a9b16b34bdc0b5ada287e221d6ebf4c5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Cost Concepts -1 COST CONCEPTS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Fixed vs Variable Direct vs Indirect Functional vs Behavioral
Cost Concepts -1 COST CONCEPTS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Fixed vs Variable Direct vs Indirect Functional vs Behavioral
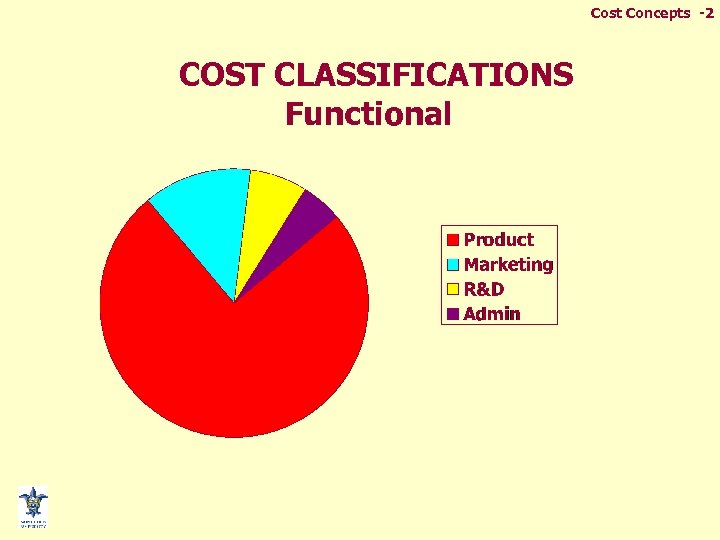 Cost Concepts -2 COST CLASSIFICATIONS Functional
Cost Concepts -2 COST CLASSIFICATIONS Functional
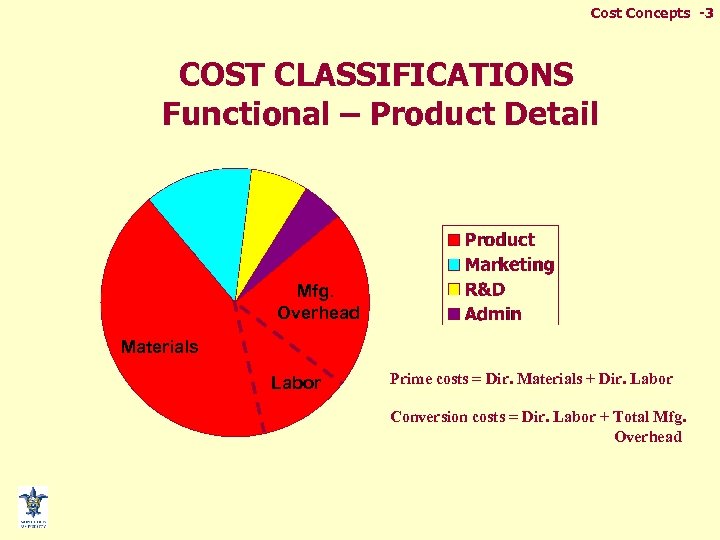 Cost Concepts -3 COST CLASSIFICATIONS Functional – Product Detail Mfg. Overhead Materials Labor Prime costs = Dir. Materials + Dir. Labor Conversion costs = Dir. Labor + Total Mfg. Overhead
Cost Concepts -3 COST CLASSIFICATIONS Functional – Product Detail Mfg. Overhead Materials Labor Prime costs = Dir. Materials + Dir. Labor Conversion costs = Dir. Labor + Total Mfg. Overhead
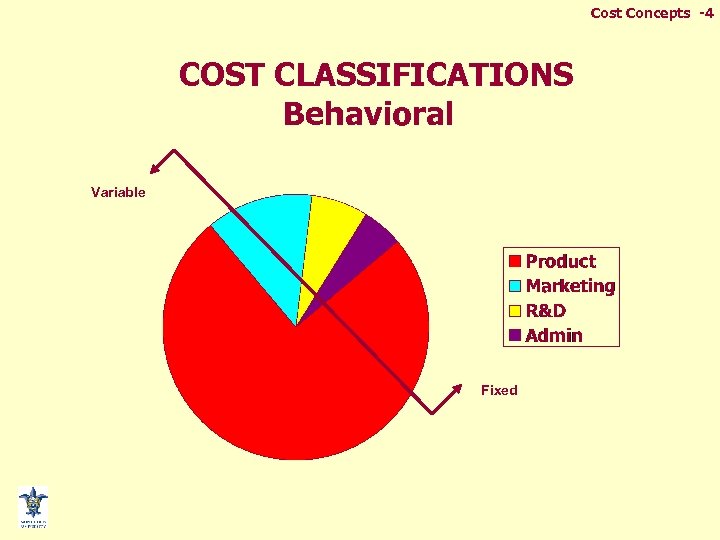 Cost Concepts -4 COST CLASSIFICATIONS Behavioral Variable Fixed
Cost Concepts -4 COST CLASSIFICATIONS Behavioral Variable Fixed
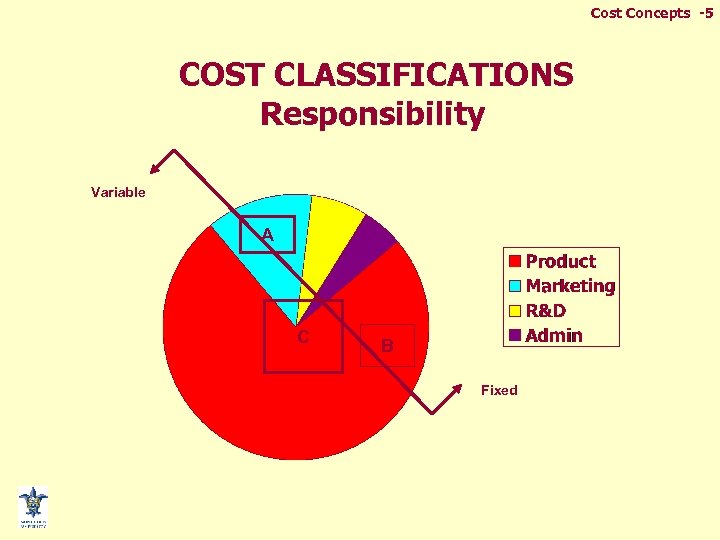 Cost Concepts -5 COST CLASSIFICATIONS Responsibility Variable A C B Fixed
Cost Concepts -5 COST CLASSIFICATIONS Responsibility Variable A C B Fixed
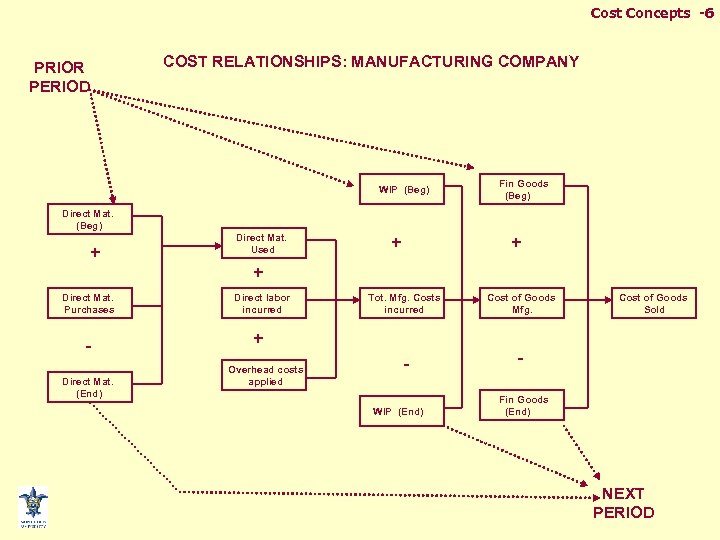 Cost Concepts -6 PRIOR PERIOD COST RELATIONSHIPS: MANUFACTURING COMPANY WIP (Beg) Fin Goods (Beg) Direct Mat. (Beg) + Direct Mat. Purchases Direct Mat. (End) Direct Mat. Used + + + Direct labor incurred Tot. Mfg. Costs incurred + Overhead costs applied WIP (End) Cost of Goods Mfg. Cost of Goods Sold Fin Goods (End) NEXT PERIOD
Cost Concepts -6 PRIOR PERIOD COST RELATIONSHIPS: MANUFACTURING COMPANY WIP (Beg) Fin Goods (Beg) Direct Mat. (Beg) + Direct Mat. Purchases Direct Mat. (End) Direct Mat. Used + + + Direct labor incurred Tot. Mfg. Costs incurred + Overhead costs applied WIP (End) Cost of Goods Mfg. Cost of Goods Sold Fin Goods (End) NEXT PERIOD
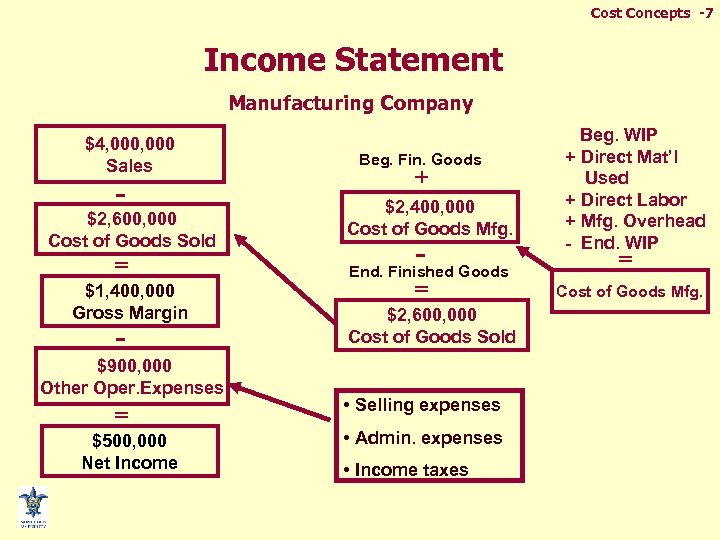 Cost Concepts -7 Income Statement Manufacturing Company $4, 000 Sales - $2, 600, 000 Cost of Goods Sold = $1, 400, 000 Gross Margin - $900, 000 Other Oper. Expenses = $500, 000 Net Income Beg. Fin. Goods + $2, 400, 000 Cost of Goods Mfg. - Goods End. Finished = $2, 600, 000 Cost of Goods Sold • Selling expenses • Admin. expenses • Income taxes Beg. WIP + Direct Mat’l Used + Direct Labor + Mfg. Overhead - End. WIP = Cost of Goods Mfg.
Cost Concepts -7 Income Statement Manufacturing Company $4, 000 Sales - $2, 600, 000 Cost of Goods Sold = $1, 400, 000 Gross Margin - $900, 000 Other Oper. Expenses = $500, 000 Net Income Beg. Fin. Goods + $2, 400, 000 Cost of Goods Mfg. - Goods End. Finished = $2, 600, 000 Cost of Goods Sold • Selling expenses • Admin. expenses • Income taxes Beg. WIP + Direct Mat’l Used + Direct Labor + Mfg. Overhead - End. WIP = Cost of Goods Mfg.
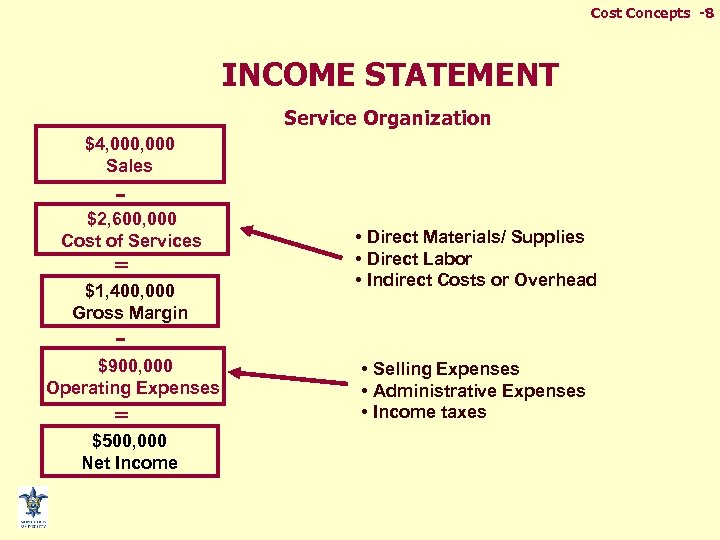 Cost Concepts -8 INCOME STATEMENT Service Organization $4, 000 Sales - $2, 600, 000 Cost of Services = $1, 400, 000 Gross Margin • Direct Materials/ Supplies • Direct Labor • Indirect Costs or Overhead - $900, 000 Operating Expenses = $500, 000 Net Income • Selling Expenses • Administrative Expenses • Income taxes
Cost Concepts -8 INCOME STATEMENT Service Organization $4, 000 Sales - $2, 600, 000 Cost of Services = $1, 400, 000 Gross Margin • Direct Materials/ Supplies • Direct Labor • Indirect Costs or Overhead - $900, 000 Operating Expenses = $500, 000 Net Income • Selling Expenses • Administrative Expenses • Income taxes
 Cost Concepts -9 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Total fixed costs do not respond to changes in unit level cost drivers within a period. Total fixed costs (Y) 0 0 Total activity (X)
Cost Concepts -9 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Total fixed costs do not respond to changes in unit level cost drivers within a period. Total fixed costs (Y) 0 0 Total activity (X)
 Cost Concepts 10 Fixed Costs Committed fixed costs are required to maintain the current service or production capacity to fill previous legal commitments.
Cost Concepts 10 Fixed Costs Committed fixed costs are required to maintain the current service or production capacity to fill previous legal commitments.
 Cost Concepts 11 Fixed Costs Discretionary fixed costs are set at a fixed amount each year at the discretion of management.
Cost Concepts 11 Fixed Costs Discretionary fixed costs are set at a fixed amount each year at the discretion of management.
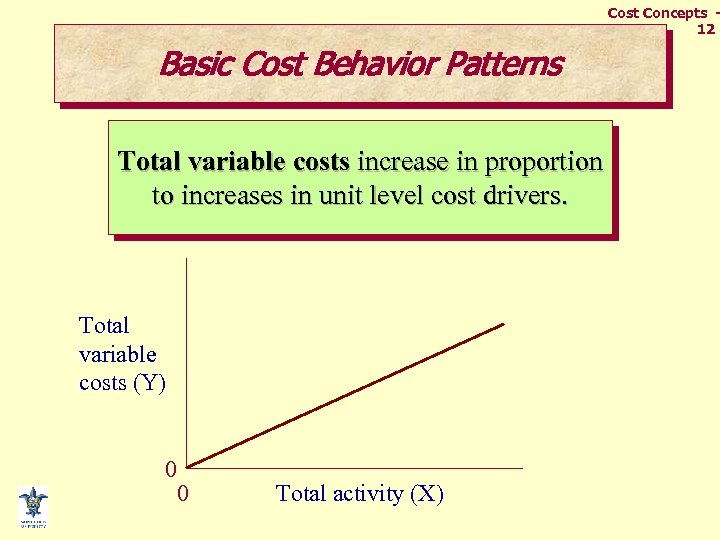 Cost Concepts 12 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Total variable costs increase in proportion to increases in unit level cost drivers. Total variable costs (Y) 0 0 Total activity (X)
Cost Concepts 12 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Total variable costs increase in proportion to increases in unit level cost drivers. Total variable costs (Y) 0 0 Total activity (X)
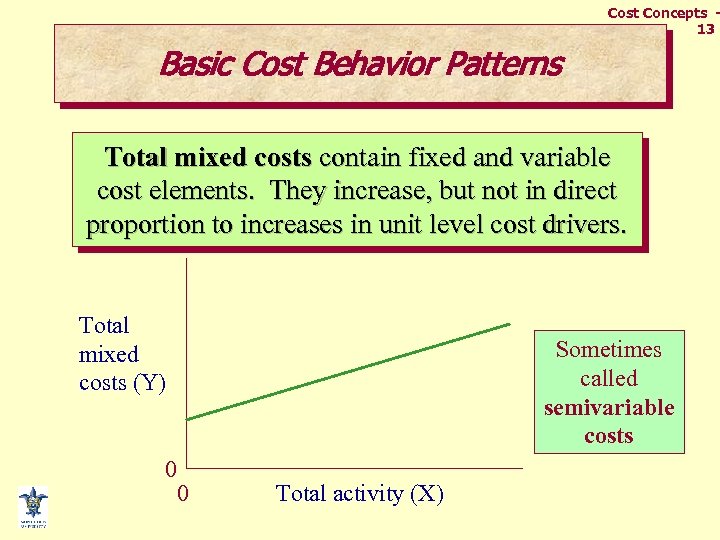 Cost Concepts 13 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Total mixed costs contain fixed and variable cost elements. They increase, but not in direct proportion to increases in unit level cost drivers. Total mixed costs (Y) 0 Sometimes called semivariable costs 0 Total activity (X)
Cost Concepts 13 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Total mixed costs contain fixed and variable cost elements. They increase, but not in direct proportion to increases in unit level cost drivers. Total mixed costs (Y) 0 Sometimes called semivariable costs 0 Total activity (X)
 Cost Concepts 14 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Total step costs are constant over a range of activity for a unit level cost driver but moves to a different amount at different ranges. Total step costs (Y) 0 0 Total activity (X)
Cost Concepts 14 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Total step costs are constant over a range of activity for a unit level cost driver but moves to a different amount at different ranges. Total step costs (Y) 0 0 Total activity (X)
 Cost Concepts 15 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Pizza Hut § Variable costs-- cost of the The ingredients used to make the pizzas § Fixed costs-Depreciation, property taxes, and property insurance § Mixed costs --Cost of electricity § Step costs-Employee wages -
Cost Concepts 15 Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Pizza Hut § Variable costs-- cost of the The ingredients used to make the pizzas § Fixed costs-Depreciation, property taxes, and property insurance § Mixed costs --Cost of electricity § Step costs-Employee wages -
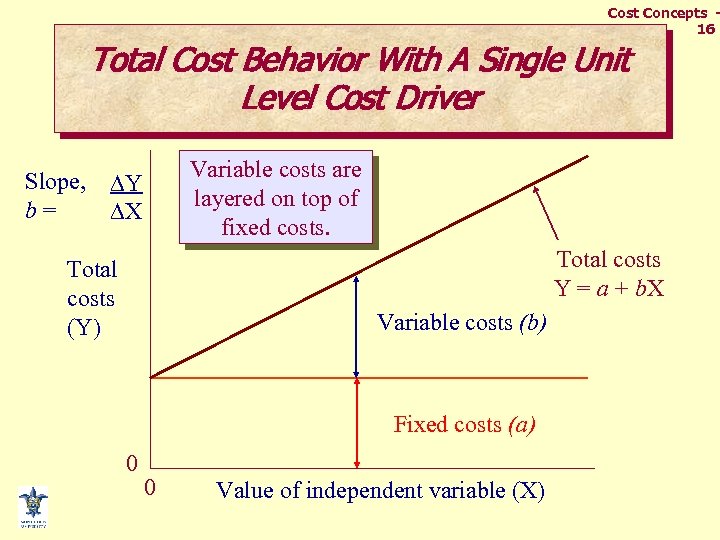 Cost Concepts 16 Total Cost Behavior With A Single Unit Level Cost Driver Slope, b= Variable costs are layered on top of fixed costs. Y X Total costs Y = a + b. X Total costs (Y) Variable costs (b) Fixed costs (a) 0 0 Value of independent variable (X)
Cost Concepts 16 Total Cost Behavior With A Single Unit Level Cost Driver Slope, b= Variable costs are layered on top of fixed costs. Y X Total costs Y = a + b. X Total costs (Y) Variable costs (b) Fixed costs (a) 0 0 Value of independent variable (X)
 Cost Concepts 17 Equation for Total Costs Y = a + b. X value of totalvertical axis intercept costs slope (an approximationindependent of of variable costs per fixed costs)unit variable of X)
Cost Concepts 17 Equation for Total Costs Y = a + b. X value of totalvertical axis intercept costs slope (an approximationindependent of of variable costs per fixed costs)unit variable of X)
 Cost Concepts 18 Methods for Separating Mixed Cost Into Fixed and Variable Components § Scatterplot Method § The High-Low Method § Specific quantitative methods – The Method of Least Squares
Cost Concepts 18 Methods for Separating Mixed Cost Into Fixed and Variable Components § Scatterplot Method § The High-Low Method § Specific quantitative methods – The Method of Least Squares
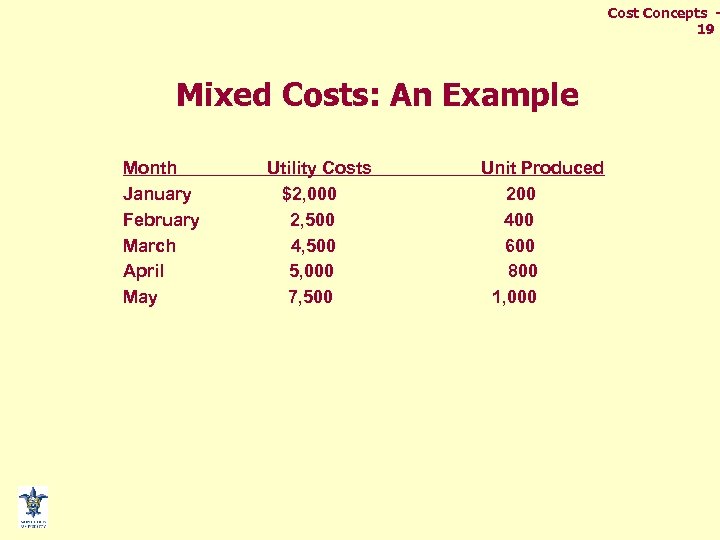 Cost Concepts 19 Mixed Costs: An Example Month January February March April May Utility Costs $2, 000 2, 500 4, 500 5, 000 7, 500 Unit Produced 200 400 600 800 1, 000
Cost Concepts 19 Mixed Costs: An Example Month January February March April May Utility Costs $2, 000 2, 500 4, 500 5, 000 7, 500 Unit Produced 200 400 600 800 1, 000
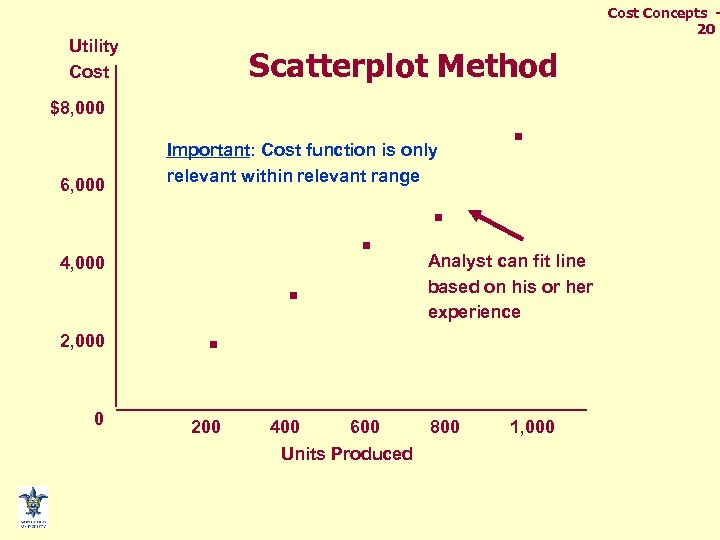 Cost Concepts 20 Utility Cost Scatterplot Method $8, 000 6, 000 Important: Cost function is only relevant within relevant range 4, 000 2, 000 . 0 200 . . Analyst can fit line based on his or her experience 400 600 800 Units Produced 1, 000
Cost Concepts 20 Utility Cost Scatterplot Method $8, 000 6, 000 Important: Cost function is only relevant within relevant range 4, 000 2, 000 . 0 200 . . Analyst can fit line based on his or her experience 400 600 800 Units Produced 1, 000
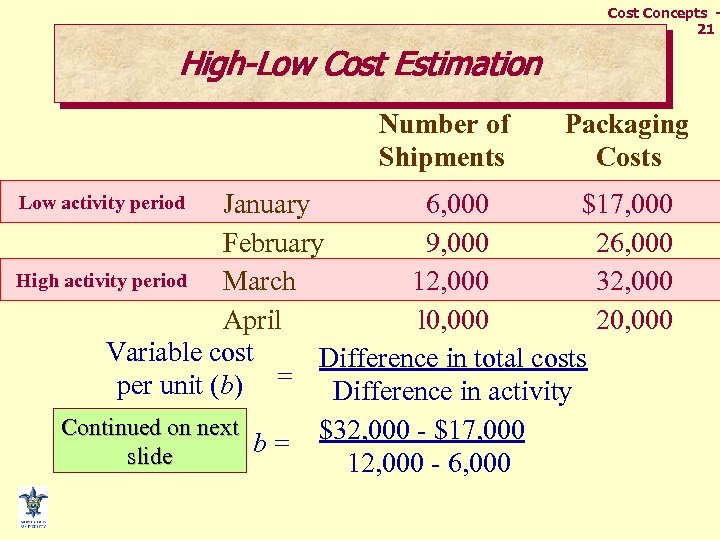 Cost Concepts 21 High-Low Cost Estimation Number of Shipments Packaging Costs January 6, 000 $17, 000 February 9, 000 26, 000 High activity period March 12, 000 32, 000 April l 0, 000 20, 000 Variable cost Difference in total costs per unit (b) = Difference in activity Continued on next b = $32, 000 - $17, 000 slide 12, 000 - 6, 000 Low activity period
Cost Concepts 21 High-Low Cost Estimation Number of Shipments Packaging Costs January 6, 000 $17, 000 February 9, 000 26, 000 High activity period March 12, 000 32, 000 April l 0, 000 20, 000 Variable cost Difference in total costs per unit (b) = Difference in activity Continued on next b = $32, 000 - $17, 000 slide 12, 000 - 6, 000 Low activity period
 Cost Concepts 22 High-Low Cost Estimation Variable cost = $2. 50 per unit (b) January a = Total costs - Variable costs $17, 000 = a + ($2. 50 x 6, 000 shipments) a = $2, 000 March Same answer! $32, 000 = a + ($2. 50 x 12, 000 shipments) a = $2, 000
Cost Concepts 22 High-Low Cost Estimation Variable cost = $2. 50 per unit (b) January a = Total costs - Variable costs $17, 000 = a + ($2. 50 x 6, 000 shipments) a = $2, 000 March Same answer! $32, 000 = a + ($2. 50 x 12, 000 shipments) a = $2, 000
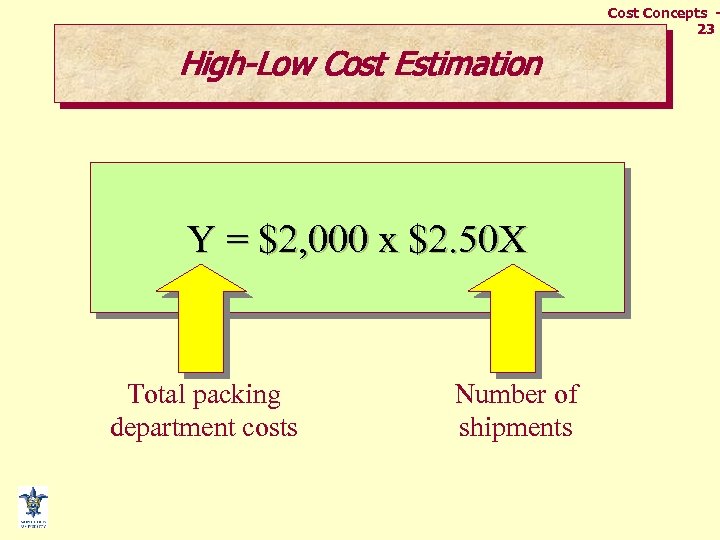 Cost Concepts 23 High-Low Cost Estimation Y = $2, 000 x $2. 50 X Total packing department costs Number of shipments
Cost Concepts 23 High-Low Cost Estimation Y = $2, 000 x $2. 50 X Total packing department costs Number of shipments
 Composition of Manufacturing Costs Cost Concepts 24 Direct materials, the cost of primary raw materials converted into finished Manufacturing overhead goods. The word “direct” includes all manufacturing costs indicates costs that are other than direct materials and easily or directly traced to a direct labor. finished product or service. Direct labor, the wages earned by production employees for the time they spend converting raw materials into finished products.
Composition of Manufacturing Costs Cost Concepts 24 Direct materials, the cost of primary raw materials converted into finished Manufacturing overhead goods. The word “direct” includes all manufacturing costs indicates costs that are other than direct materials and easily or directly traced to a direct labor. finished product or service. Direct labor, the wages earned by production employees for the time they spend converting raw materials into finished products.
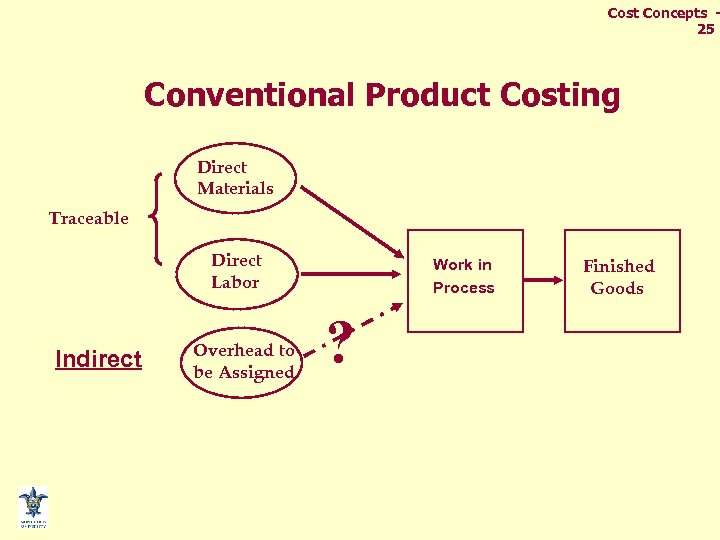 Cost Concepts 25 Conventional Product Costing Direct Materials Traceable Direct Labor Indirect Overhead to be Assigned Work in Process ? Finished Goods
Cost Concepts 25 Conventional Product Costing Direct Materials Traceable Direct Labor Indirect Overhead to be Assigned Work in Process ? Finished Goods
 Cost Concepts 26 Composition of Manufacturing Costs § Prime costs = Direct materials + Direct labor § Conversion costs = Direct labor + Manufacturing overhead (fixed & variable)
Cost Concepts 26 Composition of Manufacturing Costs § Prime costs = Direct materials + Direct labor § Conversion costs = Direct labor + Manufacturing overhead (fixed & variable)
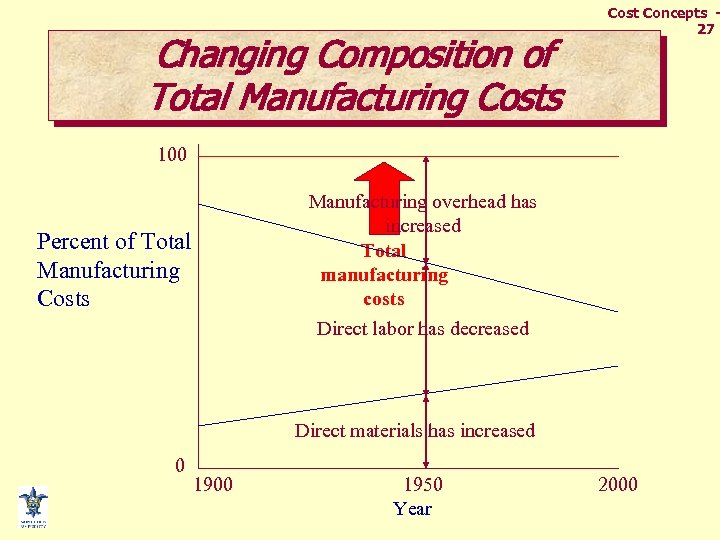 Changing Composition of Total Manufacturing Costs Cost Concepts 27 100 Manufacturing overhead has increased Total manufacturing costs Percent of Total Manufacturing Costs Direct labor has decreased Direct materials has increased 0 1900 1950 Year 2000
Changing Composition of Total Manufacturing Costs Cost Concepts 27 100 Manufacturing overhead has increased Total manufacturing costs Percent of Total Manufacturing Costs Direct labor has decreased Direct materials has increased 0 1900 1950 Year 2000
 Cost Concepts 28 The Basic Concept of Overhead Application Applied overhead = Overhead rate x Actual activity Key considerations § Applied overhead is the basis for computing per-unit overhead cost § Applied overhead is rarely equal to a period's actual overhead costs.
Cost Concepts 28 The Basic Concept of Overhead Application Applied overhead = Overhead rate x Actual activity Key considerations § Applied overhead is the basis for computing per-unit overhead cost § Applied overhead is rarely equal to a period's actual overhead costs.
 Cost Concepts 29 CONVENTIONAL PRODUCT COSTING Overhead Application Predetermined Overhead Rate Total budgeted overhead = Expected level of activity * • Conventional costing typically used volume (or a surrogate for volume such as DLH) • Problems - Budgeted overhead contains both fixed and variable costs - Selection of expected level of activity
Cost Concepts 29 CONVENTIONAL PRODUCT COSTING Overhead Application Predetermined Overhead Rate Total budgeted overhead = Expected level of activity * • Conventional costing typically used volume (or a surrogate for volume such as DLH) • Problems - Budgeted overhead contains both fixed and variable costs - Selection of expected level of activity
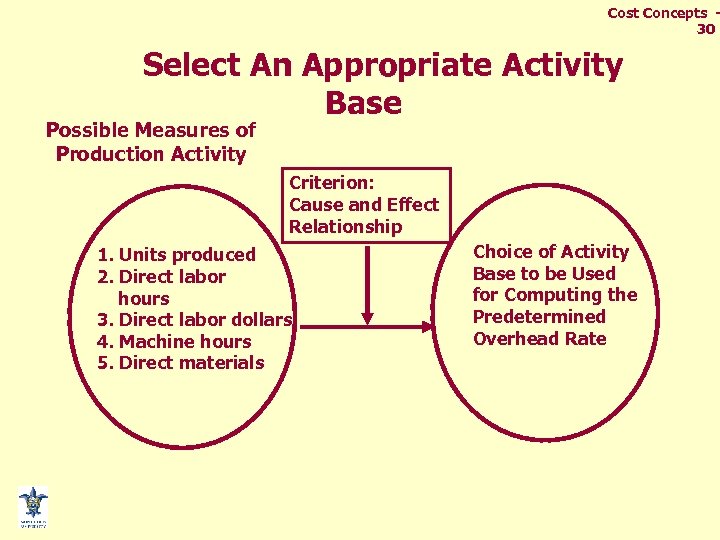 Cost Concepts 30 Select An Appropriate Activity Base Possible Measures of Production Activity Criterion: Cause and Effect Relationship 1. Units produced 2. Direct labor hours 3. Direct labor dollars 4. Machine hours 5. Direct materials Choice of Activity Base to be Used for Computing the Predetermined Overhead Rate
Cost Concepts 30 Select An Appropriate Activity Base Possible Measures of Production Activity Criterion: Cause and Effect Relationship 1. Units produced 2. Direct labor hours 3. Direct labor dollars 4. Machine hours 5. Direct materials Choice of Activity Base to be Used for Computing the Predetermined Overhead Rate
 Cost Concepts 31 Comparison of Traditional and Contemporary Cost Management Systems Traditional Contemporary Cost Information System 1. Unit-based drivers 2. Allocation intensive 3. Narrow view of product costs 4. Focus on cost mgt. 5. Little activity information 6. Maximizes unit production 7. Uses financial measures of performance 1. Uses of nonunit drivers 2. Tracing intensive 3. Expanded product costing 4. Managing activities 5. Detailed activity information 6. System-wide performance appraisals 7. Use of nonfinancial measures of performance
Cost Concepts 31 Comparison of Traditional and Contemporary Cost Management Systems Traditional Contemporary Cost Information System 1. Unit-based drivers 2. Allocation intensive 3. Narrow view of product costs 4. Focus on cost mgt. 5. Little activity information 6. Maximizes unit production 7. Uses financial measures of performance 1. Uses of nonunit drivers 2. Tracing intensive 3. Expanded product costing 4. Managing activities 5. Detailed activity information 6. System-wide performance appraisals 7. Use of nonfinancial measures of performance
 Cost Concepts 32 Impact of Computers on Manufacturing Automatic identification systems (AIS) allow inventory and production information to be entered into a computer without writing or keying.
Cost Concepts 32 Impact of Computers on Manufacturing Automatic identification systems (AIS) allow inventory and production information to be entered into a computer without writing or keying.
 Cost Concepts 33 Impact of Computers on Manufacturing Computer-aided design (CAD) involves the use of computers to design products.
Cost Concepts 33 Impact of Computers on Manufacturing Computer-aided design (CAD) involves the use of computers to design products.
 Cost Concepts 34 Impact of Computers on Manufacturing Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) involves the use of computers to control machine operations.
Cost Concepts 34 Impact of Computers on Manufacturing Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) involves the use of computers to control machine operations.
 Cost Concepts 35 Impact of Computers on Manufacturing In their advanced stages, factories utilizing flexible manufacturing systems and computer-integrated manufacturing Flexible manufacturing are sometimes systems (FMS) are an extension referred to as “lights-out factories”because they can be operated of computer-aided Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is the manufacturing techniques in the dark. through a seriesultimate extension of CAD, CAM, of and FMS manufacturing operations. concepts to a completed automated and computercontrolled factory.
Cost Concepts 35 Impact of Computers on Manufacturing In their advanced stages, factories utilizing flexible manufacturing systems and computer-integrated manufacturing Flexible manufacturing are sometimes systems (FMS) are an extension referred to as “lights-out factories”because they can be operated of computer-aided Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is the manufacturing techniques in the dark. through a seriesultimate extension of CAD, CAM, of and FMS manufacturing operations. concepts to a completed automated and computercontrolled factory.


