d4d2157d39770fb995af1e77fdf94a23.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 Week 1 (Chapter 1 a) Consumer Behavior and Consumer Research COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Week 1 (Chapter 1 a) Consumer Behavior and Consumer Research COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 A) What Is Consumer Behavior? Def: Activities people undertake when obtaining, consuming, and disposing of products and services Or Def: a field of study that focuses on consumer activities COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
A) What Is Consumer Behavior? Def: Activities people undertake when obtaining, consuming, and disposing of products and services Or Def: a field of study that focuses on consumer activities COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
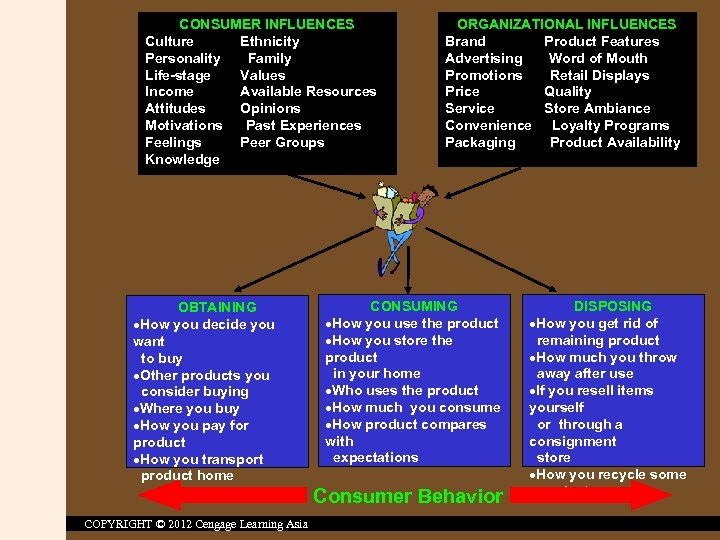 CONSUMER INFLUENCES Culture Ethnicity Personality Family Life-stage Values Income Available Resources Attitudes Opinions Motivations Past Experiences Feelings Peer Groups Knowledge OBTAINING ·How you decide you want to buy ·Other products you consider buying ·Where you buy ·How you pay for product ·How you transport product home ORGANIZATIONAL INFLUENCES Brand Product Features Advertising Word of Mouth Promotions Retail Displays Price Quality Service Store Ambiance Convenience Loyalty Programs Packaging Product Availability CONSUMING ·How you use the product ·How you store the product in your home ·Who uses the product ·How much you consume ·How product compares with expectations Consumer Behavior COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia DISPOSING ·How you get rid of remaining product ·How much you throw away after use ·If you resell items yourself or through a consignment store ·How you recycle some products
CONSUMER INFLUENCES Culture Ethnicity Personality Family Life-stage Values Income Available Resources Attitudes Opinions Motivations Past Experiences Feelings Peer Groups Knowledge OBTAINING ·How you decide you want to buy ·Other products you consider buying ·Where you buy ·How you pay for product ·How you transport product home ORGANIZATIONAL INFLUENCES Brand Product Features Advertising Word of Mouth Promotions Retail Displays Price Quality Service Store Ambiance Convenience Loyalty Programs Packaging Product Availability CONSUMING ·How you use the product ·How you store the product in your home ·Who uses the product ·How much you consume ·How product compares with expectations Consumer Behavior COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia DISPOSING ·How you get rid of remaining product ·How much you throw away after use ·If you resell items yourself or through a consignment store ·How you recycle some products
 The Study of Consumer Behaviour Ø Focused on CB (e. g: why people buy? ) ØNow: consumption analysis (e. g: Why and how people use products in addition to why and how they buy) COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
The Study of Consumer Behaviour Ø Focused on CB (e. g: why people buy? ) ØNow: consumption analysis (e. g: Why and how people use products in addition to why and how they buy) COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 B) Why Study Consumer Behavior? Consumer Behavior Determines the Economic Health of a Nation – vote for firms, hence provide jobs Consumer Behavior Determines the Success of Marketing Programs COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
B) Why Study Consumer Behavior? Consumer Behavior Determines the Economic Health of a Nation – vote for firms, hence provide jobs Consumer Behavior Determines the Success of Marketing Programs COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 Marketing can be used to influence brand choice and purchase, while Demarketing can influence people to stop harmful consumption “The Customer is King” Organization influenced by consumer needs and wants Hence, organizations that are Customer -centric use a total marketing approach to focus their resources on satisfying customers COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Marketing can be used to influence brand choice and purchase, while Demarketing can influence people to stop harmful consumption “The Customer is King” Organization influenced by consumer needs and wants Hence, organizations that are Customer -centric use a total marketing approach to focus their resources on satisfying customers COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 Why Study Consumer Behavior? Consumer Behavior Determines the Economic Health of Everyone The individual’s decisions as a consumer determine their economic health by making more effective consumption decisions while avoiding deceptive practices harmful to them Ne w Old COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia E. g. buyer beware…
Why Study Consumer Behavior? Consumer Behavior Determines the Economic Health of Everyone The individual’s decisions as a consumer determine their economic health by making more effective consumption decisions while avoiding deceptive practices harmful to them Ne w Old COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia E. g. buyer beware…
 Educating Consumers About Health Understanding consumers’ issues or problems and developing methods to reach and educate consumers COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Educating Consumers About Health Understanding consumers’ issues or problems and developing methods to reach and educate consumers COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 Educating Consumers About Health Understanding consumers’ issues or problems and developing methods to reach and educate consumers COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Educating Consumers About Health Understanding consumers’ issues or problems and developing methods to reach and educate consumers COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
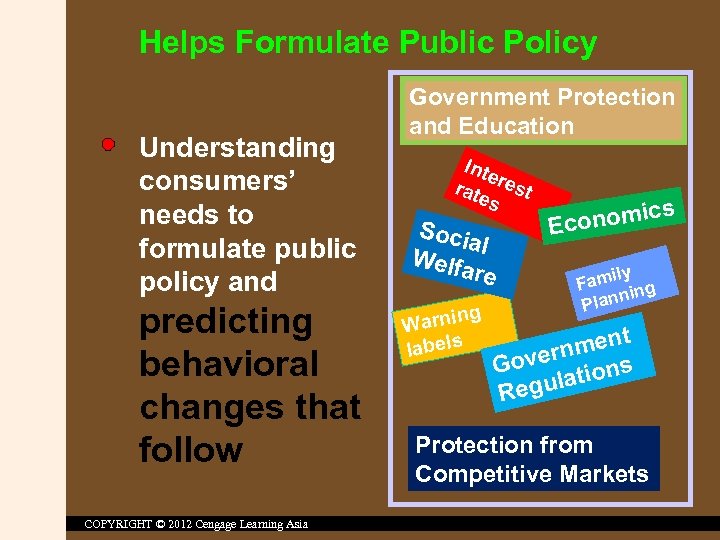 Helps Formulate Public Policy Understanding consumers’ needs to formulate public policy and predicting behavioral changes that follow COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia Government Protection and Education Inte rat rest es Soci al Welf are ng Warni labels s onomic Ec ily Fam ing n Plan t nmen r Gove tions egula R Protection from Competitive Markets
Helps Formulate Public Policy Understanding consumers’ needs to formulate public policy and predicting behavioral changes that follow COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia Government Protection and Education Inte rat rest es Soci al Welf are ng Warni labels s onomic Ec ily Fam ing n Plan t nmen r Gove tions egula R Protection from Competitive Markets
 Why Study Consumer Behavior? Consumer Behavior Affects Personal Policy Personal policy includes how you behave towards others and in buying situations, your values and beliefs, and how you live your life A person’s economic quality of life is determined by personal policy COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Why Study Consumer Behavior? Consumer Behavior Affects Personal Policy Personal policy includes how you behave towards others and in buying situations, your values and beliefs, and how you live your life A person’s economic quality of life is determined by personal policy COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
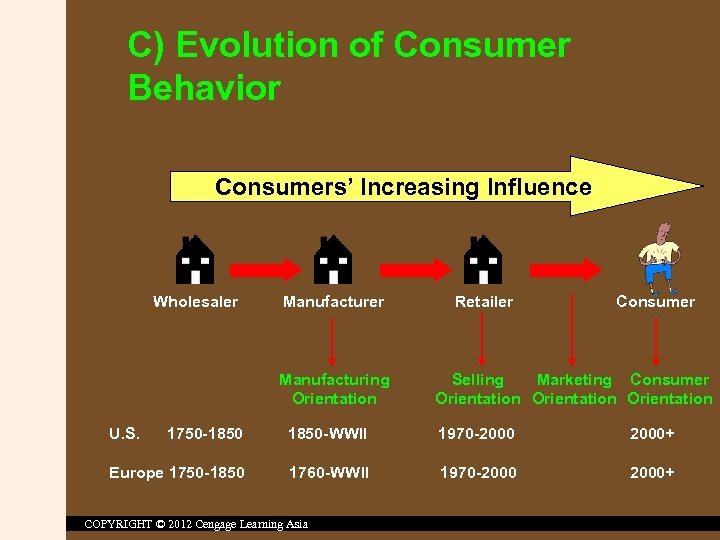 C) Evolution of Consumer Behavior Consumers’ Increasing Influence Wholesaler Manufacturing Orientation U. S. Retailer Consumer Selling Marketing Consumer Orientation 1750 -1850 -WWII 1970 -2000+ Europe 1750 -1850 1760 -WWII 1970 -2000+ COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
C) Evolution of Consumer Behavior Consumers’ Increasing Influence Wholesaler Manufacturing Orientation U. S. Retailer Consumer Selling Marketing Consumer Orientation 1750 -1850 -WWII 1970 -2000+ Europe 1750 -1850 1760 -WWII 1970 -2000+ COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 Evolution of Consumer Behavior Manufacturing Orientation Selling Orientation Marketing Orientation (motivation research, positivism (empirical data that use 1) to understand & predict CB 2) discover cause and effect relationship), postmodernismqualitative and others method to study example emotion) Consumer Orientation COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Evolution of Consumer Behavior Manufacturing Orientation Selling Orientation Marketing Orientation (motivation research, positivism (empirical data that use 1) to understand & predict CB 2) discover cause and effect relationship), postmodernismqualitative and others method to study example emotion) Consumer Orientation COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 Consumer Orientation Beyond a marketing focus How all organizations in a demand chain adapt to changing consumer lifestyles and behaviors bringing product design, logistics, manufacturing, and retailing together Role of consumers in shaping many aspects of life—society, government, social programs, health cares, and other areas COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Consumer Orientation Beyond a marketing focus How all organizations in a demand chain adapt to changing consumer lifestyles and behaviors bringing product design, logistics, manufacturing, and retailing together Role of consumers in shaping many aspects of life—society, government, social programs, health cares, and other areas COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 D) Consumer Research Methods Observation In-home observation: examining how and when consumers use and consume products in their households Shadowing: following and observing consumers in the shopping and consumption processes. Researchers may ask questions about reasons for behaviors Physiological methods: Techniques borrowed from medicine, psychology and other sciences including cameras to measure eye movement, galvanic skin response, and MRI COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
D) Consumer Research Methods Observation In-home observation: examining how and when consumers use and consume products in their households Shadowing: following and observing consumers in the shopping and consumption processes. Researchers may ask questions about reasons for behaviors Physiological methods: Techniques borrowed from medicine, psychology and other sciences including cameras to measure eye movement, galvanic skin response, and MRI COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 Consumer Research Methods Interviews and Surveys: efficient method for gathering information from a large sample of consumers by asking questions and recording responses (telephone and Internet surveys, mall intercepts, and mail questionnaires) Focus Groups: a group discussion led by a moderator skilled in persuading consumers to thoroughly discuss a topic of interest Longitudinal Studies: repeated measures of activities over time to determine changes in opinions, buying, and consumption behaviors. (e. g: panel data, membership COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Consumer Research Methods Interviews and Surveys: efficient method for gathering information from a large sample of consumers by asking questions and recording responses (telephone and Internet surveys, mall intercepts, and mail questionnaires) Focus Groups: a group discussion led by a moderator skilled in persuading consumers to thoroughly discuss a topic of interest Longitudinal Studies: repeated measures of activities over time to determine changes in opinions, buying, and consumption behaviors. (e. g: panel data, membership COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 Consumer Research Methods Experimentation Attempts to understand cause-and-effect relationships by carefully manipulating independent variables to determine how these changes affect dependent variables - Laboratory experiment - Field experiment Independent variables might include number of advertisements and package design Dependent variables might include purchase intent or behavior COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Consumer Research Methods Experimentation Attempts to understand cause-and-effect relationships by carefully manipulating independent variables to determine how these changes affect dependent variables - Laboratory experiment - Field experiment Independent variables might include number of advertisements and package design Dependent variables might include purchase intent or behavior COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 Consumer Research Methods Consumption Research Builds on the three primary research methods to examine how people use products and services rather than how they buy them May use ethnographic tools to understand how values and culture influence usage of products and other behaviors May identify new uses for existing products or new product to satisfy unmet or changing consumer needs COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
Consumer Research Methods Consumption Research Builds on the three primary research methods to examine how people use products and services rather than how they buy them May use ethnographic tools to understand how values and culture influence usage of products and other behaviors May identify new uses for existing products or new product to satisfy unmet or changing consumer needs COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
 E) The Underlying Principles of Consumer Behavior Consumer is sovereign / autonomous Consumer may accept @ reject the products @ services Consumer is global Global consumer buy same product from same retailer Consumer are different/ alike Similarities in group but different between group Consumer has right COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia Consumer has right upon product/ service
E) The Underlying Principles of Consumer Behavior Consumer is sovereign / autonomous Consumer may accept @ reject the products @ services Consumer is global Global consumer buy same product from same retailer Consumer are different/ alike Similarities in group but different between group Consumer has right COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia Consumer has right upon product/ service
 F) Challenges for the Future Gathering and interpreting information that organizations need to meet changing needs of consumers Developing effective consumer research methods to capture changes in trends and lifestyles Understanding consumer behavior from a broader perspective as an important part of life -End_ COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia
F) Challenges for the Future Gathering and interpreting information that organizations need to meet changing needs of consumers Developing effective consumer research methods to capture changes in trends and lifestyles Understanding consumer behavior from a broader perspective as an important part of life -End_ COPYRIGHT © 2012 Cengage Learning Asia


