d67f504d56aa147837bb2ddee6d16de0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Cost Concepts and Behavior Chapter 2

Learning Objectives 1. Explain the basic concept of “cost. ” 2. Explain how costs are presented in financial statements. 3. Explain the process of cost allocation. 4. Understand how material, labor, and overhead costs are added to a product at each stage of the production process. 5. Define basic cost behaviors including fixed, variable, semivariable, and step costs. 6. Identify the components of a product’s costs. 7. Understand the distinction between financial and contribution margin income statements.
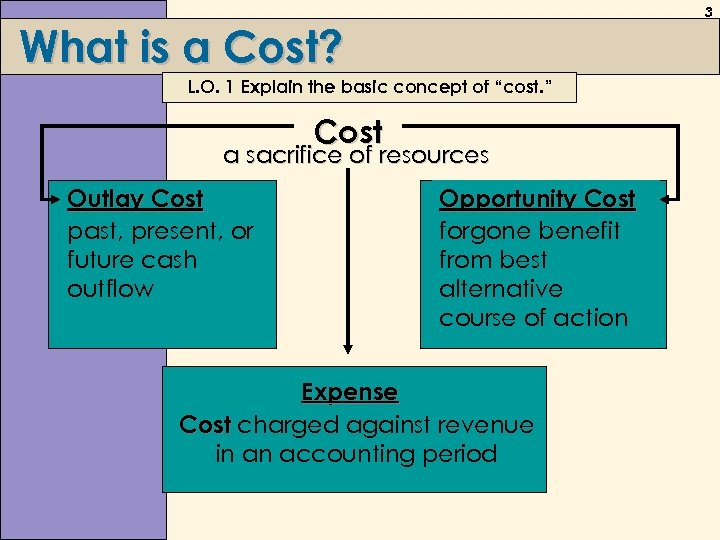
3 What is a Cost? L. O. 1 Explain the basic concept of “cost. ” Cost a sacrifice of resources Outlay Cost past, present, or future cash outflow Opportunity Cost forgone benefit from best alternative course of action Expense Cost charged against revenue in an accounting period
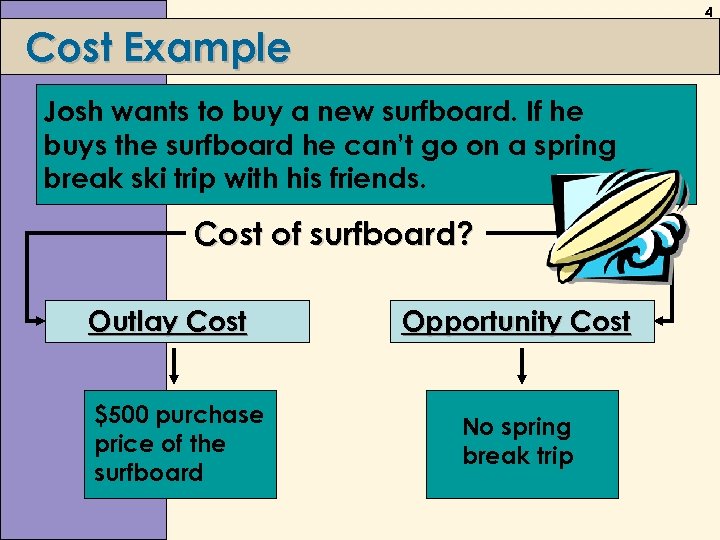
4 Cost Example Josh wants to buy a new surfboard. If he buys the surfboard he can’t go on a spring break ski trip with his friends. Cost of surfboard? Outlay Cost $500 purchase price of the surfboard Opportunity Cost No spring break trip
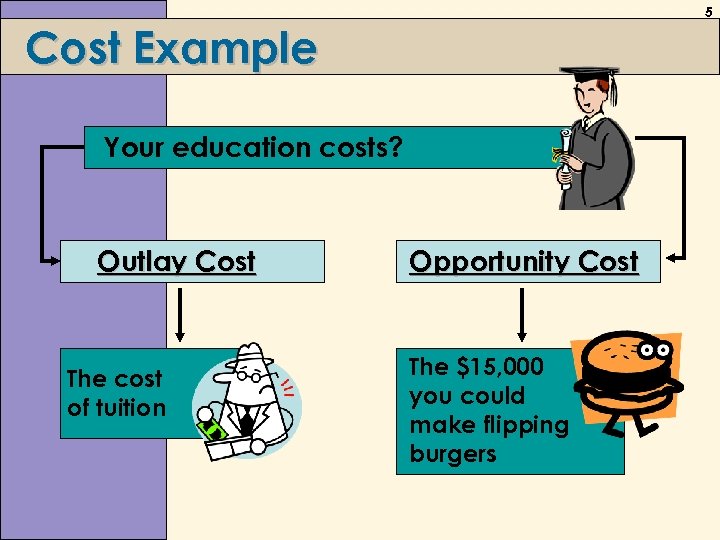
5 Cost Example Your education costs? Outlay Cost The cost of tuition Opportunity Cost The $15, 000 you could make flipping burgers
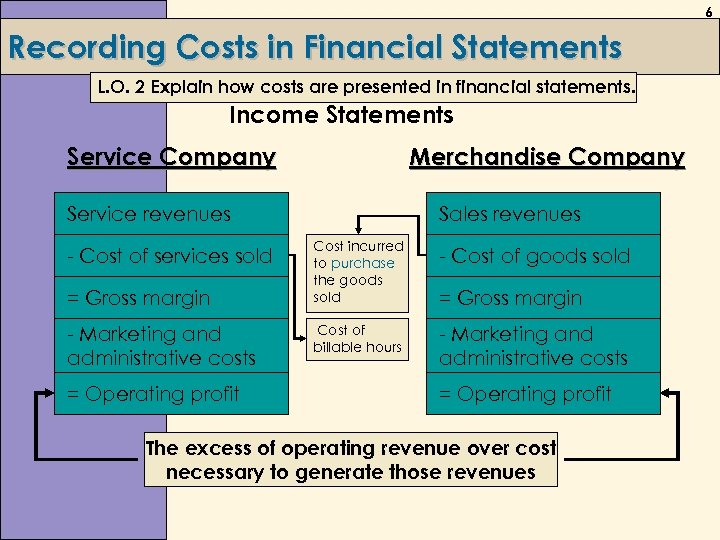
6 Recording Costs in Financial Statements L. O. 2 Explain how costs are presented in financial statements. Income Statements Service Company Merchandise Company Service revenues - Cost of services sold = Gross margin - Marketing and administrative costs = Operating profit Sales revenues Cost incurred to purchase the goods sold - Cost of goods sold Cost of billable hours - Marketing and administrative costs = Gross margin = Operating profit The excess of operating revenue over cost necessary to generate those revenues
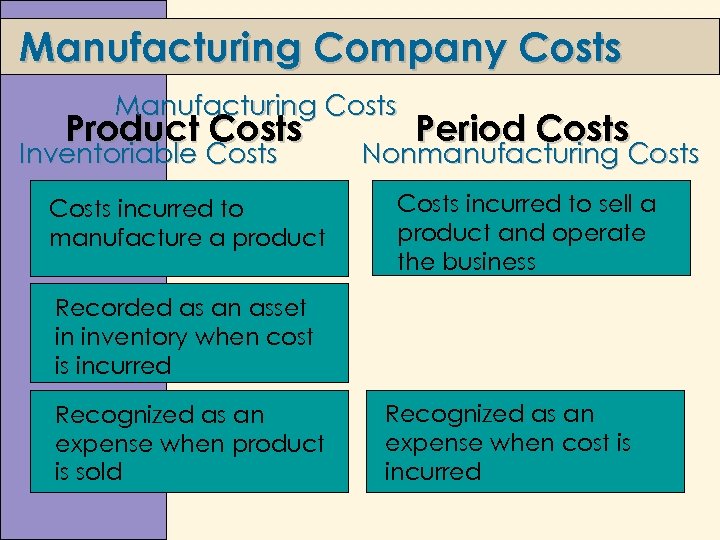
Manufacturing Company Costs Manufacturing Costs Product Costs Inventoriable Costs incurred to manufacture a product Period Costs Nonmanufacturing Costs incurred to sell a product and operate the business Recorded as an asset in inventory when cost is incurred Recognized as an expense when product is sold Recognized as an expense when cost is incurred
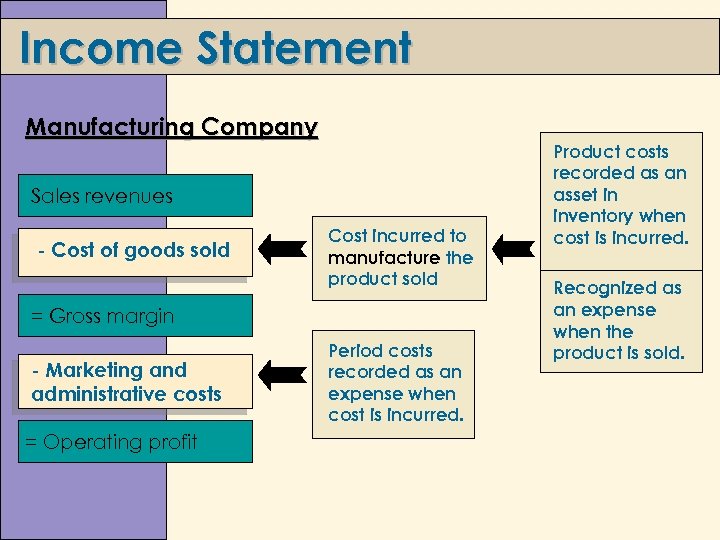
Income Statement Manufacturing Company Sales revenues - Cost of goods sold Cost incurred to manufacture the product sold = Gross margin - Marketing and administrative costs = Operating profit Period costs recorded as an expense when cost is incurred. Product costs recorded as an asset in inventory when cost is incurred. Recognized as an expense when the product is sold.
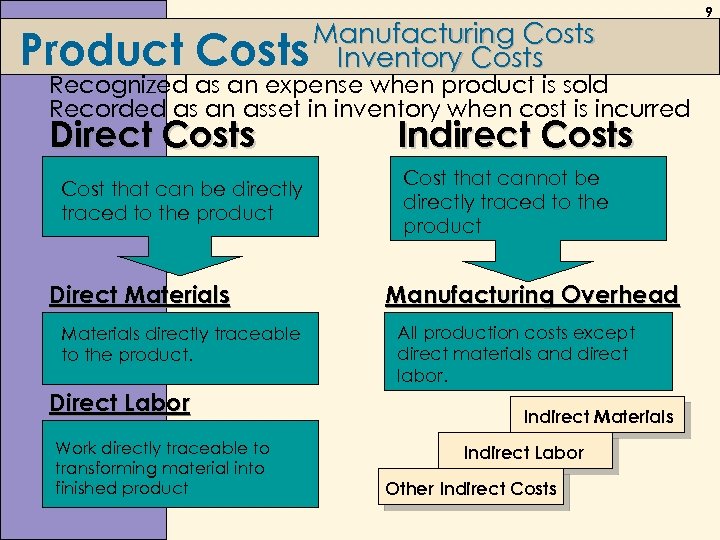
Product Manufacturing Costs Inventory Costs Recognized as an expense when product is sold Recorded as an asset in inventory when cost is incurred Direct Costs Cost that can be directly traced to the product Direct Materials directly traceable to the product. Direct Labor Work directly traceable to transforming material into finished product Indirect Costs Cost that cannot be directly traced to the product Manufacturing Overhead All production costs except direct materials and direct labor. Indirect Materials Indirect Labor Other Indirect Costs 9
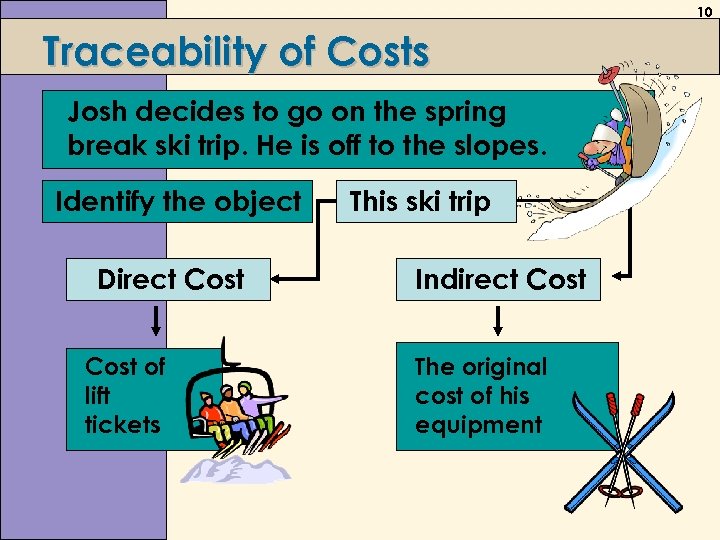
10 Traceability of Costs Josh decides to go on the spring break ski trip. He is off to the slopes. Identify the object Direct Cost of lift tickets This ski trip Indirect Cost The original cost of his equipment
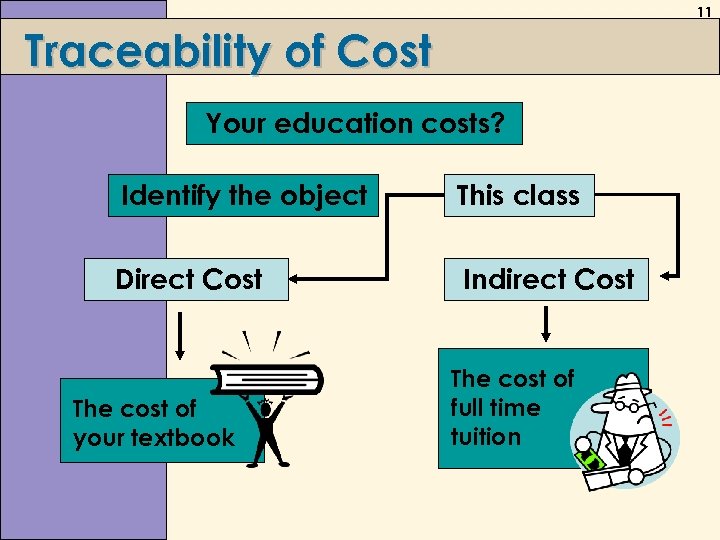
11 Traceability of Cost Your education costs? Identify the object This class Direct Cost Indirect Cost The cost of your textbook The cost of full time tuition
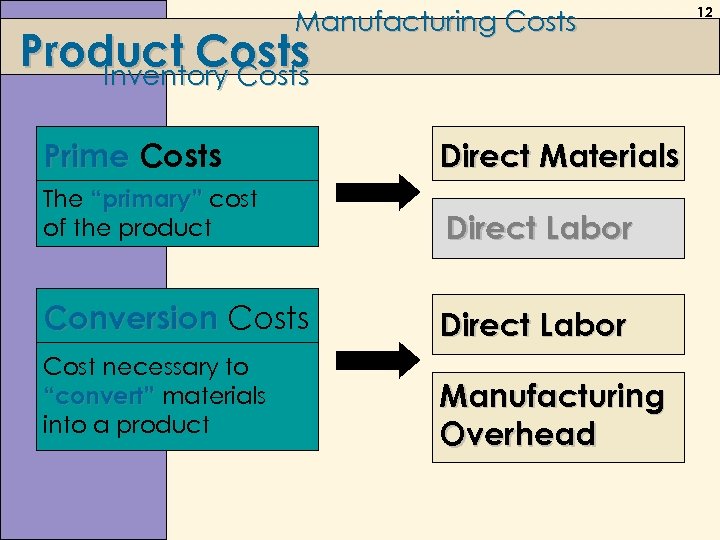
Manufacturing Costs Product Costs Inventory Costs Prime Costs Direct Materials The “primary” cost of the product Direct Labor Conversion Costs Direct Labor Cost necessary to “convert” materials into a product Manufacturing Overhead 12
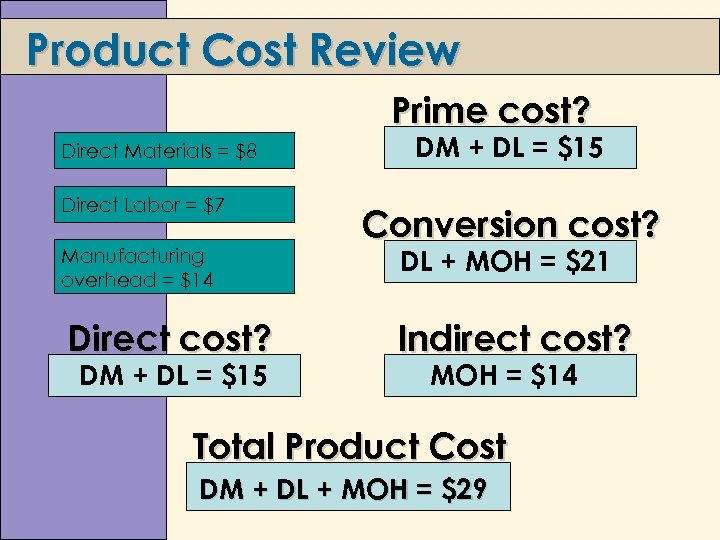
Product Cost Review Prime cost? Direct Materials = $8 Direct Labor = $7 Manufacturing overhead = $14 Direct cost? DM + DL = $15 Conversion cost? DL + MOH = $21 Indirect cost? MOH = $14 Total Product Cost DM + DL + MOH = $29
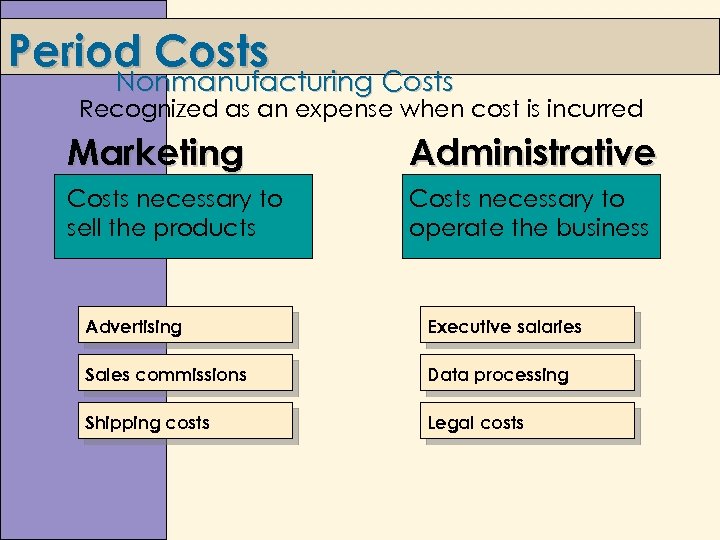
Period Costs Nonmanufacturing Costs Recognized as an expense when cost is incurred Marketing Administrative Costs necessary to sell the products Costs necessary to operate the business Advertising Executive salaries Sales commissions Data processing Shipping costs Legal costs
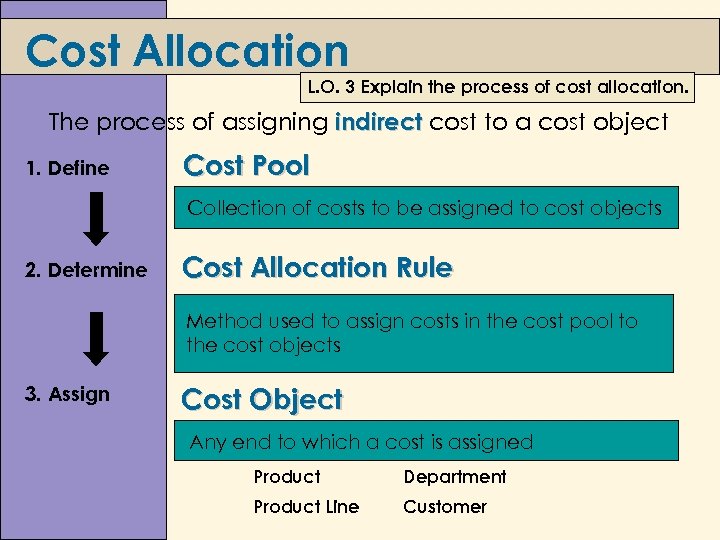
Cost Allocation L. O. 3 Explain the process of cost allocation. The process of assigning indirect cost to a cost object 1. Define Cost Pool Collection of costs to be assigned to cost objects 2. Determine Cost Allocation Rule Method used to assign costs in the cost pool to the cost objects 3. Assign Cost Object Any end to which a cost is assigned Product Department Product Line Customer
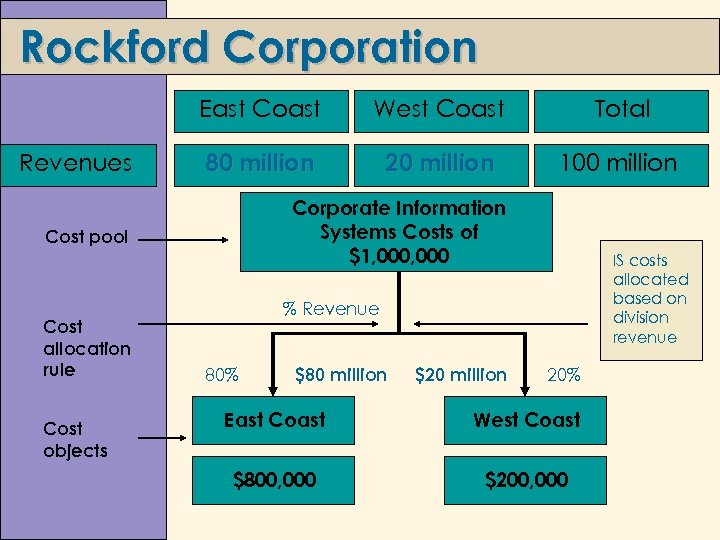
Rockford Corporation East Coast Revenues West Coast Total 80 million 20 million 100 million Corporate Information Systems Costs of $1, 000 Cost pool Cost allocation rule Cost objects IS costs allocated based on division revenue % Revenue 80% $80 million $20 million 20% East Coast West Coast $800, 000 $200, 000
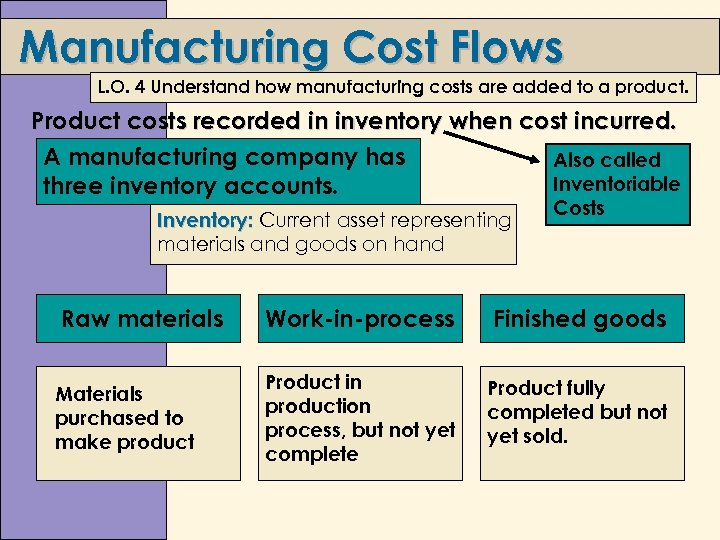
Manufacturing Cost Flows L. O. 4 Understand how manufacturing costs are added to a product. Product costs recorded in inventory when cost incurred. A manufacturing company has Also called Inventoriable three inventory accounts. Inventory: Current asset representing materials and goods on hand Costs Raw materials Work-in-process Finished goods Materials purchased to make product Product in production process, but not yet complete Product fully completed but not yet sold.
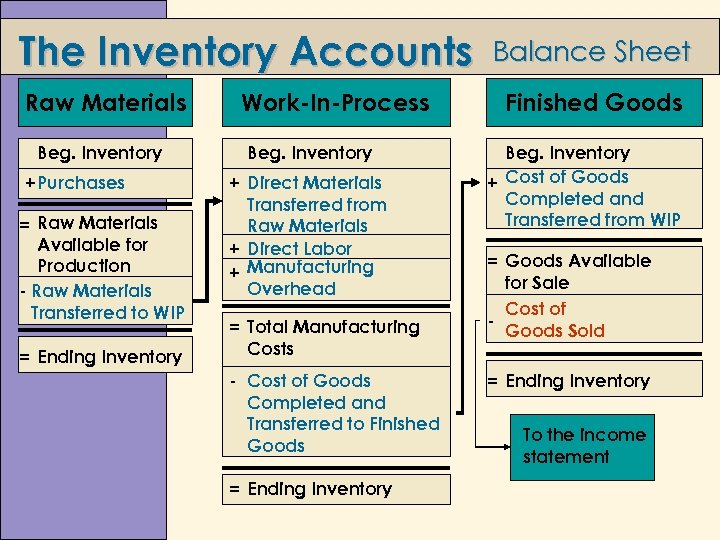
The Inventory Accounts Raw Materials Beg. Inventory +Purchases = Raw Materials Available for Production - Raw Materials Transferred to WIP = Ending Inventory Work-In-Process Beg. Inventory + Direct Materials Transferred from Raw Materials + Direct Labor + Manufacturing Overhead = Total Manufacturing Costs - Cost of Goods Completed and Transferred to Finished Goods = Ending Inventory Balance Sheet Finished Goods Beg. Inventory + Cost of Goods Completed and Transferred from WIP = Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold = Ending Inventory To the income statement

19 Jackson Gears Cost of Goods Manufactured Statement For the Year Ending December 31, 200 X Beginning Work-In-Process Inventory, January 1 $270, 000 Manufacturing cost during the year: Direct Materials Beginning Inventory, Jan. 1 Add Purchases Direct Materials Available Less Ending Inventory, Dec. 31 95, 000 5, 627, 000 $5, 722, 000 72, 000 Direct Materials put into production 5, 650, 000 Direct Labor 1, 220, 000 Manufacturing Overhead 6, 780, 000 Total Manufacturing cost incurred 13, 650, 000 Total Work-In-Process during the year 13, 920, 000 Less Ending Work-In-Process Inventory, Dec. 31 ___310, 000 Cost of goods manufactured $13, 610, 000

20 Jackson Gears Cost of Goods Sold Statement For the Year Ending December 31, 200 X Beginning Finished Goods Inventory, Jan. 1 $420, 000 Cost of goods manufactured 13, 610, 000 Finished goods available for sale 14, 030, 000 Less Ending Finished Goods Inventory, Dec. 31 Cost of goods sold _930, 000 $13, 100, 000

21 Jackson Gears Income Statement For the Year Ending December 31, 200 X Sales Less cost of goods sold $20, 450, 000 13, 100, 000 Gross Margin 7, 350, 000 Marketing and Administrative Expenses 3, 850, 000 Operating Profit $3, 500, 000
Cost Behavior L. O. 5 Define basic cost behaviors including fixed, variable, semivariable, and step costs. Cost Behavior? How costs respond to a change in activity level within the relevant range Relevant range? Range of activity where the total fixed costs or the unit variable costs remain unchanged. 22
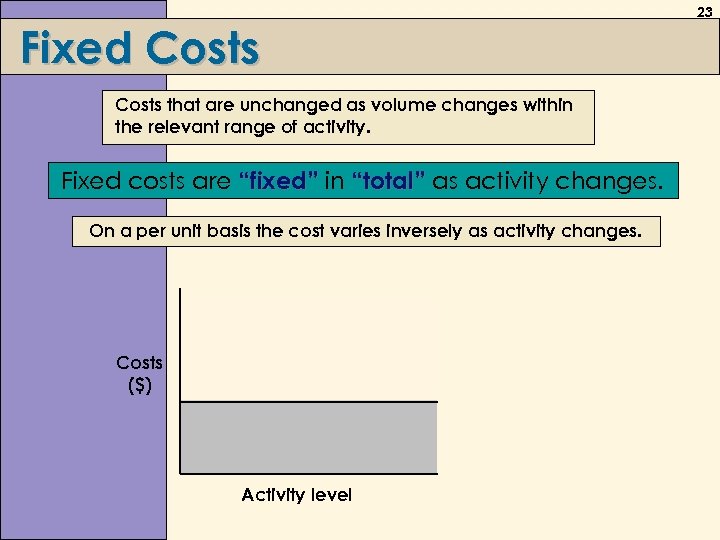
Fixed Costs that are unchanged as volume changes within the relevant range of activity. Fixed costs are “fixed” in “total” as activity changes. On a per unit basis the cost varies inversely as activity changes. Costs ($) Activity level 23
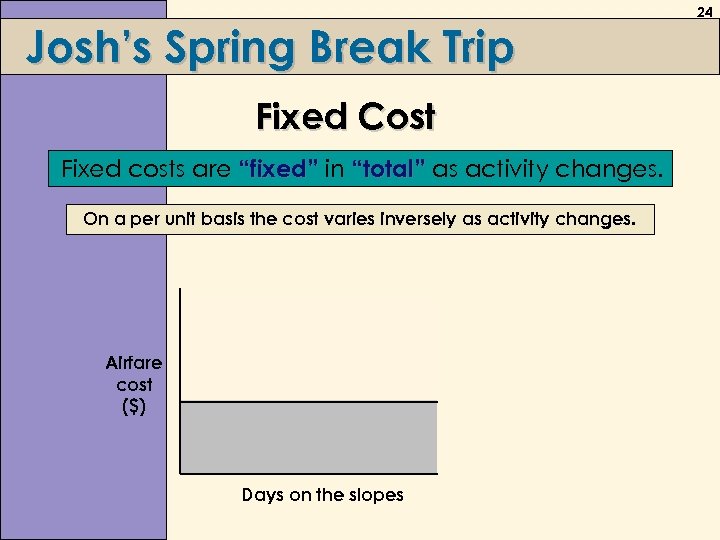
Josh’s Spring Break Trip Fixed Cost Fixed costs are “fixed” in “total” as activity changes. On a per unit basis the cost varies inversely as activity changes. Airfare cost ($) Days on the slopes 24
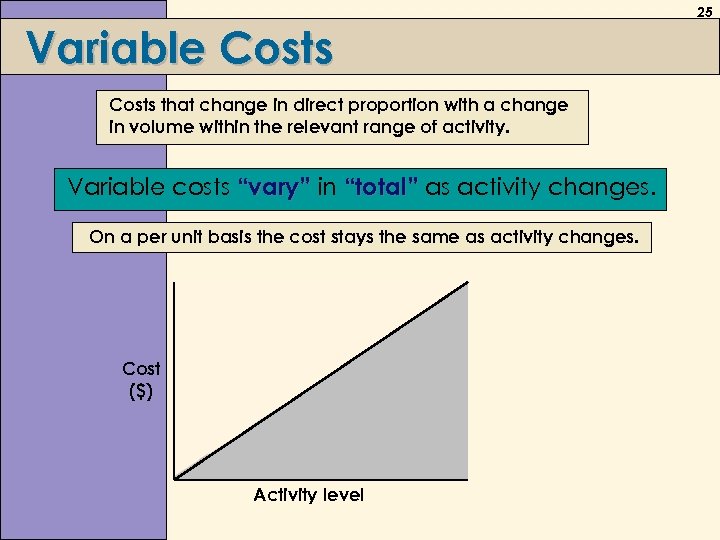
Variable Costs that change in direct proportion with a change in volume within the relevant range of activity. Variable costs “vary” in “total” as activity changes. On a per unit basis the cost stays the same as activity changes. Cost ($) Activity level 25
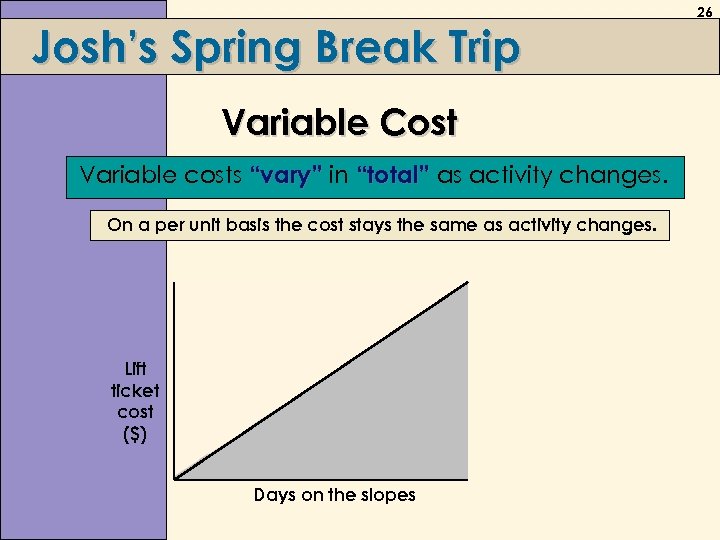
Josh’s Spring Break Trip Variable Cost Variable costs “vary” in “total” as activity changes. On a per unit basis the cost stays the same as activity changes. Lift ticket cost ($) Days on the slopes 26
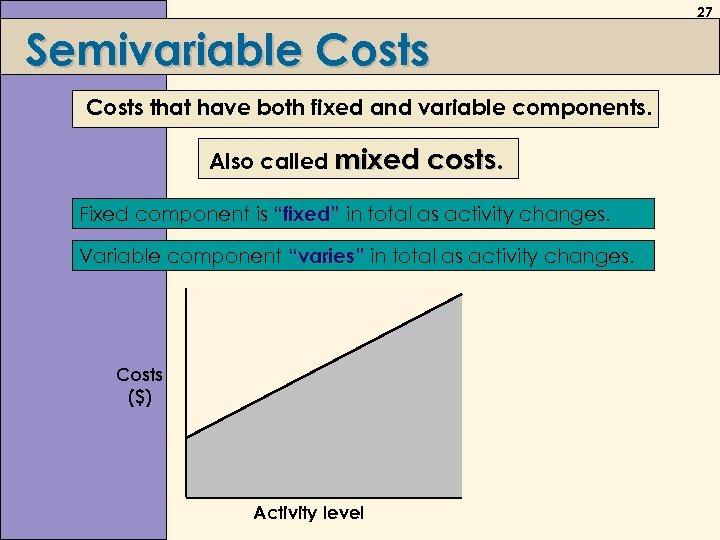
27 Semivariable Costs that have both fixed and variable components. Also called mixed costs. Fixed component is “fixed” in total as activity changes. Variable component “varies” in total as activity changes. Costs ($) Activity level
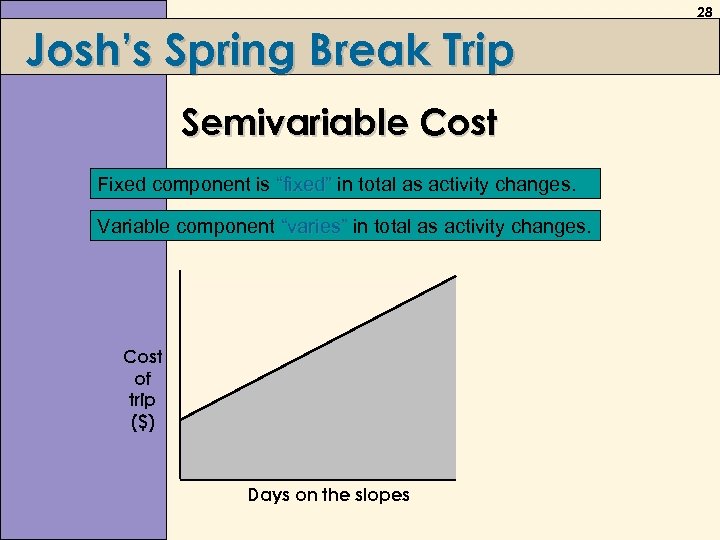
28 Josh’s Spring Break Trip Semivariable Cost Fixed component is “fixed” in total as activity changes. Variable component “varies” in total as activity changes. Cost of trip ($) Days on the slopes
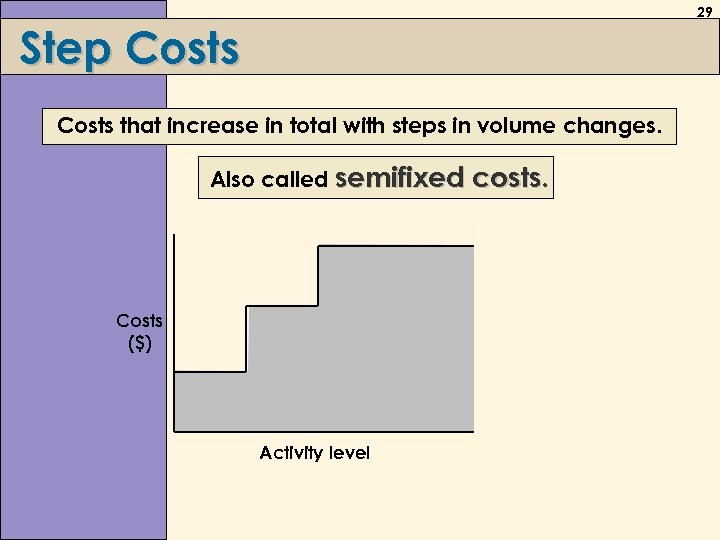
29 Step Costs that increase in total with steps in volume changes. Also called semifixed costs. Costs ($) Activity level
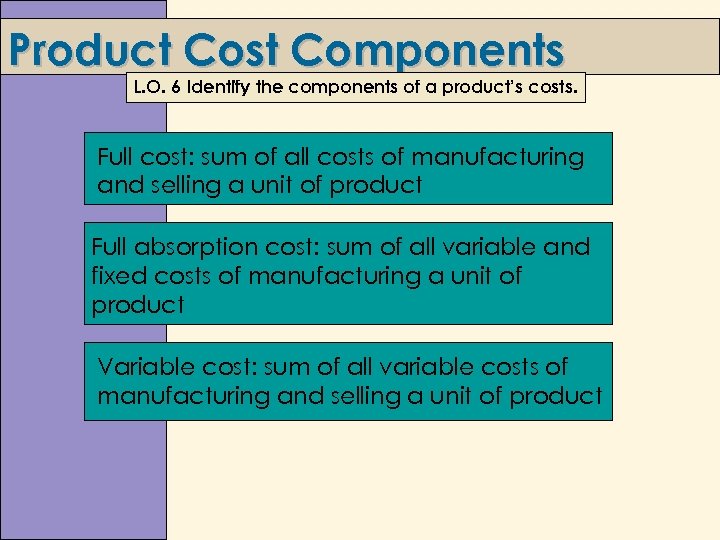
Product Cost Components L. O. 6 Identify the components of a product’s costs. Full cost: sum of all costs of manufacturing and selling a unit of product Full absorption cost: sum of all variable and fixed costs of manufacturing a unit of product Variable cost: sum of all variable costs of manufacturing and selling a unit of product

Costs: An Example Direct Materials = $8 Direct Labor = $7 Variable manufacturing overhead = $8 Fixed manufacturing overhead = $6 Variable marketing and administrative = $4 Fixed marketing and administrative = $7

32 Full Cost Direct Materials = $8 Direct Labor = $7 All costs of manufacturing and selling a unit of product Variable manufacturing overhead = $8 Fixed manufacturing overhead = $6 Variable marketing and administrative = $4 Fixed marketing and administrative = $7

33 Full Absorption Cost Direct Materials = $8 Direct Labor = $7 All variable and fixed costs of manufacturing a unit of product sold Variable manufacturing overhead = $8 Fixed manufacturing overhead = $6

34 Variable Cost Direct Materials = $8 All variable costs of manufacturing and selling a unit of product Direct Labor = $7 Variable manufacturing overhead = $8 Variable marketing and administrative = $4
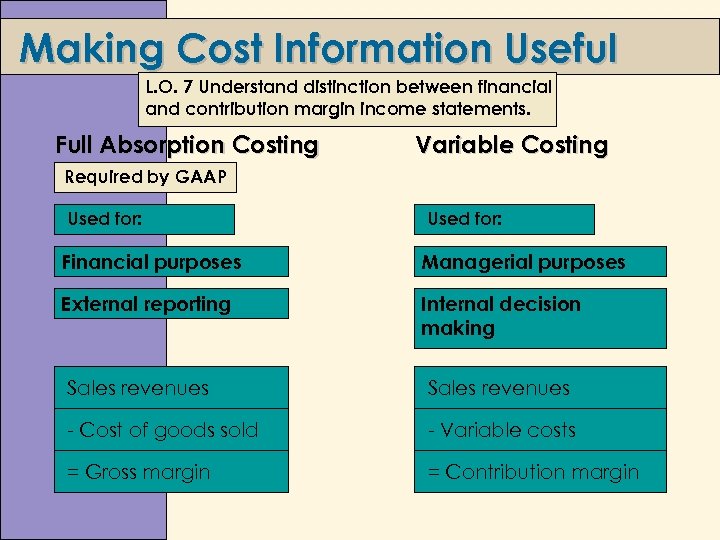
Making Cost Information Useful L. O. 7 Understand distinction between financial and contribution margin income statements. Full Absorption Costing Variable Costing Required by GAAP Used for: Financial purposes Managerial purposes External reporting Internal decision making Sales revenues - Cost of goods sold - Variable costs = Gross margin = Contribution margin
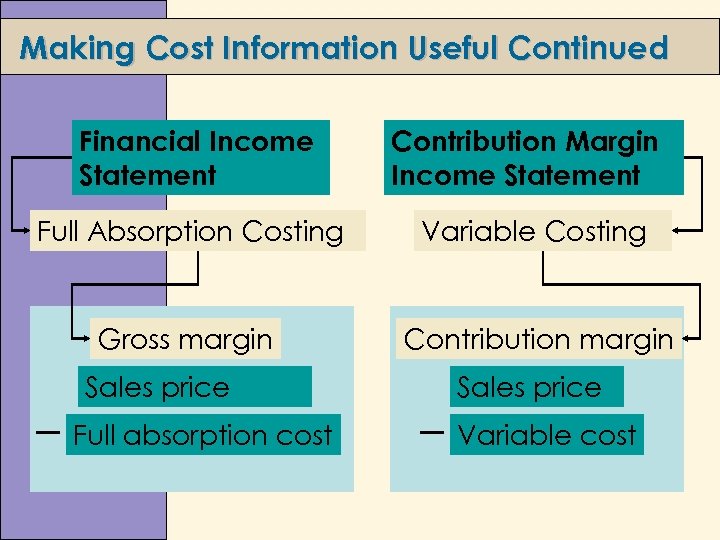
Making Cost Information Useful Continued Financial Income Statement Contribution Margin Income Statement Full Absorption Costing Variable Costing Gross margin Contribution margin Sales price Full absorption cost Sales price Variable cost
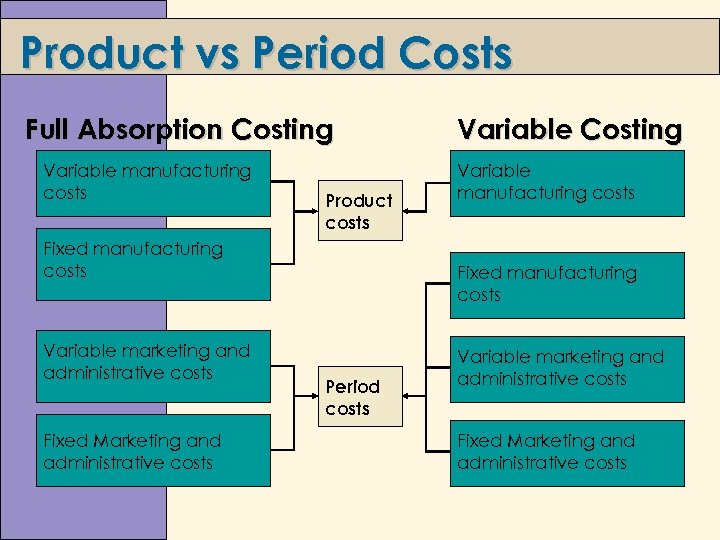
Product vs Period Costs Full Absorption Costing Variable manufacturing costs Product costs Fixed manufacturing costs Variable marketing and administrative costs Fixed Marketing and administrative costs Variable Costing Variable manufacturing costs Fixed manufacturing costs Period costs Variable marketing and administrative costs Fixed Marketing and administrative costs
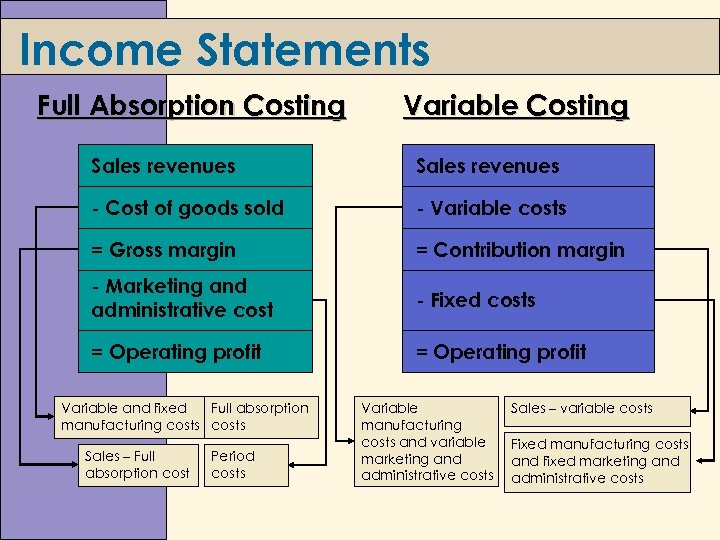
Income Statements Full Absorption Costing Variable Costing Sales revenues - Cost of goods sold - Variable costs = Gross margin = Contribution margin - Marketing and administrative cost - Fixed costs = Operating profit Variable and fixed Full absorption manufacturing costs Sales – Full absorption cost Period costs Variable manufacturing costs and variable marketing and administrative costs Sales – variable costs Fixed manufacturing costs and fixed marketing and administrative costs
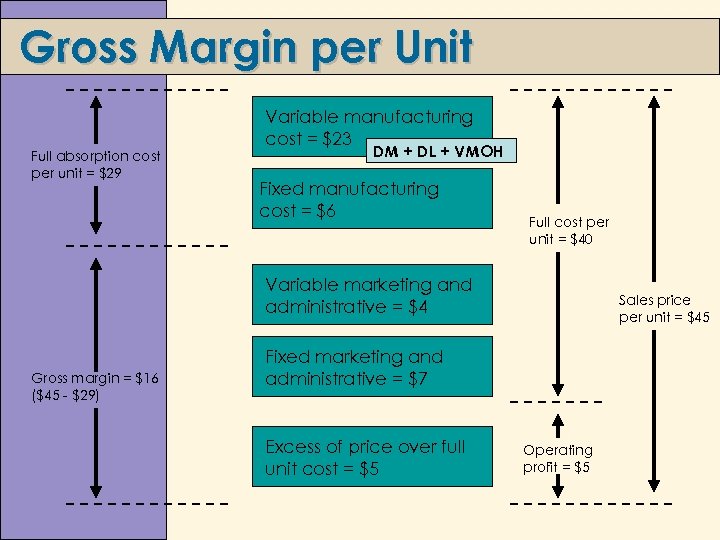
Gross Margin per Unit Full absorption cost per unit = $29 Variable manufacturing cost = $23 DM + DL + VMOH Fixed manufacturing cost = $6 Full cost per unit = $40 Variable marketing and administrative = $4 Gross margin = $16 ($45 - $29) Sales price per unit = $45 Fixed marketing and administrative = $7 Excess of price over full unit cost = $5 Operating profit = $5
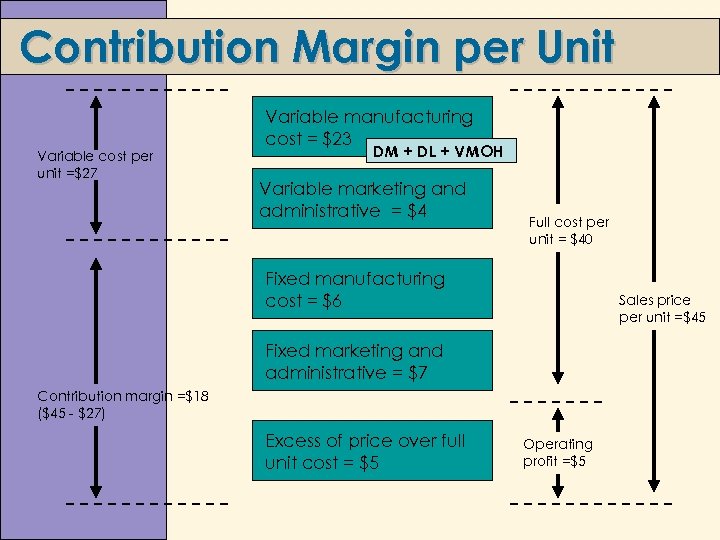
Contribution Margin per Unit Variable cost per unit =$27 Variable manufacturing cost = $23 DM + DL + VMOH Variable marketing and administrative = $4 Full cost per unit = $40 Fixed manufacturing cost = $6 Sales price per unit =$45 Fixed marketing and administrative = $7 Contribution margin =$18 ($45 - $27) Excess of price over full unit cost = $5 Operating profit =$5
41 Chapter 2
d67f504d56aa147837bb2ddee6d16de0.ppt