 CORPORAL PUNISHMENT
CORPORAL PUNISHMENT
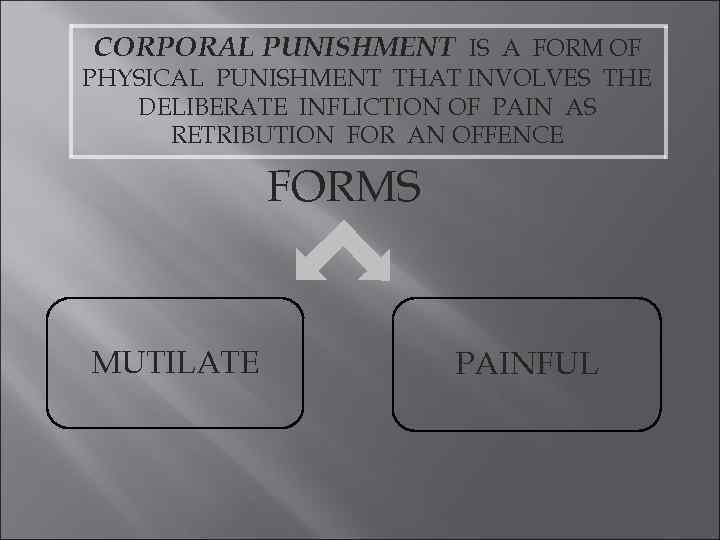 CORPORAL PUNISHMENT IS A FORM OF PHYSICAL PUNISHMENT THAT INVOLVES THE DELIBERATE INFLICTION OF PAIN AS RETRIBUTION FOR AN OFFENCE FORMS MUTILATE PAINFUL
CORPORAL PUNISHMENT IS A FORM OF PHYSICAL PUNISHMENT THAT INVOLVES THE DELIBERATE INFLICTION OF PAIN AS RETRIBUTION FOR AN OFFENCE FORMS MUTILATE PAINFUL
 MUTILATE PAINFUL BLINDNESS WHIP AMPUTATION OF HAND, FOOT, FINGERS TWIG CUTTING OFF EARS SCOURGE
MUTILATE PAINFUL BLINDNESS WHIP AMPUTATION OF HAND, FOOT, FINGERS TWIG CUTTING OFF EARS SCOURGE
 SPANKING CHILDREN IS ALSO CORPORAL PUNISHMENT
SPANKING CHILDREN IS ALSO CORPORAL PUNISHMENT
 Corporal punishment was known to The Code of Hammurabi It was widely used in the Roman Empire
Corporal punishment was known to The Code of Hammurabi It was widely used in the Roman Empire
 In Russia millions of people were condemned by the law in serf slavery & legislation was to keep the staircase of executions : sticks rods whips brand
In Russia millions of people were condemned by the law in serf slavery & legislation was to keep the staircase of executions : sticks rods whips brand
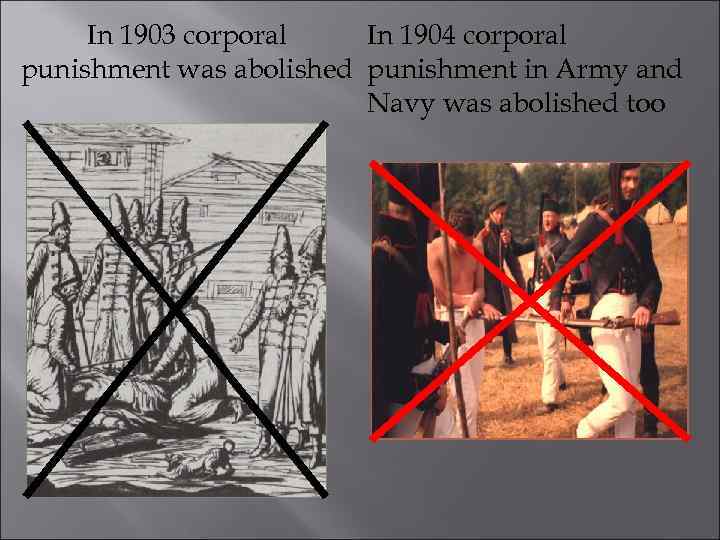 In 1903 corporal In 1904 corporal punishment was abolished punishment in Army and Navy was abolished too
In 1903 corporal In 1904 corporal punishment was abolished punishment in Army and Navy was abolished too
 Today legislations in the majority of countries consider the corporal punishment as contradictory « Universal Declaration of Human Rights» 1948 & «International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights» 1996
Today legislations in the majority of countries consider the corporal punishment as contradictory « Universal Declaration of Human Rights» 1948 & «International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights» 1996
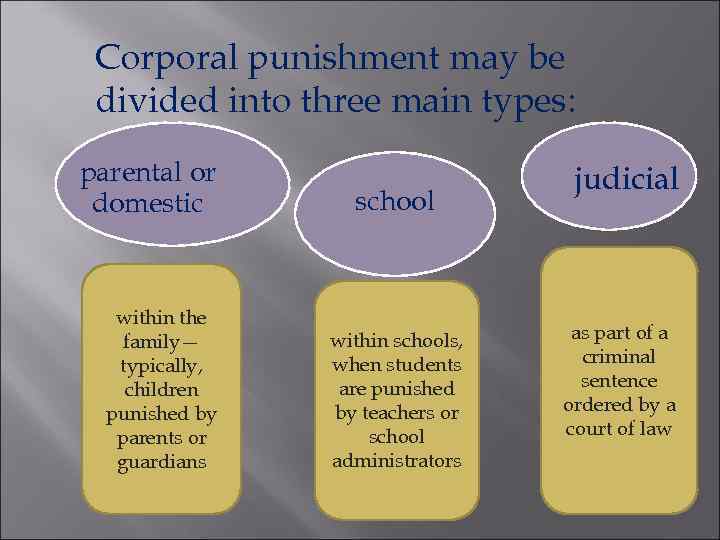 Corporal punishment may be divided into three main types: parental or domestic within the family— typically, children punished by parents or guardians school within schools, when students are punished by teachers or school administrators judicial as part of a criminal sentence ordered by a court of law
Corporal punishment may be divided into three main types: parental or domestic within the family— typically, children punished by parents or guardians school within schools, when students are punished by teachers or school administrators judicial as part of a criminal sentence ordered by a court of law
 Domestic corporal punishment In Canada, spanking by parents or legal guardians is legal, as long as the child is not under 2 years or over 12 years of age In the UK, spanking or smacking is legal, but it may not leave a mark on the body
Domestic corporal punishment In Canada, spanking by parents or legal guardians is legal, as long as the child is not under 2 years or over 12 years of age In the UK, spanking or smacking is legal, but it may not leave a mark on the body
 Corporal punishment in schools has been outlawed in Canada, Kenya, Korea, South Africa, New Zealand nearly all of Europe except France. It remains legal in some parts of the world, including 19 states of the USA
Corporal punishment in schools has been outlawed in Canada, Kenya, Korea, South Africa, New Zealand nearly all of Europe except France. It remains legal in some parts of the world, including 19 states of the USA
 Judicial or quasi-judicial punishment Some of 33 countries retain judicial corporal punishment, including a number of former British territories such as Botswana, Malaysia, Singapore and Tanzania In Saudi Arabia, Iran, Sudan and northern Nigeria, employ judicial whipping for a range of offences. But corporal punishments apply only to men
Judicial or quasi-judicial punishment Some of 33 countries retain judicial corporal punishment, including a number of former British territories such as Botswana, Malaysia, Singapore and Tanzania In Saudi Arabia, Iran, Sudan and northern Nigeria, employ judicial whipping for a range of offences. But corporal punishments apply only to men