 Correlation in Degradation of Lung Mechanics with Ventilation Distribution in Asthmatics N. T. Tgavalekos 1, 2 R. S. Harris 2, M. F. Vidal Melo 2, G. Musch 2, T. Winkler 2, K. R. Lutchen 1 and J. G. Venegas 2 1 Dept. of Biomedical Engineering, Boston University, Boston, MA 2 Dept. of Anesthesia and Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA October 2, 2003 BMES conference
Correlation in Degradation of Lung Mechanics with Ventilation Distribution in Asthmatics N. T. Tgavalekos 1, 2 R. S. Harris 2, M. F. Vidal Melo 2, G. Musch 2, T. Winkler 2, K. R. Lutchen 1 and J. G. Venegas 2 1 Dept. of Biomedical Engineering, Boston University, Boston, MA 2 Dept. of Anesthesia and Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA October 2, 2003 BMES conference
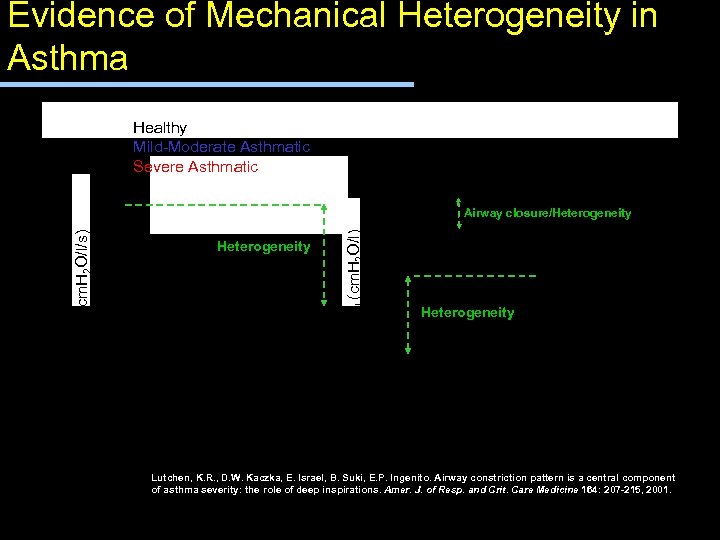 Evidence of Mechanical Heterogeneity in Asthma Healthy Mild-Moderate Asthmatic Severe Asthmatic Heterogeneity EL(cm. H 2 O/l) RL(cm. H 2 O/l/s) Airway closure/Heterogeneity Lutchen, K. R. , D. W. Kaczka, E. Israel, B. Suki, E. P. Ingenito. Airway constriction pattern is a central component of asthma severity: the role of deep inspirations. Amer. J. of Resp. and Crit. Care Medicine 164: 207 -215, 2001.
Evidence of Mechanical Heterogeneity in Asthma Healthy Mild-Moderate Asthmatic Severe Asthmatic Heterogeneity EL(cm. H 2 O/l) RL(cm. H 2 O/l/s) Airway closure/Heterogeneity Lutchen, K. R. , D. W. Kaczka, E. Israel, B. Suki, E. P. Ingenito. Airway constriction pattern is a central component of asthma severity: the role of deep inspirations. Amer. J. of Resp. and Crit. Care Medicine 164: 207 -215, 2001.
 Evidence of Heterogeneity in Ventilation Baseline Post Challenge
Evidence of Heterogeneity in Ventilation Baseline Post Challenge
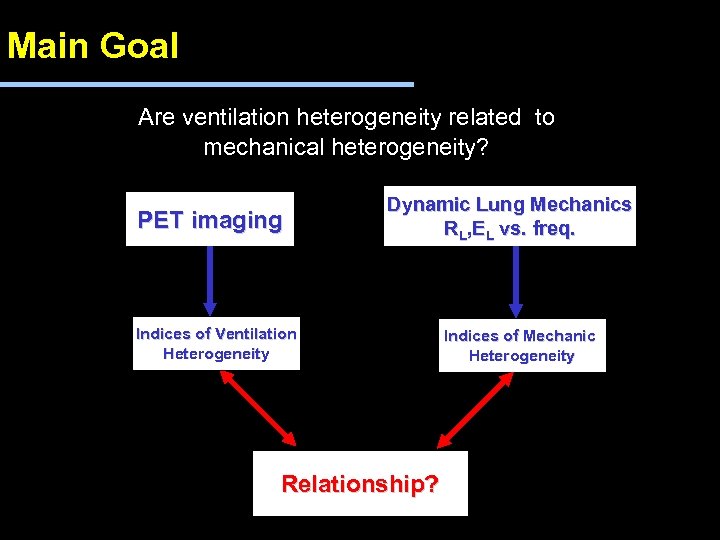 Main Goal l Are ventilation heterogeneity related to mechanical heterogeneity? PET imaging Dynamic Lung Mechanics RL, EL vs. freq. Indices of Ventilation Heterogeneity Relationship? Indices of Mechanic Heterogeneity
Main Goal l Are ventilation heterogeneity related to mechanical heterogeneity? PET imaging Dynamic Lung Mechanics RL, EL vs. freq. Indices of Ventilation Heterogeneity Relationship? Indices of Mechanic Heterogeneity
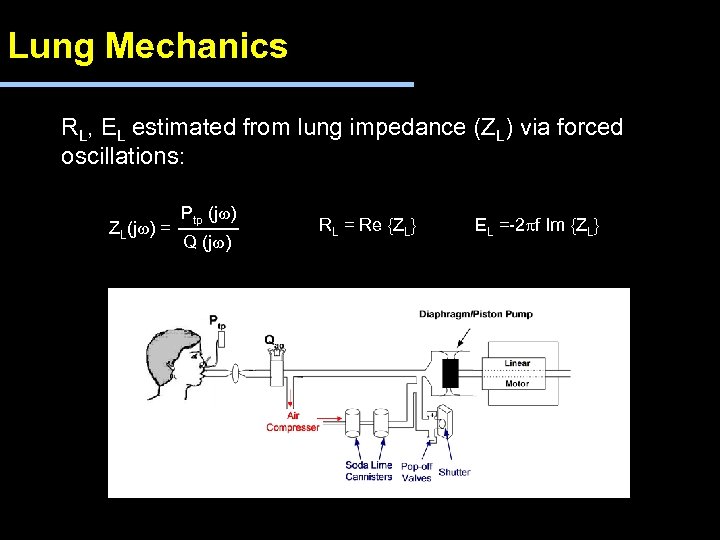 Lung Mechanics RL, EL estimated from lung impedance (ZL) via forced oscillations: ZL(jw) = Ptp (jw) Q (jw) RL = Re {ZL} EL =-2 pf Im {ZL}
Lung Mechanics RL, EL estimated from lung impedance (ZL) via forced oscillations: ZL(jw) = Ptp (jw) Q (jw) RL = Re {ZL} EL =-2 pf Im {ZL}
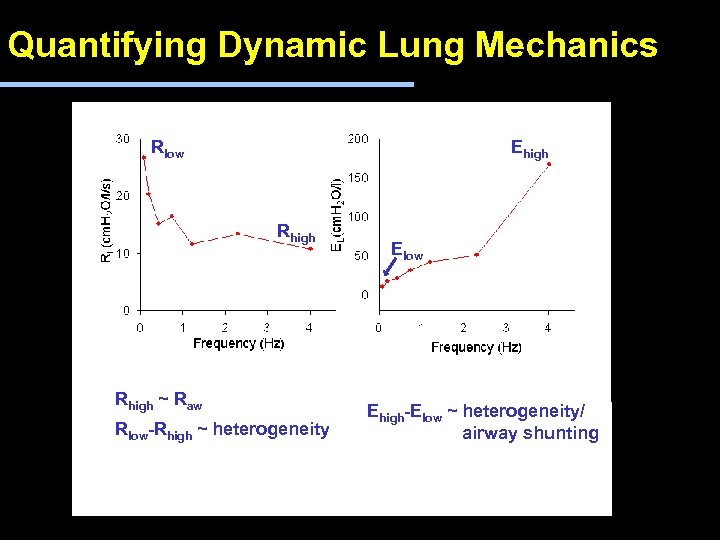 Quantifying Dynamic Lung Mechanics Rlow Ehigh Rhigh ~ Raw Rlow-Rhigh ~ heterogeneity Elow Ehigh-Elow ~ heterogeneity/ airway shunting
Quantifying Dynamic Lung Mechanics Rlow Ehigh Rhigh ~ Raw Rlow-Rhigh ~ heterogeneity Elow Ehigh-Elow ~ heterogeneity/ airway shunting
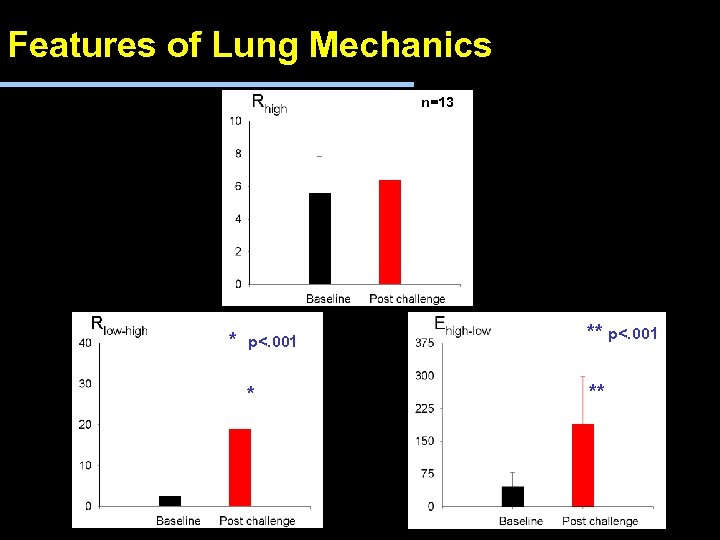 Features of Lung Mechanics n=13 * p<. 001 * **
Features of Lung Mechanics n=13 * p<. 001 * **
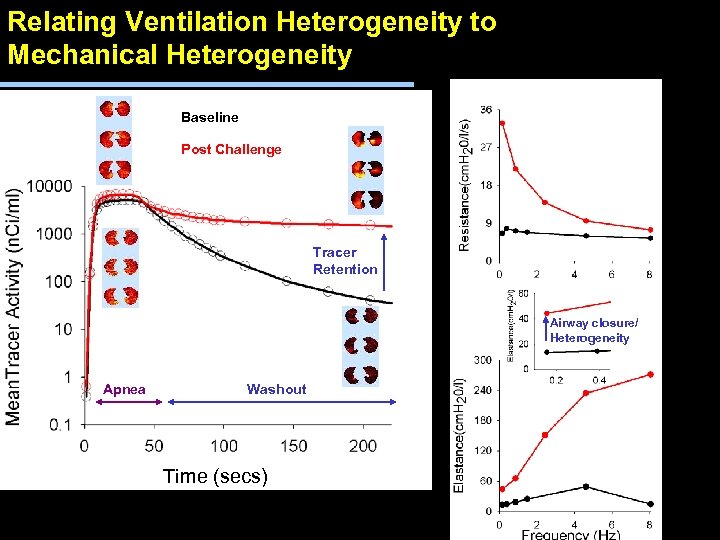 Relating Ventilation Heterogeneity to Mechanical Heterogeneity Baseline Post Challenge Tracer Retention Airway closure/ Heterogeneity Apnea Washout Time (secs)
Relating Ventilation Heterogeneity to Mechanical Heterogeneity Baseline Post Challenge Tracer Retention Airway closure/ Heterogeneity Apnea Washout Time (secs)
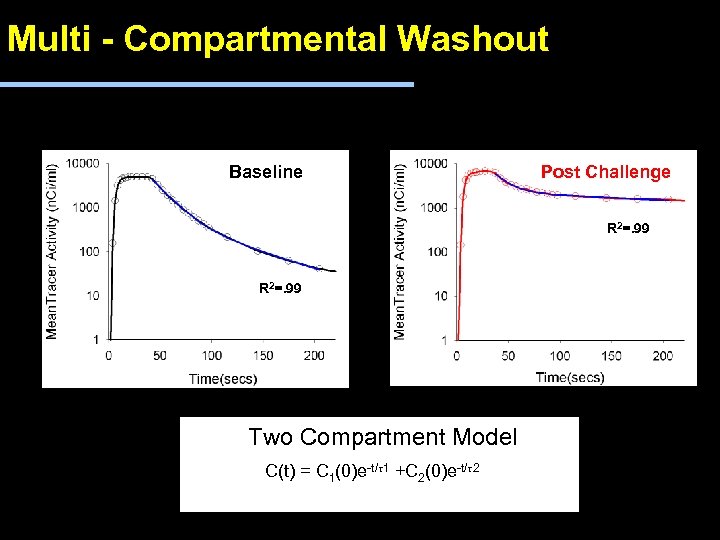 Multi - Compartmental Washout Baseline Post Challenge R 2=. 99 Two Compartment Model C(t) = C 1(0)e-t/t 1 +C 2(0)e-t/t 2
Multi - Compartmental Washout Baseline Post Challenge R 2=. 99 Two Compartment Model C(t) = C 1(0)e-t/t 1 +C 2(0)e-t/t 2
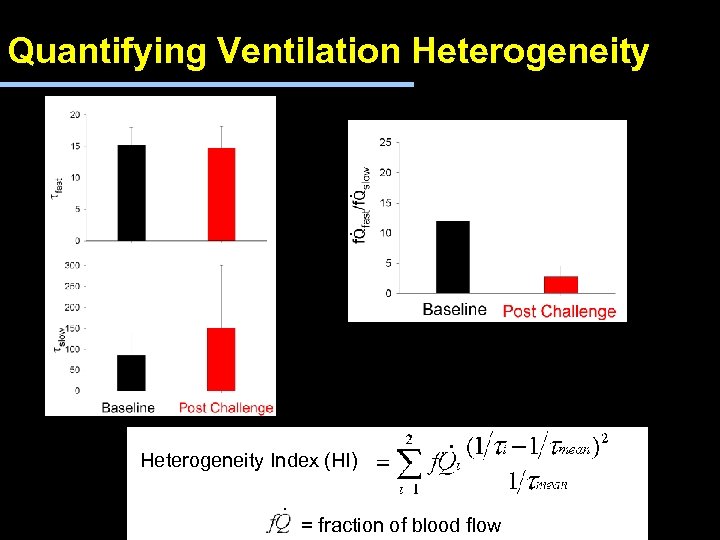 Quantifying Ventilation Heterogeneity . . Heterogeneity Index (HI) . . = fraction of blood flow
Quantifying Ventilation Heterogeneity . . Heterogeneity Index (HI) . . = fraction of blood flow
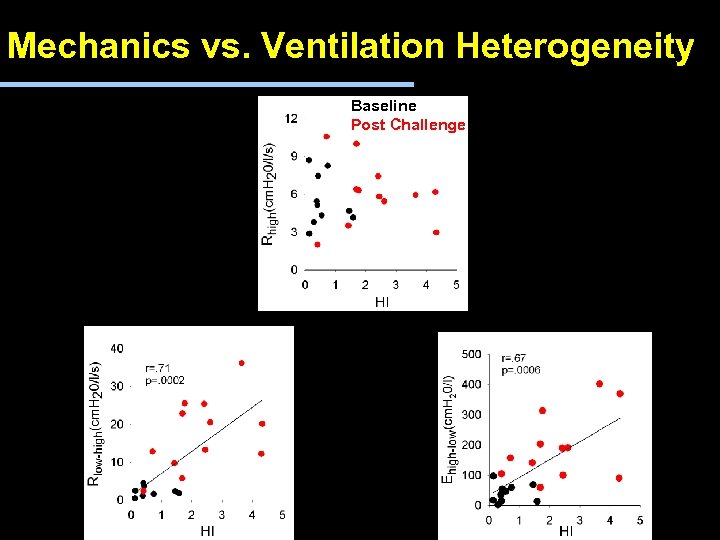 Mechanics vs. Ventilation Heterogeneity Baseline Post Challenge
Mechanics vs. Ventilation Heterogeneity Baseline Post Challenge
 Conclusions • Elevation and frequency dependence in lung mechanics is also indicative of ventilation heterogeneity • Airway constriction in asthma is inherently heterogeneous causing a distribution of poorly ventilated regions throughout the lung simultaneously with degradation lung mechanics • These data sets can be combined with airway tree models to identify what level of airways are actually closing or constricting during asthma
Conclusions • Elevation and frequency dependence in lung mechanics is also indicative of ventilation heterogeneity • Airway constriction in asthma is inherently heterogeneous causing a distribution of poorly ventilated regions throughout the lung simultaneously with degradation lung mechanics • These data sets can be combined with airway tree models to identify what level of airways are actually closing or constricting during asthma
 Acknowledgements Anesthesia & Critical Care BU Respiratory Lab José G. Venegas, Ph. D. K. R. Lutchen, Ph. D R. Scott Harris, M. D. Cortney Henderson, Ph. D Marcos Vidal Melo, M. D. Ph. D. Guido Musch, M. D. Tilo Winkler, Ph. D. Dominick Layfield, Ph. D. Carissa Bellardine, M. S. Derek Affonce, M. S
Acknowledgements Anesthesia & Critical Care BU Respiratory Lab José G. Venegas, Ph. D. K. R. Lutchen, Ph. D R. Scott Harris, M. D. Cortney Henderson, Ph. D Marcos Vidal Melo, M. D. Ph. D. Guido Musch, M. D. Tilo Winkler, Ph. D. Dominick Layfield, Ph. D. Carissa Bellardine, M. S. Derek Affonce, M. S
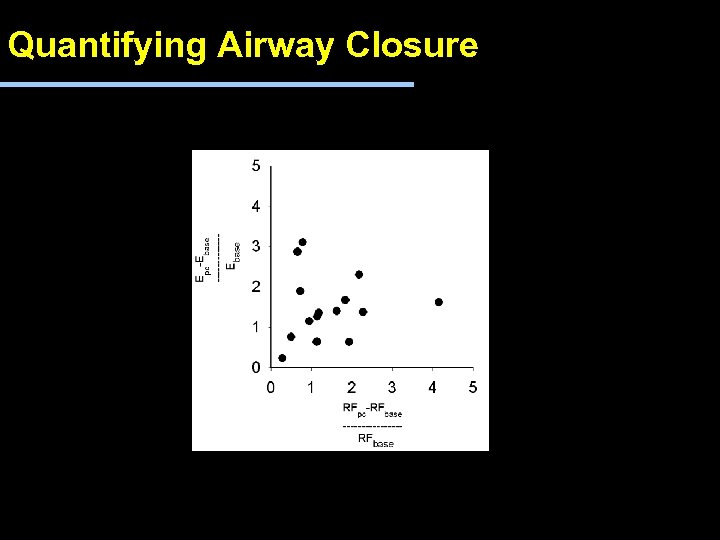 Quantifying Airway Closure
Quantifying Airway Closure
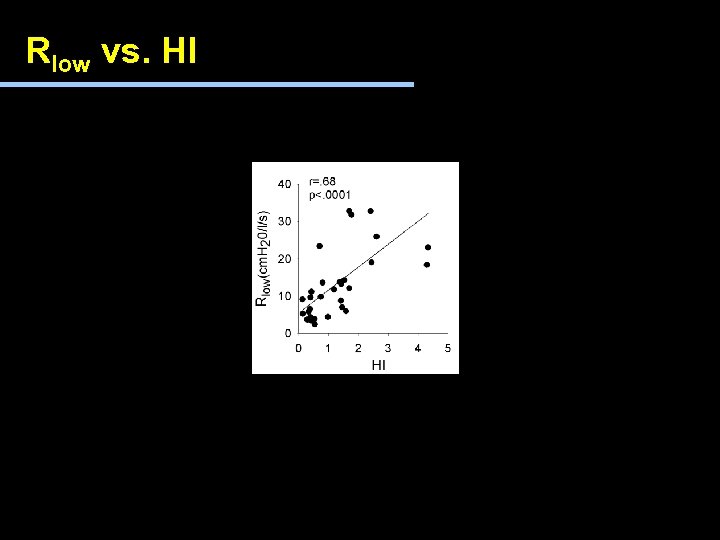 Rlow vs. HI
Rlow vs. HI
 PET Imaging in Asthmatics End Washout : Gas Trapping PET functional imaging may provide useful insights into the role of gas trapping in asthma
PET Imaging in Asthmatics End Washout : Gas Trapping PET functional imaging may provide useful insights into the role of gas trapping in asthma