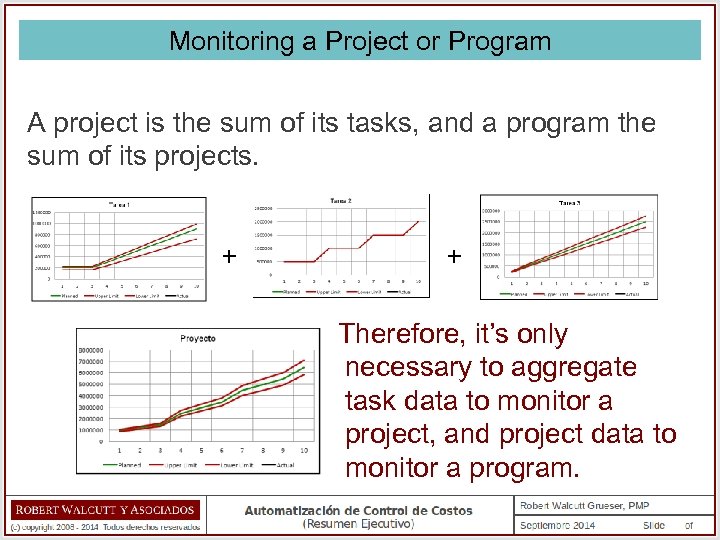
Monitoring a Project or Program A project is the sum of its tasks, and a program the sum of its projects. + + Therefore, it’s only necessary to aggregate task data to monitor a project, and project data to monitor a program.

The Importance of Monitoring at the Task Level It is completely possible that the costs of a task (or project) could be out-of-range, while the project (or program) itself is not. For this reason, it’s important to control costs at task level, because… A task with costs outside of the planned range can be an early warning of future problems, result from unidentified risks, indicate problems in execution, or errors or omissions in planning.
Types of Reports Once cost data has been captured, an unlimited number of different reports can be generated, with various levels of detail and focus. Experience indicates that the most useful include: • Comparison of Planned and Actual Costs (CV) • Cost Performance Indexes (CPI) • Remaining Cost Estimates (ETC, EAC) • Tasks/Projects Likely to Exceed Planned Budget • Budget Modifications

Levels of Detail and Organization of Reports with the following levels of detail can be generated: • Program • Project • Control Accounts • Tasks Reports can also be organized by: • Vendors • Category of Activity • Contracts • “Owner” • and others
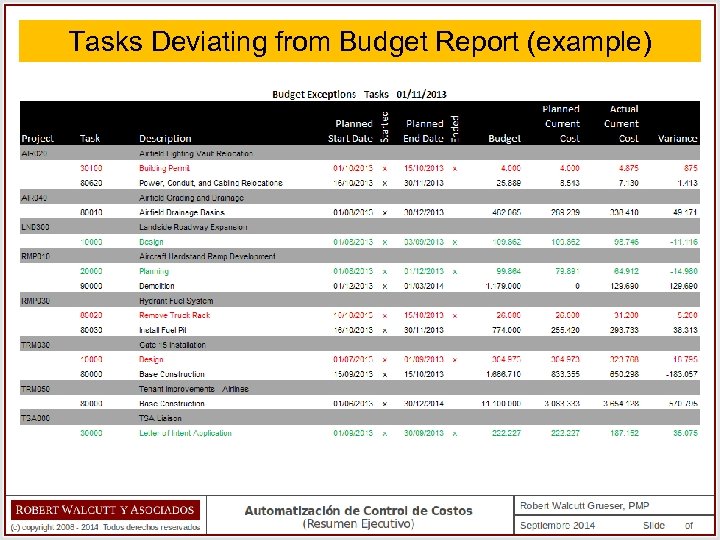
Tasks Deviating from Budget Report (example)
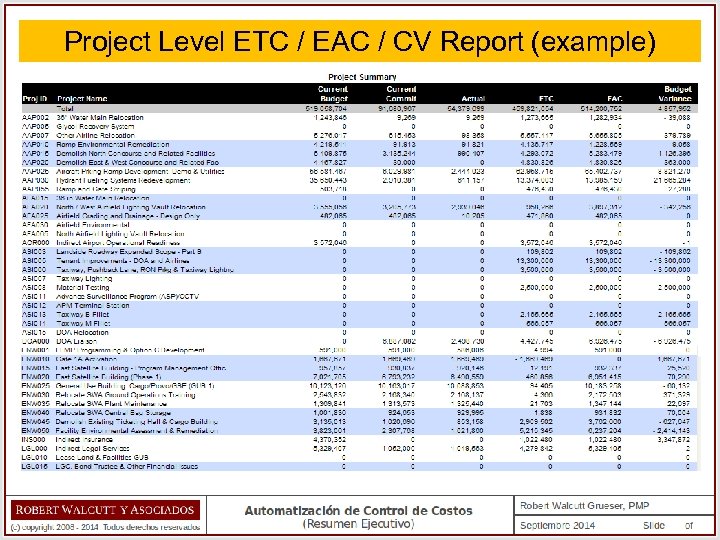
Project Level ETC / EAC / CV Report (example)
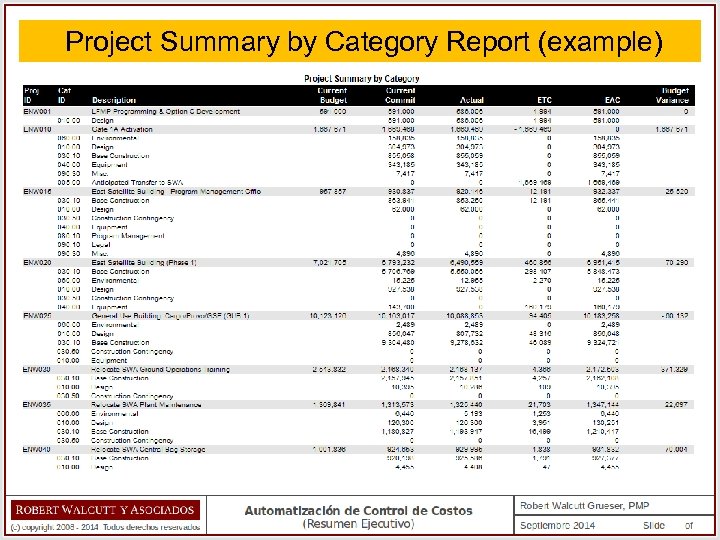
Project Summary by Category Report (example)
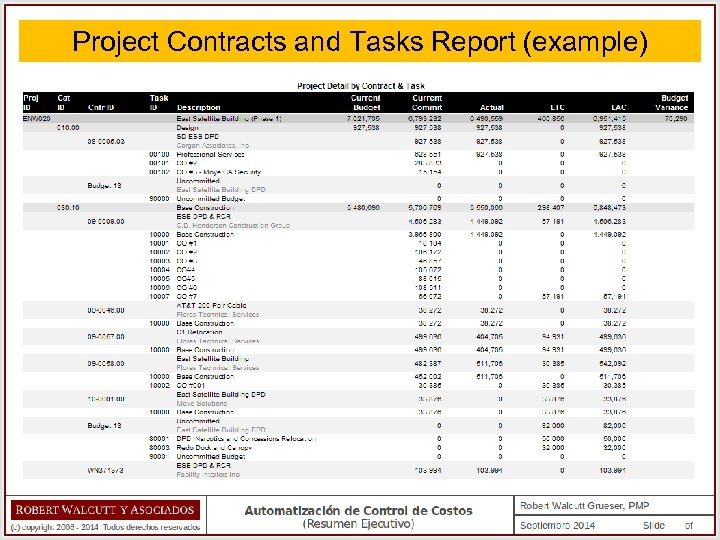
Project Contracts and Tasks Report (example)
User Interface A web interface permits fast and reliable access to the system’s data and reports, while also limiting activities based on user level. Access Level User Type Permitted Activities Unrestricted System Administrator All activities necessary for system administration Very High Manager Generate reports and manage data related to all projects High Accountant Manage data related to all projects Medium Project Manager Generate reports and manage data related to their project Low Vendor View reports and data related to their contract
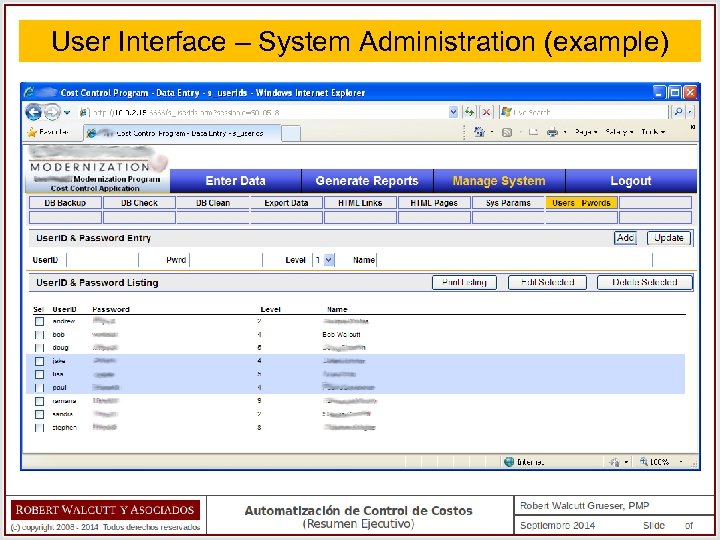
User Interface – System Administration (example)
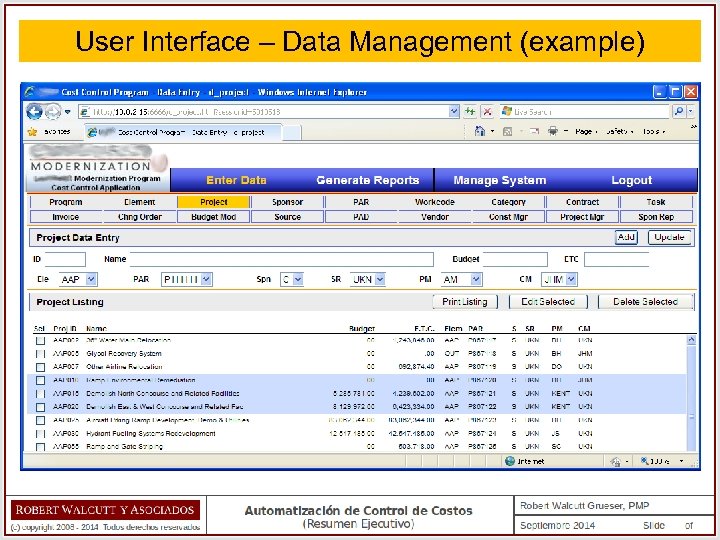
User Interface – Data Management (example)
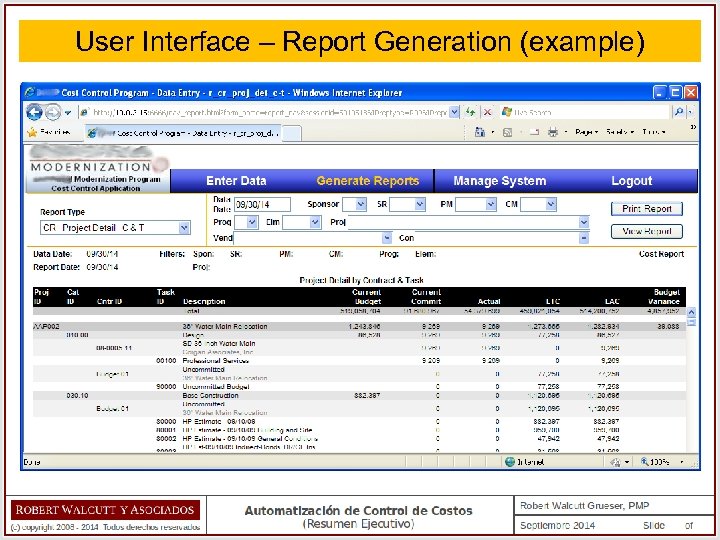
User Interface – Report Generation (example)

Summary • The implementation of an automated cost control system will facilitate performance monitoring, simplify the generation of reports as well as improve their quality, and permit better control over tasks, projects and programs. • Additionally, such a system can help identify and resolve problems in project execution, discover and mitigate risks, detect and correct omissions in planning, and forecast potential future problems. • A basic system can be implemented using commercial offthe-shelf software, and more robust systems can be designed using similar concepts.

Thank you for your attention! Robert Walcutt Grueser, PMP Project Management Consultant ROBERT WALCUTT & ASSOCIATES E-mail: rwalcutt@rwasoc. com This presentation is available at: www. rwasoc. com/EN-costos. html
692e9f4b3faacdc750b835cf64811991.ppt