Control_Premiums_amp_amp_Discounts_Team_2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Control premiums and discounts for lack of liquidity The Team № 2 Cherkasova Elisaveta Fedorova Svetlana Karachevtseva Irina Luneva Marina Pylnev Ivan
Control premiums and discounts for lack of liquidity The Team № 2 Cherkasova Elisaveta Fedorova Svetlana Karachevtseva Irina Luneva Marina Pylnev Ivan
 APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
 APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
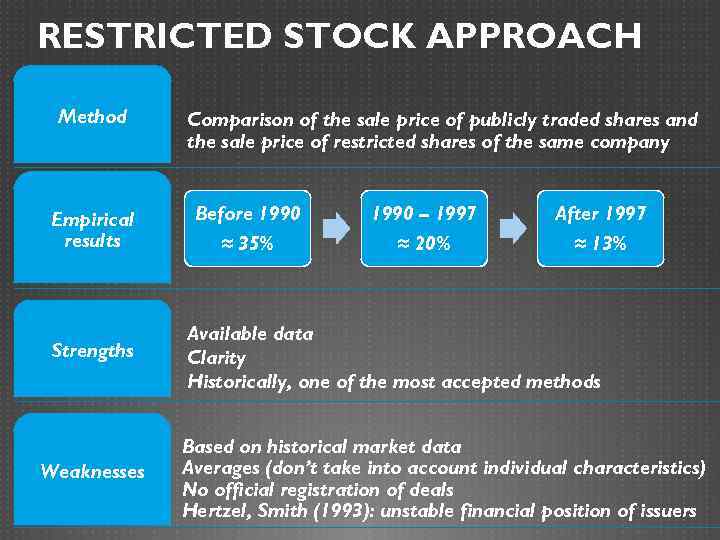 RESTRICTED STOCK APPROACH Method Empirical results Strengths Weaknesses Comparison of the sale price of publicly traded shares and the sale price of restricted shares of the same company Before 1990 ≈ 35% 1990 – 1997 ≈ 20% After 1997 ≈ 13% Available data Clarity Historically, one of the most accepted methods Based on historical market data Averages (don’t take into account individual characteristics) No official registration of deals Hertzel, Smith (1993): unstable financial position of issuers
RESTRICTED STOCK APPROACH Method Empirical results Strengths Weaknesses Comparison of the sale price of publicly traded shares and the sale price of restricted shares of the same company Before 1990 ≈ 35% 1990 – 1997 ≈ 20% After 1997 ≈ 13% Available data Clarity Historically, one of the most accepted methods Based on historical market data Averages (don’t take into account individual characteristics) No official registration of deals Hertzel, Smith (1993): unstable financial position of issuers
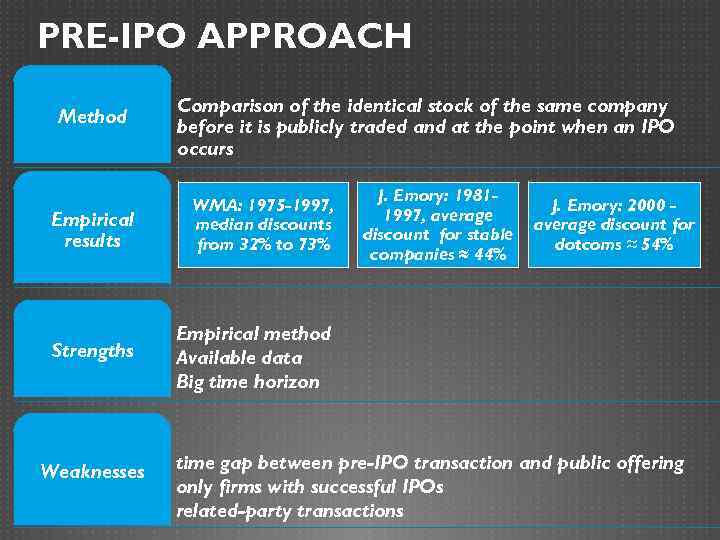 PRE-IPO APPROACH Method Comparison of the identical stock of the same company before it is publicly traded and at the point when an IPO occurs Empirical results WMA: 1975 -1997, median discounts from 32% to 73% Strengths J. Emory: 19811997, average discount for stable companies ≈ 44% Empirical method Available data Big time horizon Weaknesses J. Emory: 2000 average discount for dotcoms ≈ 54% time gap between pre-IPO transaction and public offering only firms with successful IPOs related-party transactions
PRE-IPO APPROACH Method Comparison of the identical stock of the same company before it is publicly traded and at the point when an IPO occurs Empirical results WMA: 1975 -1997, median discounts from 32% to 73% Strengths J. Emory: 19811997, average discount for stable companies ≈ 44% Empirical method Available data Big time horizon Weaknesses J. Emory: 2000 average discount for dotcoms ≈ 54% time gap between pre-IPO transaction and public offering only firms with successful IPOs related-party transactions
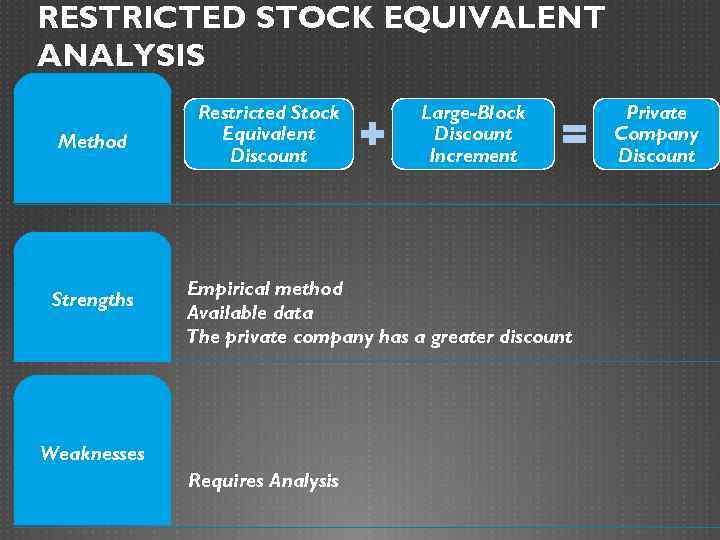 RESTRICTED STOCK EQUIVALENT ANALYSIS Method Strengths Restricted Stock Equivalent Discount Large-Block Discount Increment Empirical method Available data The private company has a greater discount Weaknesses Requires Analysis Private Company Discount
RESTRICTED STOCK EQUIVALENT ANALYSIS Method Strengths Restricted Stock Equivalent Discount Large-Block Discount Increment Empirical method Available data The private company has a greater discount Weaknesses Requires Analysis Private Company Discount
 APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
 LEAPS Method DLOM is calculated as the cost of the LEAP put option divided by the stock price Empirical One year median discounts: from 8. 3% to 17% results Two year median discounts: from 9. 3% to 31% Strengths Big number of LEAPS transactions Data can be segmented by industries Weaknesses A qualitative analysis is needed Private companies do not issue LEAPS A minimum discount
LEAPS Method DLOM is calculated as the cost of the LEAP put option divided by the stock price Empirical One year median discounts: from 8. 3% to 17% results Two year median discounts: from 9. 3% to 31% Strengths Big number of LEAPS transactions Data can be segmented by industries Weaknesses A qualitative analysis is needed Private companies do not issue LEAPS A minimum discount
 THE LONGSTAFF STUDY, 1995 Method DLOM is the present value difference between what the investor could sell the security for after the marketability restrictions have run out and the maximum price the security could have sold for during the restriction period Strengths Can be easily applied Weaknesses Assumes perfect market timing Gives a maximum benchmark Prerequisite about low volatility
THE LONGSTAFF STUDY, 1995 Method DLOM is the present value difference between what the investor could sell the security for after the marketability restrictions have run out and the maximum price the security could have sold for during the restriction period Strengths Can be easily applied Weaknesses Assumes perfect market timing Gives a maximum benchmark Prerequisite about low volatility
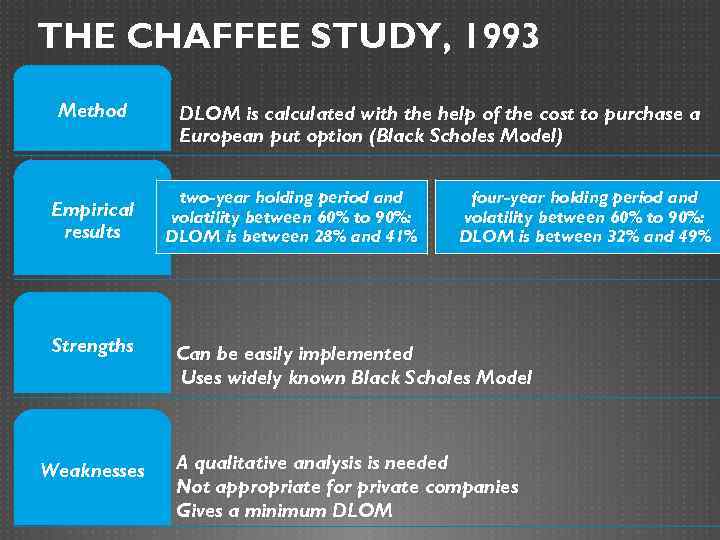 THE CHAFFEE STUDY, 1993 Method Empirical results Strengths Weaknesses DLOM is calculated with the help of the cost to purchase a European put option (Black Scholes Model) two-year holding period and volatility between 60% to 90%: DLOM is between 28% and 41% four-year holding period and volatility between 60% to 90%: DLOM is between 32% and 49% Can be easily implemented Uses widely known Black Scholes Model A qualitative analysis is needed Not appropriate for private companies Gives a minimum DLOM
THE CHAFFEE STUDY, 1993 Method Empirical results Strengths Weaknesses DLOM is calculated with the help of the cost to purchase a European put option (Black Scholes Model) two-year holding period and volatility between 60% to 90%: DLOM is between 28% and 41% four-year holding period and volatility between 60% to 90%: DLOM is between 32% and 49% Can be easily implemented Uses widely known Black Scholes Model A qualitative analysis is needed Not appropriate for private companies Gives a minimum DLOM
 APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
 ANALYTICAL APPROACHES Wruck (1989) Hertzel, Smith (1993) Bajaj et al. (2002)
ANALYTICAL APPROACHES Wruck (1989) Hertzel, Smith (1993) Bajaj et al. (2002)
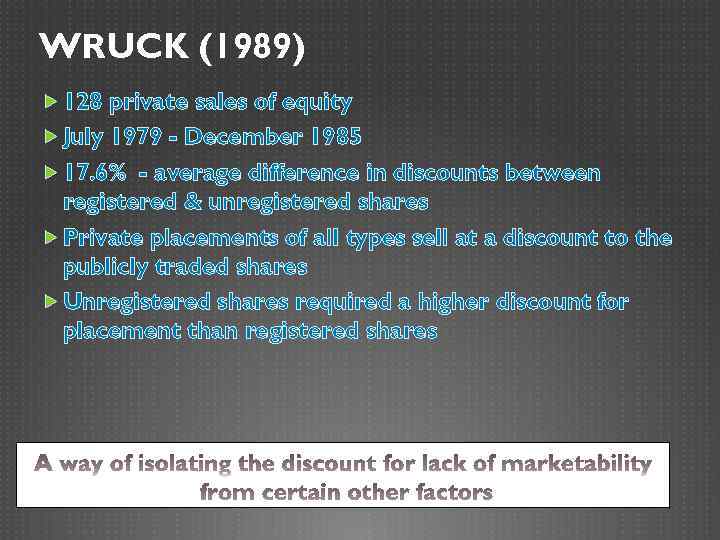 WRUCK (1989) 128 private sales of equity July 1979 - December 1985 17. 6% - average difference in discounts between registered & unregistered shares Private placements of all types sell at a discount to the publicly traded shares Unregistered shares required a higher discount for placement than registered shares
WRUCK (1989) 128 private sales of equity July 1979 - December 1985 17. 6% - average difference in discounts between registered & unregistered shares Private placements of all types sell at a discount to the publicly traded shares Unregistered shares required a higher discount for placement than registered shares
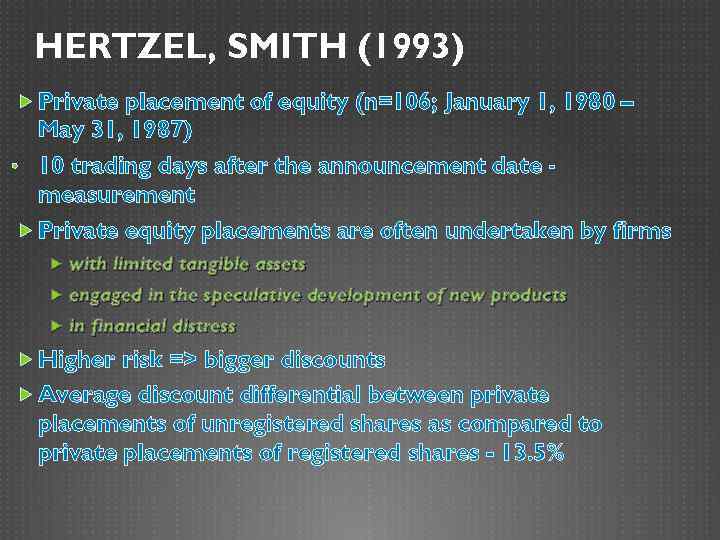 HERTZEL, SMITH (1993) Private placement of equity (n=106; January 1, 1980 – May 31, 1987) • 10 trading days after the announcement date measurement Private equity placements are often undertaken by firms with limited tangible assets engaged in the speculative development of new products in financial distress Higher risk => bigger discounts Average discount differential between private placements of unregistered shares as compared to private placements of registered shares - 13. 5%
HERTZEL, SMITH (1993) Private placement of equity (n=106; January 1, 1980 – May 31, 1987) • 10 trading days after the announcement date measurement Private equity placements are often undertaken by firms with limited tangible assets engaged in the speculative development of new products in financial distress Higher risk => bigger discounts Average discount differential between private placements of unregistered shares as compared to private placements of registered shares - 13. 5%
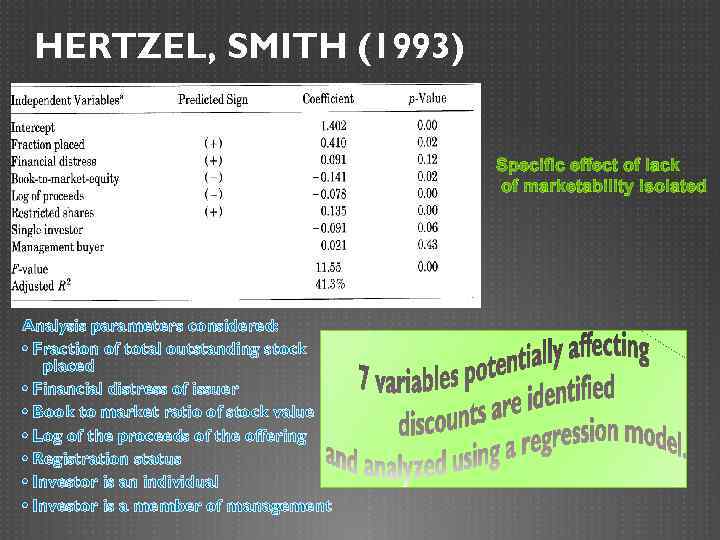 HERTZEL, SMITH (1993) Specific effect of lack of marketability isolated Analysis parameters considered: • Fraction of total outstanding stock placed • Financial distress of issuer • Book to market ratio of stock value • Log of the proceeds of the offering • Registration status • Investor is an individual • Investor is a member of management
HERTZEL, SMITH (1993) Specific effect of lack of marketability isolated Analysis parameters considered: • Fraction of total outstanding stock placed • Financial distress of issuer • Book to market ratio of stock value • Log of the proceeds of the offering • Registration status • Investor is an individual • Investor is a member of management
 BAJAJ ET AL. (2002) Factors affecting marketability: Uncertainty of the assets value Lack of availability of information on the asset to an outsider Availability of close substitutes for the asset Duration of the restriction on trades of the asset Size of the block being sold Private equity placements 88 transactions January 1, 1990 - December 31, 1995 10 trading days after the announcement date - measurement
BAJAJ ET AL. (2002) Factors affecting marketability: Uncertainty of the assets value Lack of availability of information on the asset to an outsider Availability of close substitutes for the asset Duration of the restriction on trades of the asset Size of the block being sold Private equity placements 88 transactions January 1, 1990 - December 31, 1995 10 trading days after the announcement date - measurement
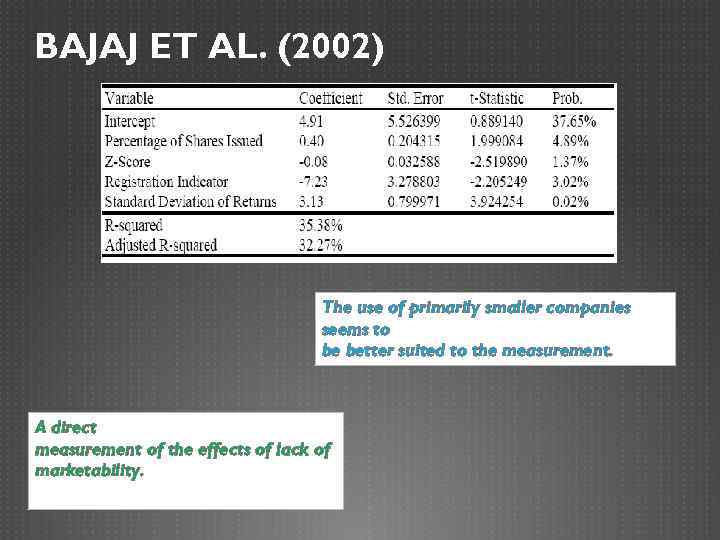 BAJAJ ET AL. (2002) The use of primarily smaller companies seems to be better suited to the measurement. A direct measurement of the effects of lack of marketability.
BAJAJ ET AL. (2002) The use of primarily smaller companies seems to be better suited to the measurement. A direct measurement of the effects of lack of marketability.
 APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
APPROACHES TO DLOM Classification: Benchmark study approaches Security-based approaches Analytical approaches Other approaches
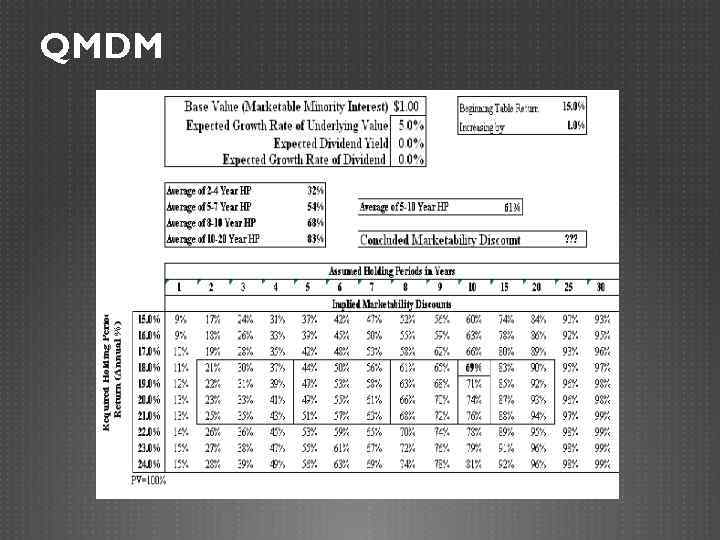 QMDM
QMDM
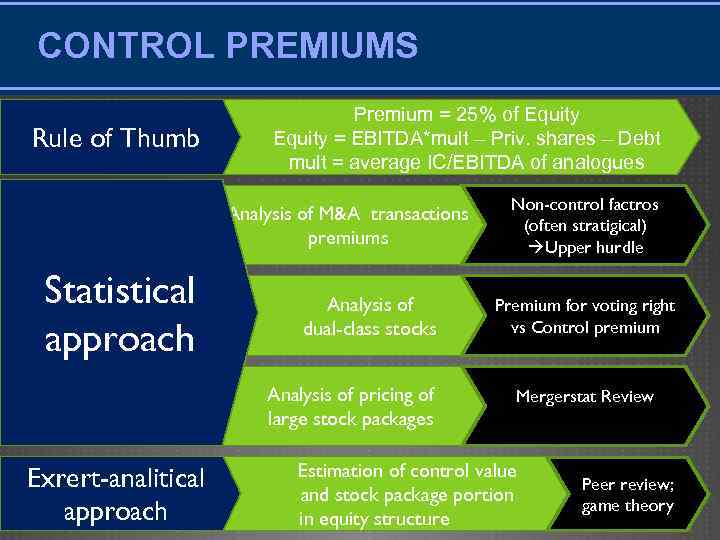 CONTROL PREMIUMS Rule of Thumb Premium = 25% of Equity = EBITDA*mult – Priv. shares – Debt mult = average IC/EBITDA of analogues Analysis of M&A transactions premiums Statistical approach Analysis of dual-class stocks Analysis of pricing of large stock packages Exrert-analitical approach Non-control factros (often stratigical) Upper hurdle Premium for voting right vs Control premium Mergerstat Review Estimation of control value and stock package portion in equity structure Peer review; game theory
CONTROL PREMIUMS Rule of Thumb Premium = 25% of Equity = EBITDA*mult – Priv. shares – Debt mult = average IC/EBITDA of analogues Analysis of M&A transactions premiums Statistical approach Analysis of dual-class stocks Analysis of pricing of large stock packages Exrert-analitical approach Non-control factros (often stratigical) Upper hurdle Premium for voting right vs Control premium Mergerstat Review Estimation of control value and stock package portion in equity structure Peer review; game theory
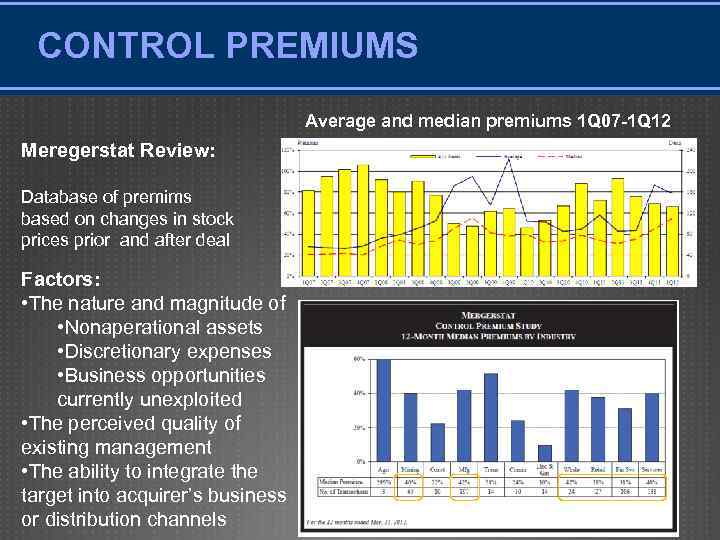 CONTROL PREMIUMS Average and median premiums 1 Q 07 -1 Q 12 Meregerstat Review: Database of premims based on changes in stock prices prior and after deal Factors: • The nature and magnitude of • Nonaperational assets • Discretionary expenses • Business opportunities currently unexploited • The perceived quality of existing management • The ability to integrate the target into acquirer’s business or distribution channels
CONTROL PREMIUMS Average and median premiums 1 Q 07 -1 Q 12 Meregerstat Review: Database of premims based on changes in stock prices prior and after deal Factors: • The nature and magnitude of • Nonaperational assets • Discretionary expenses • Business opportunities currently unexploited • The perceived quality of existing management • The ability to integrate the target into acquirer’s business or distribution channels
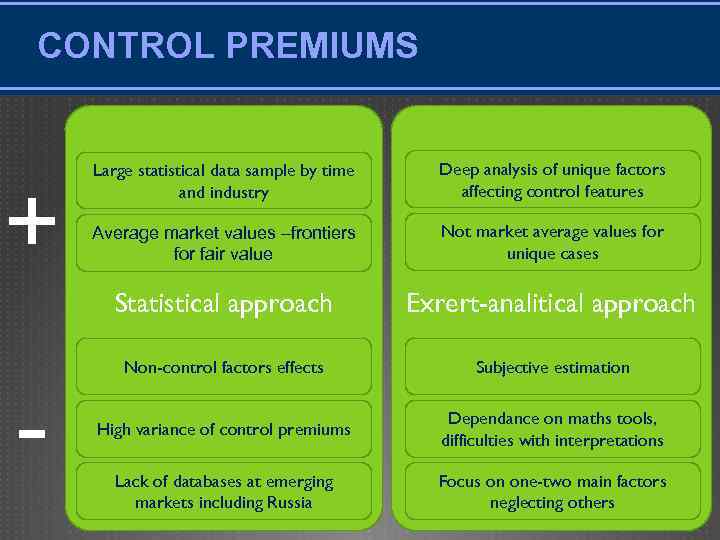 CONTROL PREMIUMS - Deep analysis of unique factors affecting control features Average market values –frontiers for fair value Not market average values for unique cases Statistical approach + Large statistical data sample by time and industry Exrert-analitical approach Non-control factors effects Subjective estimation High variance of control premiums Dependance on maths tools, difficulties with interpretations Lack of databases at emerging markets including Russia Focus on one-two main factors neglecting others
CONTROL PREMIUMS - Deep analysis of unique factors affecting control features Average market values –frontiers for fair value Not market average values for unique cases Statistical approach + Large statistical data sample by time and industry Exrert-analitical approach Non-control factors effects Subjective estimation High variance of control premiums Dependance on maths tools, difficulties with interpretations Lack of databases at emerging markets including Russia Focus on one-two main factors neglecting others
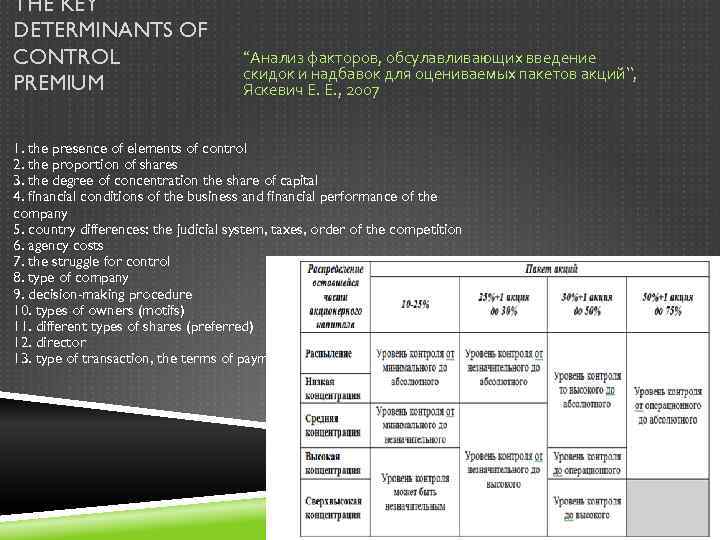 THE KEY DETERMINANTS OF CONTROL PREMIUM “Анализ факторов, обсулавливающих введение скидок и надбавок для оцениваемых пакетов акций”, Яскевич Е. Е. , 2007 1. the presence of elements of control 2. the proportion of shares 3. the degree of concentration the share of capital 4. financial conditions of the business and financial performance of the company 5. country differences: the judicial system, taxes, order of the competition 6. agency costs 7. the struggle for control 8. type of company 9. decision-making procedure 10. types of owners (motifs) 11. different types of shares (preferred) 12. director 13. type of transaction, the terms of payment
THE KEY DETERMINANTS OF CONTROL PREMIUM “Анализ факторов, обсулавливающих введение скидок и надбавок для оцениваемых пакетов акций”, Яскевич Е. Е. , 2007 1. the presence of elements of control 2. the proportion of shares 3. the degree of concentration the share of capital 4. financial conditions of the business and financial performance of the company 5. country differences: the judicial system, taxes, order of the competition 6. agency costs 7. the struggle for control 8. type of company 9. decision-making procedure 10. types of owners (motifs) 11. different types of shares (preferred) 12. director 13. type of transaction, the terms of payment
 DETERMINANTS numb er determinants 1 Key rights: • Change the board of directors, management • Identify the award managers • Production - the strategic policy • Rent, liquidation of business assets • Choose suppliers. Contractors, distributors. . . • M&A • recapitalize the company, to sell, to dissolve • IPO, etc. 2 Controlling interest (majority), non-controlling (minority) - less than 50% of voting shares. Controlling, blocking (25% +1 share) - can block 3 Table 1 4 Revenue growth + Market growth + Equity / assets Return on shareholders' equity + Financial leverage, liquidity, increase the value of assets? Debt / Assets Market / book value? nu mb er determinants 8 Private company - the premium higher Public company – premium lower 10 SR - temporary investment of resources LR - control over 11 Dividend payment (less the number of shares of voting preferred shares) below the cost of the packet No dividend payments - more value pack
DETERMINANTS numb er determinants 1 Key rights: • Change the board of directors, management • Identify the award managers • Production - the strategic policy • Rent, liquidation of business assets • Choose suppliers. Contractors, distributors. . . • M&A • recapitalize the company, to sell, to dissolve • IPO, etc. 2 Controlling interest (majority), non-controlling (minority) - less than 50% of voting shares. Controlling, blocking (25% +1 share) - can block 3 Table 1 4 Revenue growth + Market growth + Equity / assets Return on shareholders' equity + Financial leverage, liquidity, increase the value of assets? Debt / Assets Market / book value? nu mb er determinants 8 Private company - the premium higher Public company – premium lower 10 SR - temporary investment of resources LR - control over 11 Dividend payment (less the number of shares of voting preferred shares) below the cost of the packet No dividend payments - more value pack
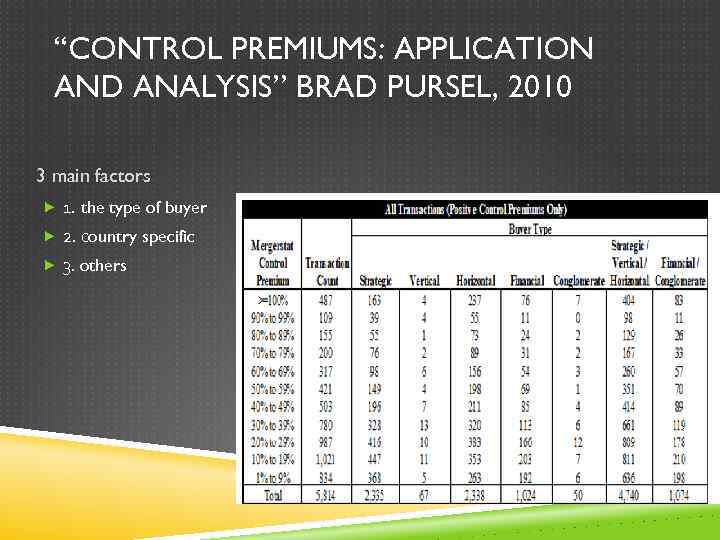 “CONTROL PREMIUMS: APPLICATION AND ANALYSIS” BRAD PURSEL, 2010 3 main factors 1. the type of buyer 2. сountry specific 3. others Control premium
“CONTROL PREMIUMS: APPLICATION AND ANALYSIS” BRAD PURSEL, 2010 3 main factors 1. the type of buyer 2. сountry specific 3. others Control premium



