7b4de51599efe5bc933e4117f857996f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Convert generic g. USE Portal into a science gateway Akos Balasko
Convert generic g. USE Portal into a science gateway Akos Balasko
 Outline – General Session: Goal Terminology – Basic Idea – Concept of ASM ● ● ● Hands-On 2
Outline – General Session: Goal Terminology – Basic Idea – Concept of ASM ● ● ● Hands-On 2
 Goal Community members want to: Execute scientific applications Using distributed systems to: • • decrease time cost Exploit storage & computational capacities use complex systems totally hidden Do not want to : learn any techniques that don't fit with scientific area of them → would like to use web-interfaces based on g. USE
Goal Community members want to: Execute scientific applications Using distributed systems to: • • decrease time cost Exploit storage & computational capacities use complex systems totally hidden Do not want to : learn any techniques that don't fit with scientific area of them → would like to use web-interfaces based on g. USE
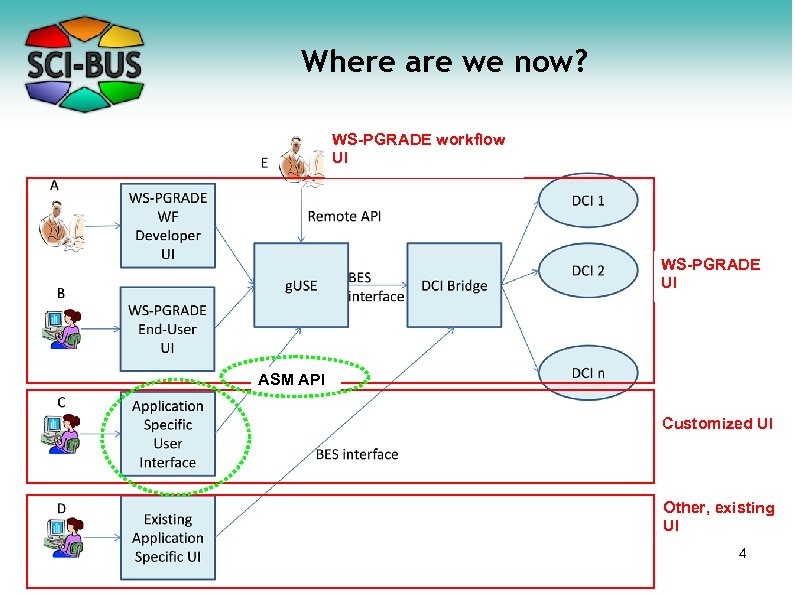 Where are we now? WS-PGRADE workflow UI WS-PGRADE UI ASM API Customized UI Other, existing UI 4
Where are we now? WS-PGRADE workflow UI WS-PGRADE UI ASM API Customized UI Other, existing UI 4
 Terminology Grid Application Developer – would like to have a Portal customized for the application and end user community – knows how to develop a grid application in g. USE/ws-PGrade or how to port a legacy application to the grid with g. USE/ws. PGrade Grid Portal Developer – He knows the Java language and JSP (Java Server Pages) or other techniques (Ice. Faces etc) – He does not need to know the source code of g. USE – He and also the end users have user certificates to access the grid
Terminology Grid Application Developer – would like to have a Portal customized for the application and end user community – knows how to develop a grid application in g. USE/ws-PGrade or how to port a legacy application to the grid with g. USE/ws. PGrade Grid Portal Developer – He knows the Java language and JSP (Java Server Pages) or other techniques (Ice. Faces etc) – He does not need to know the source code of g. USE – He and also the end users have user certificates to access the grid
 Terminology Grid Application Developer • Develops a grid application with g. USE • Exports it to the local repository of g. USE Grid Portal Developer • Develops an interface (in general a portlet) that fits to the application I/O pattern and the end users’ needs and associate it with the role • Connects the GUI to g. USE using the programming API of Application Specific Module(ASM) End Users, Scientists • execute a copy of the exported application with custom input parameters
Terminology Grid Application Developer • Develops a grid application with g. USE • Exports it to the local repository of g. USE Grid Portal Developer • Develops an interface (in general a portlet) that fits to the application I/O pattern and the end users’ needs and associate it with the role • Connects the GUI to g. USE using the programming API of Application Specific Module(ASM) End Users, Scientists • execute a copy of the exported application with custom input parameters
 Basic idea • A new module called “Application Specific Module” has been developed for g. USE that ease the creation of Application Specified Portlets – The module provides programming API to control applications developed using g. USE – The module provides programming API to access inner g. USE services • Any kind of Graphical interface can be developed on top of this module – GUI written in JSP, JSTL (Java Servlet Tag Library ) and Java – GUI can be customized for the grid application – GUI can be customized for end users
Basic idea • A new module called “Application Specific Module” has been developed for g. USE that ease the creation of Application Specified Portlets – The module provides programming API to control applications developed using g. USE – The module provides programming API to access inner g. USE services • Any kind of Graphical interface can be developed on top of this module – GUI written in JSP, JSTL (Java Servlet Tag Library ) and Java – GUI can be customized for the grid application – GUI can be customized for end users
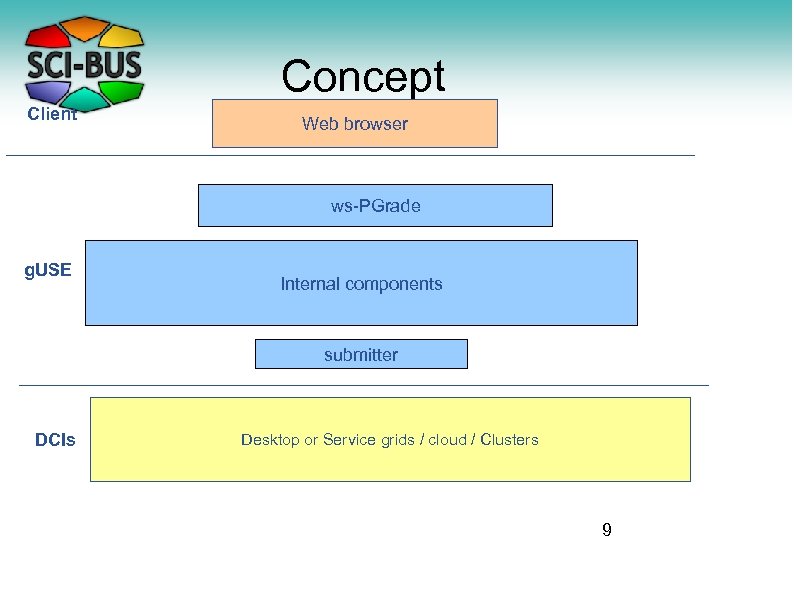 Concept Client Web browser ws-PGrade g. USE Internal components submitter DCIs Desktop or Service grids / cloud / Clusters 9
Concept Client Web browser ws-PGrade g. USE Internal components submitter DCIs Desktop or Service grids / cloud / Clusters 9
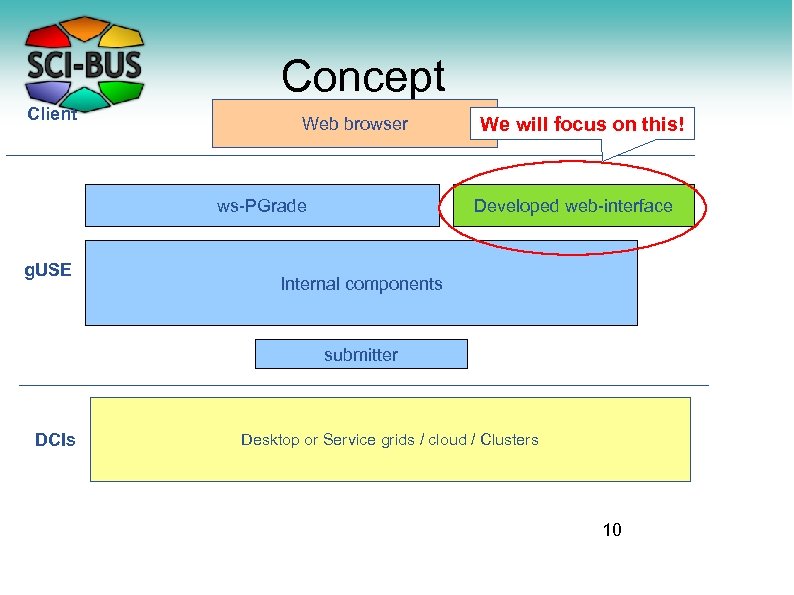 Concept Client Web browser ws-PGrade g. USE We will focus on this! Developed web-interface Internal components submitter DCIs Desktop or Service grids / cloud / Clusters 10
Concept Client Web browser ws-PGrade g. USE We will focus on this! Developed web-interface Internal components submitter DCIs Desktop or Service grids / cloud / Clusters 10
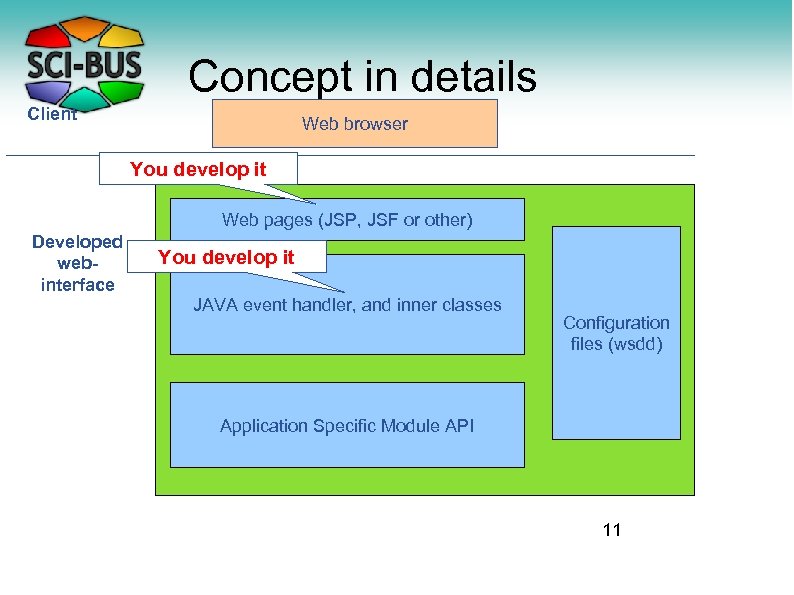 Concept in details Client Web browser You develop it Web pages (JSP, JSF or other) Developed webinterface You develop it JAVA event handler, and inner classes Configuration files (wsdd) Application Specific Module API 11
Concept in details Client Web browser You develop it Web pages (JSP, JSF or other) Developed webinterface You develop it JAVA event handler, and inner classes Configuration files (wsdd) Application Specific Module API 11
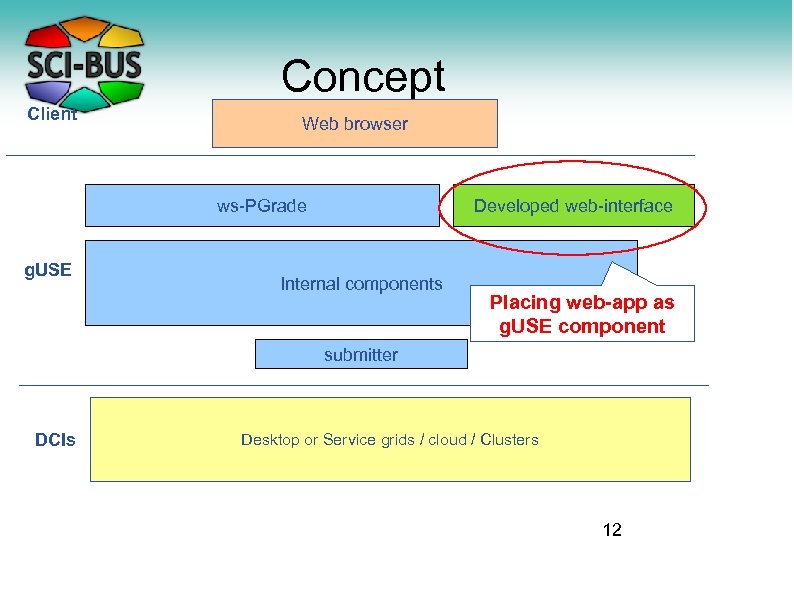 Concept Client Web browser ws-PGrade g. USE Developed web-interface Internal components Placing web-app as g. USE component submitter DCIs Desktop or Service grids / cloud / Clusters 12
Concept Client Web browser ws-PGrade g. USE Developed web-interface Internal components Placing web-app as g. USE component submitter DCIs Desktop or Service grids / cloud / Clusters 12
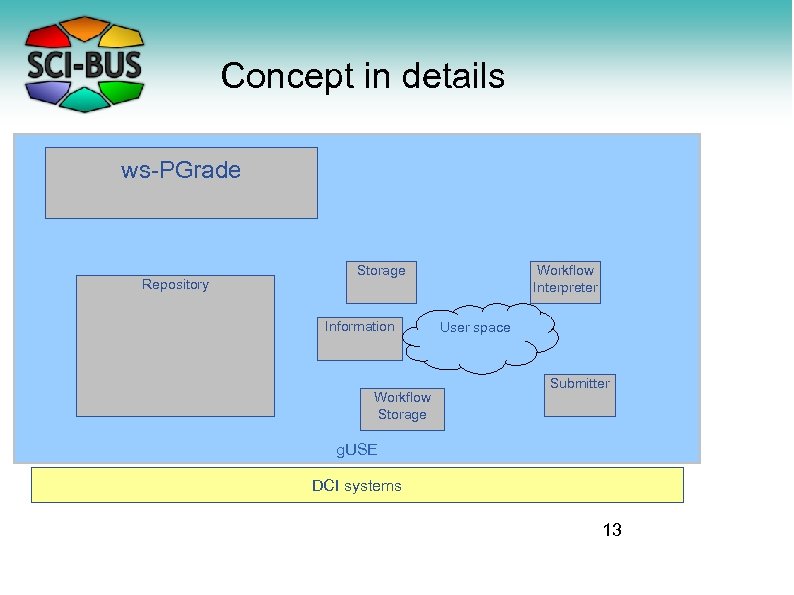 Concept in details ws-PGrade Repository Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE DCI systems 13
Concept in details ws-PGrade Repository Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE DCI systems 13
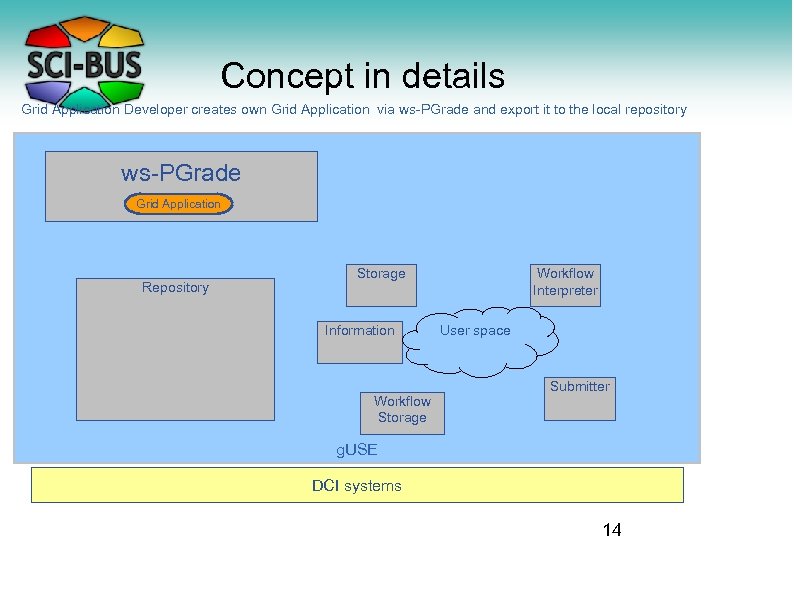 Concept in details Grid Application Developer creates own Grid Application via ws-PGrade and export it to the local repository ws-PGrade Grid Application Repository Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE DCI systems 14
Concept in details Grid Application Developer creates own Grid Application via ws-PGrade and export it to the local repository ws-PGrade Grid Application Repository Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE DCI systems 14
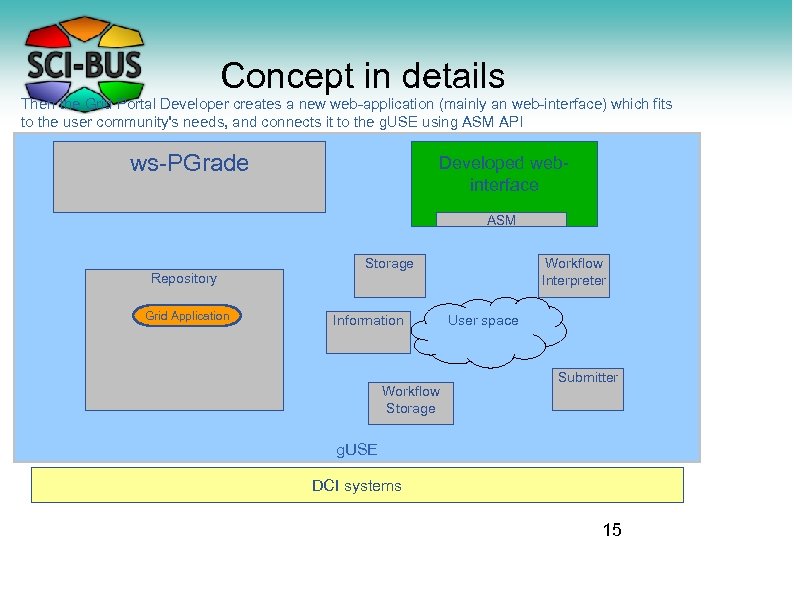 Concept in details Then the Grid Portal Developer creates a new web-application (mainly an web-interface) which fits to the user community's needs, and connects it to the g. USE using ASM API ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM Repository Grid Application Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE DCI systems 15
Concept in details Then the Grid Portal Developer creates a new web-application (mainly an web-interface) which fits to the user community's needs, and connects it to the g. USE using ASM API ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM Repository Grid Application Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE DCI systems 15
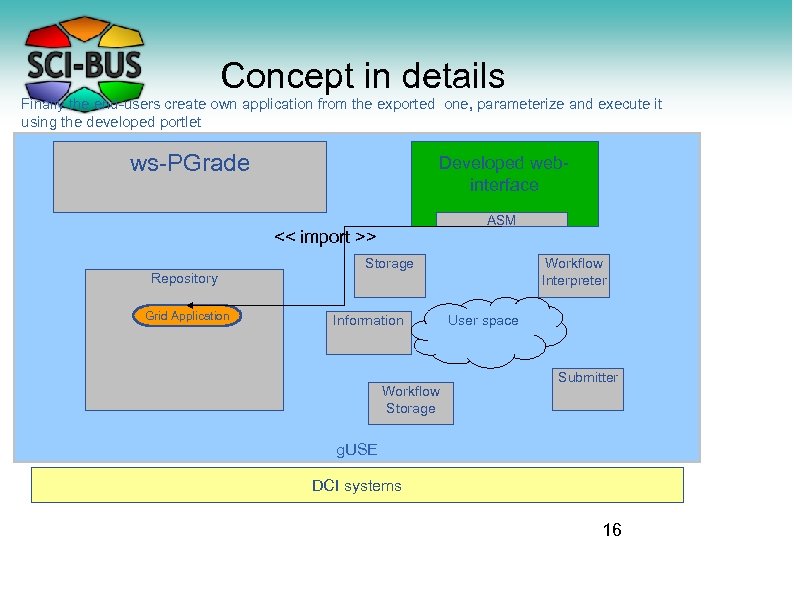 Concept in details Finally the end-users create own application from the exported one, parameterize and execute it using the developed portlet ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM << import >> Repository Grid Application Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE DCI systems 16
Concept in details Finally the end-users create own application from the exported one, parameterize and execute it using the developed portlet ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM << import >> Repository Grid Application Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE DCI systems 16
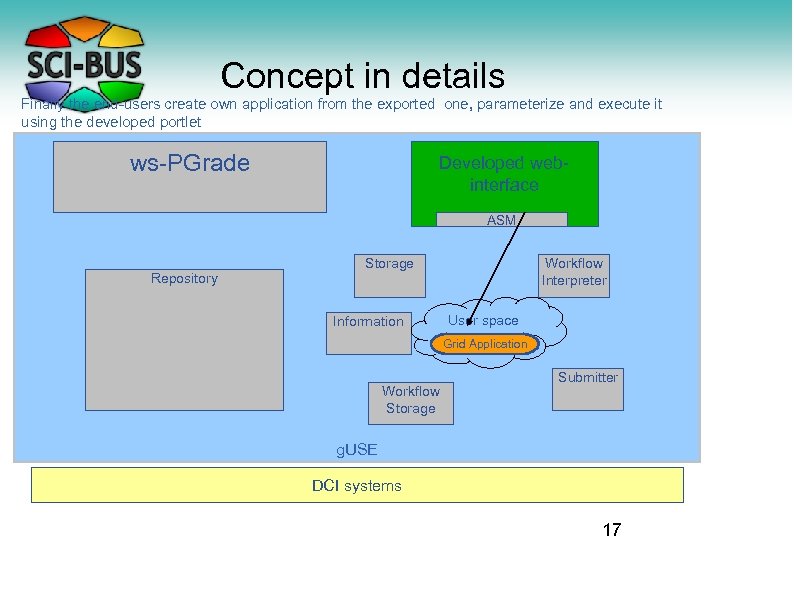 Concept in details Finally the end-users create own application from the exported one, parameterize and execute it using the developed portlet ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM Repository Storage Information Workflow Interpreter User space Grid Application Workflow Storage Submitter g. USE DCI systems 17
Concept in details Finally the end-users create own application from the exported one, parameterize and execute it using the developed portlet ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM Repository Storage Information Workflow Interpreter User space Grid Application Workflow Storage Submitter g. USE DCI systems 17
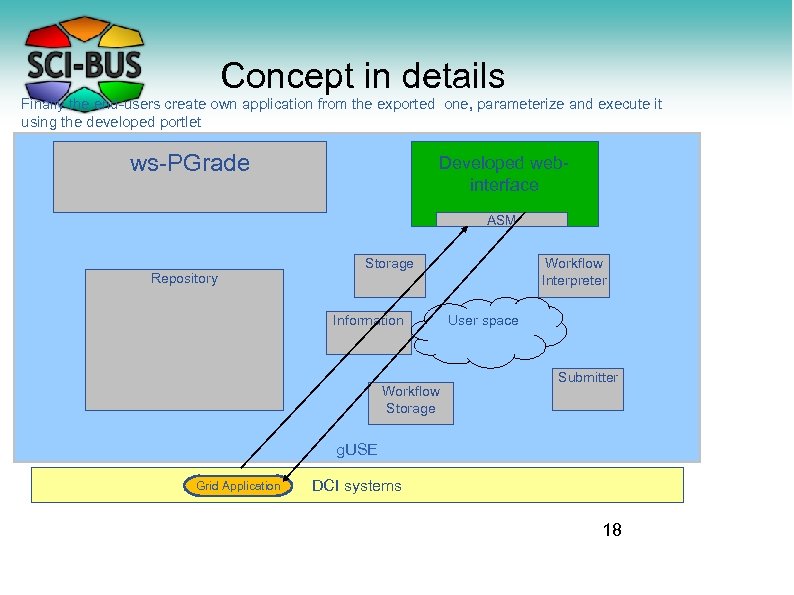 Concept in details Finally the end-users create own application from the exported one, parameterize and execute it using the developed portlet ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM Repository Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE Grid Application DCI systems 18
Concept in details Finally the end-users create own application from the exported one, parameterize and execute it using the developed portlet ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM Repository Storage Information Workflow Storage Workflow Interpreter User space Submitter g. USE Grid Application DCI systems 18
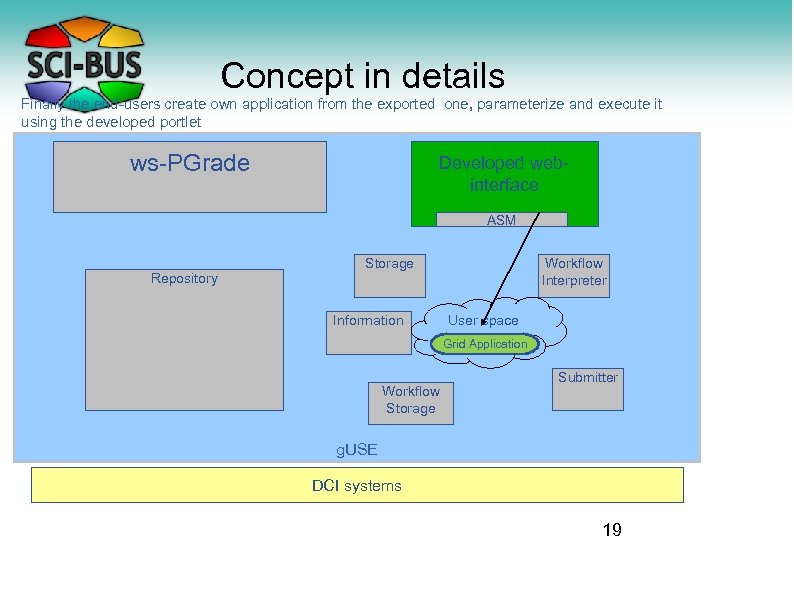 Concept in details Finally the end-users create own application from the exported one, parameterize and execute it using the developed portlet ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM Repository Storage Information Workflow Interpreter User space Grid Application Workflow Storage Submitter g. USE DCI systems 19
Concept in details Finally the end-users create own application from the exported one, parameterize and execute it using the developed portlet ws-PGrade Developed webinterface ASM Repository Storage Information Workflow Interpreter User space Grid Application Workflow Storage Submitter g. USE DCI systems 19
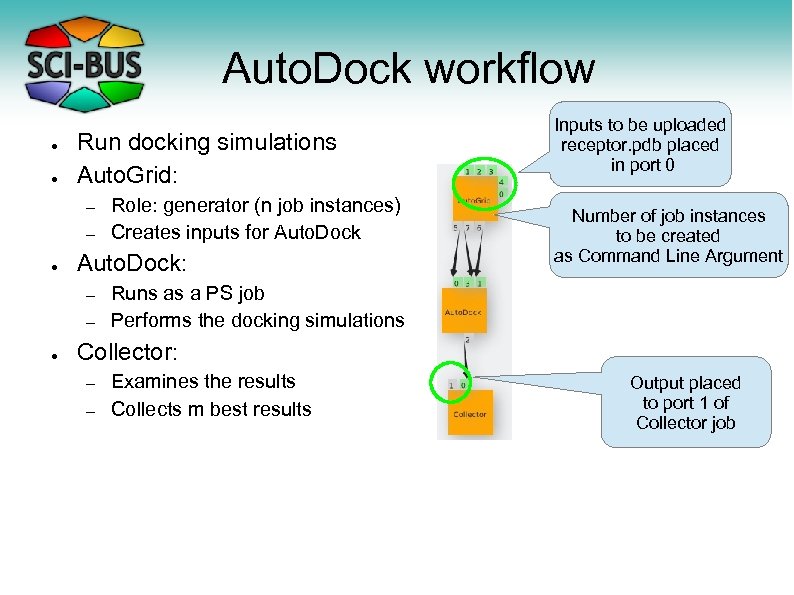 Auto. Dock workflow ● ● Run docking simulations Auto. Grid: – – ● Auto. Dock: – – ● Role: generator (n job instances) Creates inputs for Auto. Dock Inputs to be uploaded receptor. pdb placed in port 0 Number of job instances to be created as Command Line Argument Runs as a PS job Performs the docking simulations Collector: – – Examines the results Collects m best results Output placed to port 1 of Collector job
Auto. Dock workflow ● ● Run docking simulations Auto. Grid: – – ● Auto. Dock: – – ● Role: generator (n job instances) Creates inputs for Auto. Dock Inputs to be uploaded receptor. pdb placed in port 0 Number of job instances to be created as Command Line Argument Runs as a PS job Performs the docking simulations Collector: – – Examines the results Collects m best results Output placed to port 1 of Collector job
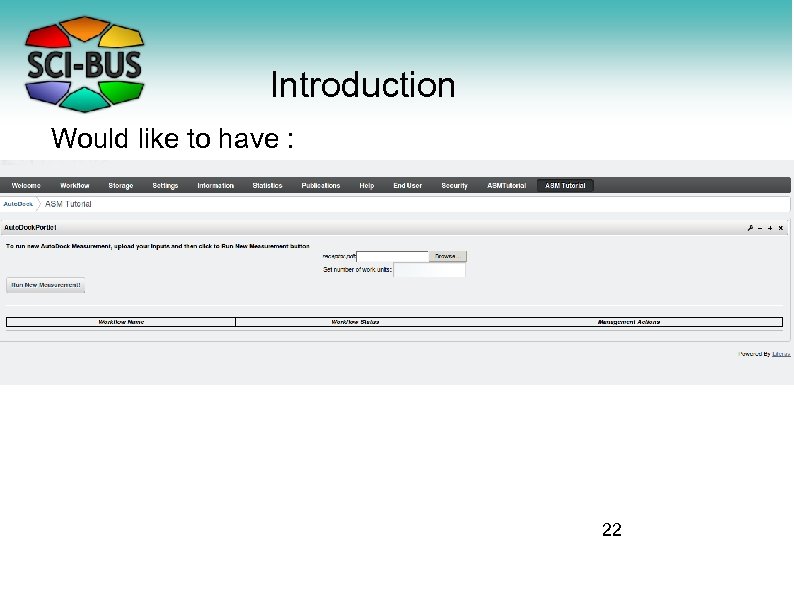 Introduction Would like to have : 22
Introduction Would like to have : 22
 Access to development framework ● Login to your cloud image: – – ● ssh -Y lpds@
Access to development framework ● Login to your cloud image: – – ● ssh -Y lpds@
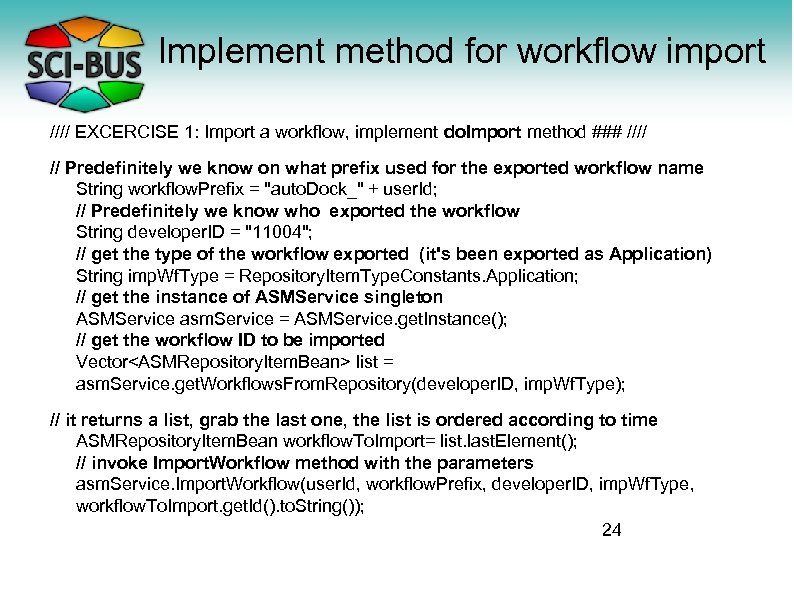 Implement method for workflow import //// EXCERCISE 1: Import a workflow, implement do. Import method ### //// // Predefinitely we know on what prefix used for the exported workflow name String workflow. Prefix = "auto. Dock_" + user. Id; // Predefinitely we know who exported the workflow String developer. ID = "11004"; // get the type of the workflow exported (it's been exported as Application) String imp. Wf. Type = Repository. Item. Type. Constants. Application; // get the instance of ASMService singleton ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); // get the workflow ID to be imported Vector
Implement method for workflow import //// EXCERCISE 1: Import a workflow, implement do. Import method ### //// // Predefinitely we know on what prefix used for the exported workflow name String workflow. Prefix = "auto. Dock_" + user. Id; // Predefinitely we know who exported the workflow String developer. ID = "11004"; // get the type of the workflow exported (it's been exported as Application) String imp. Wf. Type = Repository. Item. Type. Constants. Application; // get the instance of ASMService singleton ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); // get the workflow ID to be imported Vector
 Set command line argument //// ### EXCERCISE 2: Set command line arguments to the workflow ### //// // get ASMService instance ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); // get name of the job (its commandline arg. will be set) String job. Name = "Auto. Grid"; // invoke setcommand. Line. Arg method with the given parameters asm. Service. set. Command. Line. Arg(user. ID, workflow. Name, job. Name, work. Unit. Numb); 25
Set command line argument //// ### EXCERCISE 2: Set command line arguments to the workflow ### //// // get ASMService instance ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); // get name of the job (its commandline arg. will be set) String job. Name = "Auto. Grid"; // invoke setcommand. Line. Arg method with the given parameters asm. Service. set. Command. Line. Arg(user. ID, workflow. Name, job. Name, work. Unit. Numb); 25
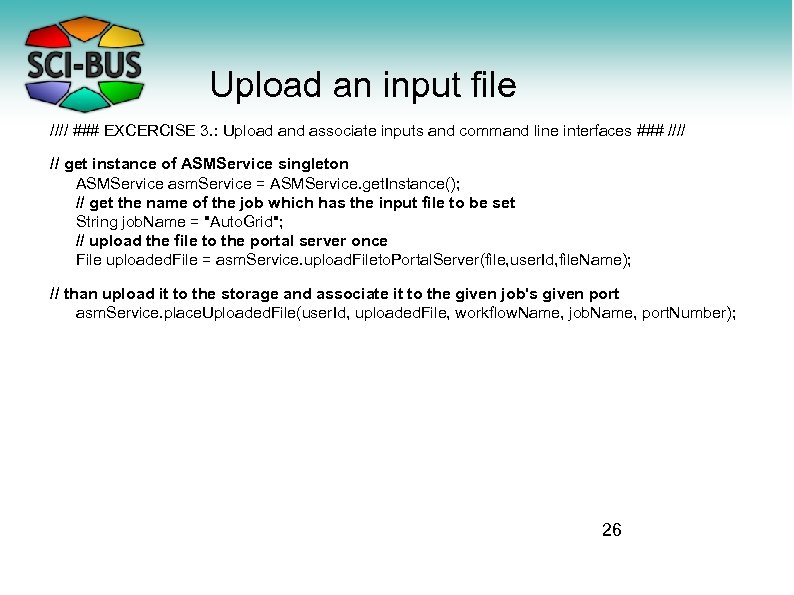 Upload an input file //// ### EXCERCISE 3. : Upload and associate inputs and command line interfaces ### //// // get instance of ASMService singleton ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); // get the name of the job which has the input file to be set String job. Name = "Auto. Grid"; // upload the file to the portal server once File uploaded. File = asm. Service. upload. Fileto. Portal. Server(file, user. Id, file. Name); // than upload it to the storage and associate it to the given job's given port asm. Service. place. Uploaded. File(user. Id, uploaded. File, workflow. Name, job. Name, port. Number); 26
Upload an input file //// ### EXCERCISE 3. : Upload and associate inputs and command line interfaces ### //// // get instance of ASMService singleton ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); // get the name of the job which has the input file to be set String job. Name = "Auto. Grid"; // upload the file to the portal server once File uploaded. File = asm. Service. upload. Fileto. Portal. Server(file, user. Id, file. Name); // than upload it to the storage and associate it to the given job's given port asm. Service. place. Uploaded. File(user. Id, uploaded. File, workflow. Name, job. Name, port. Number); 26
 Implement a method to submit a workflow Implement do. Submit method (can be found by searching for Excercise 4 in the code) try { // get user. ID from Action. Request object String user. ID = (String) request. get. Remote. User(); // get the ASMService instance ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); String workflow. Name = request. get. Parameter("selected. Workflow"); // notifytext and notify. Type can be added as empty strings. String notify. Text = ""; String notify. Type = ""; // invoke its submit function with the parameters asm. Service. submit(user. ID, workflow. Name, notify. Text, notify. Type); // catch all exceptions } catch (Class. Not. Found. Exception ex) { Logger. get. Logger(Auto. Dock. Portlet. class. get. Name()). log(Level. SEVERE, null, ex); } catch (Instantiation. Exception ex) { Logger. get. Logger(Auto. Dock. Portlet. class. get. Name()). log(Level. SEVERE, null, ex); } catch (Illegal. Access. Exception ex) { Logger. get. Logger(Auto. Dock. Portlet. class. get. Name()). log(Level. SEVERE, null, ex); 27 }
Implement a method to submit a workflow Implement do. Submit method (can be found by searching for Excercise 4 in the code) try { // get user. ID from Action. Request object String user. ID = (String) request. get. Remote. User(); // get the ASMService instance ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); String workflow. Name = request. get. Parameter("selected. Workflow"); // notifytext and notify. Type can be added as empty strings. String notify. Text = ""; String notify. Type = ""; // invoke its submit function with the parameters asm. Service. submit(user. ID, workflow. Name, notify. Text, notify. Type); // catch all exceptions } catch (Class. Not. Found. Exception ex) { Logger. get. Logger(Auto. Dock. Portlet. class. get. Name()). log(Level. SEVERE, null, ex); } catch (Instantiation. Exception ex) { Logger. get. Logger(Auto. Dock. Portlet. class. get. Name()). log(Level. SEVERE, null, ex); } catch (Illegal. Access. Exception ex) { Logger. get. Logger(Auto. Dock. Portlet. class. get. Name()). log(Level. SEVERE, null, ex); 27 }
 Implement a method to delete a workflow //// ### Excercise 5: Implement do. Delete method ### //// // get user. ID from Action. Request object String user. ID = (String) request. get. Remote. User(); // find and get the name of the selected workflow among the parameters String selected_wf = request. get. Parameter("selected. Workflow"); // get the instance of the ASMService Singleton ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); // invoke its Delete. Workflow method with the parameters asm. Service. Delete. Workflow(user. ID, selected_wf);
Implement a method to delete a workflow //// ### Excercise 5: Implement do. Delete method ### //// // get user. ID from Action. Request object String user. ID = (String) request. get. Remote. User(); // find and get the name of the selected workflow among the parameters String selected_wf = request. get. Parameter("selected. Workflow"); // get the instance of the ASMService Singleton ASMService asm. Service = ASMService. get. Instance(); // invoke its Delete. Workflow method with the parameters asm. Service. Delete. Workflow(user. ID, selected_wf);
 Deploy and execute → Deploy : Check and follow video → Restart the portal (needed if we add completely new component(e. g. ASM-based) to g. USE) – stop. sh – . /guse/apache-tomcat-6. 0. 35/bin/startup. sh Note: DO NOT use start. sh!! – Check starting logs: tailf. /guse/apache-tomcat 6. 0. 35/logs/catalina. out – Initialize the portal with the wizard. – The portlet will be shown under ASM Tutorial menuitem
Deploy and execute → Deploy : Check and follow video → Restart the portal (needed if we add completely new component(e. g. ASM-based) to g. USE) – stop. sh – . /guse/apache-tomcat-6. 0. 35/bin/startup. sh Note: DO NOT use start. sh!! – Check starting logs: tailf. /guse/apache-tomcat 6. 0. 35/logs/catalina. out – Initialize the portal with the wizard. – The portlet will be shown under ASM Tutorial menuitem
 End of Hands-On Thanks for your attention! Questions?
End of Hands-On Thanks for your attention! Questions?


