033e9f9dae3824943bcb903221623f5e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Controls for Linac Parallel Session 2/6/07 John Carwardine ANL Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 1
Controls for Linac Parallel Session 2/6/07 John Carwardine ANL Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 1
 Controls from RDR to EDR… • Develop RDR models into engineering design. • Validate/prototype key concepts in RDR models, eg – – – Network architecture. Front-end model, technical system interfaces. Synchronous 5 Hz feedback infrastructure. Standards, standardization, QA. Diagnostic Interlock Layer. • Perform targeted R&D where it is needed, eg – RF field regulation (phase & amplitude). – High availability implementation. – Fault detection and recovery. • Controls & LLRF support for test facilities. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 2
Controls from RDR to EDR… • Develop RDR models into engineering design. • Validate/prototype key concepts in RDR models, eg – – – Network architecture. Front-end model, technical system interfaces. Synchronous 5 Hz feedback infrastructure. Standards, standardization, QA. Diagnostic Interlock Layer. • Perform targeted R&D where it is needed, eg – RF field regulation (phase & amplitude). – High availability implementation. – Fault detection and recovery. • Controls & LLRF support for test facilities. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 2
 Linac specific issues • Data archiving and collection model. • Distribution of RF phase reference • Feedback infrastructure. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 3
Linac specific issues • Data archiving and collection model. • Distribution of RF phase reference • Feedback infrastructure. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 3
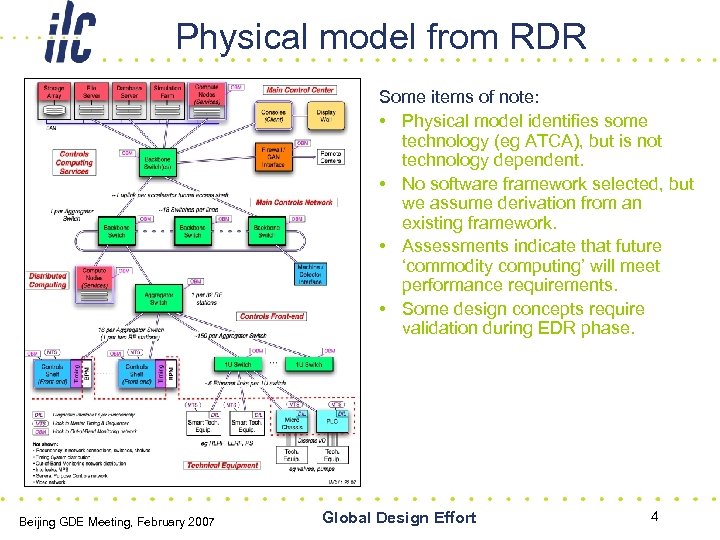 Physical model from RDR Some items of note: • Physical model identifies some technology (eg ATCA), but is not technology dependent. • No software framework selected, but we assume derivation from an existing framework. • Assessments indicate that future ‘commodity computing’ will meet performance requirements. • Some design concepts require validation during EDR phase. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 4
Physical model from RDR Some items of note: • Physical model identifies some technology (eg ATCA), but is not technology dependent. • No software framework selected, but we assume derivation from an existing framework. • Assessments indicate that future ‘commodity computing’ will meet performance requirements. • Some design concepts require validation during EDR phase. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 4
 Unknowns… • Level of effort available from each region – Controls RDR related effort has been small, and largely focused in Americas region. – Looking to expand participation. Must find overlap between needs of ILC EDR efforts and interests of collaborating institutions. – Actual work package content could change depending on the participation. • Americas planning for FY 08 identified a need for 10+ FTEs for controls on EDR and related R&D – Assumes similar participation from other regions. – Does not adequately cover all anticipated work packages, eg for RDR validation & protypying RDR design concepts. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 5
Unknowns… • Level of effort available from each region – Controls RDR related effort has been small, and largely focused in Americas region. – Looking to expand participation. Must find overlap between needs of ILC EDR efforts and interests of collaborating institutions. – Actual work package content could change depending on the participation. • Americas planning for FY 08 identified a need for 10+ FTEs for controls on EDR and related R&D – Assumes similar participation from other regions. – Does not adequately cover all anticipated work packages, eg for RDR validation & protypying RDR design concepts. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 5
 Controls work packages “To Do” • We have a list of top-level objectives, and we have some work packages identified. • Have not collected input from all regions and/or all interested parties. • Does not take credit for related activities (XFEL, ITER, etc). • How best to apportion work packages…? So far, we have not substantially apportioned specific work to specific labs/regions/groups. • How to incorporate needs and interests of potential collaborators…? Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 6
Controls work packages “To Do” • We have a list of top-level objectives, and we have some work packages identified. • Have not collected input from all regions and/or all interested parties. • Does not take credit for related activities (XFEL, ITER, etc). • How best to apportion work packages…? So far, we have not substantially apportioned specific work to specific labs/regions/groups. • How to incorporate needs and interests of potential collaborators…? Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 6
 Integration with test facilities • WPs to provide controls & LLRF for NML, XFEL, etc will presumably come from facility project managers. • Using beam-based test facilities, but they also provide a necessary test bed for controls R&D. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 7
Integration with test facilities • WPs to provide controls & LLRF for NML, XFEL, etc will presumably come from facility project managers. • Using beam-based test facilities, but they also provide a necessary test bed for controls R&D. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 7
 WP model… • Topic: High Availability Control Systems • Top-down objectives and initiatives, eg – Investigate, evaluate, and demonstrate candidate high availability design techniques. – Investigate ATCA as a candidate platform for instrumentation electronics. • Bottom-up work packages can come from many sources: – – Controls or ILC leadership Lab proposals Collaborative contributions Overlapping interests with other activities. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 8
WP model… • Topic: High Availability Control Systems • Top-down objectives and initiatives, eg – Investigate, evaluate, and demonstrate candidate high availability design techniques. – Investigate ATCA as a candidate platform for instrumentation electronics. • Bottom-up work packages can come from many sources: – – Controls or ILC leadership Lab proposals Collaborative contributions Overlapping interests with other activities. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 8
 Examples of bottom-up WPs • Controls leadership – MOU between SLAC and University of Illinois (UIUC) for investigating ATCA analog & digital performance, cabling, shelf manager, etc. • Proposal driven – Proposal from LBNL to develop prototype RF phase distribution system. – Proposal for x-ray based alignment system. – Implement bpm electronics in ATCA crate. – Port EPICS to ATCA, implement fail-over of IOC from machine to machine. • Coincidence of needs with other activities – XFEL LLRF developments. – Precision timing and RF phase distribution for APS picosecond x-ray source. – ITER remote access / remote control needs. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 9
Examples of bottom-up WPs • Controls leadership – MOU between SLAC and University of Illinois (UIUC) for investigating ATCA analog & digital performance, cabling, shelf manager, etc. • Proposal driven – Proposal from LBNL to develop prototype RF phase distribution system. – Proposal for x-ray based alignment system. – Implement bpm electronics in ATCA crate. – Port EPICS to ATCA, implement fail-over of IOC from machine to machine. • Coincidence of needs with other activities – XFEL LLRF developments. – Precision timing and RF phase distribution for APS picosecond x-ray source. – ITER remote access / remote control needs. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 9
 High Availability • HA is a requirement for all the technical systems. • Need to investigate techniques, implications, and cost-benefit for meeting reliability requirements. • Control system hardware & software both impacted. • Methodology component: – Design techniques, robust design. – Quality Control / extensive testing. – Standardization. • Engineering component: – Reliably detect and then recover from faults. – Introspection, diagnostic tools, … – Redundancy, hot spares, remote power on/off, … Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 10
High Availability • HA is a requirement for all the technical systems. • Need to investigate techniques, implications, and cost-benefit for meeting reliability requirements. • Control system hardware & software both impacted. • Methodology component: – Design techniques, robust design. – Quality Control / extensive testing. – Standardization. • Engineering component: – Reliably detect and then recover from faults. – Introspection, diagnostic tools, … – Redundancy, hot spares, remote power on/off, … Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 10
 HA technical working group…? • • HA issues apply to multiple technical systems. We should attempt to solve the issues collectively. Technical groups need to address HA in their R&D. An HA Technical Working Group would serve to guide and collect HA related activities. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 11
HA technical working group…? • • HA issues apply to multiple technical systems. We should attempt to solve the issues collectively. Technical groups need to address HA in their R&D. An HA Technical Working Group would serve to guide and collect HA related activities. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 11
 WP example: HA control systems • Investigate high availability design approaches, implications, and costbenefit for the ILC control system. • Example work package items: – Develop & evaluate controls failure modes and machine impact. Determine priorities for meeting overall availability. – Explore techniques such as virtual machine migration (Xen), clustering (heartbeat), redundant I/O controllers, etc. using [EPICS, DOOCS, Tango, …] on ATCA. – Evaluate and prototype second-tier HA techniques, eg: automated diagnosis, configuration management, coding standards. – Build vertical demonstration of all tiers of control system with HA techniques applied. Perform fault injection to test and evaluate. – Evaluate and prototype “Shelf-manager’ functionality in control system infrastructure for technical system fault management. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 12
WP example: HA control systems • Investigate high availability design approaches, implications, and costbenefit for the ILC control system. • Example work package items: – Develop & evaluate controls failure modes and machine impact. Determine priorities for meeting overall availability. – Explore techniques such as virtual machine migration (Xen), clustering (heartbeat), redundant I/O controllers, etc. using [EPICS, DOOCS, Tango, …] on ATCA. – Evaluate and prototype second-tier HA techniques, eg: automated diagnosis, configuration management, coding standards. – Build vertical demonstration of all tiers of control system with HA techniques applied. Perform fault injection to test and evaluate. – Evaluate and prototype “Shelf-manager’ functionality in control system infrastructure for technical system fault management. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 12
 WP example: ATCA evaluation • Investigate suitability of ATCA as a high availability compliant electronics platform for ILC control system. • Example work package items: – Prototype a precision instrumentation digitizer for beam position monitors. Evaluate analog & digital performance. – Prototype electronics functions to the AMC mezzanine card, and integrate with the IPMC diagnostic module. Write software drivers. – Evaluate cabling options for ATCA and AMC cards – Port [EPICS, DOOCS, Tango, …] to the ATCA platform, integrate and evaluate “Shelf Manager” functionality. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 13
WP example: ATCA evaluation • Investigate suitability of ATCA as a high availability compliant electronics platform for ILC control system. • Example work package items: – Prototype a precision instrumentation digitizer for beam position monitors. Evaluate analog & digital performance. – Prototype electronics functions to the AMC mezzanine card, and integrate with the IPMC diagnostic module. Write software drivers. – Evaluate cabling options for ATCA and AMC cards – Port [EPICS, DOOCS, Tango, …] to the ATCA platform, integrate and evaluate “Shelf Manager” functionality. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 13
 WP example: diagnostic processor • The diagnostic processor (DP) is conceived as the key element in the Diagnostic Interlock Layer (DIL). • Work package example items: – Continue development of DP hardware for Marx and 4+1 supplies. Develop generic family of DP hardware (including chip-level) suitable for integration into various technical systems. – Develop on-board software to integrate DP with IPMI-based relay rack monitoring. Client software will be developed/acquired to provide a uniform management interface to all relay racks based on current standards. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 14
WP example: diagnostic processor • The diagnostic processor (DP) is conceived as the key element in the Diagnostic Interlock Layer (DIL). • Work package example items: – Continue development of DP hardware for Marx and 4+1 supplies. Develop generic family of DP hardware (including chip-level) suitable for integration into various technical systems. – Develop on-board software to integrate DP with IPMI-based relay rack monitoring. Client software will be developed/acquired to provide a uniform management interface to all relay racks based on current standards. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 14
 WP example: RF phase distribution • Perform essential R&D on distribution techniques for the 1300 MHz timing distribution system. • Example work package items: – Investigate & evaluate strategies for phase stabilizing long fiber links modulated at 1. 3 GHz. – Demonstrate critical time of arrival stabilization at a dummy Interaction Point using NML beam test facility. – Investigate feasibility of using a beam-derived reference for locking a local phase reference. – Prototype a redundant phase reference receiver with decision logic to auto-switch upon detected failure. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 15
WP example: RF phase distribution • Perform essential R&D on distribution techniques for the 1300 MHz timing distribution system. • Example work package items: – Investigate & evaluate strategies for phase stabilizing long fiber links modulated at 1. 3 GHz. – Demonstrate critical time of arrival stabilization at a dummy Interaction Point using NML beam test facility. – Investigate feasibility of using a beam-derived reference for locking a local phase reference. – Prototype a redundant phase reference receiver with decision logic to auto-switch upon detected failure. Beijing GDE Meeting, February 2007 Global Design Effort 15


