26820fa4c0652906da6b193e6a1aca80.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Cooperative Strategy Week 8 1
Cooperative Strategy Week 8 1
 Outline § § § Types of cooperative strategies Reasons firms develop strategic alliances Business level cooperative strategies Corporate level cooperative strategies International cooperative strategies Network cooperative strategies 2
Outline § § § Types of cooperative strategies Reasons firms develop strategic alliances Business level cooperative strategies Corporate level cooperative strategies International cooperative strategies Network cooperative strategies 2
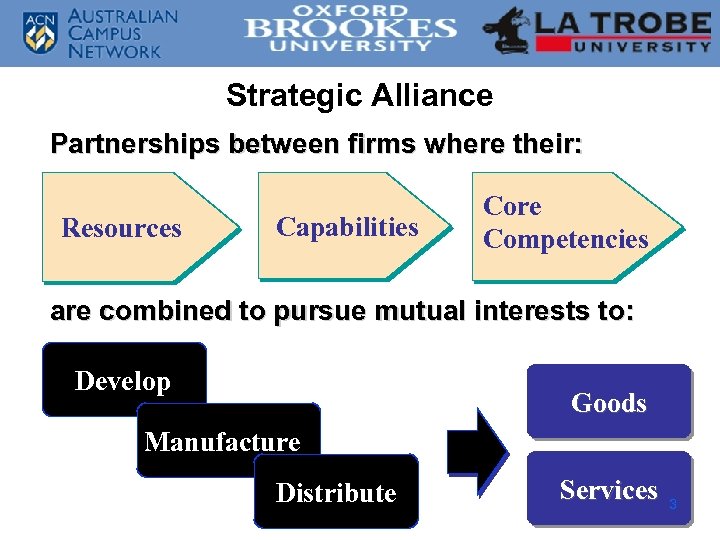 Strategic Alliance Partnerships between firms where their: Resources Capabilities Core Competencies are combined to pursue mutual interests to: Develop Goods Manufacture Distribute Services 3
Strategic Alliance Partnerships between firms where their: Resources Capabilities Core Competencies are combined to pursue mutual interests to: Develop Goods Manufacture Distribute Services 3
 Strategic Alliance § The primary cooperative strategy § Explicit forms of relationships between firms § Joint venture § Equity strategic alliance § Non-equity strategic alliance § Implicit forms § Tacit collusion § Mutual forebearance 4
Strategic Alliance § The primary cooperative strategy § Explicit forms of relationships between firms § Joint venture § Equity strategic alliance § Non-equity strategic alliance § Implicit forms § Tacit collusion § Mutual forebearance 4
 Forms of Strategic Alliance § Joint venture An independent firm is created by joining the assets of two separate firms, where each contributes 50% of the total § Equity strategic alliance A partnership where the two partners do not own equal shares § Non-equity strategic alliance § A contract is given to supply, produce or distribute a firm’s goods or services (without equity sharing) § Includes licensing, distribution agreements, supply contracts 5
Forms of Strategic Alliance § Joint venture An independent firm is created by joining the assets of two separate firms, where each contributes 50% of the total § Equity strategic alliance A partnership where the two partners do not own equal shares § Non-equity strategic alliance § A contract is given to supply, produce or distribute a firm’s goods or services (without equity sharing) § Includes licensing, distribution agreements, supply contracts 5
 Implicit Cooperative Strategies § Tacit collusion** Tacit cooperation between firms to reduce industry output below potential competitive level to maintain higher prices § Mutual forbearance** Recognition of interdependence **Illegal, unless regulated by the government 6
Implicit Cooperative Strategies § Tacit collusion** Tacit cooperation between firms to reduce industry output below potential competitive level to maintain higher prices § Mutual forbearance** Recognition of interdependence **Illegal, unless regulated by the government 6
 Types of Market § Slow Cycle § Standard Cycle § Fast Cycle 7
Types of Market § Slow Cycle § Standard Cycle § Fast Cycle 7
 Slow Cycle Markets that are sheltered or are near monopolies. § These are often used in emerging markets with restricted entry. § Cooperation is often designed to develop standards. § Government regulation generally is present to avoid price discrimination. 8
Slow Cycle Markets that are sheltered or are near monopolies. § These are often used in emerging markets with restricted entry. § Cooperation is often designed to develop standards. § Government regulation generally is present to avoid price discrimination. 8
 Standard-Cycle Markets § Are often large and oriented toward economies of scale § Alliances are more likely to be between partners with complementary resources, capabilities, and core competencies. 9
Standard-Cycle Markets § Are often large and oriented toward economies of scale § Alliances are more likely to be between partners with complementary resources, capabilities, and core competencies. 9
 Fast-Cycle Markets § Fast-cycle markets are entrepreneurial and dynamic, with new products or services imitated rapidly. 10
Fast-Cycle Markets § Fast-cycle markets are entrepreneurial and dynamic, with new products or services imitated rapidly. 10
 Reasons for Strategic Alliances In Slow-cycle markets: § Gaining access to a market that is not open to other entry strategies § Establishing a franchise in a new market § Maintaining market stability 11
Reasons for Strategic Alliances In Slow-cycle markets: § Gaining access to a market that is not open to other entry strategies § Establishing a franchise in a new market § Maintaining market stability 11
 Reasons for Strategic Alliances In Standard-cycle markets: § Gaining market power § Gaining access to complementary resources § Overcoming trade barriers § Meeting competitive challenges from other competitors § Pooling resources for very large capital projects § Learning new business techniques 12
Reasons for Strategic Alliances In Standard-cycle markets: § Gaining market power § Gaining access to complementary resources § Overcoming trade barriers § Meeting competitive challenges from other competitors § Pooling resources for very large capital projects § Learning new business techniques 12
 Reasons for Strategic Alliances In Fast cycle markets: § Speeding up the development of goods/services § Speeding up new market entry § Maintaining market leadership § Forming an industry technology standard § Sharing risky R&D expenses § Overcoming uncertainty 13
Reasons for Strategic Alliances In Fast cycle markets: § Speeding up the development of goods/services § Speeding up new market entry § Maintaining market leadership § Forming an industry technology standard § Sharing risky R&D expenses § Overcoming uncertainty 13
 Types of Strategic Alliance Complementary Alliances Business. Level Competition-Reduction Alliances Competition-Response Alliances Uncertainty-Reduction Alliances Diversification Alliances Corporate - Level Synergistic Alliances Franchising 14
Types of Strategic Alliance Complementary Alliances Business. Level Competition-Reduction Alliances Competition-Response Alliances Uncertainty-Reduction Alliances Diversification Alliances Corporate - Level Synergistic Alliances Franchising 14
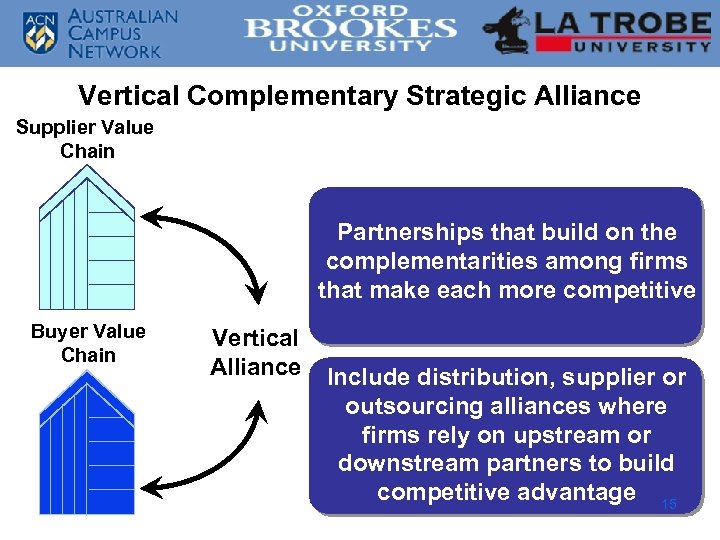 Vertical Complementary Strategic Alliance Supplier Value Chain Partnerships that build on the complementarities among firms that make each more competitive Buyer Value Chain Vertical Alliance Include distribution, supplier or outsourcing alliances where firms rely on upstream or downstream partners to build competitive advantage 15
Vertical Complementary Strategic Alliance Supplier Value Chain Partnerships that build on the complementarities among firms that make each more competitive Buyer Value Chain Vertical Alliance Include distribution, supplier or outsourcing alliances where firms rely on upstream or downstream partners to build competitive advantage 15
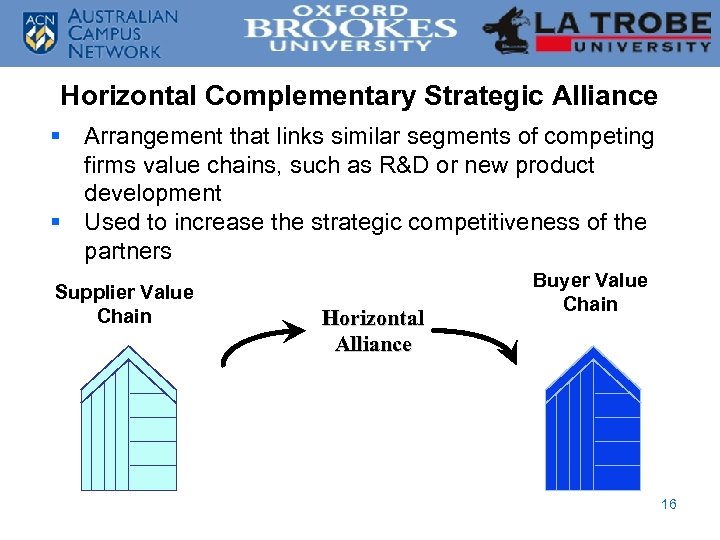 Horizontal Complementary Strategic Alliance § Arrangement that links similar segments of competing firms value chains, such as R&D or new product development § Used to increase the strategic competitiveness of the partners Supplier Value Chain Horizontal Alliance Buyer Value Chain 16
Horizontal Complementary Strategic Alliance § Arrangement that links similar segments of competing firms value chains, such as R&D or new product development § Used to increase the strategic competitiveness of the partners Supplier Value Chain Horizontal Alliance Buyer Value Chain 16
 Competition Reduction Strategies § Avoiding competition by using tacit collusion such as price fixing § Cartels such as OPEC, manufacturing and distribution cartels in Japan, industry trade organisations 17
Competition Reduction Strategies § Avoiding competition by using tacit collusion such as price fixing § Cartels such as OPEC, manufacturing and distribution cartels in Japan, industry trade organisations 17
 Competition Response Strategies § Established to enable partner firms to respond to major strategic actions initiated by their competitors 18
Competition Response Strategies § Established to enable partner firms to respond to major strategic actions initiated by their competitors 18
 Uncertainty Reduction Strategies § Alliances can be used to hedge against risk and uncertainty § Used particularly in fast cycle markets 19
Uncertainty Reduction Strategies § Alliances can be used to hedge against risk and uncertainty § Used particularly in fast cycle markets 19
 Competitive advantage? § Alliances to reduce competition are only likely to achieve average returns § Complementary alliances (especially vertical) are more likely to create competitive advantage when they lead to combined complementary resources that reduce costs or create competitive advantage. § Uncertainty reducing strategies historically resulted in competitive parity and average returns 20
Competitive advantage? § Alliances to reduce competition are only likely to achieve average returns § Complementary alliances (especially vertical) are more likely to create competitive advantage when they lead to combined complementary resources that reduce costs or create competitive advantage. § Uncertainty reducing strategies historically resulted in competitive parity and average returns 20
 Corporate level cooperative strategies Designed to facilitate product and market diversification § Diversifying § Synergistic § franchising 21
Corporate level cooperative strategies Designed to facilitate product and market diversification § Diversifying § Synergistic § franchising 21
 Synergistic Strategic Alliances § Create joint economies of scope § Are similar to horizontal acquisitions at the business level § Create synergy across multiple functions 22
Synergistic Strategic Alliances § Create joint economies of scope § Are similar to horizontal acquisitions at the business level § Create synergy across multiple functions 22
 Franchising § Cooperative strategy to spread risk and use resources, capabilities and competencies productively without merging with or acquiring another company. § Allows firms to grow and enables relatively strong centralised control without significant capital investment 23
Franchising § Cooperative strategy to spread risk and use resources, capabilities and competencies productively without merging with or acquiring another company. § Allows firms to grow and enables relatively strong centralised control without significant capital investment 23
 Franchising § Spreads risk and shares resources (including knowledge) § In Australia, about 25% of retail volume comes from franchised operations, while in the USA this figure is around 40% § The future of new business is likely to be franchising because of the associated efficiencies § An interesting corollary is the spread of national culture: Mc. Donalds, for example, provides a powerful cultural message 24
Franchising § Spreads risk and shares resources (including knowledge) § In Australia, about 25% of retail volume comes from franchised operations, while in the USA this figure is around 40% § The future of new business is likely to be franchising because of the associated efficiencies § An interesting corollary is the spread of national culture: Mc. Donalds, for example, provides a powerful cultural message 24
 International Cooperative Strategies § May create more value than if the business operated as a separate entity § Growth when these opportunities are limited within the firms home nation § Allows risk sharing by reducing financial investment § Host partner knows local market and customs 25
International Cooperative Strategies § May create more value than if the business operated as a separate entity § Growth when these opportunities are limited within the firms home nation § Allows risk sharing by reducing financial investment § Host partner knows local market and customs 25
 But. . § More complex and risky than domestic alliances § More likely to fail § Difficult to manage due to differences in management styles, cultures or regulatory constraints § Require significant processing of information to enhance partners ability to cooperate § Must gauge partner’s strategic intent so they do not gain access to important technology and become a competitor 26
But. . § More complex and risky than domestic alliances § More likely to fail § Difficult to manage due to differences in management styles, cultures or regulatory constraints § Require significant processing of information to enhance partners ability to cooperate § Must gauge partner’s strategic intent so they do not gain access to important technology and become a competitor 26
 Network Strategies § Network strategies involve a group of interrelated firms that work for the common good of all § Three types § Stable § Dynamic § Internal 27
Network Strategies § Network strategies involve a group of interrelated firms that work for the common good of all § Three types § Stable § Dynamic § Internal 27
 Network Strategies § Stable Long-term relationships that often appear in mature industries with largely predictable market cycles § Dynamic Arrangements that evolve in industries experiencing rapid technological change leading to short product life-cycles § Internal A management system used to coordinate a global web of suppliers and customers 28
Network Strategies § Stable Long-term relationships that often appear in mature industries with largely predictable market cycles § Dynamic Arrangements that evolve in industries experiencing rapid technological change leading to short product life-cycles § Internal A management system used to coordinate a global web of suppliers and customers 28
 Cooperative Buying Online § New technology facilitates cooperative strategies: for example, on-line buying and computer networking means cooperation to buy goods is easier § Fourteen of Australia’s largest companies are in a cooperative-buying operation: the buying power they achieve lowers prices 29
Cooperative Buying Online § New technology facilitates cooperative strategies: for example, on-line buying and computer networking means cooperation to buy goods is easier § Fourteen of Australia’s largest companies are in a cooperative-buying operation: the buying power they achieve lowers prices 29
 Competitive Risks § Inadequate contracts § Misrepresentation of competencies § Partners failing to make complementary resources available § Being held hostage through specific investments made with a partner § Misunderstanding a partner’s strategic intent 30
Competitive Risks § Inadequate contracts § Misrepresentation of competencies § Partners failing to make complementary resources available § Being held hostage through specific investments made with a partner § Misunderstanding a partner’s strategic intent 30
 Managing Competitive Risks can be managed § Detailed contracts, but § Costly § May prevent from taking opportunities § Monitoring § Developing trusting relationships 31
Managing Competitive Risks can be managed § Detailed contracts, but § Costly § May prevent from taking opportunities § Monitoring § Developing trusting relationships 31
 Managing Competitive Risks * Inadequate contracts * Misrepresentation of competencies * Partner fails to use complementary resources * Holding alliance partner’s specific investments hostage Risk and Asset Management Approaches * Detailed contracts and monitoring * Developing trusting relationships Outcome Value Creation 32
Managing Competitive Risks * Inadequate contracts * Misrepresentation of competencies * Partner fails to use complementary resources * Holding alliance partner’s specific investments hostage Risk and Asset Management Approaches * Detailed contracts and monitoring * Developing trusting relationships Outcome Value Creation 32
 Trust as a Strategic Asset § Creates confidence § More predictable partner actions § Less resources to monitor and control the alliance § Valuable, rare, imperfectly imitable and often non -substitutable 33
Trust as a Strategic Asset § Creates confidence § More predictable partner actions § Less resources to monitor and control the alliance § Valuable, rare, imperfectly imitable and often non -substitutable 33
 Managing Alliances: Strategic approaches § Cost-minimisation § Value creation maximisation 34
Managing Alliances: Strategic approaches § Cost-minimisation § Value creation maximisation 34
 Cost Minimisation Cost minimisation requires: § Capabilities to create effective partner contracts § Contract monitoring capabilities 35
Cost Minimisation Cost minimisation requires: § Capabilities to create effective partner contracts § Contract monitoring capabilities 35
 Value-maximisation § Partners with complementary assets § Emphasises trust 36
Value-maximisation § Partners with complementary assets § Emphasises trust 36


