e6f4dd11568ae353468b5409376c1401.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Corynebacterium and Other Non–Spore-forming Gram-Positive Rods Corynebacterium sp. Listeria monocytogenes Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Case Study u A 76 -year-old woman is receiving corticosteroid therapy u Complained of fever and headache for 7 days u CBC count showed an elevated white cell count u CSF analysis showed 4 250 WBC/cu mm 4 Glucose 30 mg/d. L 4 Protein 180 mg/d. L u Culture grew beta-hemolytic colonies on sheep blood agar, gram-positive pleomorphic rods 4 Catalase positive, motile at room temperature 4 CAMP-factor positive W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.

Points to Consider u What type of infection was suspected in this particular patient? u What predisposing risk factors were presented by the patient? u How are these organisms differentiated from other groups with similar characteristics? u What clinical forms of infections are associated with these groups of organisms? u Other points to consider W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
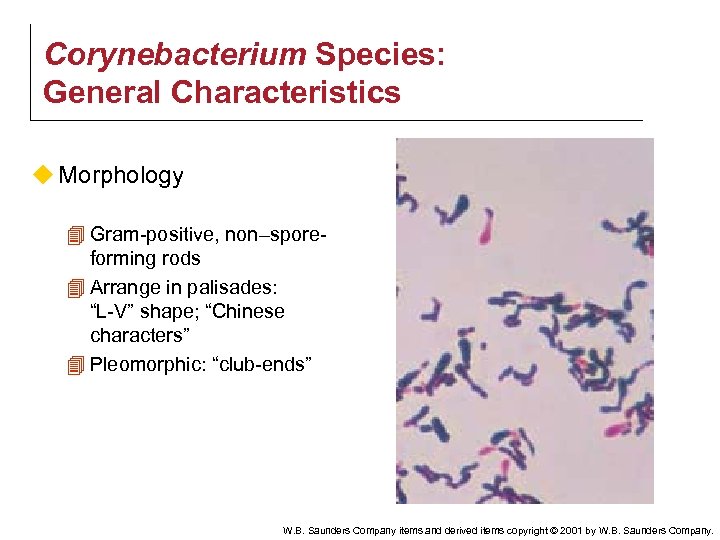
Corynebacterium Species: General Characteristics u Morphology 4 Gram-positive, non–sporeforming rods 4 Arrange in palisades: “L-V” shape; “Chinese characters” 4 Pleomorphic: “club-ends” W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
Corynebacterium Species u General characteristics 4 Found as free-living saprophytes 4 Members of the usual flora of humans and animals 4 Corynebacterium diphtheriae is the most significant pathogen 4 Other species may cause infections in the immunocompromised hosts W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
Other Corynebacteria u Significant Corynebacterium species 4 C. xerosis 4 C. pseudodiphtheriticum 4 C. pseudotuberculosis 4 C. jekeium 4 C. ulcerans u Rhodococcus equi u Arcanobacterium haemolyticum W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.

C. diphtheriae: Agent of Diphtheria u Toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae 4 Worldwide distribution F rare in places where vaccination programs exist u Exotoxin as the virulence factor 4 Diphtheria toxin 4 Toxin is produced by certain strains 4 Lysogenized by bacteriophage with toxin gene (tox+) 4 Toxin is antigenic W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
Toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae u Toxin consists of two fragments 4 A: Active fragment F Inhibits protein synthesis F Catalyzes transfer of ADPR to link with EF 2 (inactive) F Leads to cell/tissue death ADPR. EF 4 B binds to specific cell membrane receptors F Binds to specific cell membrane receptors F Mediates entry of fragment A W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
Clinical Forms of Diphtheria u Respiratory 4 Acquired by droplet spray 4 Unimmunized individuals are susceptible u Nonrespiratory 4 Systemic 4 Skin and cutaneous forms W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.

C. diphtheriae: Causative Agent of Diphtheria u Respiratory disease–diphtheria 4 Incubation period– 2 to 5 days 4 Symptoms: sore throat, fever, malaise 4 Toxin is produced locally, usually in the pharynx or tonsils 4 Toxin causes tissue necrosis 4 Forms a tough grey to white pseudomembrane W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.

Clinical Infections: Non-Respiratory Disease u Systemic infections 4 Toxin is absorbed in the blood stream and carried systemically 4 Affects the kidneys, heart, and nervous system 4 Death occurs due to cardiac failure W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.

Clinical Infections: Non-Respiratory Disease u Cutaneous form 4 More prevalent in the tropics 4 Infections occur at the site of minor abrasions 4 Maybe superinfected with Streptococcus pyogenes and/or Streptococcus aureus W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
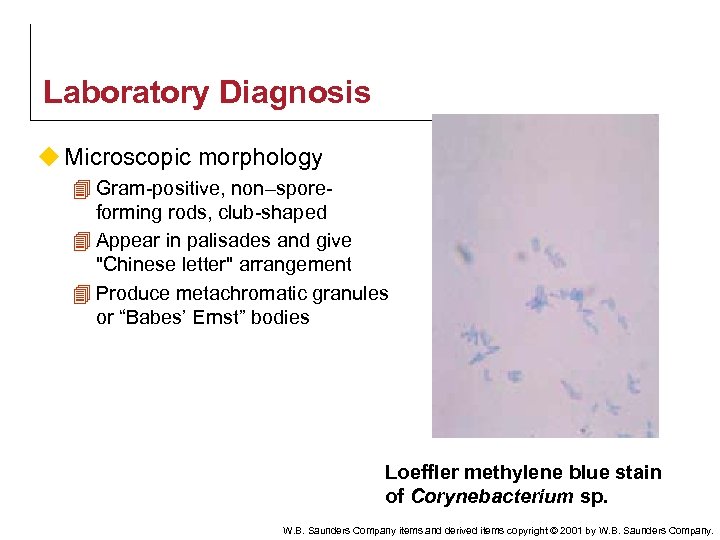
Laboratory Diagnosis u Microscopic morphology 4 Gram-positive, non–sporeforming rods, club-shaped 4 Appear in palisades and give "Chinese letter" arrangement 4 Produce metachromatic granules or “Babes’ Ernst” bodies Loeffler methylene blue stain of Corynebacterium sp. W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
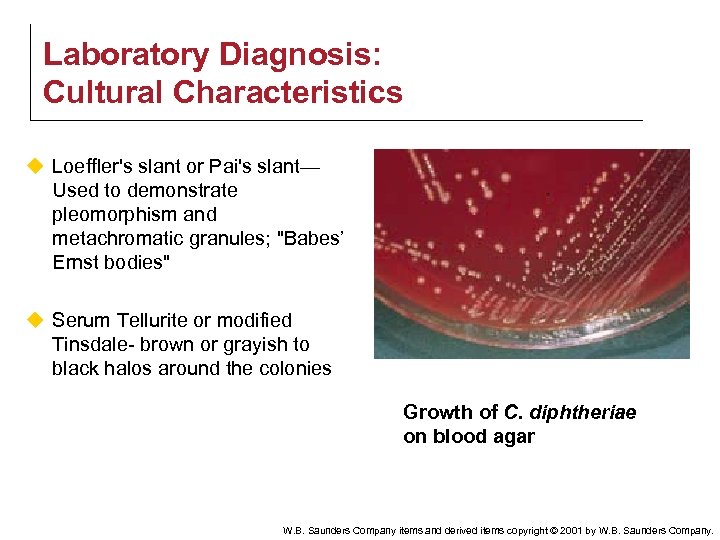
Laboratory Diagnosis: Cultural Characteristics u Loeffler's slant or Pai's slant— Used to demonstrate pleomorphism and metachromatic granules; "Babes’ Ernst bodies" u Serum Tellurite or modified Tinsdale- brown or grayish to black halos around the colonies Growth of C. diphtheriae on blood agar W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
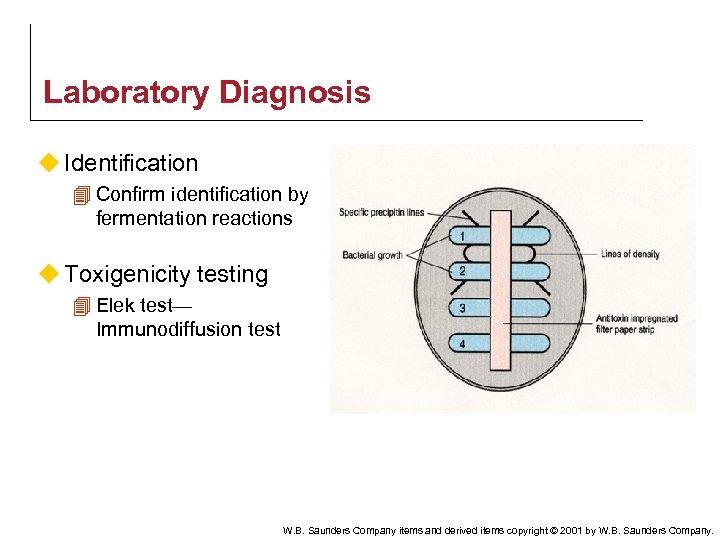
Laboratory Diagnosis u Identification 4 Confirm identification by fermentation reactions u Toxigenicity testing 4 Elek test— Immunodiffusion test W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
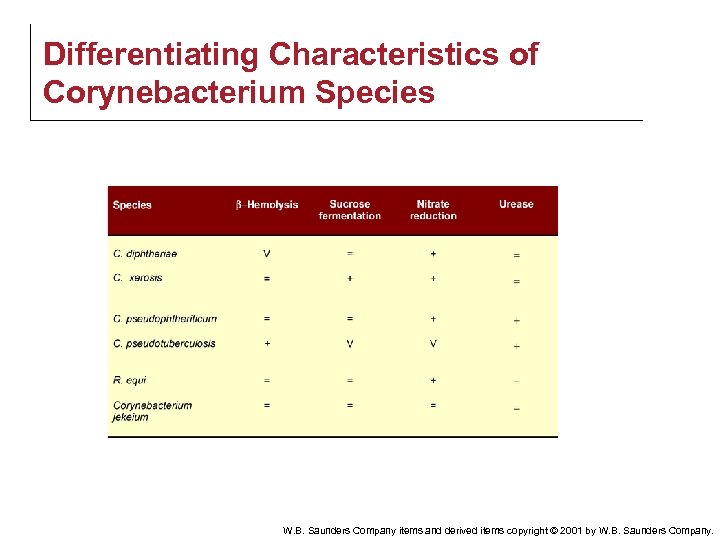
Differentiating Characteristics of Corynebacterium Species W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
Listeria Monocytogenes: General Characteristics u Gram-positive, non–spore-forming rods u Widespread in nature u Known to infect a wide variety of animals u Human exposure is limited; direct or indirect u Transient colonization occurs without disease W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
Listeria monocytogenes: Clinical Infections u Adults 4 Septicemia/meningitis in the compromised/elderly 4 Mild flu-like syndrome in pregnant women could be fatal to fetus u Neonatal 4 Early onset from intrauterine transmission results in sepsis; high mortality rate 4 Late onset manifests as meningitis; lower mortality rate W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
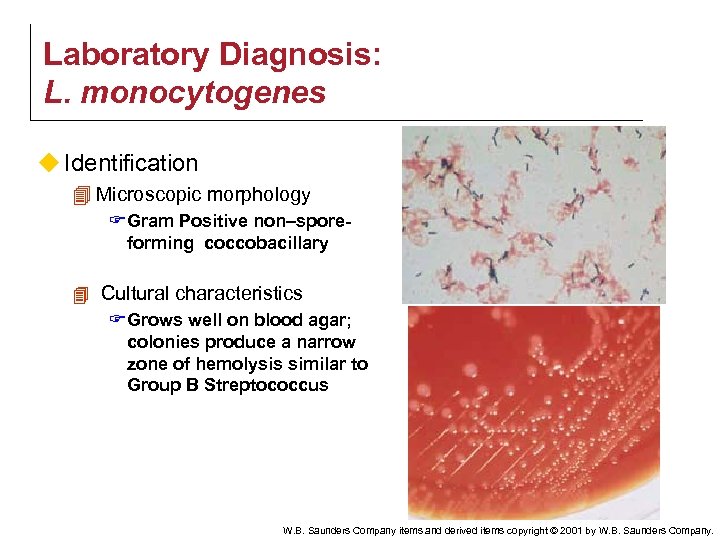
Laboratory Diagnosis: L. monocytogenes u Identification 4 Microscopic morphology F Gram Positive non–sporeforming coccobacillary 4 Cultural characteristics F Grows well on blood agar; colonies produce a narrow zone of hemolysis similar to Group B Streptococcus W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
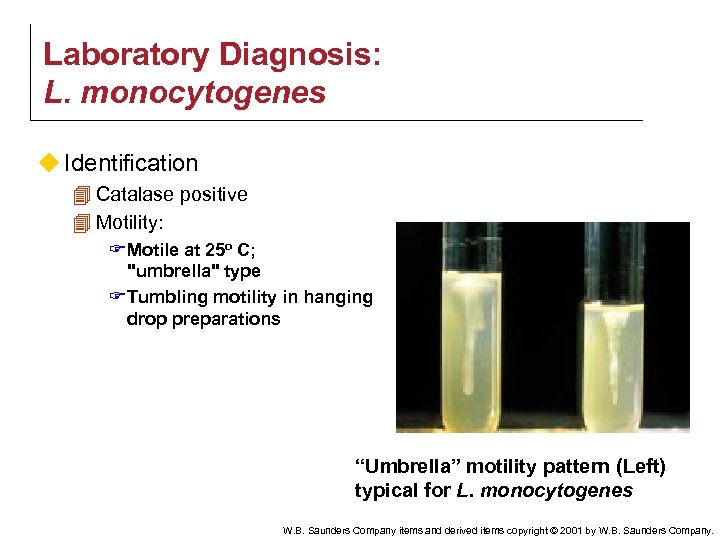
Laboratory Diagnosis: L. monocytogenes u Identification 4 Catalase positive 4 Motility: F Motile at 25 o C; "umbrella" type F Tumbling motility in hanging drop preparations “Umbrella” motility pattern (Left) typical for L. monocytogenes W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
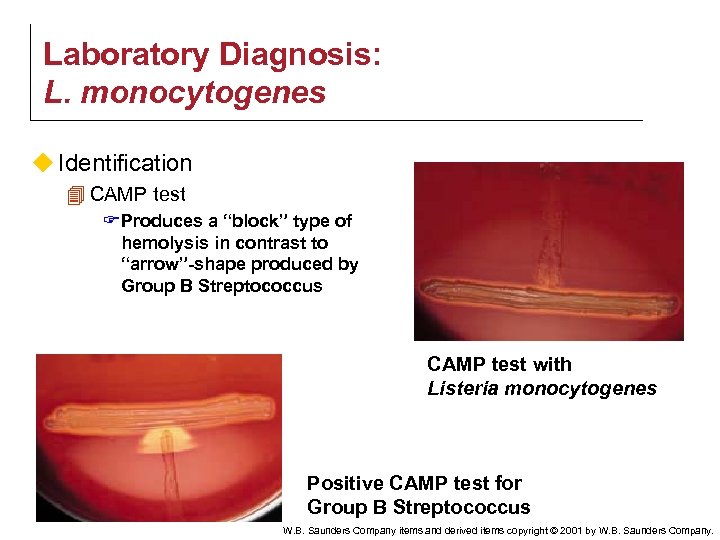
Laboratory Diagnosis: L. monocytogenes u Identification 4 CAMP test F Produces a “block” type of hemolysis in contrast to “arrow”-shape produced by Group B Streptococcus CAMP test with Listeria monocytogenes Positive CAMP test for Group B Streptococcus W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
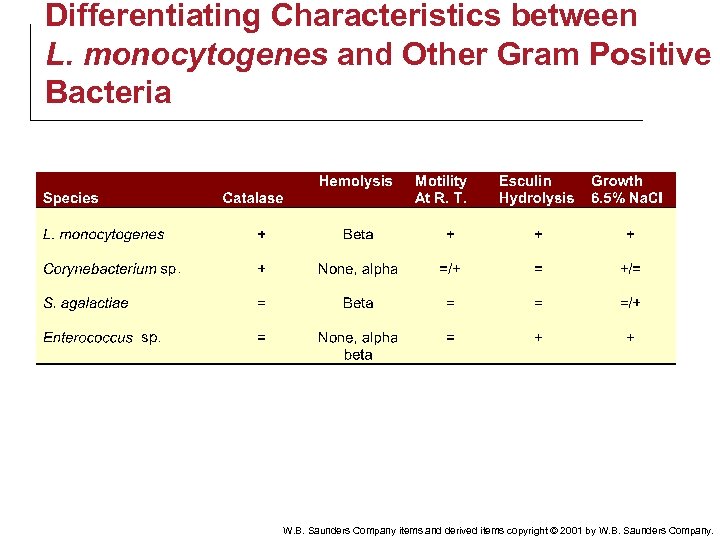
Differentiating Characteristics between L. monocytogenes and Other Gram Positive Bacteria W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.

Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: General characteristics u Gram positive, non–spore-forming, pleomorphic rods u Distributed in nature u Can cause disease in animals (swine, turkey, sheep) u Humans acquire the infection through occupational exposure W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.

Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: Clinical Infections u Erysipeloid 4 Self-limiting localized infection at the site of inoculation 4 Produces painful swelling, usually on the hands or fingers 4 Heals within 3 to 4 weeks u Endocarditis 4 May occur in those who have had valve replacements u Disseminated infections may occur, but rarely W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
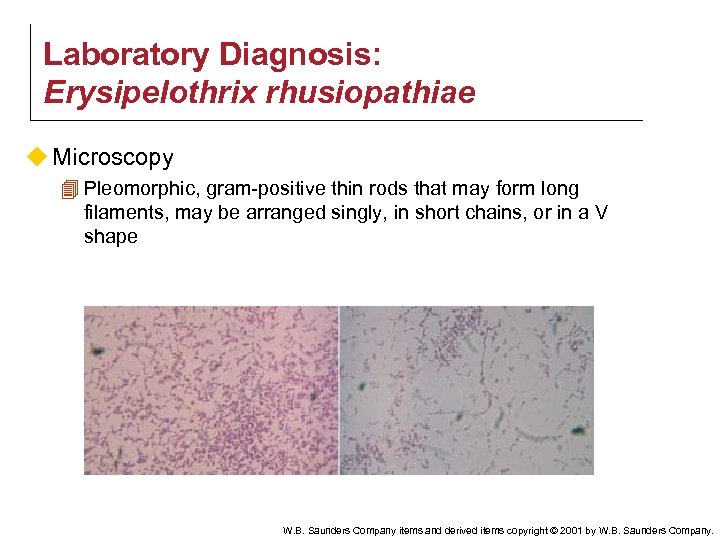
Laboratory Diagnosis: Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae u Microscopy 4 Pleomorphic, gram-positive thin rods that may form long filaments, may be arranged singly, in short chains, or in a V shape W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
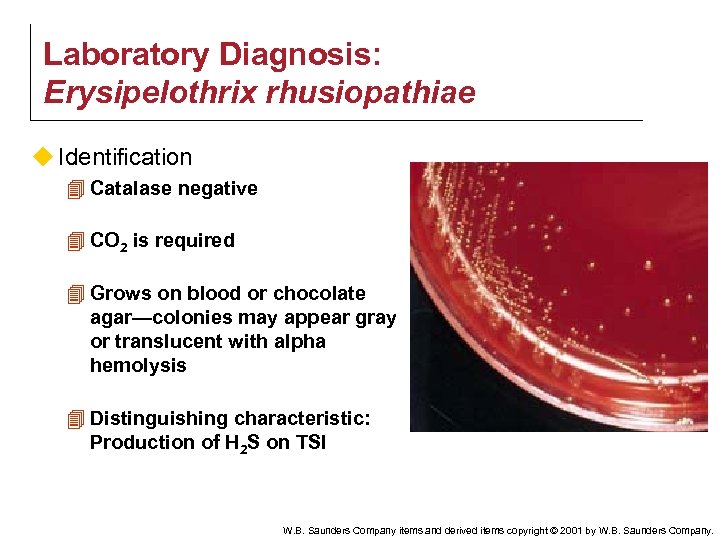
Laboratory Diagnosis: Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae u Identification 4 Catalase negative 4 CO 2 is required 4 Grows on blood or chocolate agar—colonies may appear gray or translucent with alpha hemolysis 4 Distinguishing characteristic: Production of H 2 S on TSI W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
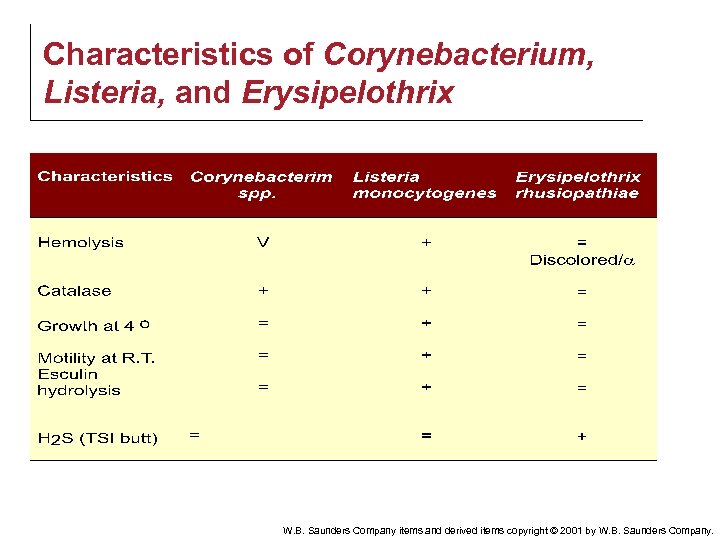
Characteristics of Corynebacterium, Listeria, and Erysipelothrix W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.

Points to Remember u Distinguishing characteristics of the genera Listeria, Corynebacterium, and Erysipelothrix from other gram positive bacteria u Clinical infections caused by each of these groups u Risk factors are associated with these infections u Biochemical and microscopic features of each of these species W. B. Saunders Company items and derived items copyright © 2001 by W. B. Saunders Company.
e6f4dd11568ae353468b5409376c1401.ppt