e9017ef77e34c4bc4d596e5cb352b267.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

Control of Drug Product Institute of Biological Products (IBP), DMSc, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand Apichai Supasansatorn 29 April 2016, AS 1

Outline: P 5 Control of Drug Product ACTD: P 5 Control of Finished Product 5. 1 ขอกำหนดมาตรฐาน (Specification) และหนงสอรบรองการวเคราะห (Certificate of Analysis) 5. 2 วธการวเคราะห (Analytical Procedures) 5. 3 การตรวจสอบความถกตองของวธการวเคราะห (Validation of Analytical Procedures) 5. 4 การวเคราะหรนการผลต (Batch analysis) 5. 5 การตรวจลกษณะเฉพาะของสารเจอปน (Characterization of Impurities) 5. 6 การชแจงเหตผลของขอกำหนดมาตรฐาน (Justification of Specification) 29 April 2016, AS 2

Drug Product The drug product is the finished dosage form of the product. The drug product contains the drug substance (s) formulated with other ingredients in the finished dosage form ready for marketing. Other ingredients, active or inactive, may include adjuvants, preservatives, stabilizers, and/or excipients. For vaccine formulation, the drug substance (s) may be diluted, adsorbed, mixed with adjuvants or additives, and/or lyophilized to become the drug product (USFDA). 29 April 2016, AS 3

Final Bulk Vaccine (ACTD: P 3. 3 Control of Critical Steps and Intermediates) Material that has undergone all the steps of production except for the final filling. It consists of one or monovalent pooled harvests, from cultures of one or more species or types of microorganism, after clarification, dilution or addition of an adjuvant or other auxiliary substance. It is treated to ensure its homogeneity and is used for filling the containers of one or more final lots (batches( 29 April 2016, AS 4

Finished pharmaceutical product (FPP) A product that has undergone all stages of production, including packaging in its final container and labeling. An FPP may contain one or more APIs. Other name: Final Product, Final Lot Finished Product 29 April 2016, AS 5

5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Specification: The rationale used to establish the acceptance criteria should be described. Based on data obtained: • Relevant development data • Lots used in preclinical, clinical studies • Lots used for demonstration of manufacturing consistency • Stability studies 29 April 2016, AS 6

5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Specification: The requirements that used as references are enclosed. (How to choose the requirement? ) • Thai Pharmacopoeia • The United State Pharmacopoeia • European Pharmacopoeia • British Pharmacopoeia • International Requirement (WHO) 29 April 2016, AS 7
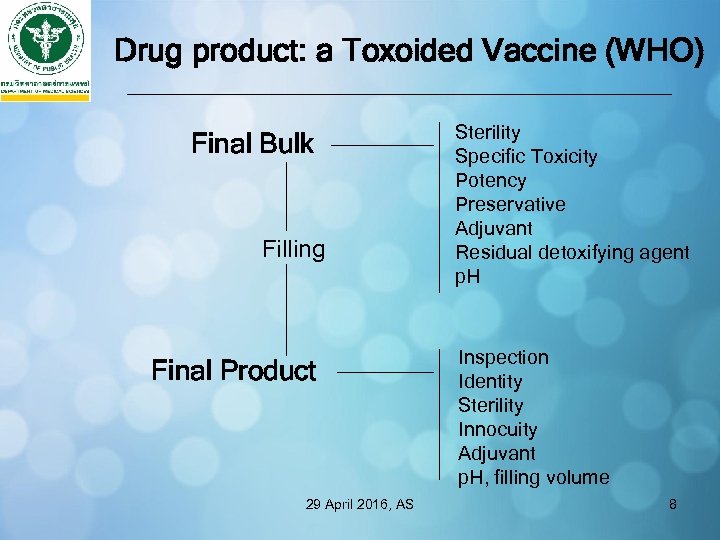
Drug product: a Toxoided Vaccine (WHO) Final Bulk Filling Final Product 29 April 2016, AS Sterility Specific Toxicity Potency Preservative Adjuvant Residual detoxifying agent p. H Inspection Identity Sterility Innocuity Adjuvant p. H, filling volume 8
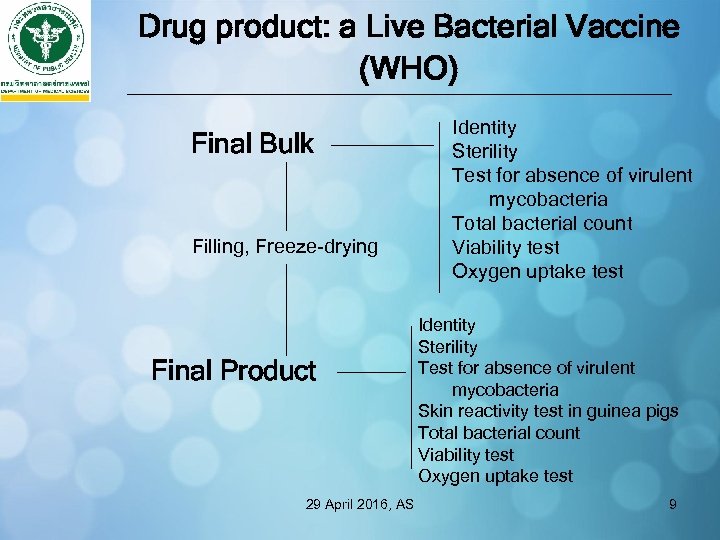
Drug product: a Live Bacterial Vaccine (WHO) Final Bulk Filling, Freeze-drying Final Product 29 April 2016, AS Identity Sterility Test for absence of virulent mycobacteria Total bacterial count Viability test Oxygen uptake test Identity Sterility Test for absence of virulent mycobacteria Skin reactivity test in guinea pigs Total bacterial count Viability test Oxygen uptake test 9
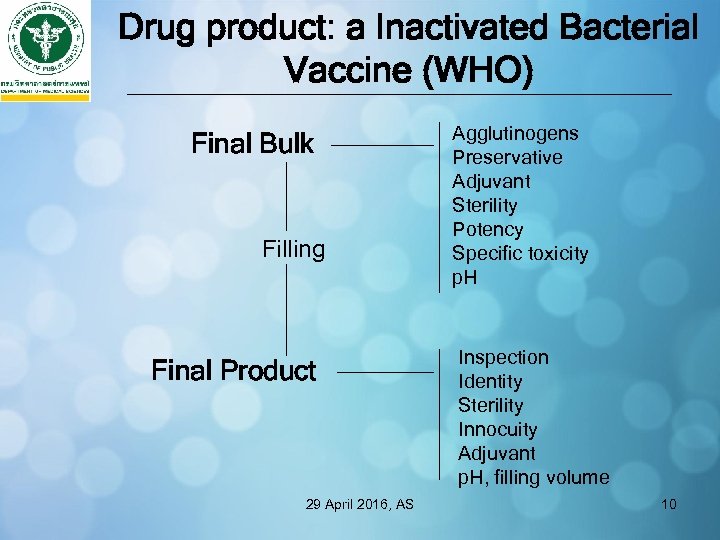
Drug product: a Inactivated Bacterial Vaccine (WHO) Final Bulk Filling Final Product 29 April 2016, AS Agglutinogens Preservative Adjuvant Sterility Potency Specific toxicity p. H Inspection Identity Sterility Innocuity Adjuvant p. H, filling volume 10
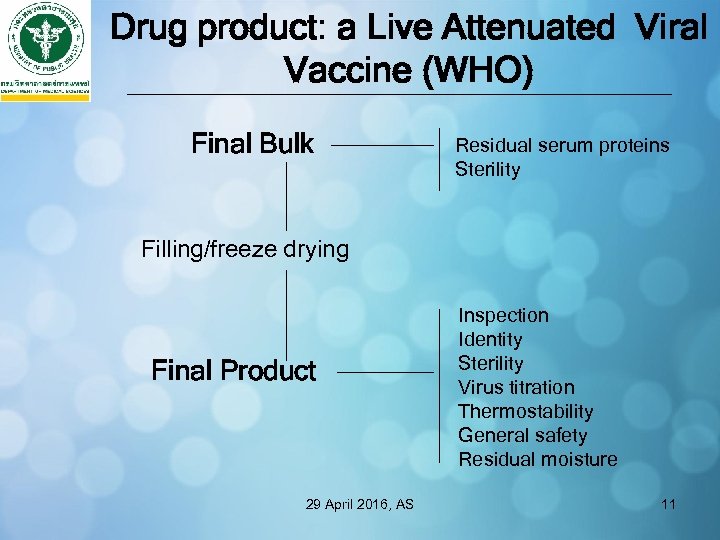
Drug product: a Live Attenuated Viral Vaccine (WHO) Final Bulk Residual serum proteins Sterility Filling/freeze drying Final Product 29 April 2016, AS Inspection Identity Sterility Virus titration Thermostability General safety Residual moisture 11
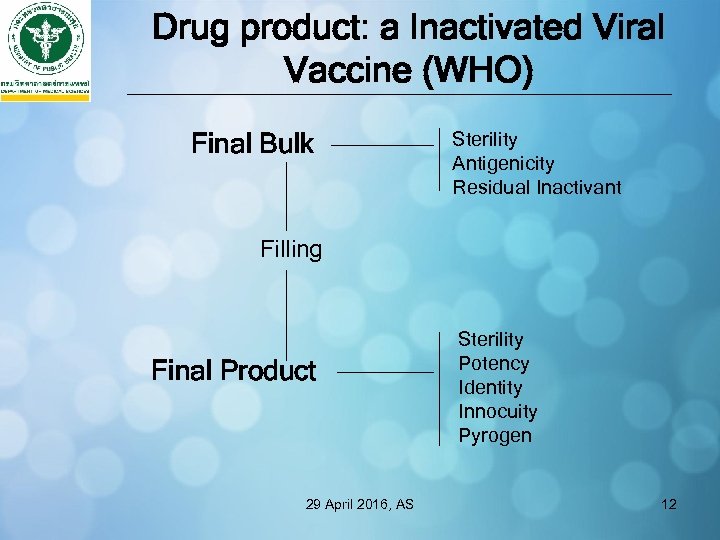
Drug product: a Inactivated Viral Vaccine (WHO) Final Bulk Sterility Antigenicity Residual Inactivant Filling Final Product 29 April 2016, AS Sterility Potency Identity Innocuity Pyrogen 12
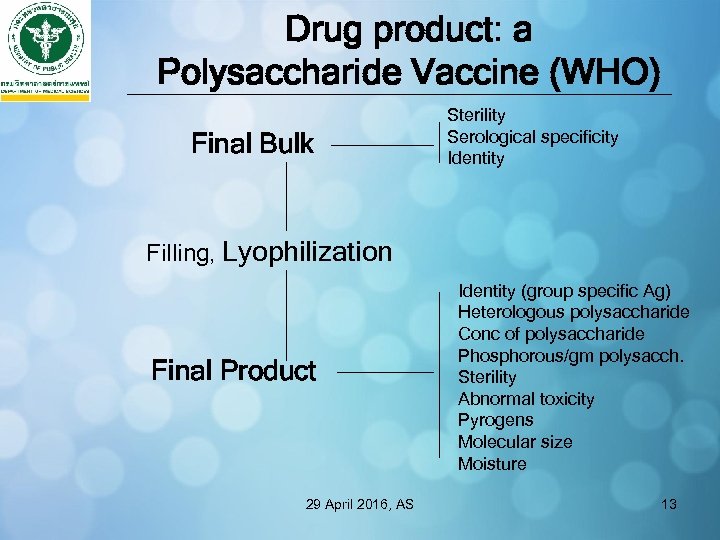
Drug product: a Polysaccharide Vaccine (WHO) Final Bulk Sterility Serological specificity Identity Filling, Lyophilization Final Product 29 April 2016, AS Identity (group specific Ag) Heterologous polysaccharide Conc of polysaccharide Phosphorous/gm polysacch. Sterility Abnormal toxicity Pyrogens Molecular size Moisture 13

Drug product: a conjugated polysaccharide vaccine (WHO) Final Bulk Sterility Filling, Lyophilization Final Product 29 April 2016, AS Identity (specific for the PRP) Potency Conc of Hib polysaccharide Preservative Sterility Abnormal toxicity (innocuity) Pyrogens Moisture 14
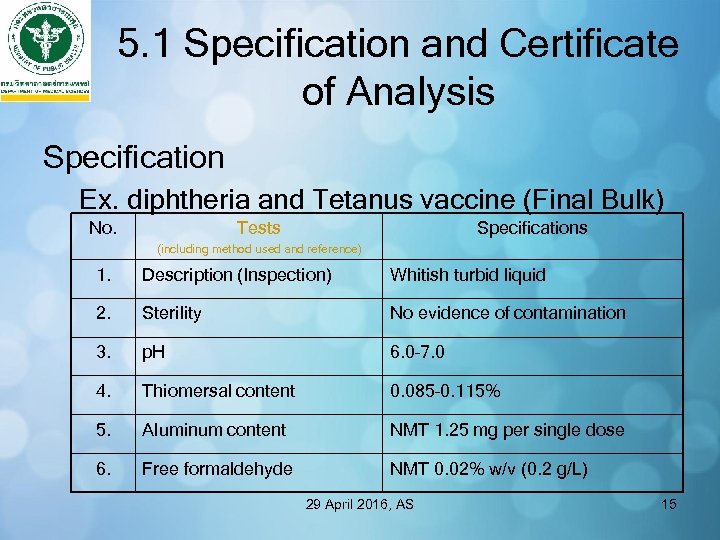
5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Specification Ex. diphtheria and Tetanus vaccine (Final Bulk) No. Tests Specifications (including method used and reference) 1. Description (Inspection) Whitish turbid liquid 2. Sterility No evidence of contamination 3. p. H 6. 0– 7. 0 4. Thiomersal content 0. 085– 0. 115% 5. Aluminum content NMT 1. 25 mg per single dose 6. Free formaldehyde NMT 0. 02% w/v (0. 2 g/L) 29 April 2016, AS 15
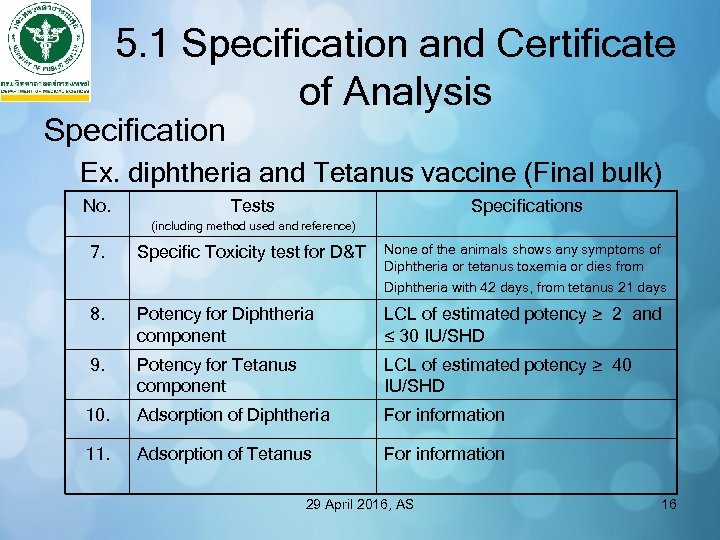
5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Specification Ex. diphtheria and Tetanus vaccine (Final bulk) No. Tests Specifications (including method used and reference) 7. Specific Toxicity test for D&T None of the animals shows any symptoms of Diphtheria or tetanus toxemia or dies from Diphtheria with 42 days, from tetanus 21 days 8. Potency for Diphtheria component LCL of estimated potency ≥ 2 and ≤ 30 IU/SHD 9. Potency for Tetanus component LCL of estimated potency ≥ 40 IU/SHD 10. Adsorption of Diphtheria For information 11. Adsorption of Tetanus For information 29 April 2016, AS 16
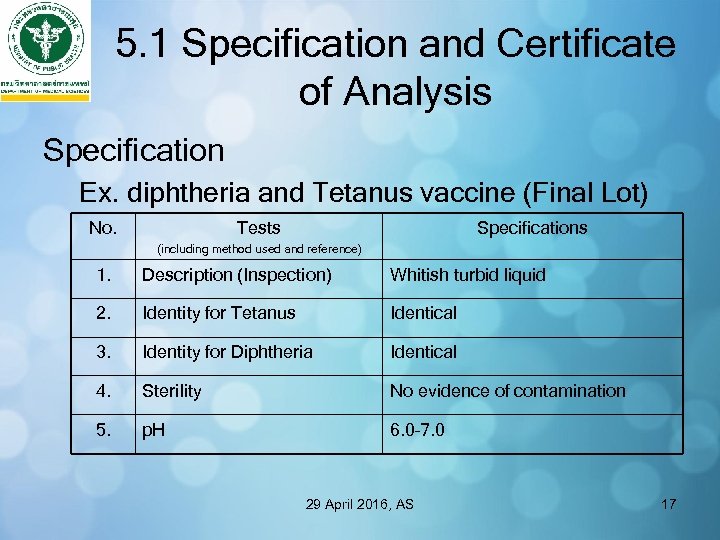
5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Specification Ex. diphtheria and Tetanus vaccine (Final Lot) No. Tests Specifications (including method used and reference) 1. Description (Inspection) Whitish turbid liquid 2. Identity for Tetanus Identical 3. Identity for Diphtheria Identical 4. Sterility No evidence of contamination 5. p. H 6. 0– 7. 0 29 April 2016, AS 17
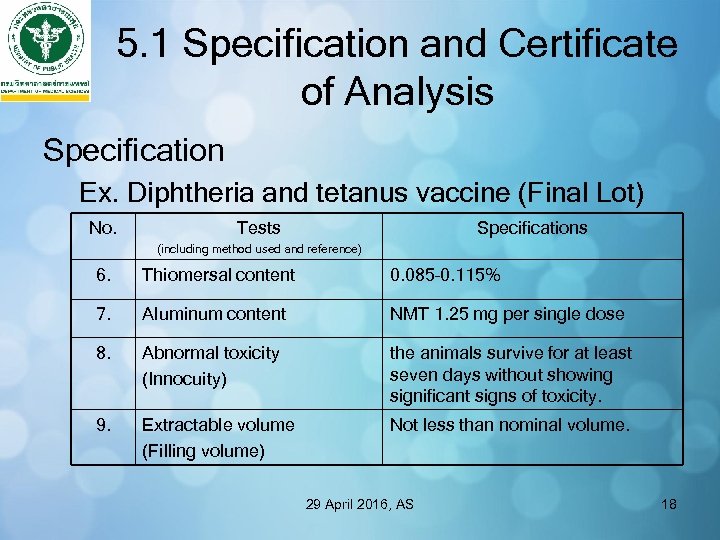
5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Specification Ex. Diphtheria and tetanus vaccine (Final Lot) No. Tests Specifications (including method used and reference) 6. Thiomersal content 0. 085– 0. 115% 7. Aluminum content NMT 1. 25 mg per single dose 8. Abnormal toxicity (Innocuity) the animals survive for at least seven days without showing significant signs of toxicity. 9. Extractable volume (Filling volume) Not less than nominal volume. 29 April 2016, AS 18
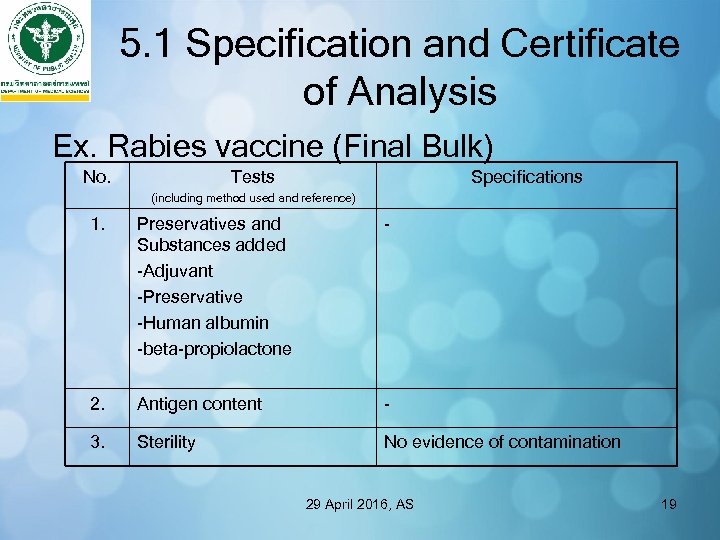
5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Ex. Rabies vaccine (Final Bulk) No. Tests Specifications (including method used and reference) 1. Preservatives and Substances added -Adjuvant -Preservative -Human albumin -beta-propiolactone - 2. Antigen content - 3. Sterility No evidence of contamination 29 April 2016, AS 19
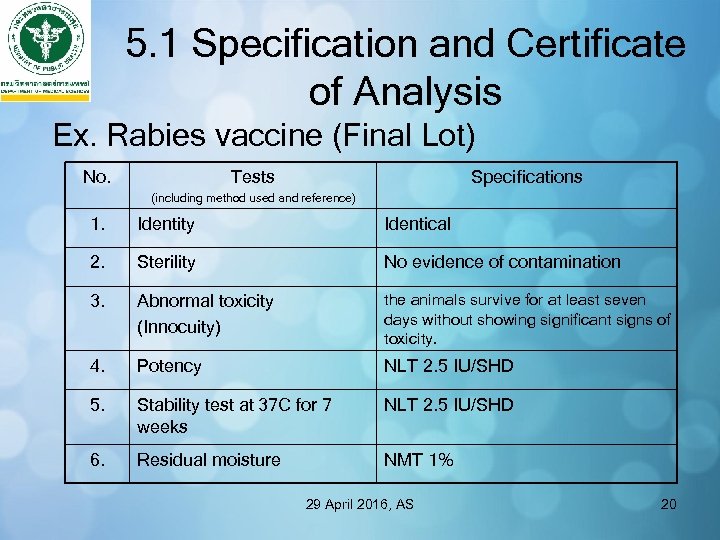
5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Ex. Rabies vaccine (Final Lot) No. Tests Specifications (including method used and reference) 1. Identity Identical 2. Sterility No evidence of contamination 3. Abnormal toxicity (Innocuity) the animals survive for at least seven days without showing significant signs of toxicity. 4. Potency NLT 2. 5 IU/SHD 5. Stability test at 37 C for 7 weeks NLT 2. 5 IU/SHD 6. Residual moisture NMT 1% 29 April 2016, AS 20

5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Ex. Rabies vaccine (Final Lot) No. Tests Specifications 7. Volume ≥ 1 ml 8. Sodium chloride 0. 85– 0. 95 % 29 April 2016, AS 21
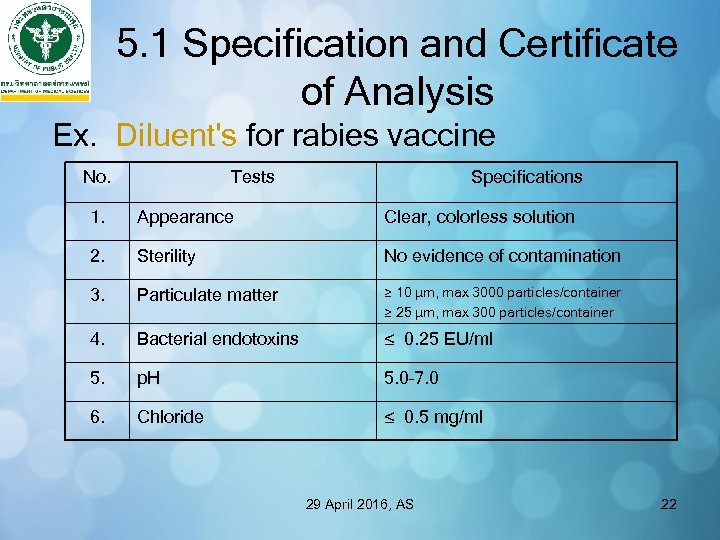
5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Ex. Diluent's for rabies vaccine No. Tests Specifications 1. Appearance Clear, colorless solution 2. Sterility No evidence of contamination 3. Particulate matter ≥ 10 µm, max 3000 particles/container ≥ 25 µm, max 300 particles/container 4. Bacterial endotoxins ≤ 0. 25 EU/ml 5. p. H 5. 0– 7. 0 6. Chloride ≤ 0. 5 mg/ml 29 April 2016, AS 22
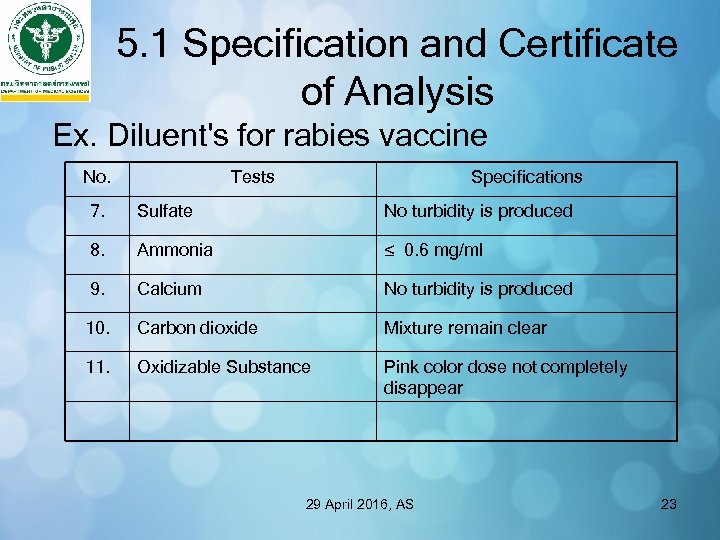
5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Ex. Diluent's for rabies vaccine No. Tests Specifications 7. Sulfate No turbidity is produced 8. Ammonia ≤ 0. 6 mg/ml 9. Calcium No turbidity is produced 10. Carbon dioxide Mixture remain clear 11. Oxidizable Substance Pink color dose not completely disappear 29 April 2016, AS 23

5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Certificate of analysis: -A batch-specific document that is used to list test methods and results, including applicable specifications, acceptance criteria, and a final batch disposition. -)USP (A list of the analytical tests, acceptance criteria, and results obtained on a particular article. 29 April 2016, AS 24

5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis Certificate of analysis: 1. Analytical tests and test procedure Ex. Sterility test (Analytical method) Direct inoculation or Membrane filtration (test procedure) 2. Specification, acceptance criteria 3. Results 29 April 2016, AS 25
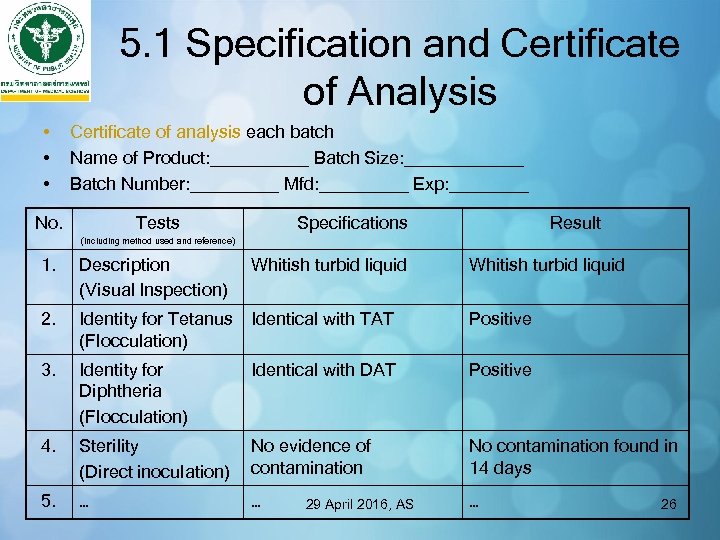
5. 1 Specification and Certificate of Analysis • • • Certificate of analysis each batch Name of Product: _____ Batch Size: ______ Batch Number: _____ Mfd: _____ Exp: ____ No. Tests Specifications Result (including method used and reference) 1. Description (Visual Inspection) Whitish turbid liquid 2. Identity for Tetanus Identical with TAT (Flocculation) Positive 3. Identity for Diphtheria (Flocculation) Identical with DAT Positive 4. Sterility (Direct inoculation) No evidence of contamination No contamination found in 14 days 5. … … … 29 April 2016, AS Whitish turbid liquid 26

5. 2 Analytical Procedures • • • ทงทเปน Compendia method และ In-House method ประกอบดวย แสดงวธการทดสอบอยางละเอยด หลกการทดสอบ สารสำคญทใช เครองมอสำคญของการทดสอบ เอกสารอางองทใชในการทดสอบ สถตทใชในการคำนวณผลการทดสอบและตวอยางการ คำนวณผล 29 April 2016, AS
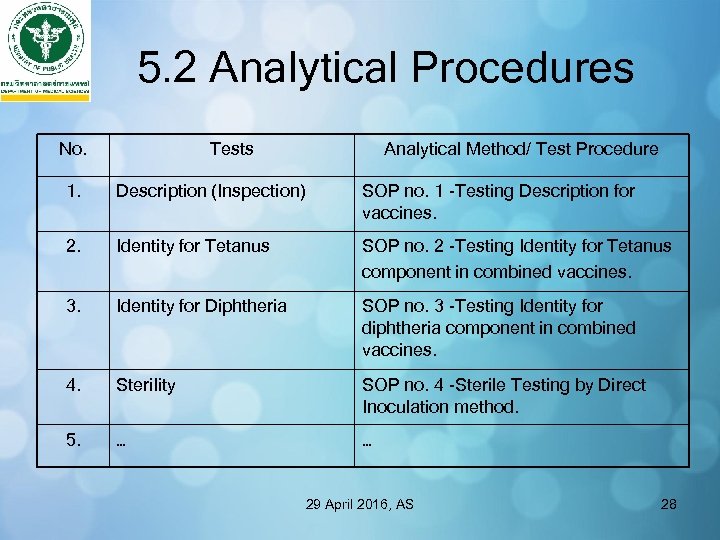
5. 2 Analytical Procedures No. Tests Analytical Method/ Test Procedure 1. Description (Inspection) SOP no. 1 -Testing Description for vaccines. 2. Identity for Tetanus SOP no. 2 -Testing Identity for Tetanus component in combined vaccines. 3. Identity for Diphtheria SOP no. 3 -Testing Identity for diphtheria component in combined vaccines. 4. Sterility SOP no. 4 -Sterile Testing by Direct Inoculation method. 5. … … 29 April 2016, AS 28
5. 3 Validation of Analytical Procedures Non compendia or In-house method • Validation Protocol • Validation Report Compendia method • Verification protocol • Verification report Reference Ex. ICH Q 2 (R 1) 29 April 2016, AS
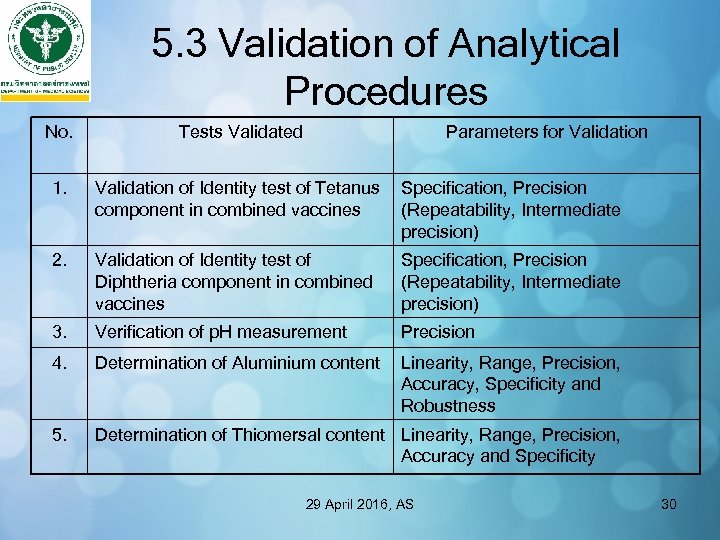
5. 3 Validation of Analytical Procedures No. Tests Validated Parameters for Validation 1. Validation of Identity test of Tetanus component in combined vaccines Specification, Precision (Repeatability, Intermediate precision) 2. Validation of Identity test of Diphtheria component in combined vaccines Specification, Precision (Repeatability, Intermediate precision) 3. Verification of p. H measurement Precision 4. Determination of Aluminium content Linearity, Range, Precision, Accuracy, Specificity and Robustness 5. Determination of Thiomersal content Linearity, Range, Precision, Accuracy and Specificity 29 April 2016, AS 30

5. 4 Batch analysis ประกอบดวย • Batch description (มการวเคราะหวจารณเหมอนหรอตางจาก clinical ถาตางทำอะไรตอ) • จำนวนสามรนการผลต • แสดงในรป Summary table • ม Summary Production Protocol (SPP) ประกอบในแตละรนการผลต 29 April 2016, AS
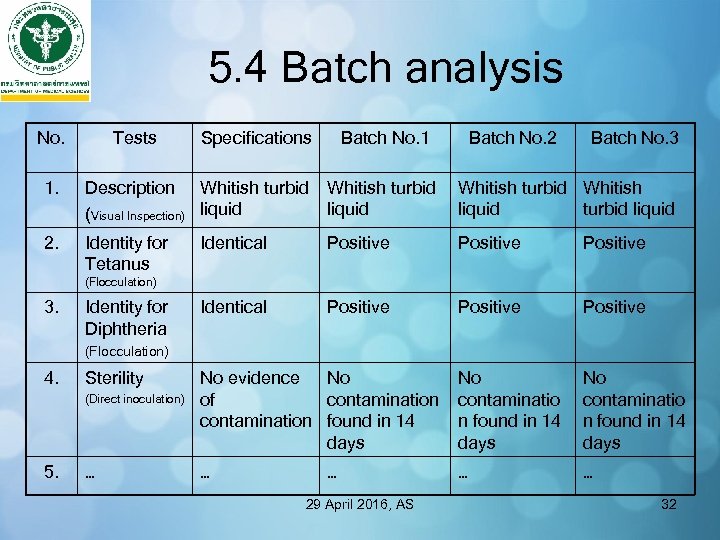
5. 4 Batch analysis No. Tests Specifications Batch No. 1 Batch No. 2 Batch No. 3 1. Description Whitish turbid liquid (Visual Inspection) liquid Whitish turbid Whitish liquid turbid liquid 2. Identity for Tetanus Identical Positive Positive No evidence No of contamination found in 14 days No contaminatio n found in 14 days … … … (Flocculation) 3. Identity for Diphtheria (Flocculation) 4. Sterility (Direct inoculation) 5. … … 29 April 2016, AS 32

5. 5 Characterization of Impurities Impurity: A foreign agent or material either introduced as part of processing (such as buffers or salts added during chromatography) or intrinsic to the nature of bioprocessing (such as product variants and cellular debris. ( 29 April 2016, AS 33

5. 5 Characterization of Impurities Impurity Profile: )ICH Q 3 B (R 2)) A description of the identified and unidentified impurities present in a drug product. 29 April 2016, AS 34

5. 5 Characterization of Impurities Impurity Profile: A description of the identified and unidentified impurities present in a typical batch of API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) produced by a specific controlled production process. It includes the identity or some qualitative analytical designation (e. g. retention time), the range of each impurity observed, and type of each identified impurity. For each API there should be an impurity profile describing the identified and unidentified impurities present in a typical batch. The impurity profile is normally dependent upon the process or origin of the API. 29 April 2016, AS 35
5. 5 Characterization of Impurities The impurities are derived from 1. Process-related impurities and contaminates: -Cell substrates (e. g. , host cell protein, host cell DNA) -Cell culture (e. g. , inducers, antibiotics, Serum, media component) -Downstream (e. g. , enzymes, chemical and biochemical processing reagents) 29 April 2016, AS 36
5. 5 Characterization of Impurities The impurities are derived from 2. Product-related impurities including degradation products: -Truncated forms: Hydrolytic enzymes or chemicals may catalyse the cleavge peptide bonds. -Other modified forms: Deamidated, isomerised, mismatched S-S linked, oxidiesd -Aggregates: includes dimers and higher multiples of the desired product. 29 April 2016, AS 37

5. 5 Characterization of Impurities การตรวจลกษณะสารเจอปน Physiochemical characterizations 1. Structural characterization and confirmation -Amino acid and Terminal Amino acid sequence -Amino acid composition -Peptide map -Sulfhydryl group (s) and disulfide bridges -Carbohydrate structure 2016, AS 29 April 38

5. 5 Characterization of Impurities 2. Physicochemical properties -Molecular weight or size -Isoform pattern -Electrophoretic pattern -Liquid chromatographic pattern -Spectroscopic profiles 29 April 2016, AS 39

5. 5 Characterization of Impurities Technique used: -SDS-PAGE -HPLC -Western-blot -Mass spectroscopy -Capillary electrophoresis -Size exclusion chromatography, etc. 29 April 2016, AS 40

5. 6 Justification of Specification The setting of specifications for drug substance and drug product is part of an overall control strategy which includes control of raw materials and excipients, inprocess testing, process evaluation or validation, adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices, stability testing, and testing for consistency of lots. When combined in total, these elements provide assurance that the appropriate quality of the product will be maintained. Since specifications are chosen to confirm the quality rather than to characterize the product, the manufacturer should provide the rationale and justification for including and/or excluding testing for specific quality attributes. The following points should be taken into consideration when establish in scientifically justifiable specifications. (ICH Q 6 B) 29 April 2016, AS 41

5. 6 Justification of Specification Based on data from • Linked to a manufacturing process. • Account for the stability of drug substance and drug product. • Linked to preclinical and clinical studies. • Linked to analytical procedures 29 April 2016, AS 42

Reference • คมอ/หลกเกณฑการขนทะเบยนตำรบยาสามญใหม (New Generic Drugs) แบบ ASEAN HARMONIZATION, กนยายน 2556 • WHO TRS No. 980, 2014 (D, T) • WHO TRS No. 941, 2007 (Rabies) • ICH Q 6 B • PHARMACEUTICAL AND VACCINE QUALITY ILLUSTRATED, ÜMİT H. KARTOĞLU, 2015 • https//: www. ispe. org/glossary? term 29 April 2016, AS 43

Question? t. HAn. K You
e9017ef77e34c4bc4d596e5cb352b267.ppt