Lecture 3_Conventional representation.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 24

Conventional representation of the object’s elements THEME 3

Introduction Russian standards are established the special rules and requirement for universal representation of the common-features that are widely used in different details and parts of equipment for technical drawings. There are 1) threaded elements, 2) springs, 3) gears, 4) splined details

Threaded elements Thread is a surface manufactured by screw motion of plate shape on the cylindrical or conical surface. Bolt fastener joint Screw Stud-bolt Nut Jack screw Clamping screw Adapting pipe Tubing tee
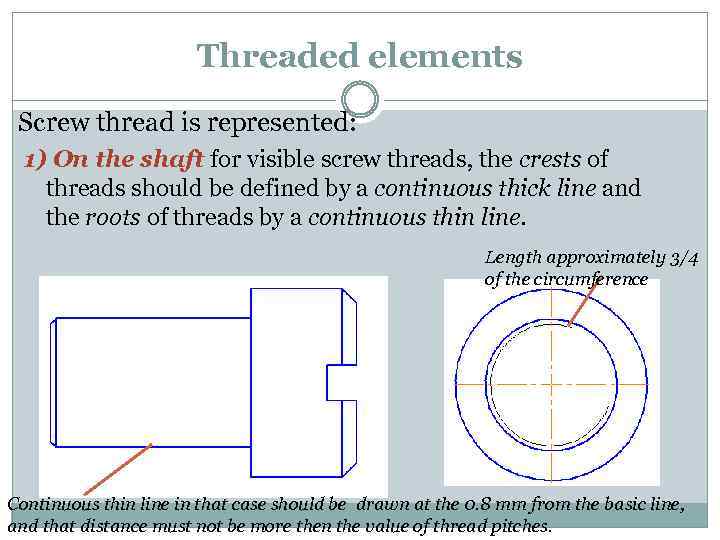
Threaded elements Screw thread is represented: 1) On the shaft for visible screw threads, the crests of threads should be defined by a continuous thick line and the roots of threads by a continuous thin line. Length approximately 3/4 of the circumference Continuous thin line in that case should be drawn at the 0. 8 mm from the basic line, and that distance must not be more then the value of thread pitches.
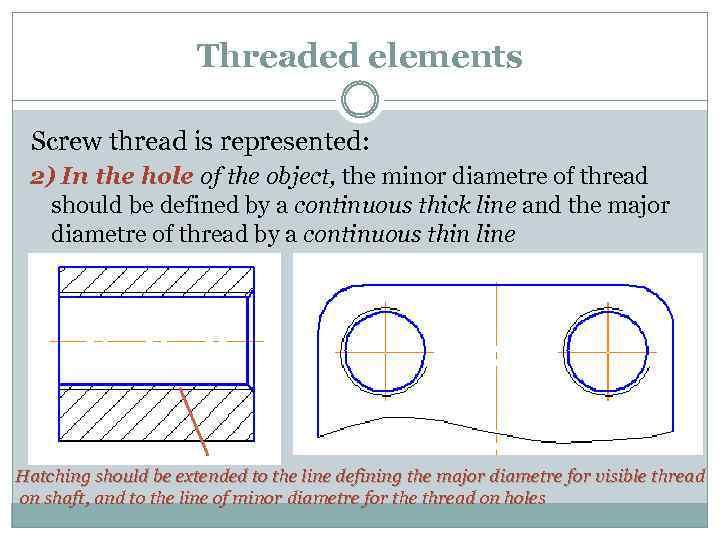
Threaded elements Screw thread is represented: 2) In the hole of the object, the minor diametre of thread should be defined by a continuous thick line and the major diametre of thread by a continuous thin line Hatching should be extended to the line defining the major diametre for visible thread on shaft, and to the line of minor diametre for the thread on holes
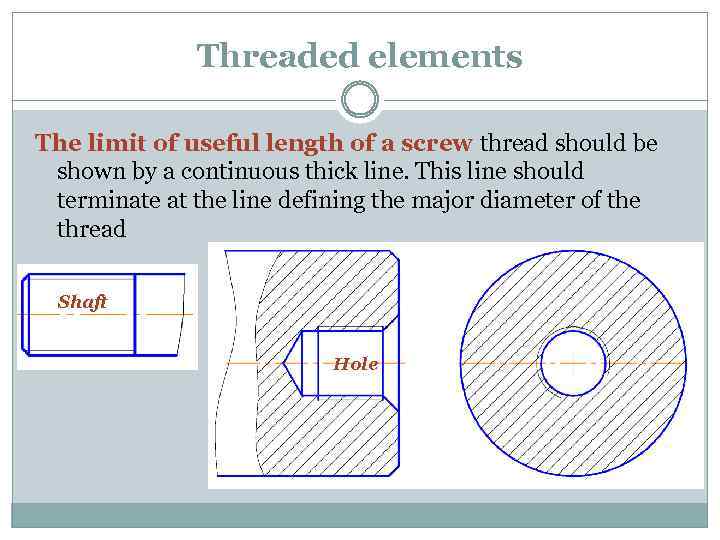
Threaded elements The limit of useful length of a screw thread should be shown by a continuous thick line. This line should terminate at the line defining the major diameter of the thread Shaft Hole
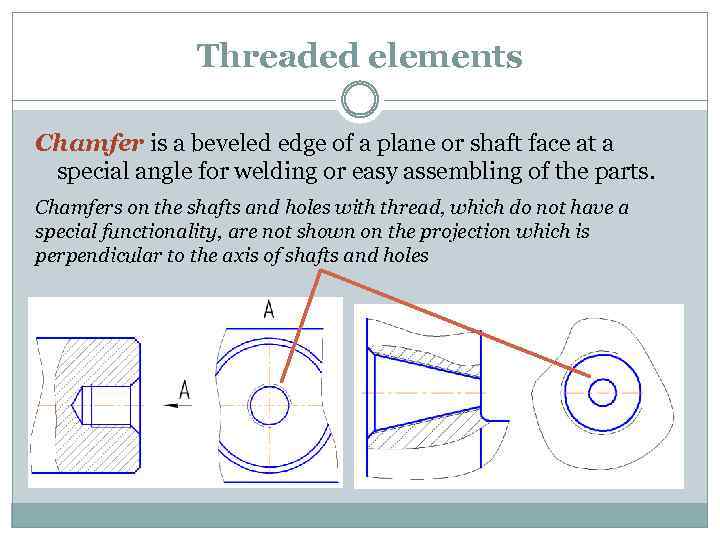
Threaded elements Chamfer is a beveled edge of a plane or shaft face at a special angle for welding or easy assembling of the parts. Chamfers on the shafts and holes with thread, which do not have a special functionality, are not shown on the projection which is perpendicular to the axis of shafts and holes
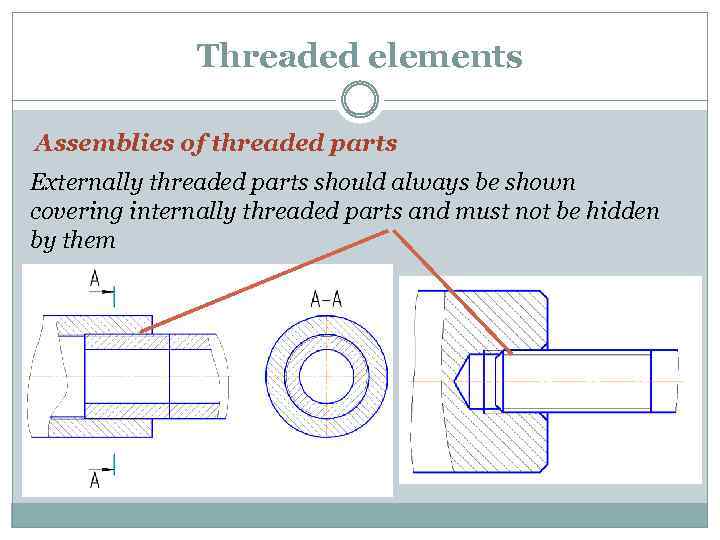
Threaded elements Assemblies of threaded parts Externally threaded parts should always be shown covering internally threaded parts and must not be hidden by them
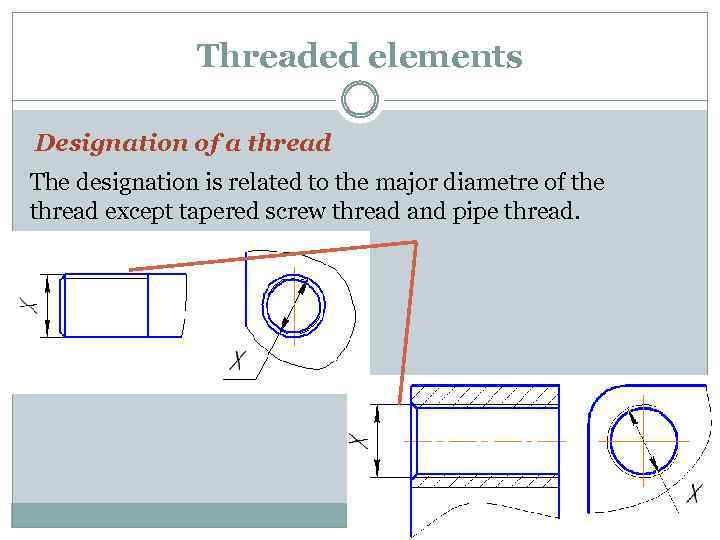
Threaded elements Designation of a thread The designation is related to the major diametre of the thread except tapered screw thread and pipe thread.
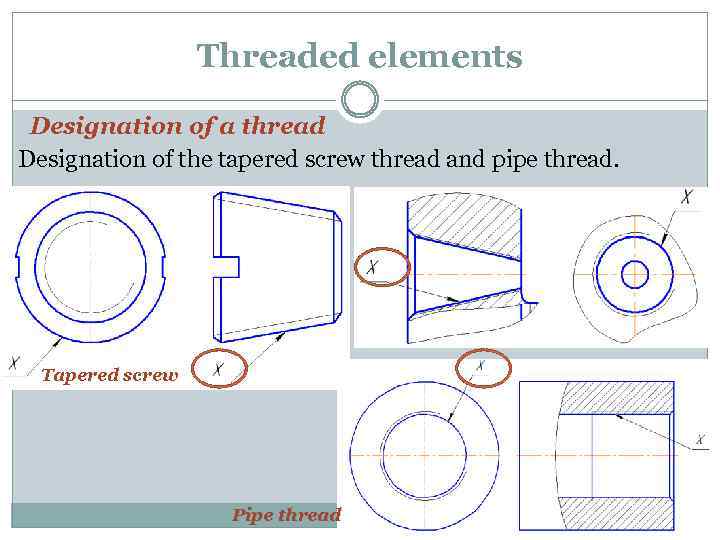
Threaded elements Designation of a thread Designation of the tapered screw thread and pipe thread. Tapered screw Pipe thread
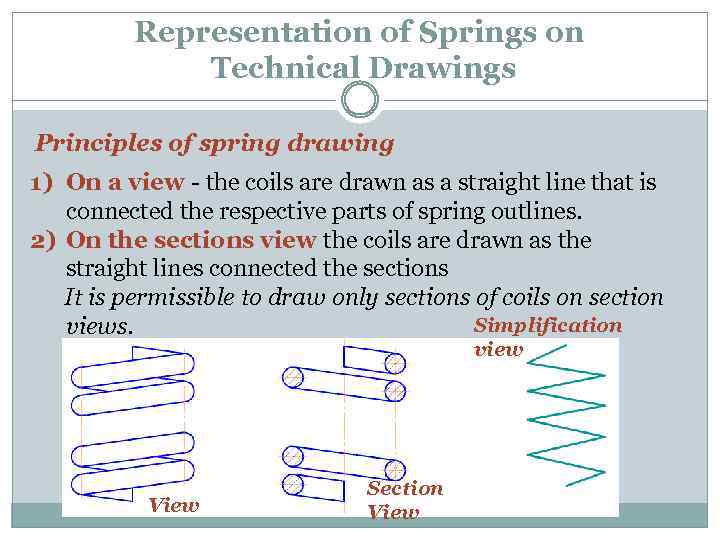
Representation of Springs on Technical Drawings Principles of spring drawing 1) On a view - the coils are drawn as a straight line that is connected the respective parts of spring outlines. 2) On the sections view the coils are drawn as the straight lines connected the sections It is permissible to draw only sections of coils on section Simplification views. view View Section View
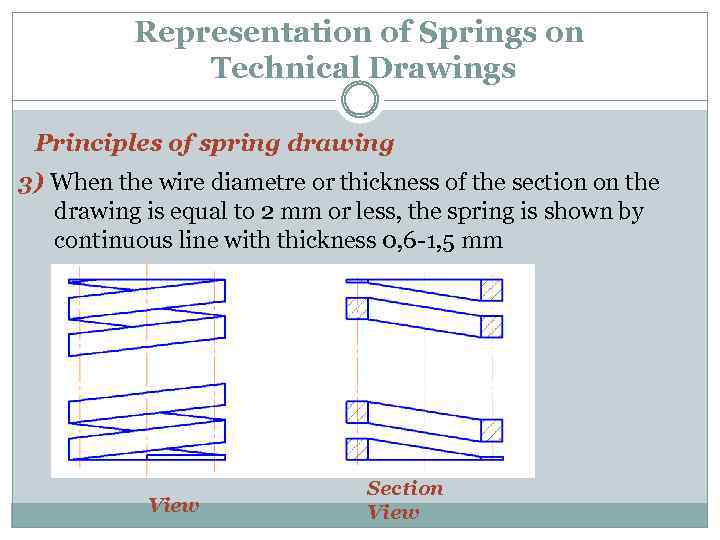
Representation of Springs on Technical Drawings Principles of spring drawing 3) When the wire diametre or thickness of the section on the drawing is equal to 2 mm or less, the spring is shown by continuous line with thickness 0, 6 -1, 5 mm View Section View
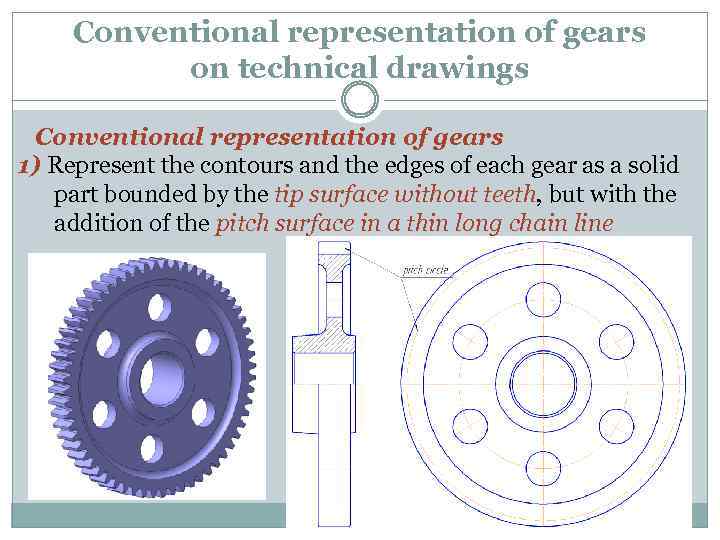
Conventional representation of gears on technical drawings Conventional representation of gears 1) Represent the contours and the edges of each gear as a solid part bounded by the tip surface without teeth, but with the addition of the pitch surface in a thin long chain line
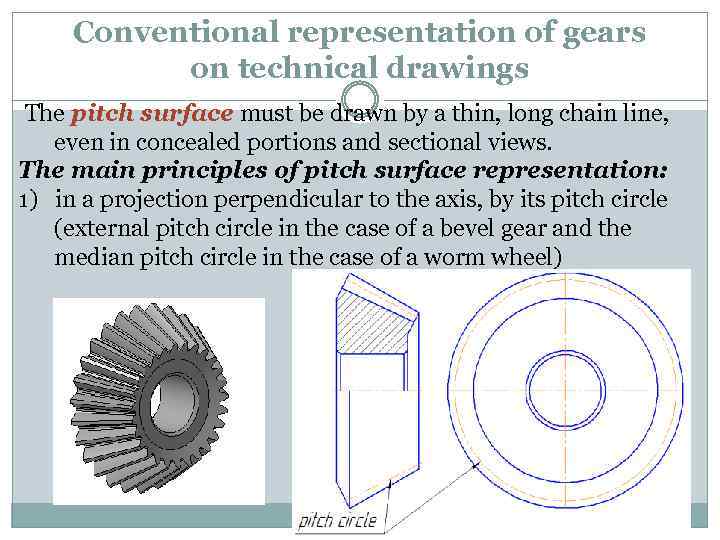
Conventional representation of gears on technical drawings The pitch surface must be drawn by a thin, long chain line, even in concealed portions and sectional views. The main principles of pitch surface representation: 1) in a projection perpendicular to the axis, by its pitch circle (external pitch circle in the case of a bevel gear and the median pitch circle in the case of a worm wheel)
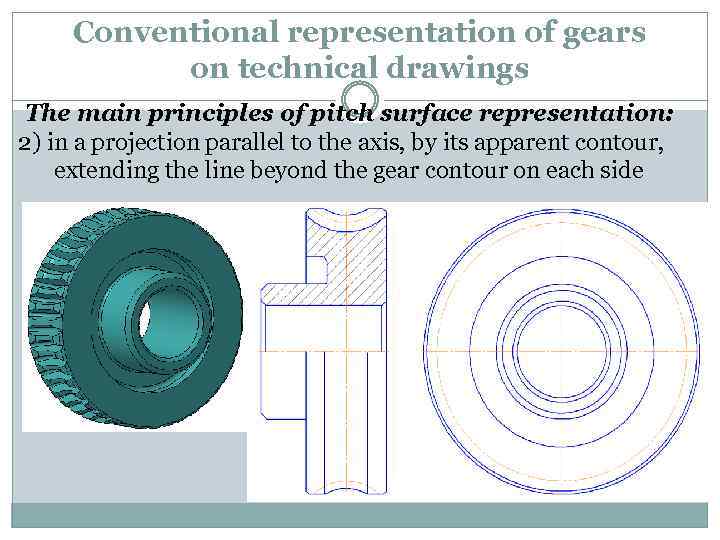
Conventional representation of gears on technical drawings The main principles of pitch surface representation: 2) in a projection parallel to the axis, by its apparent contour, extending the line beyond the gear contour on each side
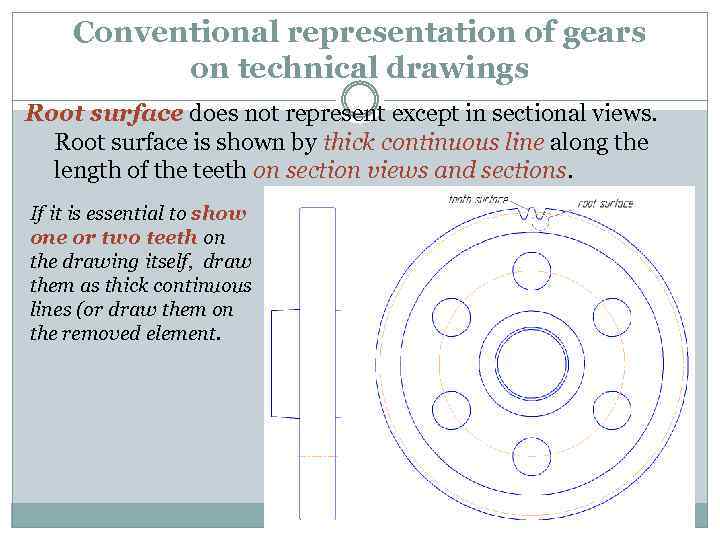
Conventional representation of gears on technical drawings Root surface does not represent except in sectional views. Root surface is shown by thick continuous line along the length of the teeth on section views and sections. If it is essential to show one or two teeth on the drawing itself, draw them as thick continuous lines (or draw them on the removed element.
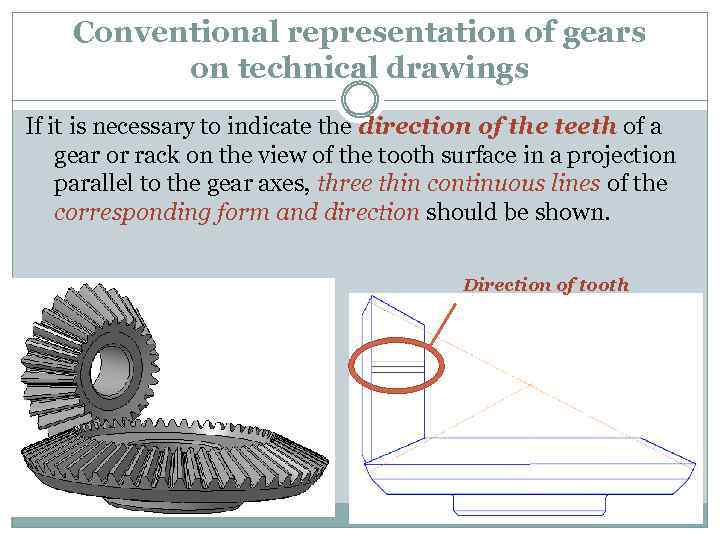
Conventional representation of gears on technical drawings If it is necessary to indicate the direction of the teeth of a gear or rack on the view of the tooth surface in a projection parallel to the gear axes, three thin continuous lines of the corresponding form and direction should be shown. Direction of tooth
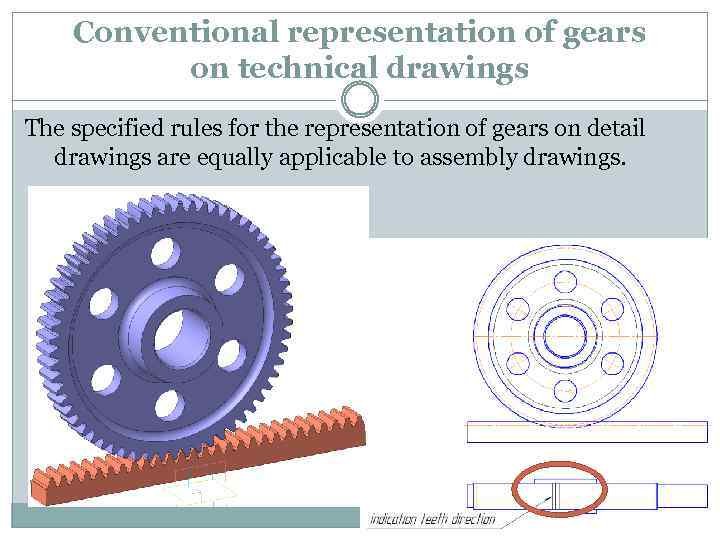
Conventional representation of gears on technical drawings The specified rules for the representation of gears on detail drawings are equally applicable to assembly drawings.
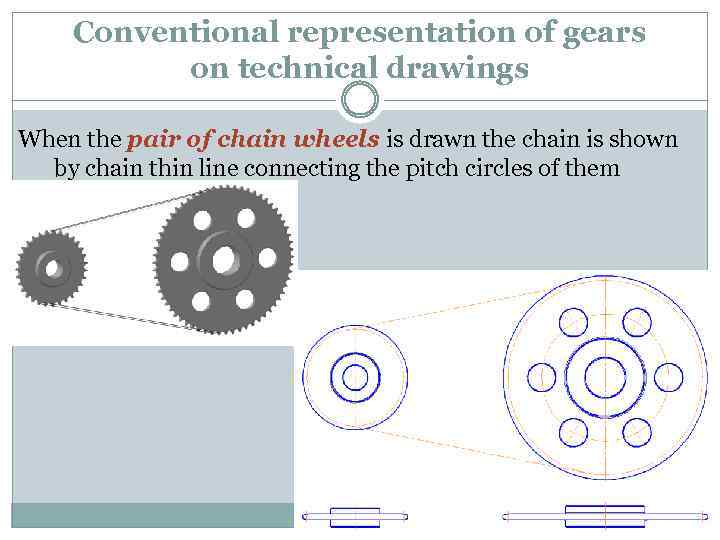
Conventional representation of gears on technical drawings When the pair of chain wheels is drawn the chain is shown by chain thin line connecting the pitch circles of them
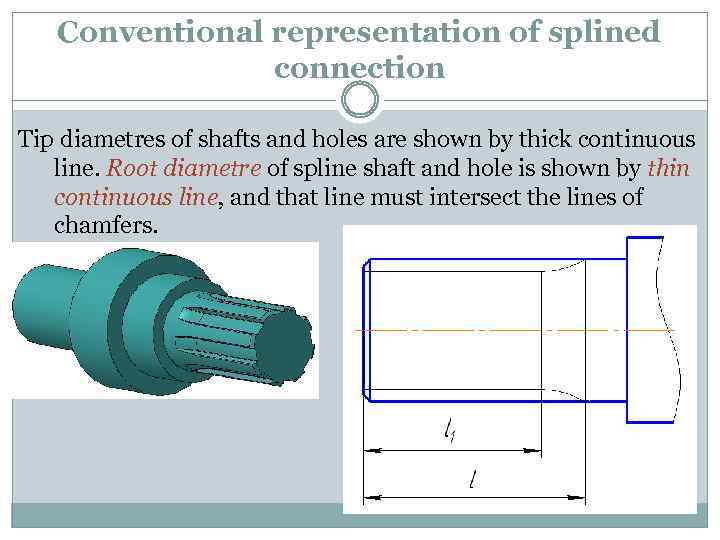
Conventional representation of splined connection Tip diametres of shafts and holes are shown by thick continuous line. Root diametre of spline shaft and hole is shown by thin continuous line, and that line must intersect the lines of chamfers.
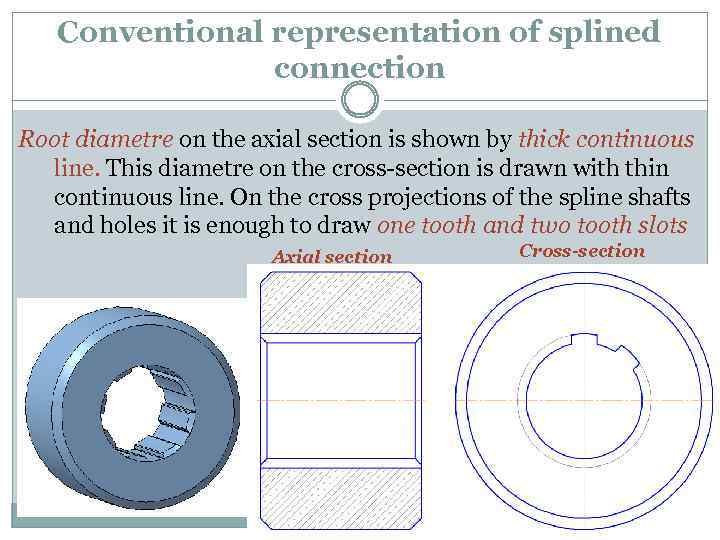
Conventional representation of splined connection Root diametre on the axial section is shown by thick continuous line. This diametre on the cross-section is drawn with thin continuous line. On the cross projections of the spline shafts and holes it is enough to draw one tooth and two tooth slots Axial section Cross-section
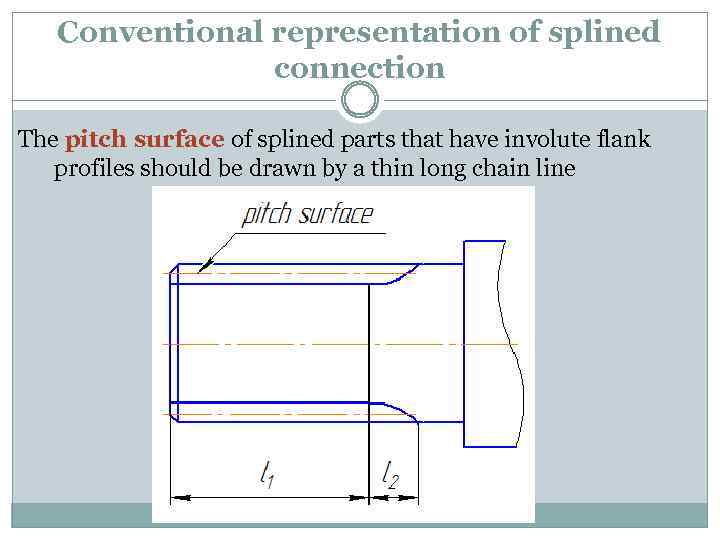
Conventional representation of splined connection The pitch surface of splined parts that have involute flank profiles should be drawn by a thin long chain line

Conventional representation of splined connection Hatching on the splined shaft and hole sections: - on axial sections – to the line of root; - on cross-sections – to the tip line. When the cutting plane passed through the axis of splined joint the part of the hub tip surface is shown that is open from the teeth of the shaft
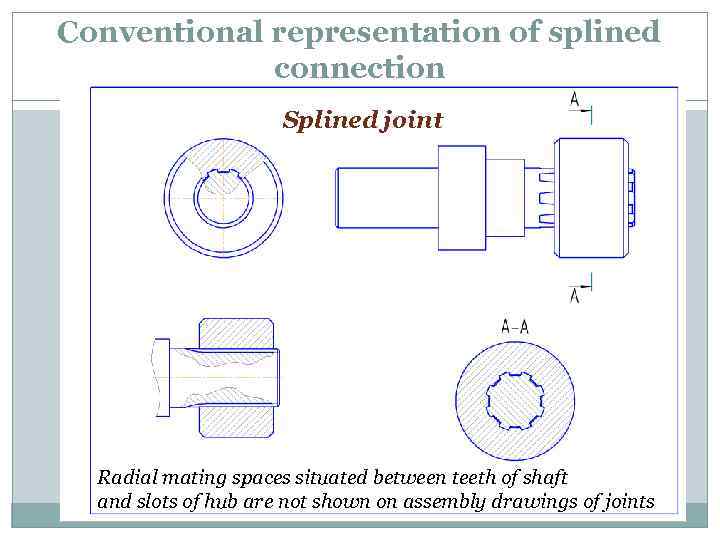
Conventional representation of splined connection Splined joint Radial mating spaces situated between teeth of shaft and slots of hub are not shown on assembly drawings of joints
Lecture 3_Conventional representation.pptx