ef9799143b2541e0e63344949743bbf7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45

Cosmic Variability ─ The Next Frontier in Astrophysics: Wen-Ping Chen Institute of Astronomy National Central University, Taiwan 2010 June 22 Tashkent

Outline n Era of time-domain astrophysics n Niche of observational astronomy in Taiwan - Taiwanese-American Occultation Survey - Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System n Local infrastructure n Conclusion

Frontiers in Observational Astrophysics n Resolution ── angular (details), spectroscopic n Sensitivity Next domain: Time The Sun oscillates on minute time scales; it also evolves on billion year time scales. In between? What do celestial objects change in various time scales? Why? Time-domain astrophysics. How? Projects in Taiwan Local Infrastructure
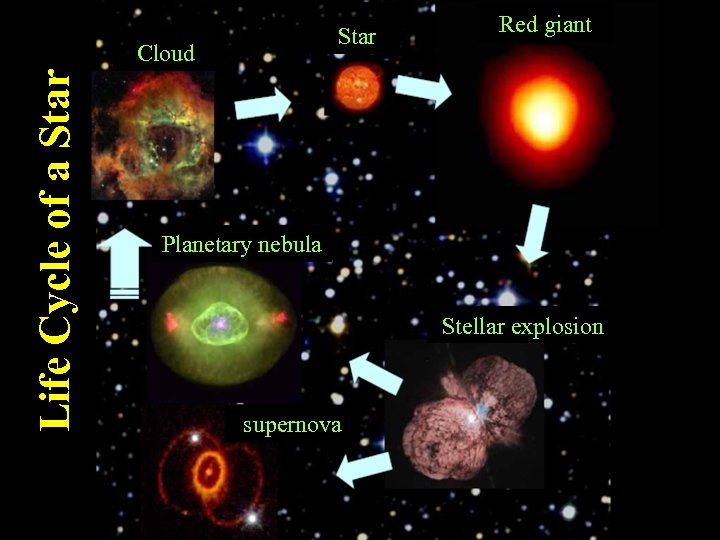
Star Life Cycle of a Star Cloud Red giant Planetary nebula Stellar explosion supernova
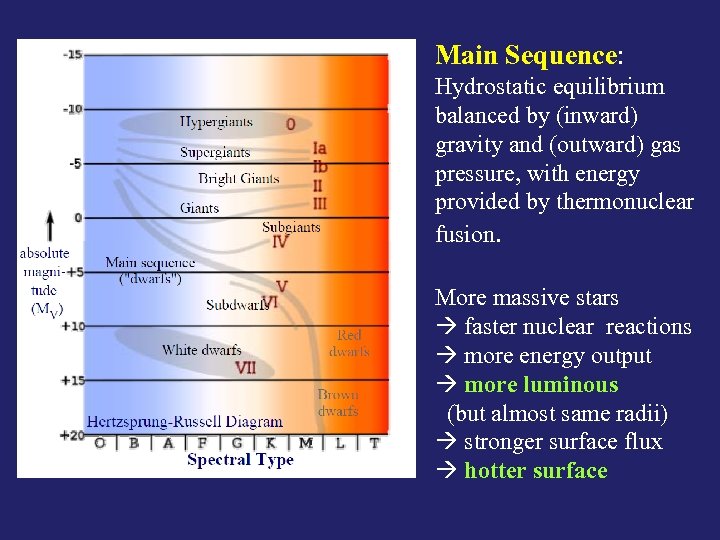
Main Sequence: Hydrostatic equilibrium balanced by (inward) gravity and (outward) gas pressure, with energy provided by thermonuclear fusion. More massive stars faster nuclear reactions more energy output more luminous (but almost same radii) stronger surface flux hotter surface
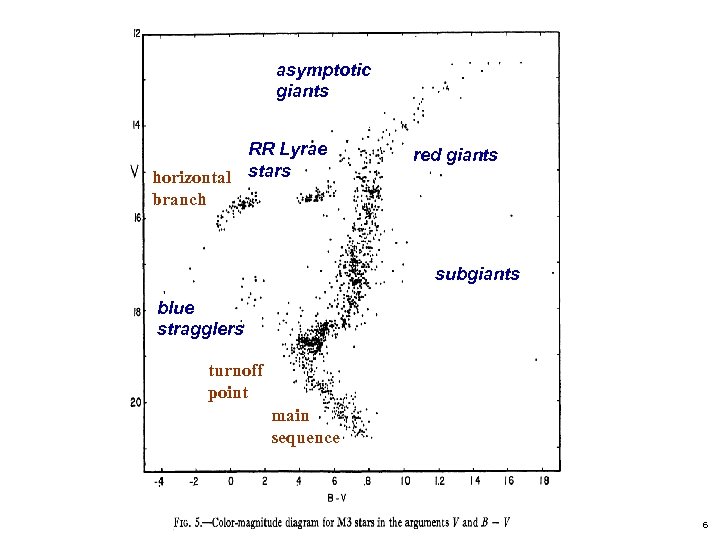
asymptotic giants RR Lyrae horizontal stars branch red giants subgiants blue stragglers turnoff point main sequence 6
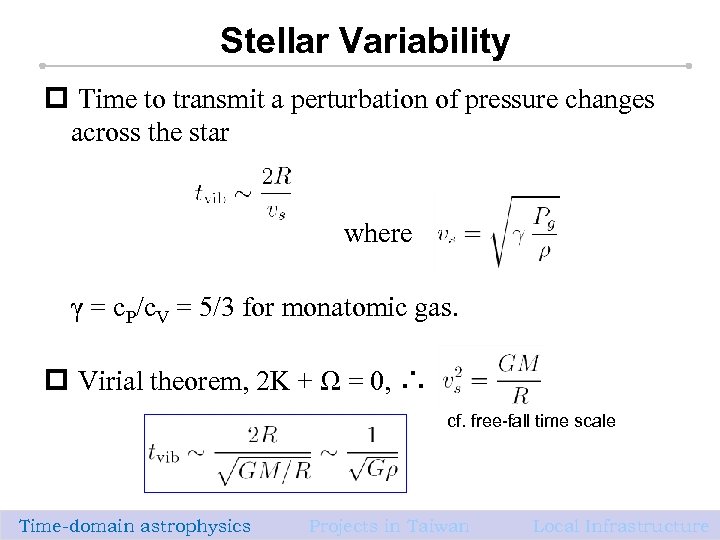
Stellar Variability p Time to transmit a perturbation of pressure changes across the star where γ = c. P/c. V = 5/3 for monatomic gas. p Virial theorem, 2 K + Ω = 0, ∴ cf. free-fall time scale Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan 7 Local Infrastructure

Supernova (explosion) A catastrophic burst of energy triggered by (i) a collapsing core of an aging massive star after it ceases to produce energy from thermonuclear fusion. Collapse of a 3000 km iron core in 0. 1 s. (ii) a white dwarf (relic of a low-mass star like our Sun) accreting sufficient material from a stellar companion Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan Local Infrastructure
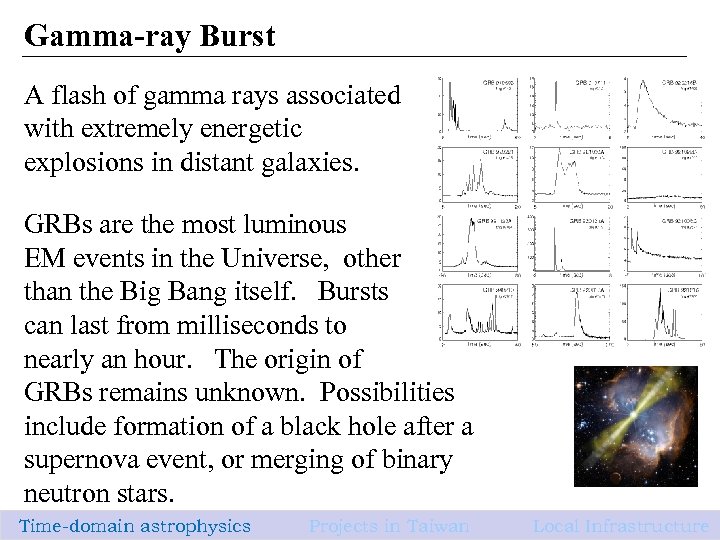
Gamma-ray Burst A flash of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions in distant galaxies. GRBs are the most luminous EM events in the Universe, other than the Big Bang itself. Bursts can last from milliseconds to nearly an hour. The origin of GRBs remains unknown. Possibilities include formation of a black hole after a supernova event, or merging of binary neutron stars. Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan 9 Local Infrastructure
Advantages in Taiwan: - Many high mountains - Western Pacific longitude - Low latitude variability studies

LULIN OBSERVATORY 鹿林天文台 Altitude 2862 m; often above the inversion layer … seen from Yusan (Jade Mt) 玉山 4000 -m

Scientific Activities at Lulin • Time Variability - Part of global network - Mass data processing - Data mining • TAOS (Taiwan, USA, Korea) • LELIS (NCU) • Taiwan Oscillation Network (NTHU) • Sprite (NCKU) • Taiwan Earth-Shine Network (NTHU) • Atmospheric Experiments NCU/Lulin Observatory from Yusan North Peak So far, discoveries of 10+ supernovae, 800+ asteroids, 1 comet, variable stars …
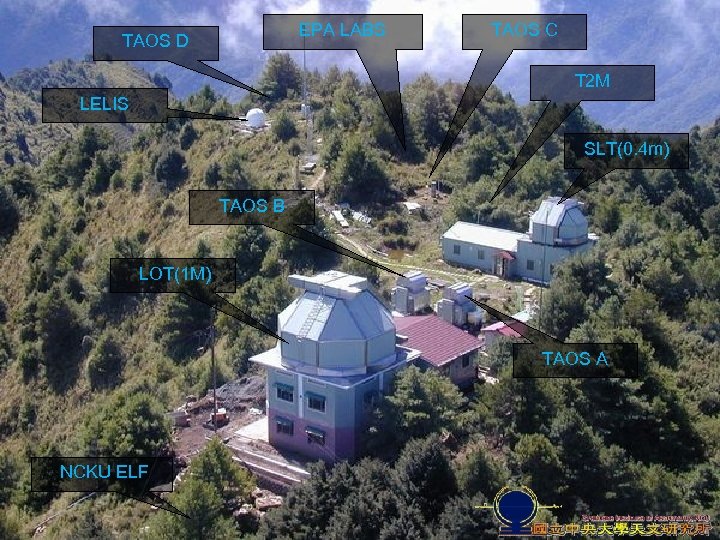

EPA LABS TAOS D TAOS C T 2 M LELIS SLT(0. 4 m) TAOS B LOT(1 M) TAOS A NCKU ELF
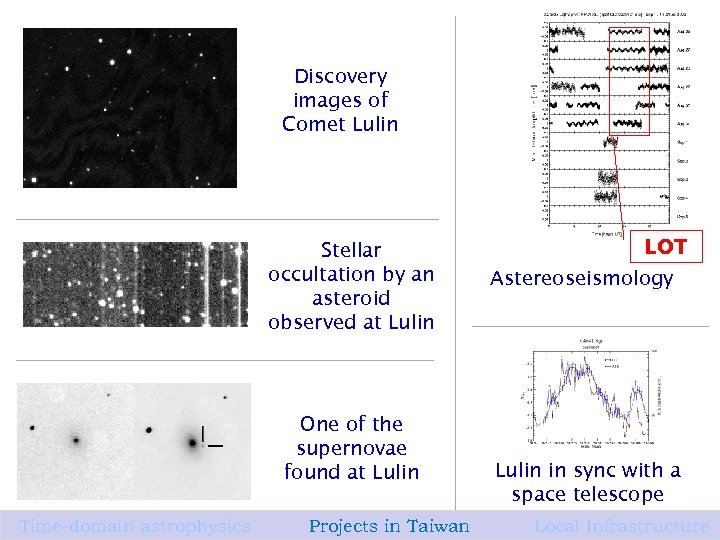
Discovery images of Comet Lulin Stellar occultation by an asteroid observed at Lulin One of the supernovae found at Lulin Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan LOT Astereoseismology Lulin in sync with a space telescope Local Infrastructure

Outline 中美掩星計畫 Fully operational; in Taiwan TAOS Taiwan-America Occultation Survey Pan-STARRS Panoramic Survey Telescope & Rapid Response System Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan 泛星計畫 Commissioning; in Hawaii, USA 16 Local Infrastructure
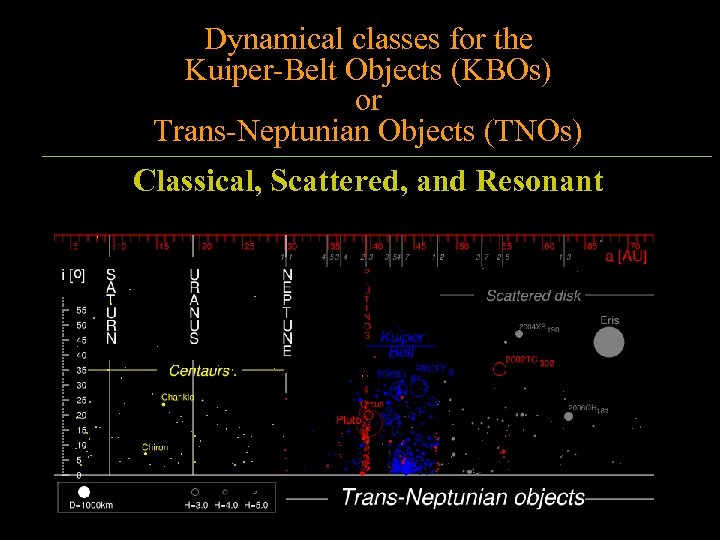
Dynamical classes for the Kuiper-Belt Objects (KBOs) or Trans-Neptunian Objects (TNOs) Classical, Scattered, and Resonant
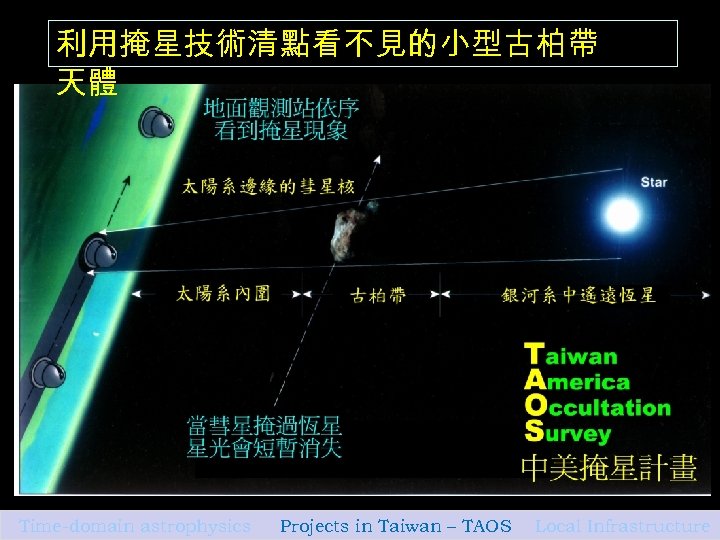
利用掩星技術清點看不見的小型古柏帶 天體 Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – TAOS Local Infrastructure
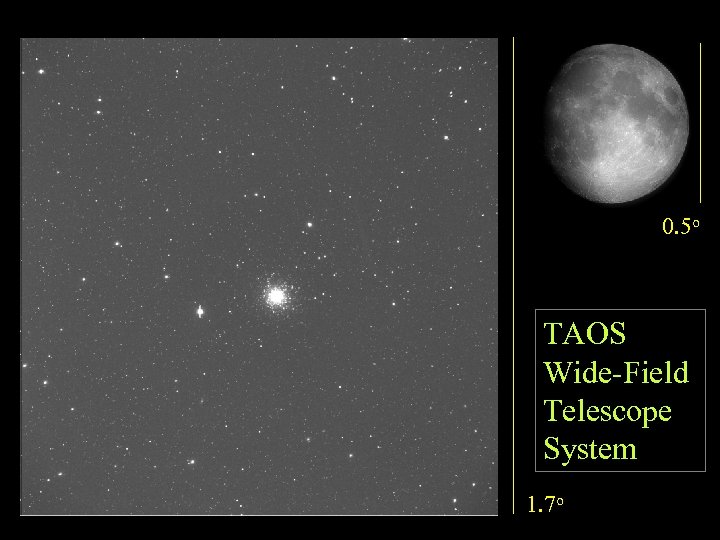

0. 5 o TAOS Wide-Field Telescope System 1. 7 o

Data Acquisition Regular Imaging Every star, together with surrounding skies, get exposure at the same time TAOS “Imaging” Integrate for 200 ms and then read out 32 rows of pixels, with the shutter remains open The sequence continues, so each star appears as a series of dots ‘zipper’ ‘Fake’ neighboring stars and skies! Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – TAOS Local Infrastructure

TAOS Telescopes Lulin Observatory altitude=2862 m TAOS is the only one of its kind in the world to conduct a census of small (1 -2 km size) icy bodies at the outer reach of the solar system. With a special data acquisition and a nonparametric statistical analysis scheme 100 GB/night C B D A
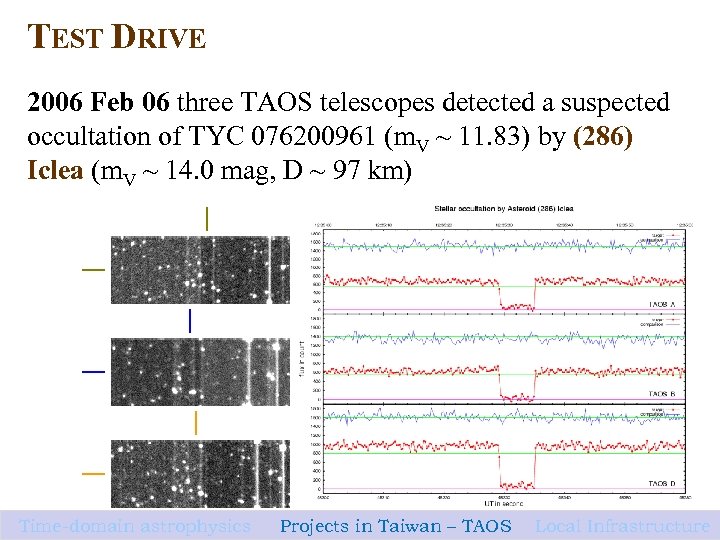
TEST DRIVE 2006 Feb 06 three TAOS telescopes detected a suspected occultation of TYC 076200961 (m. V ~ 11. 83) by (286) Iclea (m. V ~ 14. 0 mag, D ~ 97 km) Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – TAOS Local Infrastructure
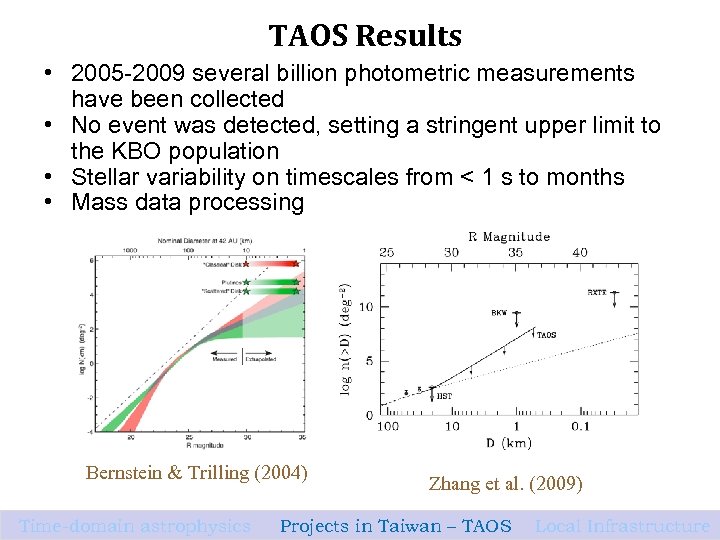
TAOS Results • 2005 -2009 several billion photometric measurements have been collected • No event was detected, setting a stringent upper limit to the KBO population • Stellar variability on timescales from < 1 s to months • Mass data processing Bernstein & Trilling (2004) Time-domain astrophysics Zhang et al. (2009) Projects in Taiwan – TAOS Local Infrastructure

Panoramic Survey Telescope And 泛星 Rapid Response System p To patrol the entire observable sky (3π) several times a month p An array of 4 telescopes, located in Hawaii, each of D=1. 8 m, equipped with a 1. 4 gigapixel camera of an Orthogonal Transfer Array CCD detector (= 40 cm square focal plane) 7 square-degree FOV with 0. 26” pixels p Detection of moving, transient, p Wide-Field Imaging and variable celestial objects p Short Duty Cycle down to very faint limits p Efficient Operations p Very deep cumulative sky images Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure

Wide-Field Optics PS 1 - Prototype PS 4 PS 1– Haleakala, Maui Time-domain astrophysics PS 4– Mauna Kea, Hawaii Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure
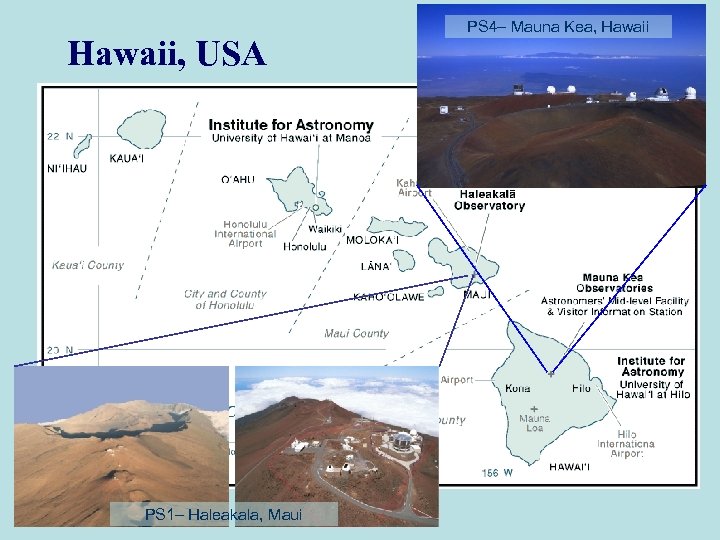
Hawaii, USA PS 1– Haleakala, Maui PS 4– Mauna Kea, Hawaii
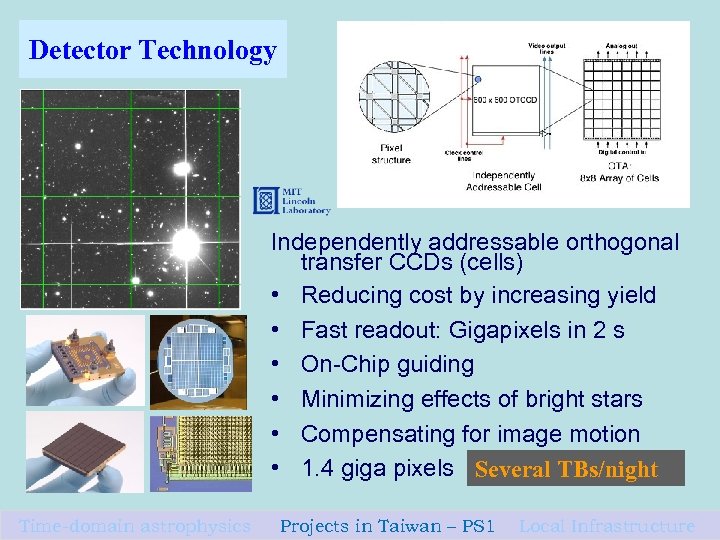
Detector Technology Independently addressable orthogonal transfer CCDs (cells) • Reducing cost by increasing yield • Fast readout: Gigapixels in 2 s • On-Chip guiding • Minimizing effects of bright stars • Compensating for image motion • 1. 4 giga pixels Several TBs/night Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure

Operations u $60 M funded by Congress through the US Air Force (2002/09); funding for construction only --- telescopes, detectors, and “working” software/analysis pipelines u Annual operations cost ~$3. 6 M/year u Science Consortium formed to support operations University of Hawaii (UH) 美國夏威夷大學 Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Heidelberg, the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Garching 德國 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics/ the Las Cumbres Observatory 美國哈佛大學 Johns Hopkins University 美國約翰霍普金斯大學 Durham University/University of Edinburgh/Queen’s University Belfast 英國 Taiwan台灣 (中大、清大、台大、成大、中研院) Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure
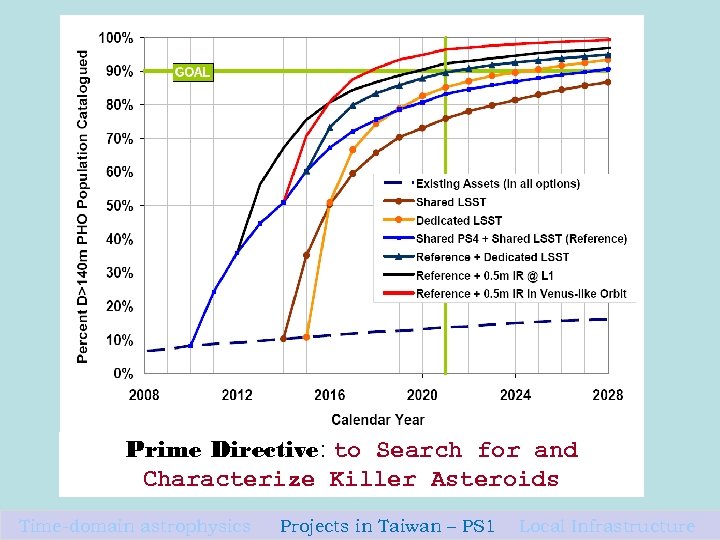
Prime Directive: to Search for and Characterize Killer Asteroids Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure 29

2007/08/22 PS 1/GPC first-light image of the giga-pixel camera First GPC image on the sky. Dark blob in center is obscuration from deployed Shack. Hartmann apparatus, for collimation and alignment, and will not normally be deployed over the focal plane. All devices functioning. Illuminated portion exceeds 3 degree field of view (Only expect 3 degree circle to have good image quality. The two open rectangles visible at the top outside the 3 degree circle are positions of wavefront sensing apparatus.

IT Challenges Each raw image from a single Pan-STARRS camera will contain 2 Gbytes (2 bytes per pixel). In the full survey mode, a typical exposure takes 30 seconds, so the raw data rate is several terabytes per night for the full telescope. Tremendous challenges in information technology to store, process, distribute, and archive the huge amount of data (and metadata, etc) Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure
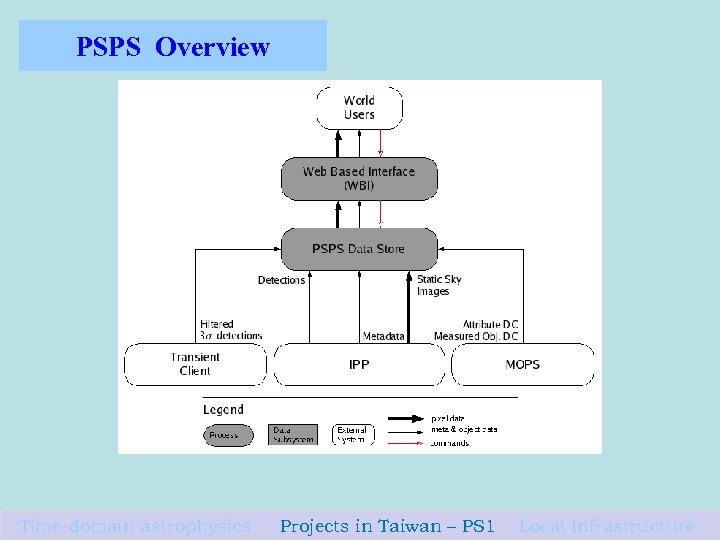
PSPS Overview Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure
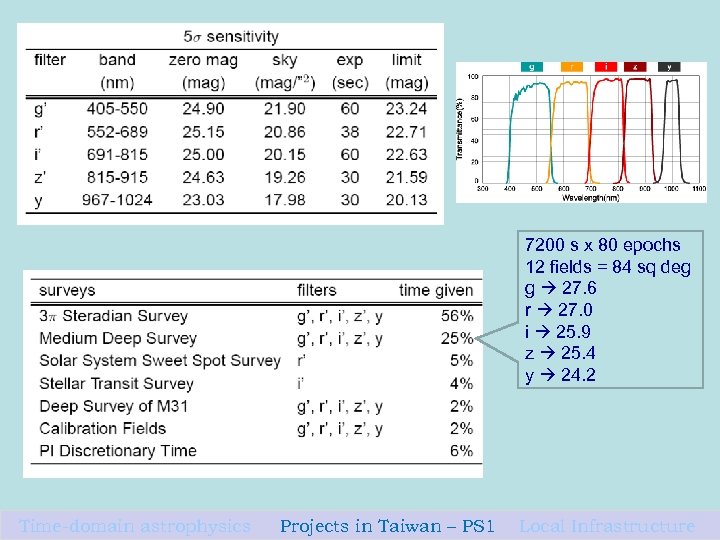
7200 s x 80 epochs 12 fields = 84 sq deg g 27. 6 r 27. 0 i 25. 9 z 25. 4 y 24. 2 Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure

PS 1 Key Projects 1. Inner solar system 2. Outer solar system 3. Low-mass stars, brown dwarfs and young stars 4. Exoplanets by stellar transit surveys 5. Milky Way structure and Local Group 6. M 31 7. Massive stars and supernova progenitors 8. Cosmology with variable stars and explosive transients 9. Galaxies 10. AGNs and high redshift quasars 11. Cosmological lensing 12. Large scale structure Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure
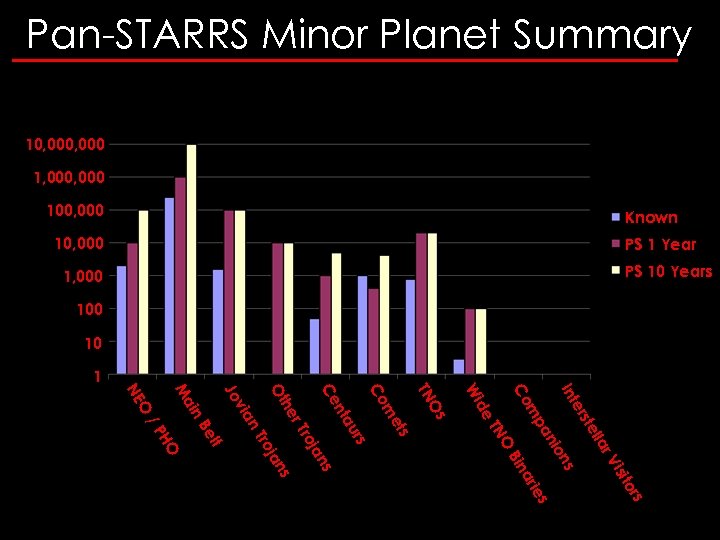
Pan-STARRS Minor Planet Summary 10, 000 1, 000 Known 100, 000 PS 1 Year 10, 000 PS 10 Years 1, 000 10 1 s or isit s V ar ell rst e Int ies ar Bin n nio O TN pa m Co de Wi Os TN s et m Co s ns ja ro ro r. T ur nta Ce he Ot n. T via Jo lt Be HO /P in Ma O NE
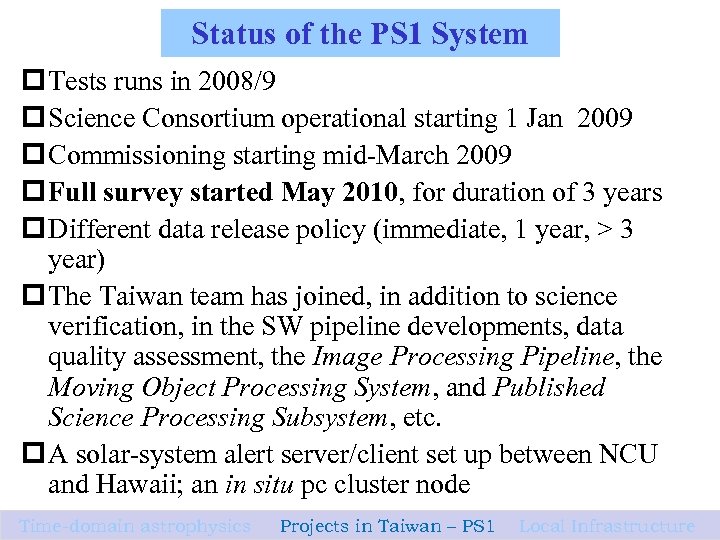
Status of the PS 1 System p Tests runs in 2008/9 p Science Consortium operational starting 1 Jan 2009 p Commissioning starting mid-March 2009 p Full survey started May 2010, for duration of 3 years p Different data release policy (immediate, 1 year, > 3 year) p The Taiwan team has joined, in addition to science verification, in the SW pipeline developments, data quality assessment, the Image Processing Pipeline, the Moving Object Processing System, and Published Science Processing Subsystem, etc. p A solar-system alert server/client set up between NCU and Hawaii; an in situ pc cluster node Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure

Now the real fun starts PS 1 will find many peculiar phenomena …


Lulin Observatory A 2 m was scheduled to be ready in 2010 for basic research, education and timely PS follow-up observations to “secure” the discoveries. Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure

The Lulin 2 m Telescope p PS 1 will find many peculiar objects/phenomena, and Lulin will follow them up in the first opportunity Secure the discoveries p Equipped with niche instruments, the Lulin 2 m will be very competitive scientifically p Telescope already in Taiwan p But the site is not, currently clearing the environmental impact assessment … 2010/03
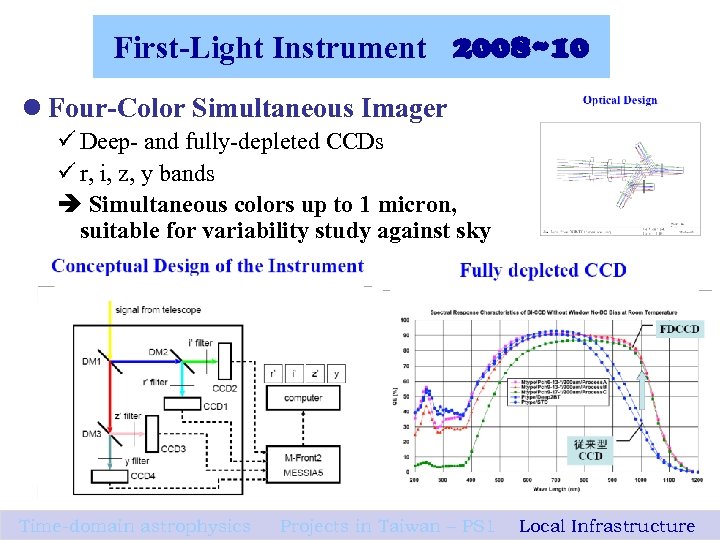
First-Light Instrument 2008~10 l Four-Color Simultaneous Imager ü Deep- and fully-depleted CCDs ü r, i, z, y bands Simultaneous colors up to 1 micron, suitable for variability study against sky Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure
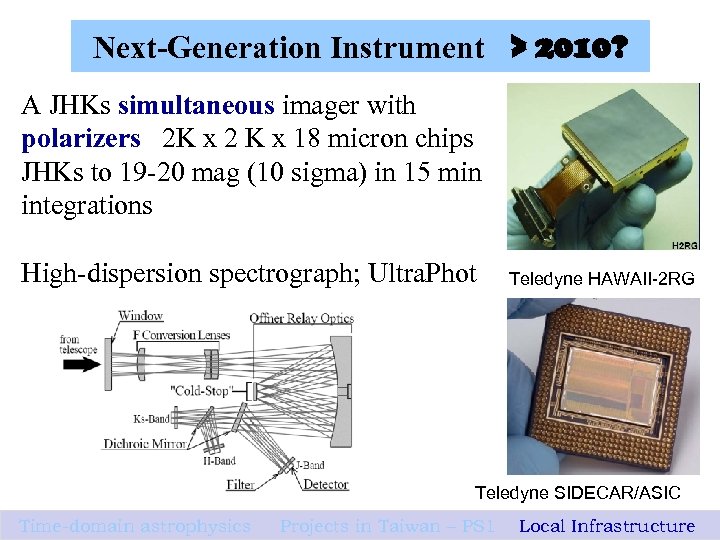
Next-Generation Instrument > 2010? A JHKs simultaneous imager with polarizers 2 K x 2 K x 18 micron chips JHKs to 19 -20 mag (10 sigma) in 15 min integrations High-dispersion spectrograph; Ultra. Phot Teledyne HAWAII-2 RG Teledyne SIDECAR/ASIC Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure
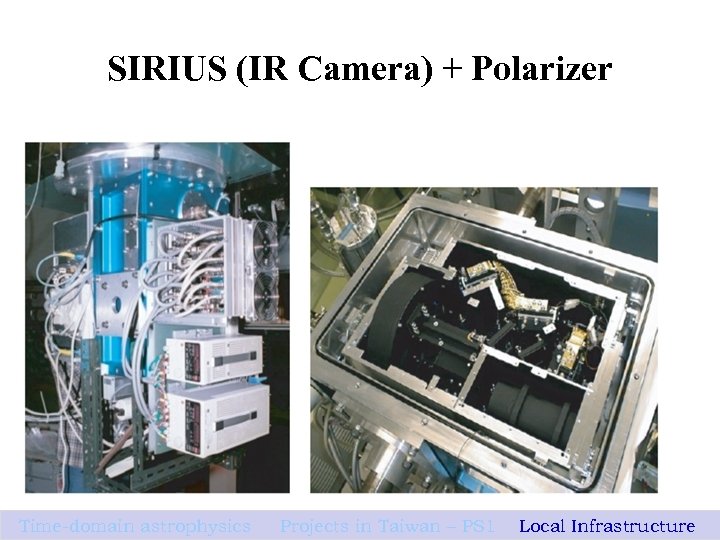
SIRIUS (IR Camera) + Polarizer Time-domain astrophysics Projects in Taiwan – PS 1 Local Infrastructure

Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) The LSST is a proposed ground-based 8. 4 -meter, 10 squaredegree-field telescope that will provide digital imaging of faint astronomical objects across the entire sky, night after night. In a relentless campaign of 15 second exposures, LSST will cover the available sky every three nights, opening a movie-like window on objects that change or move on rapid timescales: exploding supernovae, potentially hazardous near-Earth asteroids, and distant Kuiper Belt Objects. The superb images from the LSST will also be used to trace billions of remote galaxies and measure the distortions in their shapes produced by lumps of Dark Matter, providing multiple tests of the mysterious Dark Energy.

Conclusions u Time domain is one of the next major frontiers in astrophysics; Pan-STARRS is leading the wave, ready to provide huge amounts of high-quality data for a variety of cosmic problems u Strategic project planning <big and small, 1+1 >>1> from the very beginning from experimental design, data acquisition, analysis, storage, distribution, analysis, and writing papers ($1 hardware, $1 software, $1 database) u Find the niche in the international collaboration and competition. Please join us: projects, postdocs, visitors, students
ef9799143b2541e0e63344949743bbf7.ppt