Copyright© 2004 South-Western 1212 The Design of the






































- Размер: 1.9 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 50
Описание презентации Copyright© 2004 South-Western 1212 The Design of the по слайдам
 Copyright© 2004 South-Western 1212 The Design of the Tax System
Copyright© 2004 South-Western 1212 The Design of the Tax System
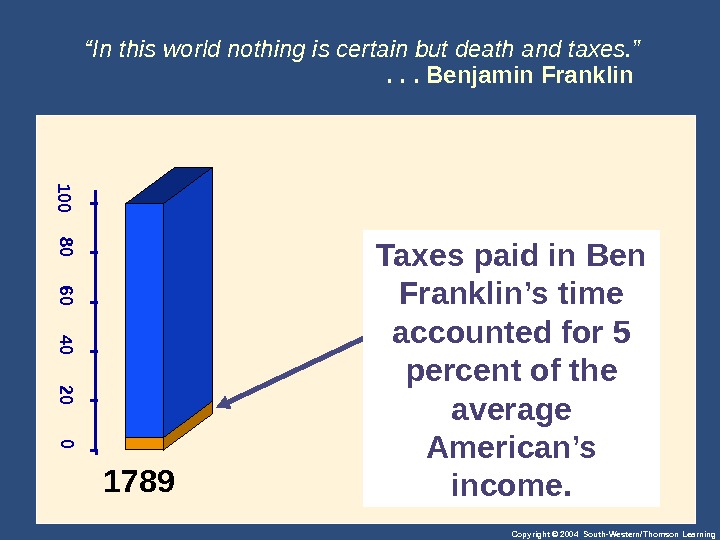
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning“ In this world nothing is certain but death and taxes. ” . . . Benjamin Franklin 0 20 40 60 80 100 Taxes paid in Ben Franklin’s time accounted for 5 percent of the average American’s income.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning“ In this world nothing is certain but death and taxes. ” . . . Benjamin Franklin 0 20 40 60 80 100 Taxes paid in Ben Franklin’s time accounted for 5 percent of the average American’s income.
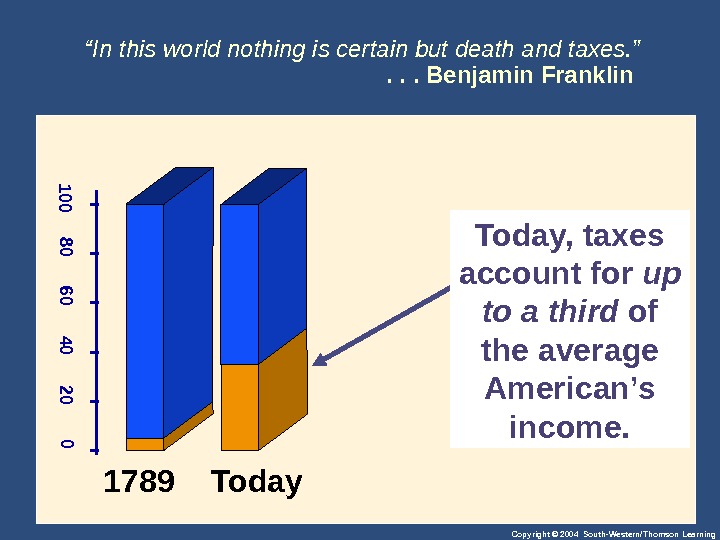
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning“ In this world nothing is certain but death and taxes. ” . . . Benjamin Franklin 0 20 40 60 80 100 1789 Today, taxes account for up to a third of the average American’s income.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning“ In this world nothing is certain but death and taxes. ” . . . Benjamin Franklin 0 20 40 60 80 100 1789 Today, taxes account for up to a third of the average American’s income.
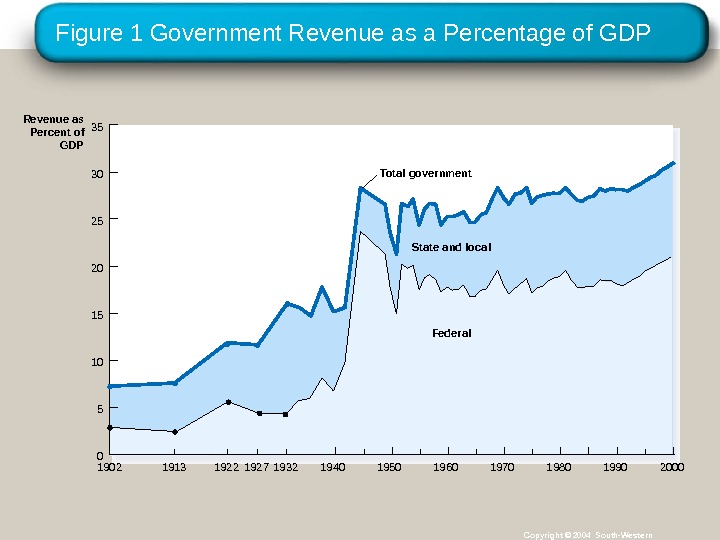
 Figure 1 Government Revenue as a Percentage of GDP Copyright © 2004 South-Western. State and local Federal 05101520253035 Revenue as Percent of GDP Total government
Figure 1 Government Revenue as a Percentage of GDP Copyright © 2004 South-Western. State and local Federal 05101520253035 Revenue as Percent of GDP Total government
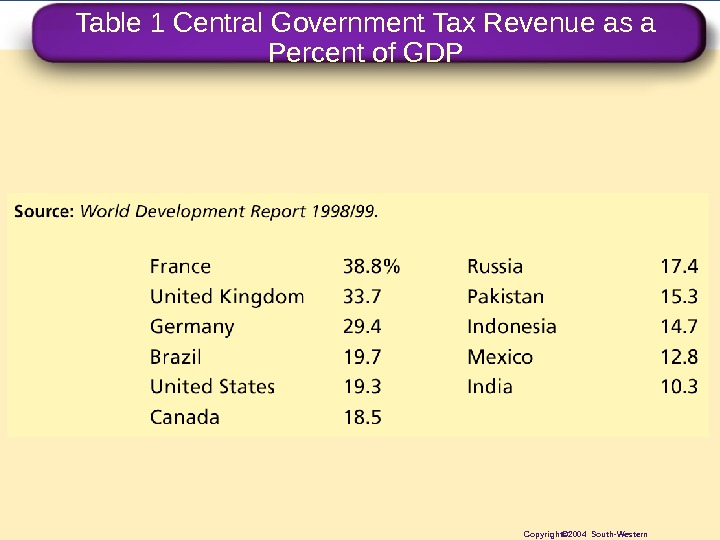
 Table 1 Central Government Tax Revenue as a Percent of GDP Copyright© 2004 South-Western
Table 1 Central Government Tax Revenue as a Percent of GDP Copyright© 2004 South-Western
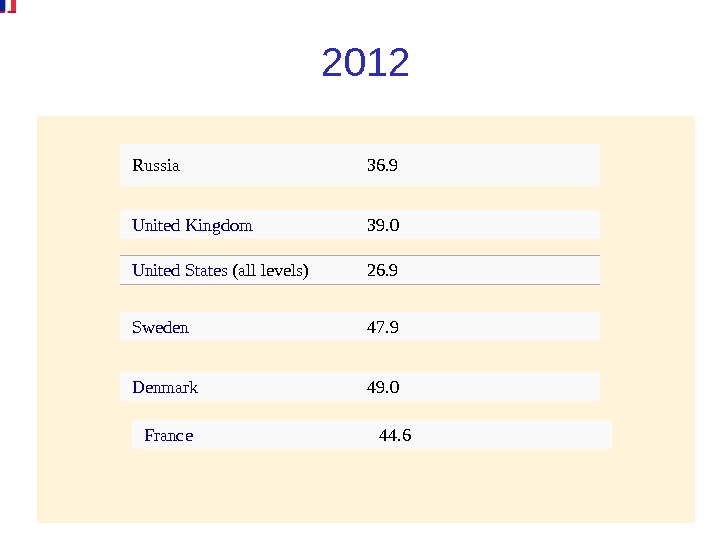
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning 2012 Russia 36. 9 United. States (alllevels) 26. 9 United. Kingdom 39. 0 Sweden 47. 9 Denmark 49. 0 France 44.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning 2012 Russia 36. 9 United. States (alllevels) 26. 9 United. Kingdom 39. 0 Sweden 47. 9 Denmark 49. 0 France 44.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • The. U. S. federalgovernmentcollectsabout two-thirdsofthetaxesinoureconomy.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • The. U. S. federalgovernmentcollectsabout two-thirdsofthetaxesinoureconomy.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Thelargestsourceofrevenueforthefederal governmentistheindividualincometax.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Thelargestsourceofrevenueforthefederal governmentistheindividualincometax.
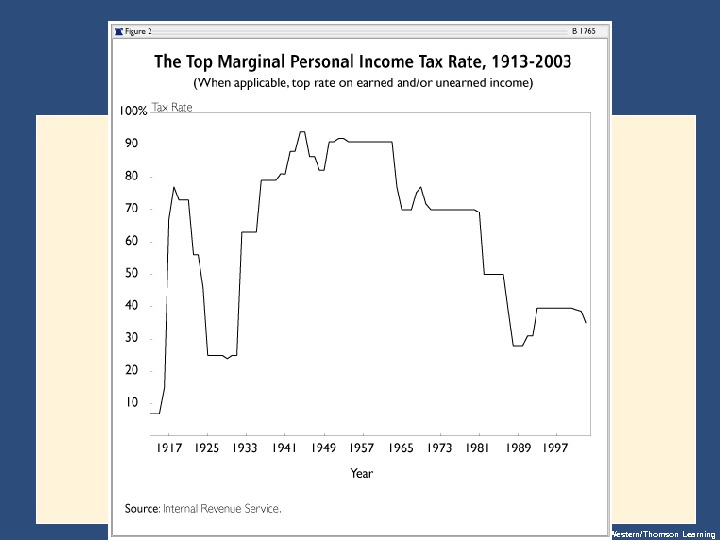
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Individual. Income. Taxes • The marginal tax rate isthetaxrateappliedtoeach additionaldollarofincome. • Higher-incomefamiliespayalargerpercentageof theirincomeintaxes.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Individual. Income. Taxes • The marginal tax rate isthetaxrateappliedtoeach additionaldollarofincome. • Higher-incomefamiliespayalargerpercentageof theirincomeintaxes.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • The. Federal. Governmentand. Taxes • Payroll. Taxes: taxonthewagesthatafirmpaysits workers. • Social. Insurance. Taxes: taxesonwagesthatis earmarkedtopayfor. Social. Securityand. Medicare. • Excise. Taxes: taxesonspecificgoodslikegasoline, cigarettes, andalcoholicbeverages.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • The. Federal. Governmentand. Taxes • Payroll. Taxes: taxonthewagesthatafirmpaysits workers. • Social. Insurance. Taxes: taxesonwagesthatis earmarkedtopayfor. Social. Securityand. Medicare. • Excise. Taxes: taxesonspecificgoodslikegasoline, cigarettes, andalcoholicbeverages.
 Table 2 Receipts of the Federal Government: 2001 Copyright© 2004 South-Western
Table 2 Receipts of the Federal Government: 2001 Copyright© 2004 South-Western
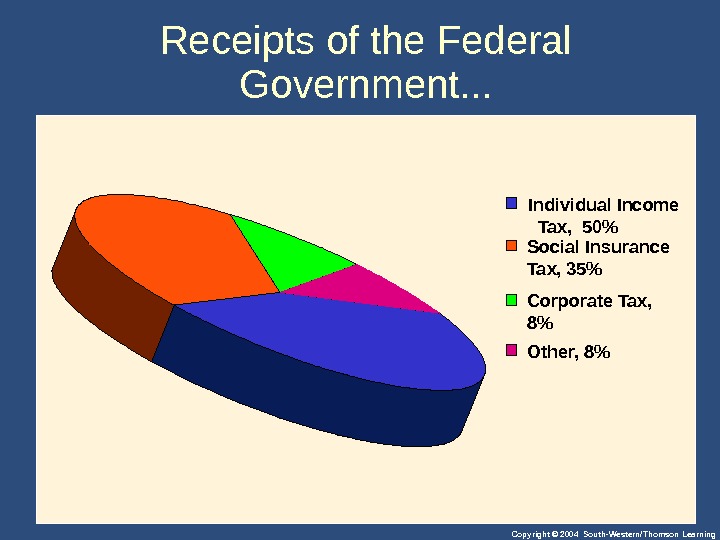
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Receipts of the Federal Government. . . Individual Income Tax, 50% Social Insurance Tax, 35% Corporate Tax, 8% Other, 8%
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Receipts of the Federal Government. . . Individual Income Tax, 50% Social Insurance Tax, 35% Corporate Tax, 8% Other, 8%
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Federal. Government. Spending • Governmentspendingincludestransferpayments andthepurchaseofpublicgoodsandservices. • Transferpaymentsaregovernmentpaymentsnotmadein exchangeforagoodoraservice. • Transferpaymentsarethelargestofthegovernment’s expenditures.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Federal. Government. Spending • Governmentspendingincludestransferpayments andthepurchaseofpublicgoodsandservices. • Transferpaymentsaregovernmentpaymentsnotmadein exchangeforagoodoraservice. • Transferpaymentsarethelargestofthegovernment’s expenditures.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Federal. Government. Spending • Expense. Category: • Social. Security • National. Defense • Income. Security • Net. Interest • Medicare • Health • Other
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Federal. Government. Spending • Expense. Category: • Social. Security • National. Defense • Income. Security • Net. Interest • Medicare • Health • Other
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Budget. Surplus • A budget surplus isanexcessofgovernment receiptsovergovernmentspending. • Budget. Deficit • A budget deficit isanexcessofgovernment spendingovernmentreceipts.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Budget. Surplus • A budget surplus isanexcessofgovernment receiptsovergovernmentspending. • Budget. Deficit • A budget deficit isanexcessofgovernment spendingovernmentreceipts.
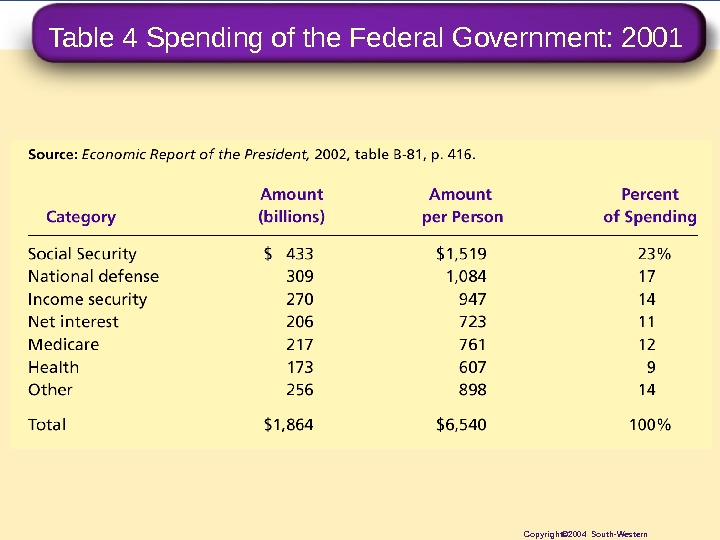
 Table 4 Spending of the Federal Government: 2001 Copyright© 2004 South-Western
Table 4 Spending of the Federal Government: 2001 Copyright© 2004 South-Western
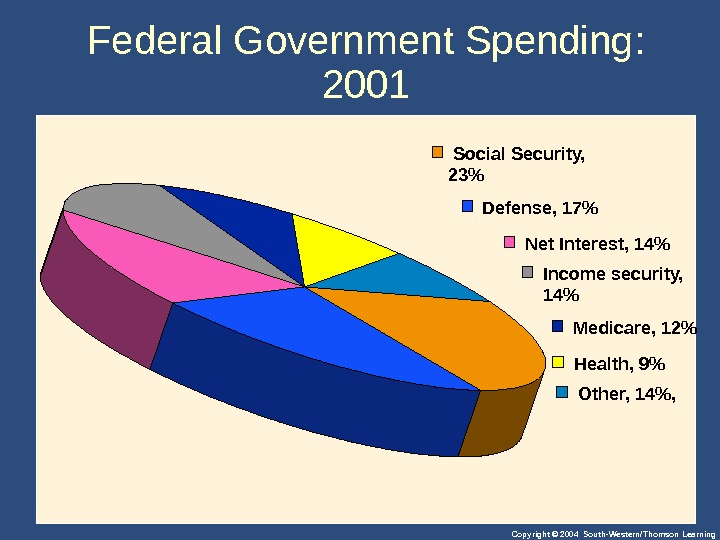
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Federal Government Spending: 2001 Social Security, 23% Defense, 17% Net Interest, 14% Income security, 14% Medicare, 12% Health, 9% Other, 14%,
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Federal Government Spending: 2001 Social Security, 23% Defense, 17% Net Interest, 14% Income security, 14% Medicare, 12% Health, 9% Other, 14%,
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Financial. Conditionsofthe. Federal. Budget • Abudgetdeficitoccurswhenthereisanexcessof governmentspendingovernmentreceipts. • Governmentfinancesthedeficitbyborrowingfromthe public. • Abudgetsurplusoccurswhengovernmentreceipts aregreaterthangovernmentspending. • Abudgetsurplusmaybeusedtoreducethe government’soutstandingdebts.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. The Federal Government • Financial. Conditionsofthe. Federal. Budget • Abudgetdeficitoccurswhenthereisanexcessof governmentspendingovernmentreceipts. • Governmentfinancesthedeficitbyborrowingfromthe public. • Abudgetsurplusoccurswhengovernmentreceipts aregreaterthangovernmentspending. • Abudgetsurplusmaybeusedtoreducethe government’soutstandingdebts.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. State and Local Governments • Stateandlocalgovernmentscollectabout 40 percentoftaxespaid.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. State and Local Governments • Stateandlocalgovernmentscollectabout 40 percentoftaxespaid.
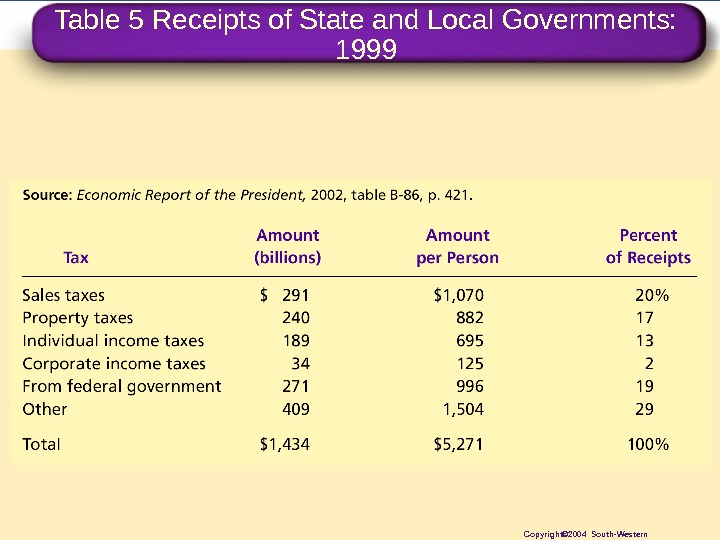
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. State and Local Government • Receipts • Sales. Taxes • Property. Taxes • Individual. Income. Taxes • Corporate. Income. Taxes • Federalgovernment • Other Taxes $
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. State and Local Government • Receipts • Sales. Taxes • Property. Taxes • Individual. Income. Taxes • Corporate. Income. Taxes • Federalgovernment • Other Taxes $
 Table 5 Receipts of State and Local Governments: 1999 Copyright© 2004 South-Western
Table 5 Receipts of State and Local Governments: 1999 Copyright© 2004 South-Western
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. State and Local Government • Spending • Education • Public. Welfare • Highways • Other
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. State and Local Government • Spending • Education • Public. Welfare • Highways • Other
 Table 6 Spending of State and Local Governments: 1999 Copyright© 2004 South-Western
Table 6 Spending of State and Local Governments: 1999 Copyright© 2004 South-Western
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EFFICIENCY • Policymakershavetwoobjectivesindesigning ataxsystem. . . • Efficiency • Equity
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EFFICIENCY • Policymakershavetwoobjectivesindesigning ataxsystem. . . • Efficiency • Equity
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EFFICIENCY • Onetaxsystemismore efficient thananotherif itraisesthesameamountofrevenueata smallercosttotaxpayers. • An efficient taxsystemisonethatimposes smalldeadweightlossesandsmall administrativeburdens.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EFFICIENCY • Onetaxsystemismore efficient thananotherif itraisesthesameamountofrevenueata smallercosttotaxpayers. • An efficient taxsystemisonethatimposes smalldeadweightlossesandsmall administrativeburdens.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EFFICIENCY • The. Costof. Taxesto. Taxpayers • Thetaxpaymentitself • Deadweightlosses • Administrativeburdens
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EFFICIENCY • The. Costof. Taxesto. Taxpayers • Thetaxpaymentitself • Deadweightlosses • Administrativeburdens
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Deadweight Losses • Becausetaxesdistortincentives, theyentail deadweightlosses. • Thedeadweightlossofataxisthereductionofthe economicwell-beingoftaxpayersinexcessofthe amountofrevenueraisedbythegovernment.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Deadweight Losses • Becausetaxesdistortincentives, theyentail deadweightlosses. • Thedeadweightlossofataxisthereductionofthe economicwell-beingoftaxpayersinexcessofthe amountofrevenueraisedbythegovernment.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Administrative Burdens • Complyingwithtaxlawscreatesadditional deadweightlosses. • Taxpayersloseadditionaltimeandmoney documenting, computing, andavoidingtaxesover andabovetheactualtaxestheypay. • Theadministrativeburdenofanytaxsystemispart oftheinefficiencyitcreates.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Administrative Burdens • Complyingwithtaxlawscreatesadditional deadweightlosses. • Taxpayersloseadditionaltimeandmoney documenting, computing, andavoidingtaxesover andabovetheactualtaxestheypay. • Theadministrativeburdenofanytaxsystemispart oftheinefficiencyitcreates.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Marginal Tax Rates versus Average Tax Rates • The average tax rate istotaltaxespaiddivided bytotalincome. • The marginal tax rate istheextrataxespaidon anadditionaldollarofincome.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Marginal Tax Rates versus Average Tax Rates • The average tax rate istotaltaxespaiddivided bytotalincome. • The marginal tax rate istheextrataxespaidon anadditionaldollarofincome.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Lump-Sum Taxes • Alump-sumtaxisataxthatisthesameamount foreveryperson, regardlessofearningsorany actionsthatthepersonmighttake. • ( аккордныйналог)
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Lump-Sum Taxes • Alump-sumtaxisataxthatisthesameamount foreveryperson, regardlessofearningsorany actionsthatthepersonmighttake. • ( аккордныйналог)
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EQUITY • Howshouldtheburdenoftaxesbedivided amongthepopulation? • Howdoweevaluatewhetherataxsystemis fair?
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EQUITY • Howshouldtheburdenoftaxesbedivided amongthepopulation? • Howdoweevaluatewhetherataxsystemis fair?
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EQUITY • Principlesof. Taxation • Benefitsprinciple • Ability-to-payprinciple $
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. TAXES AND EQUITY • Principlesof. Taxation • Benefitsprinciple • Ability-to-payprinciple $
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Benefits Principle • The benefits principle istheideathatpeople shouldpaytaxesbasedonthebenefitsthey receivefromgovernmentservices. • Anexampleisagasolinetax: • Taxrevenuesfromagasolinetaxareusedtofinance ourhighwaysystem. • Peoplewhodrivethemostalsopaythemosttoward maintainingroads.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Benefits Principle • The benefits principle istheideathatpeople shouldpaytaxesbasedonthebenefitsthey receivefromgovernmentservices. • Anexampleisagasolinetax: • Taxrevenuesfromagasolinetaxareusedtofinance ourhighwaysystem. • Peoplewhodrivethemostalsopaythemosttoward maintainingroads.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Ability-to-Pay Principle • The ability-to-pay principle istheideathat taxesshouldbeleviedonapersonaccordingto howwellthatpersoncanshouldertheburden. • Theability-to-payprincipleleadstotwo corollarynotionsofequity. • Verticalequity • Horizontalequity
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Ability-to-Pay Principle • The ability-to-pay principle istheideathat taxesshouldbeleviedonapersonaccordingto howwellthatpersoncanshouldertheburden. • Theability-to-payprincipleleadstotwo corollarynotionsofequity. • Verticalequity • Horizontalequity
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Ability-to-Pay Principle • Vertical equity istheideathattaxpayerswitha greaterabilitytopaytaxesshouldpaylarger amounts. • Forexample, peoplewithhigherincomesshould paymorethanpeoplewithlowerincomes.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Ability-to-Pay Principle • Vertical equity istheideathattaxpayerswitha greaterabilitytopaytaxesshouldpaylarger amounts. • Forexample, peoplewithhigherincomesshould paymorethanpeoplewithlowerincomes.
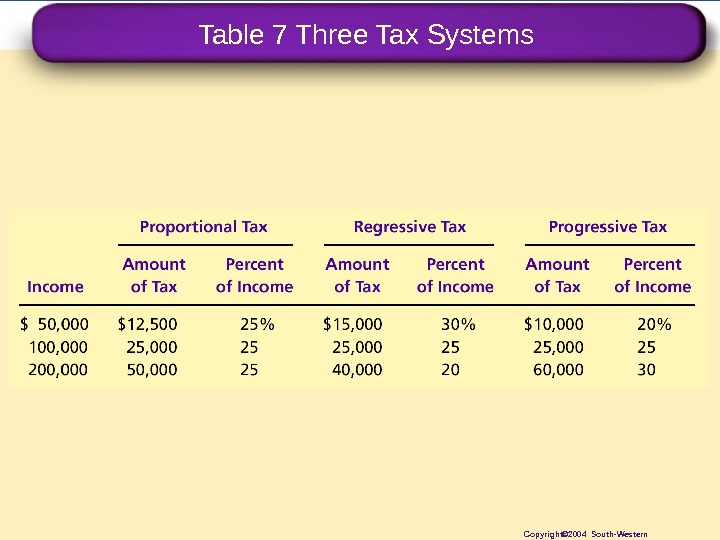
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Ability-to-Pay Principle • Vertical. Equityand. Alternative. Tax. Systems • A proportional tax isoneforwhichhigh-income andlow-incometaxpayerspaythesamefractionof income. • A regressive tax isoneforwhichhigh-income taxpayerspayasmallerfractionoftheirincome thandolow-incometaxpayers. • A progressive tax isoneforwhichhigh-income taxpayerspayalargerfractionoftheirincomethan dolow-incometaxpayers.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Ability-to-Pay Principle • Vertical. Equityand. Alternative. Tax. Systems • A proportional tax isoneforwhichhigh-income andlow-incometaxpayerspaythesamefractionof income. • A regressive tax isoneforwhichhigh-income taxpayerspayasmallerfractionoftheirincome thandolow-incometaxpayers. • A progressive tax isoneforwhichhigh-income taxpayerspayalargerfractionoftheirincomethan dolow-incometaxpayers.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Ability-to-Pay Principle • Horizontal. Equity • Horizontal equity istheideathattaxpayerswith similarabilitiestopaytaxesshouldpaythesame amounts. • Forexample, twofamilieswiththesamenumberof dependentsandthesameincomelivingindifferent partsofthecountryshouldpaythesamefederal taxes.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Ability-to-Pay Principle • Horizontal. Equity • Horizontal equity istheideathattaxpayerswith similarabilitiestopaytaxesshouldpaythesame amounts. • Forexample, twofamilieswiththesamenumberof dependentsandthesameincomelivingindifferent partsofthecountryshouldpaythesamefederal taxes.
 Table 7 Three Tax Systems Copyright© 2004 South-Western
Table 7 Three Tax Systems Copyright© 2004 South-Western
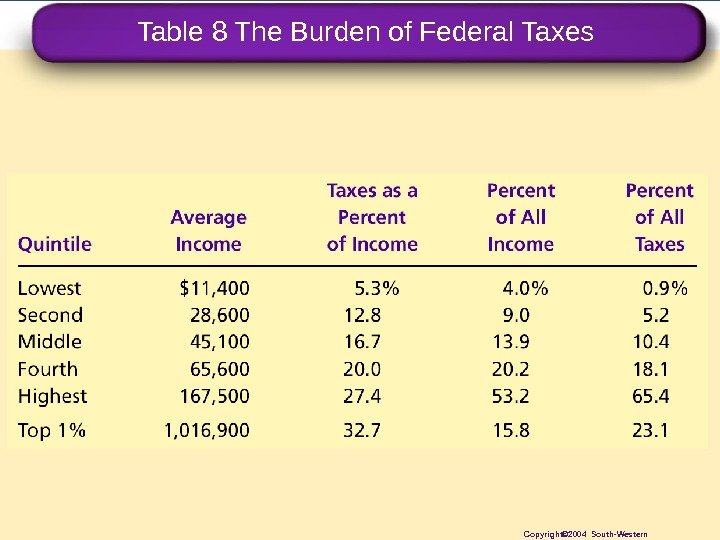
 Table 8 The Burden of Federal Taxes Copyright© 2004 South-Western
Table 8 The Burden of Federal Taxes Copyright© 2004 South-Western
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Федеральныеналогиисборы: Налогнадобавленнуюстоимость18 Акцизы Налогнадоходыфизическихлиц13 Соц. страховые взносы 22+2. 9+5. 1 Налогнаприбыльорганизаций 20 Налогнадобычуполезныхископаемых Водныйналог Сборызапользованиеобъектамиживотногомираиза пользованиеобъектамиводныхбиологическихресурсов Государственнаяпошлина
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Федеральныеналогиисборы: Налогнадобавленнуюстоимость18 Акцизы Налогнадоходыфизическихлиц13 Соц. страховые взносы 22+2. 9+5. 1 Налогнаприбыльорганизаций 20 Налогнадобычуполезныхископаемых Водныйналог Сборызапользованиеобъектамиживотногомираиза пользованиеобъектамиводныхбиологическихресурсов Государственнаяпошлина
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Региональныеналоги: Налогнаимуществоорганизаций Налогнаигорныйбизнес Транспортныйналог Местныеналоги: Земельныйналог Налогнаимуществофизическихлиц Специальныеналоговыережимы: Единыйсельскохозяйственныйналог—ЕСХН Упрощеннаясистеманалогообложения Единыйналогнавменённыйдоход Системаналогообложенияпривыполнениисоглашенийо разделепродукции
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Региональныеналоги: Налогнаимуществоорганизаций Налогнаигорныйбизнес Транспортныйналог Местныеналоги: Земельныйналог Налогнаимуществофизическихлиц Специальныеналоговыережимы: Единыйсельскохозяйственныйналог—ЕСХН Упрощеннаясистеманалогообложения Единыйналогнавменённыйдоход Системаналогообложенияпривыполнениисоглашенийо разделепродукции
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. CASE STUDY: Horizontal Equity and the Marriage Tax • Marriageaffectsthetaxliabilityofacouplein thattaxlawtreatsamarriedcoupleasasingle taxpayer. • Whenacouplegetsmarried, theystoppaying taxesasindividualsandstartpayingtaxesasa family. • Ifeachhasasimilarincome, theirtotaltax liabilityriseswhentheygetmarried.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. CASE STUDY: Horizontal Equity and the Marriage Tax • Marriageaffectsthetaxliabilityofacouplein thattaxlawtreatsamarriedcoupleasasingle taxpayer. • Whenacouplegetsmarried, theystoppaying taxesasindividualsandstartpayingtaxesasa family. • Ifeachhasasimilarincome, theirtotaltax liabilityriseswhentheygetmarried.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Tax Incidence and Tax Equity • Thedifficultyinformulatingtaxpolicyis balancingtheoftenconflictinggoalsof efficiency and equity. • Thestudyofwhobearstheburdenoftaxesis centraltoevaluatingtaxequity. • Thisstudyiscalled tax incidence.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Tax Incidence and Tax Equity • Thedifficultyinformulatingtaxpolicyis balancingtheoftenconflictinggoalsof efficiency and equity. • Thestudyofwhobearstheburdenoftaxesis centraltoevaluatingtaxequity. • Thisstudyiscalled tax incidence.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Tax Incidence and Tax Equity • Flypaper. Theoryof. Tax. Incidence • Accordingtothe flypaper theory , theburdenofa tax, likeaflyonflypaper, stickswhereveritfirst lands. • (thisiswrong, ofcourse)
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Tax Incidence and Tax Equity • Flypaper. Theoryof. Tax. Incidence • Accordingtothe flypaper theory , theburdenofa tax, likeaflyonflypaper, stickswhereveritfirst lands. • (thisiswrong, ofcourse)
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Summary • The. U. S. governmentraisesrevenueusing varioustaxes. • Incometaxesandpayrolltaxesraisethemost revenueforthefederalgovernment. • Salestaxesandpropertytaxesraisethemost revenueforthestateandlocalgovernments.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Summary • The. U. S. governmentraisesrevenueusing varioustaxes. • Incometaxesandpayrolltaxesraisethemost revenueforthefederalgovernment. • Salestaxesandpropertytaxesraisethemost revenueforthestateandlocalgovernments.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Summary • Equityandefficiencyarethetwomost importantgoalsofthetaxsystem. • Theefficiencyofataxsystemreferstothe costsitimposesonthetaxpayers. • Theequityofataxsystemconcernswhether thetaxburdenisdistributedfairlyamongthe population.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Summary • Equityandefficiencyarethetwomost importantgoalsofthetaxsystem. • Theefficiencyofataxsystemreferstothe costsitimposesonthetaxpayers. • Theequityofataxsystemconcernswhether thetaxburdenisdistributedfairlyamongthe population.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Summary • Accordingtothebenefitsprinciple, itisfairfor peopletopaytaxesbasedonthebenefitsthey receivefromthegovernment. • Accordingtotheability-to-payprinciple, itis fairforpeopletopaytaxesontheircapabilityto handlethefinancialburden.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Summary • Accordingtothebenefitsprinciple, itisfairfor peopletopaytaxesbasedonthebenefitsthey receivefromthegovernment. • Accordingtotheability-to-payprinciple, itis fairforpeopletopaytaxesontheircapabilityto handlethefinancialburden.
 Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Summary • Thedistributionoftaxburdensisnotthesame asthedistributionoftaxbills. • Muchofthedebateovertaxpolicyarises becausepeoplegivedifferentweightstothe twogoalsofefficiencyandequity.
Copyright © 2004 South-Western/Thomson Learning. Summary • Thedistributionoftaxburdensisnotthesame asthedistributionoftaxbills. • Muchofthedebateovertaxpolicyarises becausepeoplegivedifferentweightstothe twogoalsofefficiencyandequity.

