 CORE MARKETING CONCEPTS
CORE MARKETING CONCEPTS
 • The three major challenges faced by business today are: - globalization; - advances in technology; - deregulation.
• The three major challenges faced by business today are: - globalization; - advances in technology; - deregulation.
 Marketing Social definition: marketing is a process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering, and exchanging products and services of value freely with others. Managerial definition (The American Marketing Association): marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals.
Marketing Social definition: marketing is a process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering, and exchanging products and services of value freely with others. Managerial definition (The American Marketing Association): marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals.
 The aim of marketing is NOT to sell products. The aim of marketing is to know and understand the customer so well that the product or service fits him (her) and sells itself.
The aim of marketing is NOT to sell products. The aim of marketing is to know and understand the customer so well that the product or service fits him (her) and sells itself.
 The Scope of Marketing 1. Goods 2. Services 3. Experiences 4. Events 5. Persons 6. Places 7. Properties 8. Organizations 9. Information 10. Ideas
The Scope of Marketing 1. Goods 2. Services 3. Experiences 4. Events 5. Persons 6. Places 7. Properties 8. Organizations 9. Information 10. Ideas
 COMPANY ORIENTATIONS TOWARD THE MARKETPLACE • The production concept assumes that consumers want widely available, affordable products. Managers of productionoriented businesses concentrate on achieving high production efficiency, low costs, and mass distribution. • The product concept assumes that consumers want products with the most quality, performance, or innovative features. Managers in these organizations focus on making superior products and improving them over time, assuming that buyers can appraise quality and performance. • The selling concept assumes that customers will not buy enough products without an aggressive selling and promotion effort. • The marketing concept assumes the firm must be better than competitors in creating, delivering, and communicating customer value to its chosen target markets.
COMPANY ORIENTATIONS TOWARD THE MARKETPLACE • The production concept assumes that consumers want widely available, affordable products. Managers of productionoriented businesses concentrate on achieving high production efficiency, low costs, and mass distribution. • The product concept assumes that consumers want products with the most quality, performance, or innovative features. Managers in these organizations focus on making superior products and improving them over time, assuming that buyers can appraise quality and performance. • The selling concept assumes that customers will not buy enough products without an aggressive selling and promotion effort. • The marketing concept assumes the firm must be better than competitors in creating, delivering, and communicating customer value to its chosen target markets.
 Types of demand • negative demand (avoidance of a product), • no demand (lack of awareness or interest in a product), • latent demand (a strong need that cannot be satisfied by existing products), • declining demand (lower demand), • irregular demand (demand varying by season, day, or hour), • full demand (a satisfying level of demand), • overfull demand (more demand than can be handled), • unwholesome demand (demand for unhealthy or dangerous products).
Types of demand • negative demand (avoidance of a product), • no demand (lack of awareness or interest in a product), • latent demand (a strong need that cannot be satisfied by existing products), • declining demand (lower demand), • irregular demand (demand varying by season, day, or hour), • full demand (a satisfying level of demand), • overfull demand (more demand than can be handled), • unwholesome demand (demand for unhealthy or dangerous products).
 Demand States and Marketing Tasks • Negative demand • No demand A major part of the market dislikes the product and may even pay a price to avoid it – vaccination, dental work, and gallbladder operations, for instance. Employers have a negative demand for exconvicts and alcoholics as employees. The marketing tasks is to analyze why the market dislikes the product and whether a marketing program consulting of product redesign, lower prices, and more positive promotion can change beliefs and attitudes. Target consumers may be unaware of or uninterested in the product. Farmers may not be interested in a new farming method, and college students may not be interested in foreign-language courses. The marketing tasks is to find ways to connect the benefits of the product with people's natural needs and interests.
Demand States and Marketing Tasks • Negative demand • No demand A major part of the market dislikes the product and may even pay a price to avoid it – vaccination, dental work, and gallbladder operations, for instance. Employers have a negative demand for exconvicts and alcoholics as employees. The marketing tasks is to analyze why the market dislikes the product and whether a marketing program consulting of product redesign, lower prices, and more positive promotion can change beliefs and attitudes. Target consumers may be unaware of or uninterested in the product. Farmers may not be interested in a new farming method, and college students may not be interested in foreign-language courses. The marketing tasks is to find ways to connect the benefits of the product with people's natural needs and interests.
 Target Markets and Segmentation Market segments are distinct groups of buyers who might prefer or require varying products and marketing mixes. Segments can be identified by examining demographic, psychographic, and behavioral differences among buyers. Target markets are segments presenting the greatest opportunity for the firm.
Target Markets and Segmentation Market segments are distinct groups of buyers who might prefer or require varying products and marketing mixes. Segments can be identified by examining demographic, psychographic, and behavioral differences among buyers. Target markets are segments presenting the greatest opportunity for the firm.
 Marketplace and Marketspace The marketplace is physical, as when one goes shopping in a store; marketspace is digital, as when one goes shopping on the Internet.
Marketplace and Marketspace The marketplace is physical, as when one goes shopping in a store; marketspace is digital, as when one goes shopping on the Internet.
 Marketers and Prospects A marketer is someone who is seeking a response (attention, a purchase, a vote) from another party, called the prospect. If two parties are seeking to sell something to each other, both are marketers.
Marketers and Prospects A marketer is someone who is seeking a response (attention, a purchase, a vote) from another party, called the prospect. If two parties are seeking to sell something to each other, both are marketers.
 Needs, Wants, and Demands Needs describe human requirements. These needs become wants when they are directed to specific objects that might satisfy the need. Demands are wants for specific products backed by an ability to pay.
Needs, Wants, and Demands Needs describe human requirements. These needs become wants when they are directed to specific objects that might satisfy the need. Demands are wants for specific products backed by an ability to pay.
 CUSTOMER NEEDS Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs Self-actualization needs Self-fulfillment, enriching experience Esteem needs accomplishment, self-respect, prestige Social needs companionship, friendship, love Safety needs protection, security Physiological needs food, water, sleep
CUSTOMER NEEDS Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs Self-actualization needs Self-fulfillment, enriching experience Esteem needs accomplishment, self-respect, prestige Social needs companionship, friendship, love Safety needs protection, security Physiological needs food, water, sleep
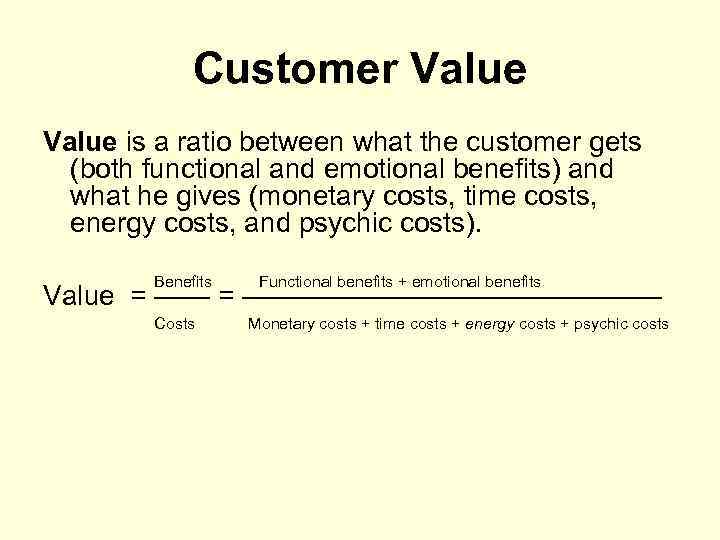 Customer Value is a ratio between what the customer gets (both functional and emotional benefits) and what he gives (monetary costs, time costs, energy costs, and psychic costs). Benefits Functional benefits + emotional benefits Value = ————————— Costs Monetary costs + time costs + energy costs + psychic costs
Customer Value is a ratio between what the customer gets (both functional and emotional benefits) and what he gives (monetary costs, time costs, energy costs, and psychic costs). Benefits Functional benefits + emotional benefits Value = ————————— Costs Monetary costs + time costs + energy costs + psychic costs
 Customer Satisfaction is a person's feelings of pleasure or disappointment resulting from comparing a product's perceived performance (or outcome) in relation to his or her expectations
Customer Satisfaction is a person's feelings of pleasure or disappointment resulting from comparing a product's perceived performance (or outcome) in relation to his or her expectations
 What Determines Satisfaction • • Product performance Consumption feelings Expectations Additional influences on customer satisfaction: – Having а more personalized experience with companies you do business with – Ability to customize а particular product or а service according to your own preferences – Getting rewards and discounts in exchange for participating in customer loyalty or preferred customer programs – Being able to communicate with companies online – Online shopping – Participating in customer surveys
What Determines Satisfaction • • Product performance Consumption feelings Expectations Additional influences on customer satisfaction: – Having а more personalized experience with companies you do business with – Ability to customize а particular product or а service according to your own preferences – Getting rewards and discounts in exchange for participating in customer loyalty or preferred customer programs – Being able to communicate with companies online – Online shopping – Participating in customer surveys
 The Importance of Customer Satisfaction • It influences repeat buying • It shapes word-of-mouth and word-ofmouse communication • Dissatisfaction can lead to complaints and lawsuits • Satisfaction lowers consumers' price sensitivity • It is critical for customer recruitment • It ultimately affects shareholder value
The Importance of Customer Satisfaction • It influences repeat buying • It shapes word-of-mouth and word-ofmouse communication • Dissatisfaction can lead to complaints and lawsuits • Satisfaction lowers consumers' price sensitivity • It is critical for customer recruitment • It ultimately affects shareholder value
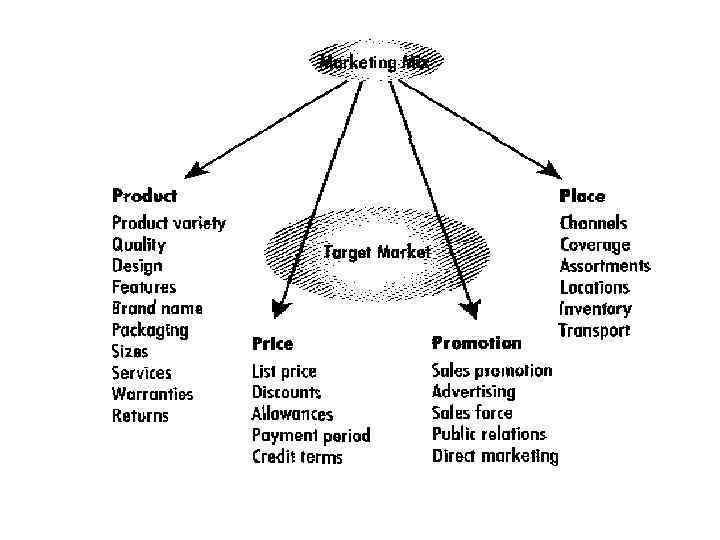
 Marketing mix The marketing mix is the set of marketing tools that the firm uses to pursue its marketing objectives in the target market.
Marketing mix The marketing mix is the set of marketing tools that the firm uses to pursue its marketing objectives in the target market.
 Discussion questions 1. The three major challenges faced by business today are globalization, advances in technology and deregulation. Which of these affords the greatest opportunity for established business? Which affords the greatest opportunity for new business? Why? 2. Can you identify the trends that have made the marketing concept, the customer concept, and the societal marketing concept more attractive models for contemporary marketing managers? 3. Can you name a category of products for which your negative feelings have softened? What precipitated this change?
Discussion questions 1. The three major challenges faced by business today are globalization, advances in technology and deregulation. Which of these affords the greatest opportunity for established business? Which affords the greatest opportunity for new business? Why? 2. Can you identify the trends that have made the marketing concept, the customer concept, and the societal marketing concept more attractive models for contemporary marketing managers? 3. Can you name a category of products for which your negative feelings have softened? What precipitated this change?


