47d00fb9b515928c6ec4a742d11b3fa2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Managing Marketing Information • Chapter 6 • Powerpoint slides • Extendit! version • Instructor name • Course name • School name • Date Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Managing Marketing Information • Chapter 6 • Powerpoint slides • Extendit! version • Instructor name • Course name • School name • Date Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 Learning Objectives 2 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • After studying this chapter, you should be able to: – Explain the importance of information to the company – Define the marketing information system and discuss its parts – Outline the four steps in the marketing research process – Explain how companies analyze and distribute marketing information – Discuss the special issues some marketing researchers face, including public policy and ethics issues Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
Learning Objectives 2 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • After studying this chapter, you should be able to: – Explain the importance of information to the company – Define the marketing information system and discuss its parts – Outline the four steps in the marketing research process – Explain how companies analyze and distribute marketing information – Discuss the special issues some marketing researchers face, including public policy and ethics issues Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Opening Vignette: The New Coke Debacle 3 • Coca-Cola began over 100 years, one of the world’s best known and valuable brands • “Don’t mess with Mother Coke” ignored in 1985, when the original formulation was changed • Poor marketing research blamed • Two years, and $7. 8 million spent on taste testing proved that consumers like the taste of “new Coke” better than Pepsi and existing Coke • Research dealt only with taste, did not explore consumers’ attachment to the product, and all of its intangibles • Coke Classic quickly introduced, new Coke quietly fades into the background Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Opening Vignette: The New Coke Debacle 3 • Coca-Cola began over 100 years, one of the world’s best known and valuable brands • “Don’t mess with Mother Coke” ignored in 1985, when the original formulation was changed • Poor marketing research blamed • Two years, and $7. 8 million spent on taste testing proved that consumers like the taste of “new Coke” better than Pepsi and existing Coke • Research dealt only with taste, did not explore consumers’ attachment to the product, and all of its intangibles • Coke Classic quickly introduced, new Coke quietly fades into the background Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
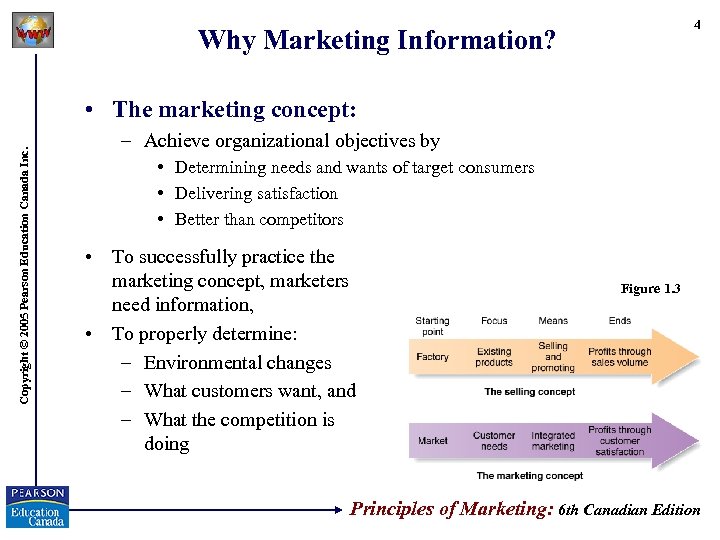 4 Why Marketing Information? Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • The marketing concept: – Achieve organizational objectives by • Determining needs and wants of target consumers • Delivering satisfaction • Better than competitors • To successfully practice the marketing concept, marketers need information, • To properly determine: – Environmental changes – What customers want, and – What the competition is doing Figure 1. 3 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
4 Why Marketing Information? Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • The marketing concept: – Achieve organizational objectives by • Determining needs and wants of target consumers • Delivering satisfaction • Better than competitors • To successfully practice the marketing concept, marketers need information, • To properly determine: – Environmental changes – What customers want, and – What the competition is doing Figure 1. 3 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
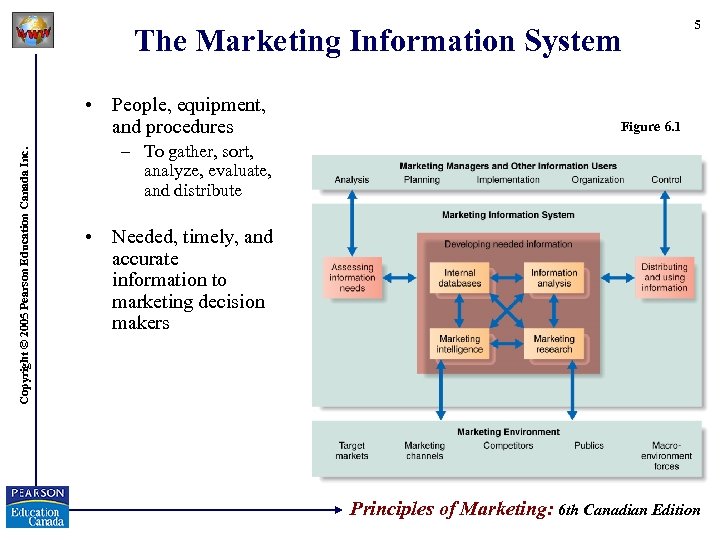 The Marketing Information System Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • People, equipment, and procedures 5 Figure 6. 1 – To gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute • Needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Information System Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • People, equipment, and procedures 5 Figure 6. 1 – To gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute • Needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 The Marketing Information System 6 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Assessing information needs: – Remember, the objective is to make better marketing decisions – Must consider needs of all users – Must balance information wants with decision making needs and feasibility (and costs) of offering it – The value of information comes from its use, not its existence • Developing information: – Internal data – Marketing intelligence (on competitors) ( – Marketing research (design, collection, analysis, reporting) Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Information System 6 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Assessing information needs: – Remember, the objective is to make better marketing decisions – Must consider needs of all users – Must balance information wants with decision making needs and feasibility (and costs) of offering it – The value of information comes from its use, not its existence • Developing information: – Internal data – Marketing intelligence (on competitors) ( – Marketing research (design, collection, analysis, reporting) Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 Developing Information 7 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Internal data: – Information collected from different sources within the company, and stored within the organization’s information system • Accounting system • Operations/production • Sales reporting system • Past research studies – Internal data is cheap, quick, and easy – May not be in a usable form for the decision to be made – May be too much information to sort through Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
Developing Information 7 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Internal data: – Information collected from different sources within the company, and stored within the organization’s information system • Accounting system • Operations/production • Sales reporting system • Past research studies – Internal data is cheap, quick, and easy – May not be in a usable form for the decision to be made – May be too much information to sort through Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Developing Information 8 • Marketing intelligence: – Systematic collection and analysis of publicly available information about competitors and market developments – Proactive approach to keeping track of what is going on within the organization’s marketing environment • Sources: employees, customers, trade shows, websites, marketing communications, suppliers, resellers, professional information services, and “dumpster diving” Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Developing Information 8 • Marketing intelligence: – Systematic collection and analysis of publicly available information about competitors and market developments – Proactive approach to keeping track of what is going on within the organization’s marketing environment • Sources: employees, customers, trade shows, websites, marketing communications, suppliers, resellers, professional information services, and “dumpster diving” Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 9 The Marketing Research Process Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Marketing research: – Systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting data relevant to a specific marketing situation facing the organization – A multi-step, purpose-driven process – Measure effectiveness of marketing actions, sales potential, try to understand consumer behaviour, customer needs, distribution systems – Can be done by company personnel or contracted out to outside companies Figure 6. 2 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
9 The Marketing Research Process Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Marketing research: – Systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting data relevant to a specific marketing situation facing the organization – A multi-step, purpose-driven process – Measure effectiveness of marketing actions, sales potential, try to understand consumer behaviour, customer needs, distribution systems – Can be done by company personnel or contracted out to outside companies Figure 6. 2 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 The Marketing Research Process (continued) 10 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Defining the problem – Helps to know what you are looking for! – Can be the most difficult step in the process – Need to scope the project large enough in order to understand what really causes the problem. It can be done through: Figure 6. 2 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Research Process (continued) 10 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Defining the problem – Helps to know what you are looking for! – Can be the most difficult step in the process – Need to scope the project large enough in order to understand what really causes the problem. It can be done through: Figure 6. 2 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 The Marketing Research Process (continued) 11 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Objectives of research – Exploratory research: • Research conducted to gather information to help better define problems and opportunities • Secondary research, focus group discussions and depth interviews are commonly used for this purpose – Descriptive research: • Research conducted to better describe marketing problems, situations, or markets, such as • Demographic characteristics of markets, attitudes of consumers, and market potential for a product • Surveys and personal interviews are commonly used – Causal research: • Research to test cause and effect relationships between variables of interest, such as experiments Figure 6. 2 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Research Process (continued) 11 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Objectives of research – Exploratory research: • Research conducted to gather information to help better define problems and opportunities • Secondary research, focus group discussions and depth interviews are commonly used for this purpose – Descriptive research: • Research conducted to better describe marketing problems, situations, or markets, such as • Demographic characteristics of markets, attitudes of consumers, and market potential for a product • Surveys and personal interviews are commonly used – Causal research: • Research to test cause and effect relationships between variables of interest, such as experiments Figure 6. 2 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. The Marketing Research Process (continued) 12 • Developing the research plan: – Translating the research objectives into specific information needs – Research plan presented in a written proposal for approval • Gathering data – Secondary data: information that already exists, having been collected for another purpose • Internal data, academic, and commercial sources • Faster and cheaper than primary data collection, but may not be in a suitable form for decision making • Helps to see what work has already been done in the area – Primary data collection: • Information collected for the specific purpose • Must look for relevance, accuracy, current, and unbiased Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. The Marketing Research Process (continued) 12 • Developing the research plan: – Translating the research objectives into specific information needs – Research plan presented in a written proposal for approval • Gathering data – Secondary data: information that already exists, having been collected for another purpose • Internal data, academic, and commercial sources • Faster and cheaper than primary data collection, but may not be in a suitable form for decision making • Helps to see what work has already been done in the area – Primary data collection: • Information collected for the specific purpose • Must look for relevance, accuracy, current, and unbiased Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
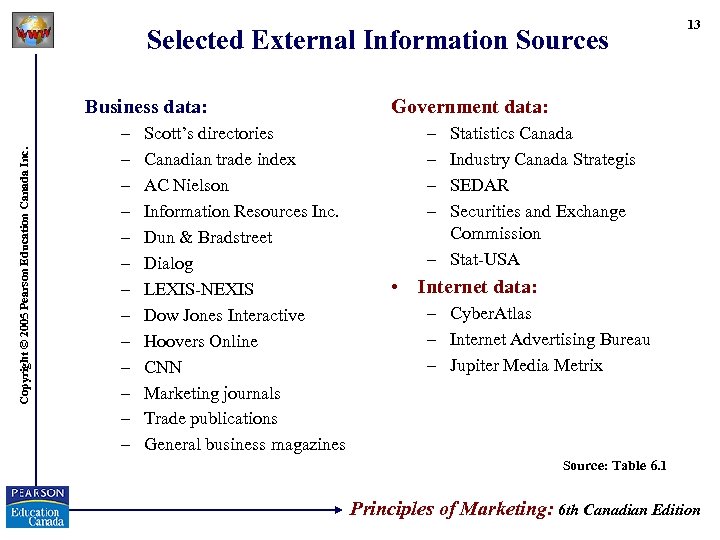 Selected External Information Sources Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Business data: – – – – Scott’s directories Canadian trade index AC Nielson Information Resources Inc. Dun & Bradstreet Dialog LEXIS-NEXIS Dow Jones Interactive Hoovers Online CNN Marketing journals Trade publications General business magazines 13 Government data: – – Statistics Canada Industry Canada Strategis SEDAR Securities and Exchange Commission – Stat-USA • Internet data: – Cyber. Atlas – Internet Advertising Bureau – Jupiter Media Metrix Source: Table 6. 1 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
Selected External Information Sources Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Business data: – – – – Scott’s directories Canadian trade index AC Nielson Information Resources Inc. Dun & Bradstreet Dialog LEXIS-NEXIS Dow Jones Interactive Hoovers Online CNN Marketing journals Trade publications General business magazines 13 Government data: – – Statistics Canada Industry Canada Strategis SEDAR Securities and Exchange Commission – Stat-USA • Internet data: – Cyber. Atlas – Internet Advertising Bureau – Jupiter Media Metrix Source: Table 6. 1 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 The Marketing Research Process (continued) 14 Primary data collection methods Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Observational research: – Gathering of primary data by strictly observing relevant people, actions, and situations – Ethnographic research combines observation with interviews to get a better insight – Mechanical observation: scanner data – Useful but difficult to ascertain feelings, attitudes, or motives Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Research Process (continued) 14 Primary data collection methods Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Observational research: – Gathering of primary data by strictly observing relevant people, actions, and situations – Ethnographic research combines observation with interviews to get a better insight – Mechanical observation: scanner data – Useful but difficult to ascertain feelings, attitudes, or motives Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 The Marketing Research Process (continued) 15 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Survey research: – Gathering primary data by asking people questions – Good to know about people’s knowledge, attitudes, preferences, and buying behaviour – Best suited for gathering descriptive information – Single-source data systems: • Electronic monitoring systems that link exposure to various marketing activities through advertising (using meters) and what they buy in stores (checkout scanners) • Survey research is flexible but may suffer bias due to self-reporting or lack of understanding of what is being asked Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Research Process (continued) 15 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Survey research: – Gathering primary data by asking people questions – Good to know about people’s knowledge, attitudes, preferences, and buying behaviour – Best suited for gathering descriptive information – Single-source data systems: • Electronic monitoring systems that link exposure to various marketing activities through advertising (using meters) and what they buy in stores (checkout scanners) • Survey research is flexible but may suffer bias due to self-reporting or lack of understanding of what is being asked Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 The Marketing Research Process (continued) 16 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Experimental research: – Gathering primary data by selecting matched groups of subjects – Giving them different treatments – Controlling unrelated factors – Checking for differences in group responses • Experimental research is used when attempting to explain cause and effect relationships • Difficult to control for all situations or variables that have an influence on behaviour Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Research Process (continued) 16 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Experimental research: – Gathering primary data by selecting matched groups of subjects – Giving them different treatments – Controlling unrelated factors – Checking for differences in group responses • Experimental research is used when attempting to explain cause and effect relationships • Difficult to control for all situations or variables that have an influence on behaviour Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
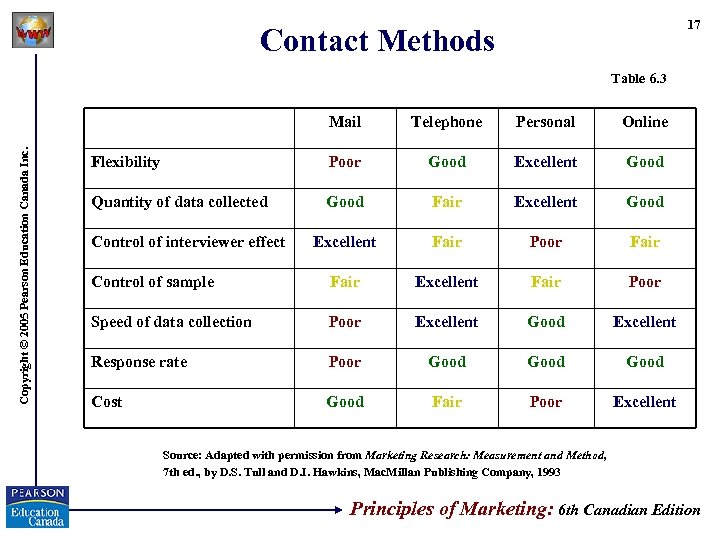 17 Contact Methods Table 6. 3 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Mail Telephone Personal Online Flexibility Poor Good Excellent Good Quantity of data collected Good Fair Excellent Good Excellent Fair Poor Fair Control of sample Fair Excellent Fair Poor Speed of data collection Poor Excellent Good Excellent Response rate Poor Good Cost Good Fair Poor Excellent Control of interviewer effect Source: Adapted with permission from Marketing Research: Measurement and Method, 7 th ed. , by D. S. Tull and D. I. Hawkins, Mac. Millan Publishing Company, 1993 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
17 Contact Methods Table 6. 3 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Mail Telephone Personal Online Flexibility Poor Good Excellent Good Quantity of data collected Good Fair Excellent Good Excellent Fair Poor Fair Control of sample Fair Excellent Fair Poor Speed of data collection Poor Excellent Good Excellent Response rate Poor Good Cost Good Fair Poor Excellent Control of interviewer effect Source: Adapted with permission from Marketing Research: Measurement and Method, 7 th ed. , by D. S. Tull and D. I. Hawkins, Mac. Millan Publishing Company, 1993 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 The Marketing Research Process (continued) 18 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Sample: – A segment of the population selected for marketing research – To represent the population as a whole • Who should be surveyed? Sampling unit • How many should be surveyed? Sample size • How should they be chosen? Sampling procedure Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Research Process (continued) 18 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Sample: – A segment of the population selected for marketing research – To represent the population as a whole • Who should be surveyed? Sampling unit • How many should be surveyed? Sample size • How should they be chosen? Sampling procedure Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 The Marketing Research Process (continued) 19 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Research instruments: – – – Questionnaires are the most commonly used Mechanical devices are the other option Questions asked can be open or closed Writing good (valid) questions can be difficult Wording and order are important – Pre-testing is important to ensure good results Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Research Process (continued) 19 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Research instruments: – – – Questionnaires are the most commonly used Mechanical devices are the other option Questions asked can be open or closed Writing good (valid) questions can be difficult Wording and order are important – Pre-testing is important to ensure good results Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 The Marketing Research Process (continued) 20 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Implementing the research plan: – Collecting, processing, and analyzing the information – Data collection is expensive and most subject to error – Field work needs to be supervised to ensure accuracy • Interpreting the results: – Attempting to find meaning to the data collected – Need to be careful to avoid bias in interpretation; getting the answer that was favored in the beginning or that suits a particular political agenda (Challenging a report made by a coworker) Figure 6. 2 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
The Marketing Research Process (continued) 20 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Implementing the research plan: – Collecting, processing, and analyzing the information – Data collection is expensive and most subject to error – Field work needs to be supervised to ensure accuracy • Interpreting the results: – Attempting to find meaning to the data collected – Need to be careful to avoid bias in interpretation; getting the answer that was favored in the beginning or that suits a particular political agenda (Challenging a report made by a coworker) Figure 6. 2 Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 Customer Relationship Management 21 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Customer relationship management (CRM): – Managing detailed information about individual customers at all “touch pointst to maximize customer loyalty through a better servicing (Bell, Banks) – Use data warehouses and use datamining techniques to dig out relevant information – Purpose is to make better use of the information the company already has – The goal is to provide higher levels of customer service Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
Customer Relationship Management 21 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • Customer relationship management (CRM): – Managing detailed information about individual customers at all “touch pointst to maximize customer loyalty through a better servicing (Bell, Banks) – Use data warehouses and use datamining techniques to dig out relevant information – Purpose is to make better use of the information the company already has – The goal is to provide higher levels of customer service Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Other Marketing Research Considerations 22 • Research in small businesses and non-profit organizations • International marketing research • Public policy and ethics in marketing research: – Privacy of information – Selling under the guise of conducting research activities – Misuse of research findings for promotional purposes – Acceptable lies and non acceptable ones Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. Other Marketing Research Considerations 22 • Research in small businesses and non-profit organizations • International marketing research • Public policy and ethics in marketing research: – Privacy of information – Selling under the guise of conducting research activities – Misuse of research findings for promotional purposes – Acceptable lies and non acceptable ones Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
 In Conclusion… 23 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • The learning objectives for this chapter were: – Explain the importance of information to the company – Define the marketing information system and discuss its parts – Outline the four steps in the marketing research process – Explain how companies analyze and distribute marketing information – Discuss the special issues some marketing researchers face, including public policy and ethics issues Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition
In Conclusion… 23 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. • The learning objectives for this chapter were: – Explain the importance of information to the company – Define the marketing information system and discuss its parts – Outline the four steps in the marketing research process – Explain how companies analyze and distribute marketing information – Discuss the special issues some marketing researchers face, including public policy and ethics issues Principles of Marketing: 6 th Canadian Edition


