955ab31f7570d5bc4d7ecf1e84884dee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 COSC 513 Operating System THE UNIX FILE SYSTEM By Chokechai Chuensukanant ID 121779 1
COSC 513 Operating System THE UNIX FILE SYSTEM By Chokechai Chuensukanant ID 121779 1
 Why you should know UNIX - FREE !!!!!! - Source code is openly available - Linux, its background in UNIX, will soon have a lead position in the mid to high-end server market 2
Why you should know UNIX - FREE !!!!!! - Source code is openly available - Linux, its background in UNIX, will soon have a lead position in the mid to high-end server market 2
 The UNIX File System • DISK ORGANIZATION - UNIX allows you to divide your hard disk into many units (called directories), sub units (called subdirectories) - UNIX provides commands to create, organize, and keep track of directories and files on the disk. 3
The UNIX File System • DISK ORGANIZATION - UNIX allows you to divide your hard disk into many units (called directories), sub units (called subdirectories) - UNIX provides commands to create, organize, and keep track of directories and files on the disk. 3
 FILE TYPES UNDER UNIX • Regular files -Contain sequences of bytes that could be programming code, data, text, and so on. • Directories files -Contain information (like the file name) about other files. It consists of a number of such records in special format defined by your operating system. • Special Files (device files( -Contain specific information corresponding to peripheral devices such as printers, disk, and so on. UNIX treats I/O devices as files, and each device in your system. 4
FILE TYPES UNDER UNIX • Regular files -Contain sequences of bytes that could be programming code, data, text, and so on. • Directories files -Contain information (like the file name) about other files. It consists of a number of such records in special format defined by your operating system. • Special Files (device files( -Contain specific information corresponding to peripheral devices such as printers, disk, and so on. UNIX treats I/O devices as files, and each device in your system. 4
 ABOUT DIRECTORY • The directory structure is organized in levels and is known as a hierarchical structure. • The highest level is called the ‘root’. • Do not contain the information but instead provide a reference path to allow you to organize your files. 5
ABOUT DIRECTORY • The directory structure is organized in levels and is known as a hierarchical structure. • The highest level is called the ‘root’. • Do not contain the information but instead provide a reference path to allow you to organize your files. 5
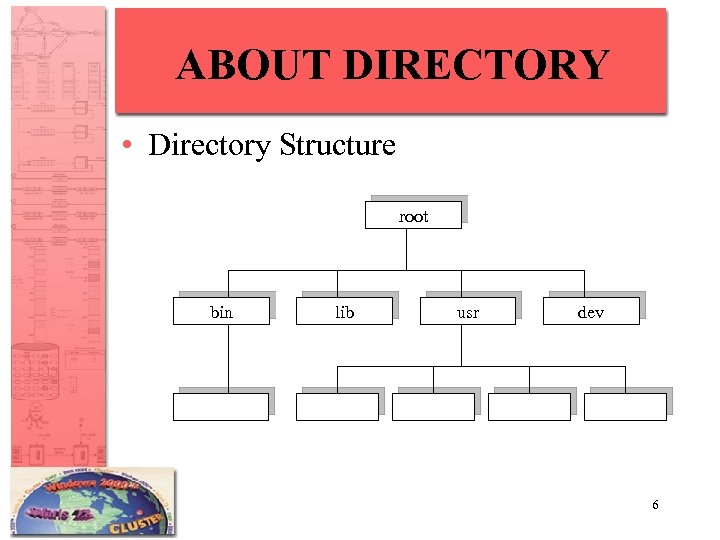 ABOUT DIRECTORY • Directory Structure root bin lib usr dev 6
ABOUT DIRECTORY • Directory Structure root bin lib usr dev 6
 Important Directories • /usr : holds users’ home directories. Similarly to /home in Linux • /bin : holds many of the basic UNIX program files. bin stands for binary, and these files are executable files. • /dev : holds device files. • /etc : holds many of UNIX configuration files. • /sbin : holds system files that usually are run automatically by UNIX system. 7
Important Directories • /usr : holds users’ home directories. Similarly to /home in Linux • /bin : holds many of the basic UNIX program files. bin stands for binary, and these files are executable files. • /dev : holds device files. • /etc : holds many of UNIX configuration files. • /sbin : holds system files that usually are run automatically by UNIX system. 7
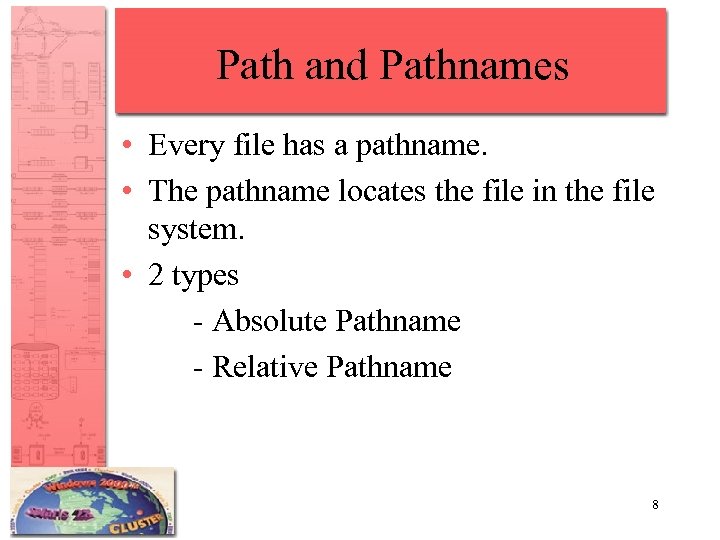 Path and Pathnames • Every file has a pathname. • The pathname locates the file in the file system. • 2 types - Absolute Pathname - Relative Pathname 8
Path and Pathnames • Every file has a pathname. • The pathname locates the file in the file system. • 2 types - Absolute Pathname - Relative Pathname 8
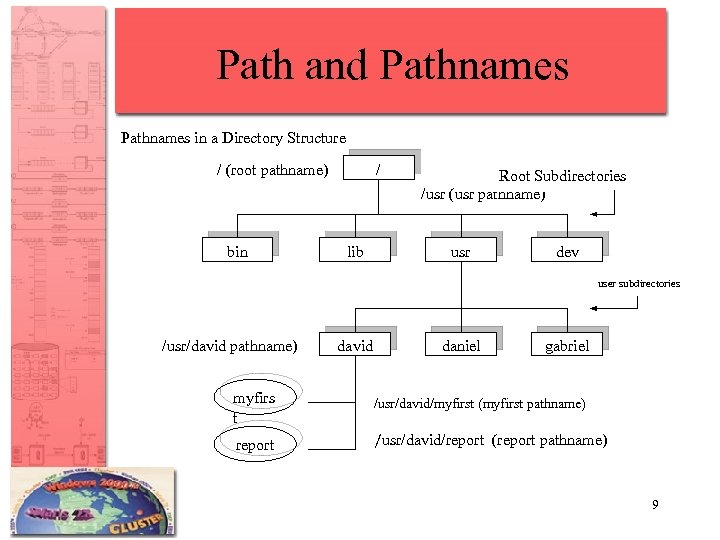 Path and Pathnames in a Directory Structure / (root pathname) bin / lib Root Subdirectories /usr (usr pathname) usr dev user subdirectories /usr/david pathname) david daniel gabriel myfirs t /usr/david/myfirst (myfirst pathname) report /usr/david/report (report pathname) 9
Path and Pathnames in a Directory Structure / (root pathname) bin / lib Root Subdirectories /usr (usr pathname) usr dev user subdirectories /usr/david pathname) david daniel gabriel myfirs t /usr/david/myfirst (myfirst pathname) report /usr/david/report (report pathname) 9
 Absolute Pathname • Traces a path from the root to the file. • Using when you want to access file that is not in your current directory. • Always use the forward slash (/) at the beginning of the pathname for the root directory. 10
Absolute Pathname • Traces a path from the root to the file. • Using when you want to access file that is not in your current directory. • Always use the forward slash (/) at the beginning of the pathname for the root directory. 10
 Relative Pathname • Traces a path from current directory to the file. • Using when you want to access file that is in your subdirectories of your current directory. • There is no initial forward slash (/) 11
Relative Pathname • Traces a path from current directory to the file. • Using when you want to access file that is in your subdirectories of your current directory. • There is no initial forward slash (/) 11
 Using File and Directory Name • The maximum length depend on the UNIX version, up to 255 characters. • Avoid to use^, $, -, ’, ”, ? , *, {}, [], (), <> • Can’t use spaces ( ), in files name • Using more than one dot is allowed in UNIX • Case sensitive 12
Using File and Directory Name • The maximum length depend on the UNIX version, up to 255 characters. • Avoid to use^, $, -, ’, ”, ? , *, {}, [], (), <> • Can’t use spaces ( ), in files name • Using more than one dot is allowed in UNIX • Case sensitive 12
 Directory Command • Displaying a Directory pathname: The pwd (print working directory) command. • Changing your Working Directory: The cd command • Creating Directories The mkdir Command • Removing Directories: The rmdir Command • Listing Directories: The ls Command 13
Directory Command • Displaying a Directory pathname: The pwd (print working directory) command. • Changing your Working Directory: The cd command • Creating Directories The mkdir Command • Removing Directories: The rmdir Command • Listing Directories: The ls Command 13
 The pwd command • Display the absolute pathname of your working directory. • Similarly to chdir command in DOS 14
The pwd command • Display the absolute pathname of your working directory. • Similarly to chdir command in DOS 14
 The cd command • Change your current directory • cd $HOME using when want to return your directory. • Similarly to cd command in DOS 15
The cd command • Change your current directory • cd $HOME using when want to return your directory. • Similarly to cd command in DOS 15
 The mkdir Command • Create new subdirectory under your working directory • Similarly to md or mkdir command in DOS • Using option –p to create level directories in single command Example mkdir –p /level 1/level 2/level 3 means create directory level 1 in current directory and create directory level 2 in level 1 directory and create level 3 in level 2 directory 16
The mkdir Command • Create new subdirectory under your working directory • Similarly to md or mkdir command in DOS • Using option –p to create level directories in single command Example mkdir –p /level 1/level 2/level 3 means create directory level 1 in current directory and create directory level 2 in level 1 directory and create level 3 in level 2 directory 16
 The rmdir Command • Remove existing directory • Must be in the parent directory to remove subdirectory. • Must remove only empty directory. • Similarly to rd or rmdir command in DOS 17
The rmdir Command • Remove existing directory • Must be in the parent directory to remove subdirectory. • Must remove only empty directory. • Similarly to rd or rmdir command in DOS 17
 The ls Command • List subdirectories and files in current directory. • Can use multiple options in single line • Similarly to dir command in DOS 18
The ls Command • List subdirectories and files in current directory. • Can use multiple options in single line • Similarly to dir command in DOS 18
 Display File Contents: • Using the cat Command - To display file contents. - Usually use with small files. -Similarly to type command in DOS. 19
Display File Contents: • Using the cat Command - To display file contents. - Usually use with small files. -Similarly to type command in DOS. 19
 Printing File Contents • The lp command - To send a copy of a file to the printer for producing a hard copy of the file. - Can specify several files on one command line. -Similarly to print command in DOS. 20
Printing File Contents • The lp command - To send a copy of a file to the printer for producing a hard copy of the file. - Can specify several files on one command line. -Similarly to print command in DOS. 20
 Printing File Contents • The cancel command -To cancel request for print jobs made with the lp command. • The lpstat command -To obtain information about printing requests and the status on the printers. 21
Printing File Contents • The cancel command -To cancel request for print jobs made with the lp command. • The lpstat command -To obtain information about printing requests and the status on the printers. 21
 FILE MANIPULATION COMMANDS ØCopying Files: The cp Command ØMoving Files: The mv Command ØLinking Files: The ln Command ØDeleting files : The rm command 22
FILE MANIPULATION COMMANDS ØCopying Files: The cp Command ØMoving Files: The mv Command ØLinking Files: The ln Command ØDeleting files : The rm command 22
 The cp Command • Used to create a copy (duplicate) of a file. • Syntax $cp [option] [Source] [Destination] • Source and Destination could be file or directory. • Could have more than one source on single line but Destination must be directory. • Similarly to copy command in DOS 23
The cp Command • Used to create a copy (duplicate) of a file. • Syntax $cp [option] [Source] [Destination] • Source and Destination could be file or directory. • Could have more than one source on single line but Destination must be directory. • Similarly to copy command in DOS 23
 The mv Command • Used to move a file from one place to another or to change the name of a file or directory • Syntax $ mv [option] [Source] [Destination] • Source and Destination could be file or directory. • Could have more than one source on single line but Destination must be directory. • Similarly to move command in DOS 24
The mv Command • Used to move a file from one place to another or to change the name of a file or directory • Syntax $ mv [option] [Source] [Destination] • Source and Destination could be file or directory. • Could have more than one source on single line but Destination must be directory. • Similarly to move command in DOS 24
 The ln Command • To create new links (name) between an existing file and a new filename. • In the other word, create additional names for an existing file • Syntax $ln [option] [existing file name] [new name] 25
The ln Command • To create new links (name) between an existing file and a new filename. • In the other word, create additional names for an existing file • Syntax $ln [option] [existing file name] [new name] 25
 The rm command • UNIX does not give you any warning message, so think twice before using this command. • Syntax $rm [Existing file names] • Similarly to del command in DOS. 26
The rm command • UNIX does not give you any warning message, so think twice before using this command. • Syntax $rm [Existing file names] • Similarly to del command in DOS. 26
 Summary • This presentation just show you a few basic command in UNIX. • In more advance, I have summary more command keep them at http: //www 10. brinkster. com/boyb 1917/unix. htm • If you want to know more about UNIX , please check that out or register UNIX class on next quadmester and I will see you there. • GOOD LUCK !!!!! 27
Summary • This presentation just show you a few basic command in UNIX. • In more advance, I have summary more command keep them at http: //www 10. brinkster. com/boyb 1917/unix. htm • If you want to know more about UNIX , please check that out or register UNIX class on next quadmester and I will see you there. • GOOD LUCK !!!!! 27


