fd5dfe77ca82c4457f419260747e98b8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Cooley, Mead, Freud, Erikson and Levinson Behind the Theories on Development

Charles Cooley (1864 -1929)

Cooley He said that the self develops through process of social interaction

Cooley Influenced by family primarily, then later peergroups.

Cooley Used the analogy of a Looking-Glass (mirror) to describe the 3 stage process of self

Cooley 1. We imagine how our actions appear to others 2. We imagine how others judge our actions 3. We make some sort of self-judgment based on 1& 2

George Herbert Mead (1863 -1931)

Mead He traced people’s awareness of self to primary caregiver

Mead He said the self is composed of 2 parts“I” and “Me”

Mead I like Mead! Very Much!!! The “I” portion wishes to have self expression, to be active and spontaneous

Mead • The “Me” portion is made up of the things learned through the socialization process. The “Me” makes normal social interaction possible


Mead He said the self develops in 3 stages

Mead • Preparatory stage-child imitates others

Mead • Play stage-child has acquired language and not only imitates, but form role expectations: playing house, cops and robbers.

Mead o Game stage-child learns there are rules that specify the correct and proper relationship among the players. o We learn the expectations of various positions which we interact as well as the expectations of the general audience

Sigmund Freud (1856 -1939)

Freud • He said the self has 3 separately functioning parts, in which the individual is constantly at struggle.

Freud Id-the drives and instincts that every human inherits, mostly remain unconscious

Freud • Superego-society’s norms and expectations, primarily learned from parents

Freud • Ego-mediates the eternal conflict of the id and superego, also finds socially acceptable ways to express id’s drives.

Erikson (1902 -1994)

Erikson Human development is accomplished in 8 stages

Erikson 1. Trust vs. Mistrust (up to 1 year) 2. Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt (1 -4) 3. Initiative vs. guilt (4 -5) 4. Industry vs. Inferiority (6 -12) 5. Identity vs. role confusion (adolescence) 6. Intimacy vs. isolation (young adulthood) 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation (30’s to 50’s) 8. Integrity vs. Despair (old age)

No Pictures!!!! Daniel Levinson (1920 -1994)

Levinson • He focused on adult development-said there were 6 stages

Levinson Early adult period 18 -22 Leave adolescence, make preliminary choices for life Leave the family of origin

Levinson Getting into adult world 22 -28 “form a dream” Make initial choices in love, occupation, friendship, love and values

Levinson However, I have no flaws! • Age 30 transitional periodseeks to correct flaws • Changes in life occur

• Settling down-has reworked flaws and seeks order and stability Levinson

Levinson Age 40 transitional period-mid-life crisis

Levinson • Beginning of middle adulthood-mid 40’s • Reflect on life’s accomplishments
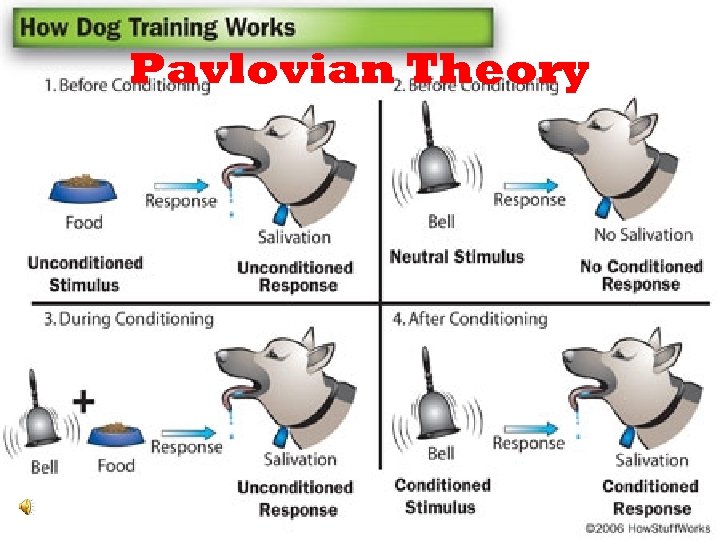
Pavlovian Theory


That’s All Folks!!
fd5dfe77ca82c4457f419260747e98b8.ppt