26abf2a0019ce7191df18c04a552de82.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Continuous Auditing: A Core Competency for Regulatory Compliance Sabino Ramos Regional Director, ACL Services
Continuous Auditing: A Core Competency for Regulatory Compliance Sabino Ramos Regional Director, ACL Services
 Today’s Agenda Continuous auditing: what it is and why it is important Relationship between continuous auditing (CA) and continuous controls monitoring (CCM) Impact of CA and CCM on controls assessment and testing to support regulatory compliance Practical implementation issues Q&A
Today’s Agenda Continuous auditing: what it is and why it is important Relationship between continuous auditing (CA) and continuous controls monitoring (CCM) Impact of CA and CCM on controls assessment and testing to support regulatory compliance Practical implementation issues Q&A
 The Need for Continuous Auditing Continuous auditing à Discussed for many years à Increasing extent of implementation, but not widespread SOX Sec 404 now driving the need to à Efficiently and cost-effectively sustain controls assessment and testing efforts à Determine on a timely basis when control deficiencies occur à Quantify the impact of control deficiencies à Improve effectiveness of controls à Gain assurance over effectiveness of controls
The Need for Continuous Auditing Continuous auditing à Discussed for many years à Increasing extent of implementation, but not widespread SOX Sec 404 now driving the need to à Efficiently and cost-effectively sustain controls assessment and testing efforts à Determine on a timely basis when control deficiencies occur à Quantify the impact of control deficiencies à Improve effectiveness of controls à Gain assurance over effectiveness of controls
 IIA/ACL 2006 Survey: Impact of Compliance Recent poll of 858 audit executives worldwide at corporations with more than $100 M in revenues (50% over $1 B) à 20% felt independence has been compromised à 44% were concerned that ability to complete thorough and timely audits impacted à 44% agreed that emphasis on financial reporting-related risks created imbalance in overall risk-based approach to internal auditing
IIA/ACL 2006 Survey: Impact of Compliance Recent poll of 858 audit executives worldwide at corporations with more than $100 M in revenues (50% over $1 B) à 20% felt independence has been compromised à 44% were concerned that ability to complete thorough and timely audits impacted à 44% agreed that emphasis on financial reporting-related risks created imbalance in overall risk-based approach to internal auditing
 CA & CCM in the Spotlight “I am pleased to see that the audit professionals surveyed [2005 CAE Survey] strongly endorsed the value of continuous monitoring and auditing to support ongoing Sarbanes-Oxley compliance. Until there is mainstream adoption of these best practices, companies will continue to experience challenges managing their compliance processes. Technologies that automate and monitor controls – on an ongoing basis – will be critical for achieving true success in the future. " Honorable David M. Walker Comptroller General of the United States and Chair of the Center for Continuous Auditing Advisory Board
CA & CCM in the Spotlight “I am pleased to see that the audit professionals surveyed [2005 CAE Survey] strongly endorsed the value of continuous monitoring and auditing to support ongoing Sarbanes-Oxley compliance. Until there is mainstream adoption of these best practices, companies will continue to experience challenges managing their compliance processes. Technologies that automate and monitor controls – on an ongoing basis – will be critical for achieving true success in the future. " Honorable David M. Walker Comptroller General of the United States and Chair of the Center for Continuous Auditing Advisory Board
 IIA 2005 Global Technology Audit Guide #3 “Continuous Auditing: Implications for Assurance, Monitoring and Risk Assessment” à Key concepts à Relationship of Continuous Auditing, Continuous Monitoring and Continuous Assurance à Areas for the Application of Continuous Auditing à Implementing Continuous Auditing à Examples à Standards à Continuous Auditing Self Assessment
IIA 2005 Global Technology Audit Guide #3 “Continuous Auditing: Implications for Assurance, Monitoring and Risk Assessment” à Key concepts à Relationship of Continuous Auditing, Continuous Monitoring and Continuous Assurance à Areas for the Application of Continuous Auditing à Implementing Continuous Auditing à Examples à Standards à Continuous Auditing Self Assessment
 Continuous Auditing Shift from traditional approach of periodic cyclical audit processes Method used to automatically perform control and risk assessments on an ongoing basis Allows audit to provide ongoing risk and control assessments Technology is key
Continuous Auditing Shift from traditional approach of periodic cyclical audit processes Method used to automatically perform control and risk assessments on an ongoing basis Allows audit to provide ongoing risk and control assessments Technology is key
 Traditional Role of Technology in Controls Assessment & Testing Internal Audit has demonstrated effectiveness of using transactional data analysis to test internal controls on historical basis: à Examines transactions to determine if evidence of an exception to a control rule à Examines transactions to determine if there is an indication of events occurring for which no control rule has been established Data analysis also used successfully to test controls not directly evidenced by transactional data à Review of ERP access / authorization tables to determine inappropriate Segregation of Duties à Security log reviews
Traditional Role of Technology in Controls Assessment & Testing Internal Audit has demonstrated effectiveness of using transactional data analysis to test internal controls on historical basis: à Examines transactions to determine if evidence of an exception to a control rule à Examines transactions to determine if there is an indication of events occurring for which no control rule has been established Data analysis also used successfully to test controls not directly evidenced by transactional data à Review of ERP access / authorization tables to determine inappropriate Segregation of Duties à Security log reviews
 Limitations of Traditional Audit Approach Retrospective view à Analysis frequently occurs long after transaction has taken place à Too late for action Lack of timely visibility into control risks and deficiencies Problems escalate, increasing business risk The Solution Independently test all transactions for compliance with controls at, or soon after, point at which they occur
Limitations of Traditional Audit Approach Retrospective view à Analysis frequently occurs long after transaction has taken place à Too late for action Lack of timely visibility into control risks and deficiencies Problems escalate, increasing business risk The Solution Independently test all transactions for compliance with controls at, or soon after, point at which they occur
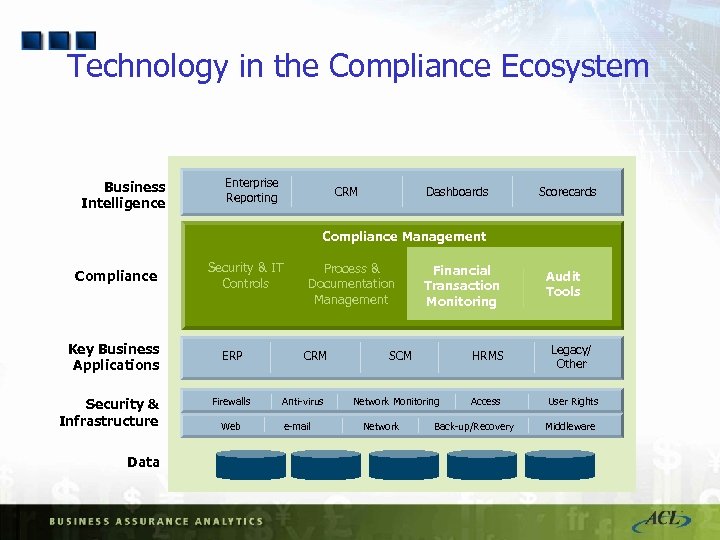 Technology in the Compliance Ecosystem Business Intelligence Enterprise Reporting CRM Dashboards Scorecards Compliance Management Compliance Key Business Applications Security & Infrastructure Data Security & IT Controls ERP Firewalls Web Process & Documentation Management CRM Anti-virus e-mail Financial Transaction Monitoring HRMS SCM Network Monitoring Network Audit Tools Legacy/ Other Access User Rights Back-up/Recovery Middleware
Technology in the Compliance Ecosystem Business Intelligence Enterprise Reporting CRM Dashboards Scorecards Compliance Management Compliance Key Business Applications Security & Infrastructure Data Security & IT Controls ERP Firewalls Web Process & Documentation Management CRM Anti-virus e-mail Financial Transaction Monitoring HRMS SCM Network Monitoring Network Audit Tools Legacy/ Other Access User Rights Back-up/Recovery Middleware
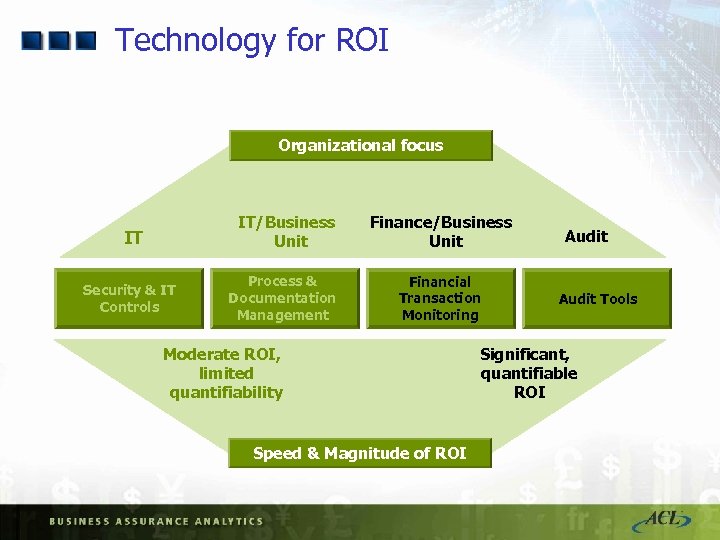 Technology for ROI Organizational focus IT IT/Business Unit Finance/Business Unit Security & IT Controls Process & Documentation Management Financial Transaction Monitoring Moderate ROI, limited quantifiability Speed & Magnitude of ROI Audit Tools Significant, quantifiable ROI
Technology for ROI Organizational focus IT IT/Business Unit Finance/Business Unit Security & IT Controls Process & Documentation Management Financial Transaction Monitoring Moderate ROI, limited quantifiability Speed & Magnitude of ROI Audit Tools Significant, quantifiable ROI
 Continuous Controls Monitoring Process performed by management to determine whether policies and controls are operating effectively Establishes control objectives and assurance assertions – and uses automated tests to identify activities and transactions that fail to comply with controls Allows management to fix control problems on a timely basis – improves controls and improves operational performance Technology is key
Continuous Controls Monitoring Process performed by management to determine whether policies and controls are operating effectively Establishes control objectives and assurance assertions – and uses automated tests to identify activities and transactions that fail to comply with controls Allows management to fix control problems on a timely basis – improves controls and improves operational performance Technology is key
 Model for Continuous Monitoring of Controls Identify control rule for each internal control point within given business process area (using COSO framework) Establish tests that, using transactional data analysis, will validate each control rule Establish tests that will identify suspect transactions, using transactional profiling techniques Subject all transactions to suite of tests on regular, timely basis Identify all transactions that fail tests Notify appropriate personnel Investigate any transactions that fail and, as appropriate à Correct the transactions à Correct the control problem
Model for Continuous Monitoring of Controls Identify control rule for each internal control point within given business process area (using COSO framework) Establish tests that, using transactional data analysis, will validate each control rule Establish tests that will identify suspect transactions, using transactional profiling techniques Subject all transactions to suite of tests on regular, timely basis Identify all transactions that fail tests Notify appropriate personnel Investigate any transactions that fail and, as appropriate à Correct the transactions à Correct the control problem
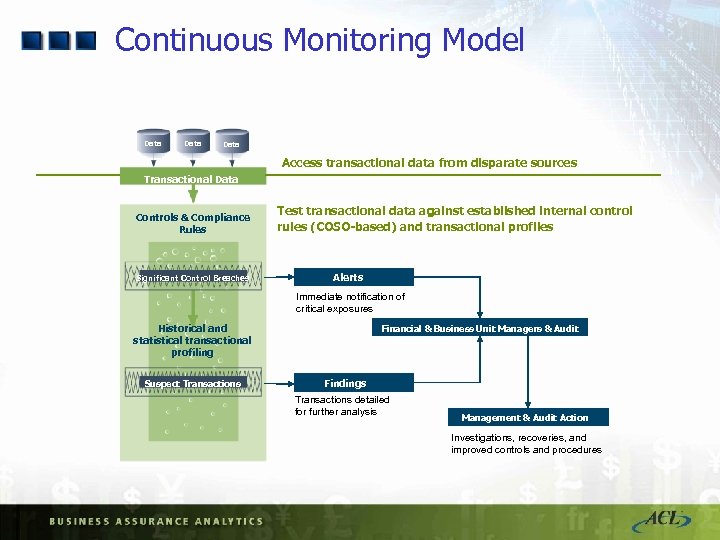 Continuous Monitoring Model Data Access transactional data from disparate sources Transactional Data Controls & Compliance Rules Significant Control Breaches Test transactional data against established internal control rules (COSO-based) and transactional profiles Alerts Immediate notification of critical exposures Historical and statistical transactional profiling Suspect Transactions Financial & Business Unit Managers & Audit Findings Transactions detailed for further analysis Management & Audit Action Investigations, recoveries, and improved controls and procedures
Continuous Monitoring Model Data Access transactional data from disparate sources Transactional Data Controls & Compliance Rules Significant Control Breaches Test transactional data against established internal control rules (COSO-based) and transactional profiles Alerts Immediate notification of critical exposures Historical and statistical transactional profiling Suspect Transactions Financial & Business Unit Managers & Audit Findings Transactions detailed for further analysis Management & Audit Action Investigations, recoveries, and improved controls and procedures
 Model for Continuous Monitoring of Controls Issues of timing and independence In theory, ideal is for all transactions to be tested in “real time”, before they complete Some systems, particularly ERPs, designed to do this In practice, controls in ERPs rarely implemented in comprehensive way Pragmatic model is to independently test all transactions and not rely exclusively upon system controls
Model for Continuous Monitoring of Controls Issues of timing and independence In theory, ideal is for all transactions to be tested in “real time”, before they complete Some systems, particularly ERPs, designed to do this In practice, controls in ERPs rarely implemented in comprehensive way Pragmatic model is to independently test all transactions and not rely exclusively upon system controls
 CA and CCM: An Integrated Approach Many of techniques used in CA and CCM similar How can both approaches be integrated? How does this affect roles and responsibilities of audit and management?
CA and CCM: An Integrated Approach Many of techniques used in CA and CCM similar How can both approaches be integrated? How does this affect roles and responsibilities of audit and management?
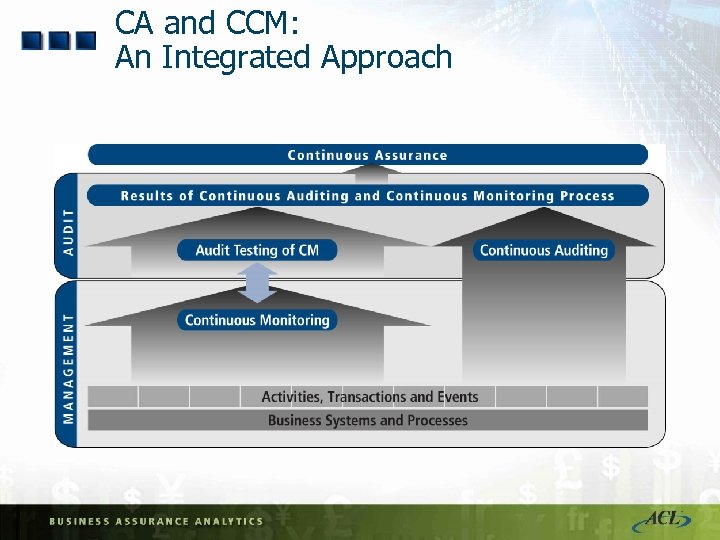 CA and CCM: An Integrated Approach
CA and CCM: An Integrated Approach
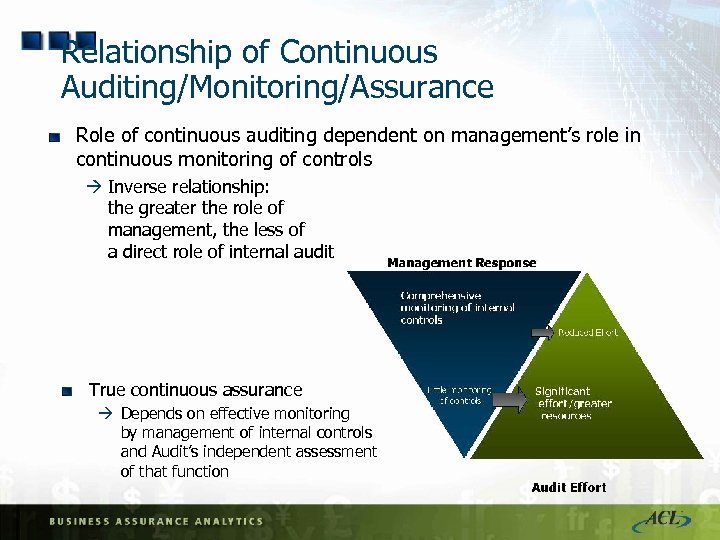 Relationship of Continuous Auditing/Monitoring/Assurance Role of continuous auditing dependent on management’s role in continuous monitoring of controls à Inverse relationship: the greater the role of management, the less of a direct role of internal audit True continuous assurance à Depends on effective monitoring by management of internal controls and Audit’s independent assessment of that function
Relationship of Continuous Auditing/Monitoring/Assurance Role of continuous auditing dependent on management’s role in continuous monitoring of controls à Inverse relationship: the greater the role of management, the less of a direct role of internal audit True continuous assurance à Depends on effective monitoring by management of internal controls and Audit’s independent assessment of that function
 CA and CCM: An Integrated Approach Effective use of automated CA and CCM techniques can substantially reduce time required for regulatory controls assessment and testing Helps make clear to management that they –not audit – primarily responsible for determining effectiveness of controls Audit (internal and external) needs to be able to rely upon à CA processes à Integrity of CCM process
CA and CCM: An Integrated Approach Effective use of automated CA and CCM techniques can substantially reduce time required for regulatory controls assessment and testing Helps make clear to management that they –not audit – primarily responsible for determining effectiveness of controls Audit (internal and external) needs to be able to rely upon à CA processes à Integrity of CCM process
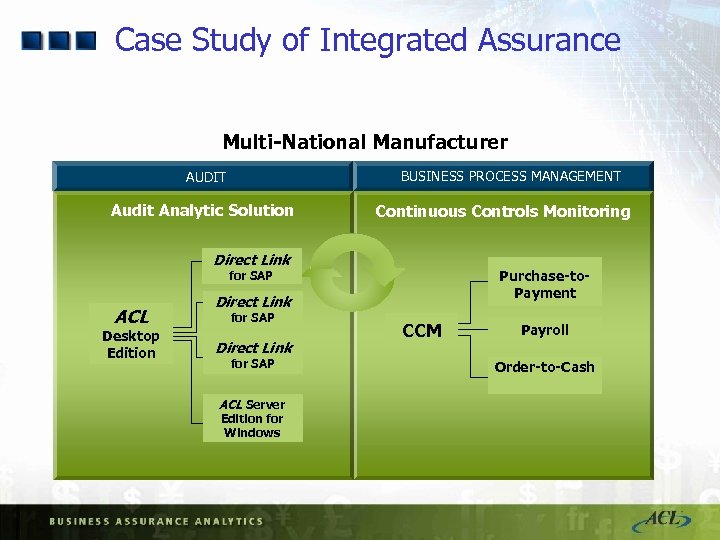 Case Study of Integrated Assurance Multi-National Manufacturer BUSINESS PROCESS MANAGEMENT AUDIT Audit Analytic Solution Continuous Controls Monitoring Direct Link Purchase-to. Payment for SAP ACL Desktop Edition Direct Link for SAP ACL Server Edition for Windows CCM Payroll Order-to-Cash
Case Study of Integrated Assurance Multi-National Manufacturer BUSINESS PROCESS MANAGEMENT AUDIT Audit Analytic Solution Continuous Controls Monitoring Direct Link Purchase-to. Payment for SAP ACL Desktop Edition Direct Link for SAP ACL Server Edition for Windows CCM Payroll Order-to-Cash
 Scope and Applicability of CCM and CA Any controls area where à Data available à Control rule can be established à Examination of data evidence of controls’ effectiveness Business/financial process transactions à Financial, operational and regulatory controls within transactional process areas à Use COSO control objectives and audit assertions to determine rules to be tested System controls à Access and authorization tables (SOD) à Access and security logs à System configuration settings à Use Cob. IT control objectives
Scope and Applicability of CCM and CA Any controls area where à Data available à Control rule can be established à Examination of data evidence of controls’ effectiveness Business/financial process transactions à Financial, operational and regulatory controls within transactional process areas à Use COSO control objectives and audit assertions to determine rules to be tested System controls à Access and authorization tables (SOD) à Access and security logs à System configuration settings à Use Cob. IT control objectives
 Automation of Controls Testing Must be possible to define rule of a control, for example, à Invoice payment not to be entered and approved by same person à Payments >$X must be approved by Y à Inventory items shipped must be matched by invoice details à ERP application control for duplicate payments should be on Or, indicators of control breaches need to be able to be established, for example, à Transactions that fall outside of statistical norms à Profile/trend analysis
Automation of Controls Testing Must be possible to define rule of a control, for example, à Invoice payment not to be entered and approved by same person à Payments >$X must be approved by Y à Inventory items shipped must be matched by invoice details à ERP application control for duplicate payments should be on Or, indicators of control breaches need to be able to be established, for example, à Transactions that fall outside of statistical norms à Profile/trend analysis
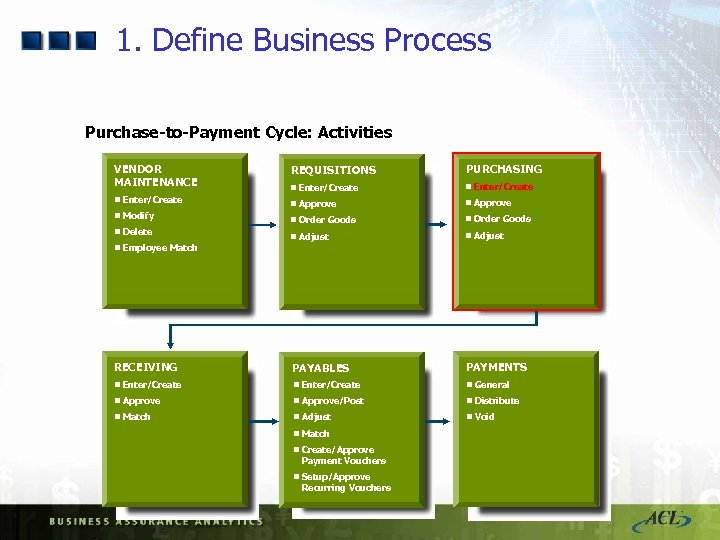 1. Define Business Process Purchase-to-Payment Cycle: Activities VENDOR MAINTENANCE REQUISITIONS PURCHASING n Enter/Create n Approve n Modify n Order Goods n Delete n Adjust RECEIVING PAYABLES PAYMENTS n Enter/Create n General n Approve/Post n Distribute n Match n Adjust n Void n Employee Match n Create/Approve Payment Vouchers n Setup/Approve Recurring Vouchers
1. Define Business Process Purchase-to-Payment Cycle: Activities VENDOR MAINTENANCE REQUISITIONS PURCHASING n Enter/Create n Approve n Modify n Order Goods n Delete n Adjust RECEIVING PAYABLES PAYMENTS n Enter/Create n General n Approve/Post n Distribute n Match n Adjust n Void n Employee Match n Create/Approve Payment Vouchers n Setup/Approve Recurring Vouchers
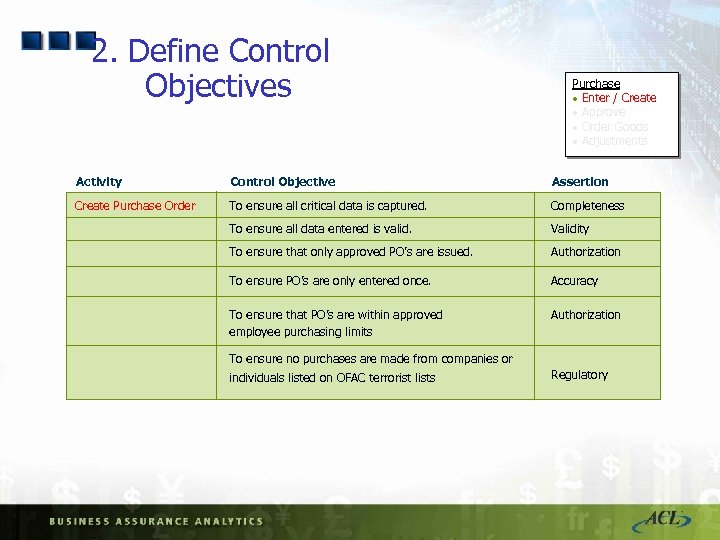 2. Define Control Objectives Purchase · Enter / Create · Approve · Order Goods · Adjustments Activity Control Objective Assertion Create Purchase Order To ensure all critical data is captured. Completeness To ensure all data entered is valid. Validity To ensure that only approved PO’s are issued. Authorization To ensure PO’s are only entered once. Accuracy To ensure that PO’s are within approved employee purchasing limits Authorization To ensure no purchases are made from companies or individuals listed on OFAC terrorist lists Regulatory
2. Define Control Objectives Purchase · Enter / Create · Approve · Order Goods · Adjustments Activity Control Objective Assertion Create Purchase Order To ensure all critical data is captured. Completeness To ensure all data entered is valid. Validity To ensure that only approved PO’s are issued. Authorization To ensure PO’s are only entered once. Accuracy To ensure that PO’s are within approved employee purchasing limits Authorization To ensure no purchases are made from companies or individuals listed on OFAC terrorist lists Regulatory
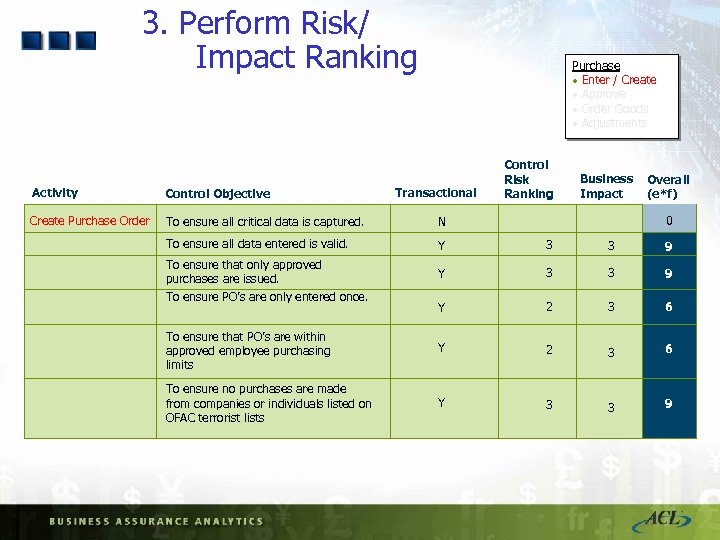 3. Perform Risk/ Impact Ranking Purchase · Enter / Create · Approve · Order Goods · Adjustments Transactional Control Risk Ranking Business Impact Overall (e*f) Activity Control Objective Create Purchase Order To ensure all critical data is captured. N To ensure all data entered is valid. Y 3 3 9 Y 2 3 6 To ensure that PO’s are within approved employee purchasing limits Y 2 3 6 To ensure no purchases are made from companies or individuals listed on OFAC terrorist lists Y 3 3 9 To ensure that only approved purchases are issued. To ensure PO’s are only entered once. 0
3. Perform Risk/ Impact Ranking Purchase · Enter / Create · Approve · Order Goods · Adjustments Transactional Control Risk Ranking Business Impact Overall (e*f) Activity Control Objective Create Purchase Order To ensure all critical data is captured. N To ensure all data entered is valid. Y 3 3 9 Y 2 3 6 To ensure that PO’s are within approved employee purchasing limits Y 2 3 6 To ensure no purchases are made from companies or individuals listed on OFAC terrorist lists Y 3 3 9 To ensure that only approved purchases are issued. To ensure PO’s are only entered once. 0
 Technology Requirements for Integrated Approach Comprehensive range of control tests Ability to access and monitor data, transactions and activities from across the enterprise Handle large transactional volumes with no negative impact on operational system performance Security and control over monitoring process Auditability of monitoring process Integration with ERM software Provide variable parameters for tests Manage alert notifications Ability to view and manage results Ad hoc analysis to support CCM and CA process
Technology Requirements for Integrated Approach Comprehensive range of control tests Ability to access and monitor data, transactions and activities from across the enterprise Handle large transactional volumes with no negative impact on operational system performance Security and control over monitoring process Auditability of monitoring process Integration with ERM software Provide variable parameters for tests Manage alert notifications Ability to view and manage results Ad hoc analysis to support CCM and CA process
 The Result Improved efficiency and effectiveness of Sec 404 assessments Timely determination whether controls in application and financial reporting systems are operating effectively Rapid identification of specific deficiencies and anomalies Independent assurance of integrity of transactions processed by business application systems An additional layer of control Reduction in costs and revenue leakage Quantification of control deficiencies
The Result Improved efficiency and effectiveness of Sec 404 assessments Timely determination whether controls in application and financial reporting systems are operating effectively Rapid identification of specific deficiencies and anomalies Independent assurance of integrity of transactions processed by business application systems An additional layer of control Reduction in costs and revenue leakage Quantification of control deficiencies
 Key Steps to Implementation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Establish audit objectives and requirements Gain executive-level support Ascertain degree to which management is performing monitoring role Select appropriate technology solutions Identify information sources and gain access Understand business processes and identify key controls and risks Build audit skill set Manage and report results
Key Steps to Implementation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Establish audit objectives and requirements Gain executive-level support Ascertain degree to which management is performing monitoring role Select appropriate technology solutions Identify information sources and gain access Understand business processes and identify key controls and risks Build audit skill set Manage and report results
 Implementation Challenges Timely data access Minimizing impact on systems’ operational performance Defining appropriate analytics Setting appropriate thresholds for exceptions Developing suitable scoring / weighting mechanism to prioritize exceptions Management of results
Implementation Challenges Timely data access Minimizing impact on systems’ operational performance Defining appropriate analytics Setting appropriate thresholds for exceptions Developing suitable scoring / weighting mechanism to prioritize exceptions Management of results
 Implementation Issues Managing the CA/CM process: Executive sponsorship Managing notifications and results Varying parameters and thresholds Ranking and quantification of findings Response to findings / case management
Implementation Issues Managing the CA/CM process: Executive sponsorship Managing notifications and results Varying parameters and thresholds Ranking and quantification of findings Response to findings / case management
 Audit Reliance on Continuous Controls Monitoring Validation of control monitoring tests à Design à Processing Control of the Continuous Auditing process à Change controls à Totals reconciliations à Audit trails Security over access to the CCM system Security over changes to tests and test parameters Processing audit trail Follow up procedures – response to control deficiencies detected
Audit Reliance on Continuous Controls Monitoring Validation of control monitoring tests à Design à Processing Control of the Continuous Auditing process à Change controls à Totals reconciliations à Audit trails Security over access to the CCM system Security over changes to tests and test parameters Processing audit trail Follow up procedures – response to control deficiencies detected
 ACL Experience Increasing recognition by internal audit and operational management that continuous controls monitoring process should be owned by management Internal audit designing procedures around integrated continuous auditing and controls monitoring processes External auditing firms beginning to consider issues of audit reliance on continuous controls monitoring – security and control process a significant concern ROI argument for continuous controls monitoring repeatedly validated
ACL Experience Increasing recognition by internal audit and operational management that continuous controls monitoring process should be owned by management Internal audit designing procedures around integrated continuous auditing and controls monitoring processes External auditing firms beginning to consider issues of audit reliance on continuous controls monitoring – security and control process a significant concern ROI argument for continuous controls monitoring repeatedly validated
 Benefits Increased scope of audit activities Increased ability to mitigate risk Reduced cost of internal control assessment Improvements to financial operations Reduced financial errors and potential for fraud Reduced revenue leakage for improved bottom-line results Sustainable and cost-effective means to support compliance
Benefits Increased scope of audit activities Increased ability to mitigate risk Reduced cost of internal control assessment Improvements to financial operations Reduced financial errors and potential for fraud Reduced revenue leakage for improved bottom-line results Sustainable and cost-effective means to support compliance
 Benefits Quantification of control deficiencies Independent assurance of integrity of transactions to support compliance à Confidence that controls are working as intended Return on compliance investment by identifying opportunities for à Improving operational efficiencies à Detecting fraud à Reducing revenue leakage Documented evidence for internal and external auditors
Benefits Quantification of control deficiencies Independent assurance of integrity of transactions to support compliance à Confidence that controls are working as intended Return on compliance investment by identifying opportunities for à Improving operational efficiencies à Detecting fraud à Reducing revenue leakage Documented evidence for internal and external auditors
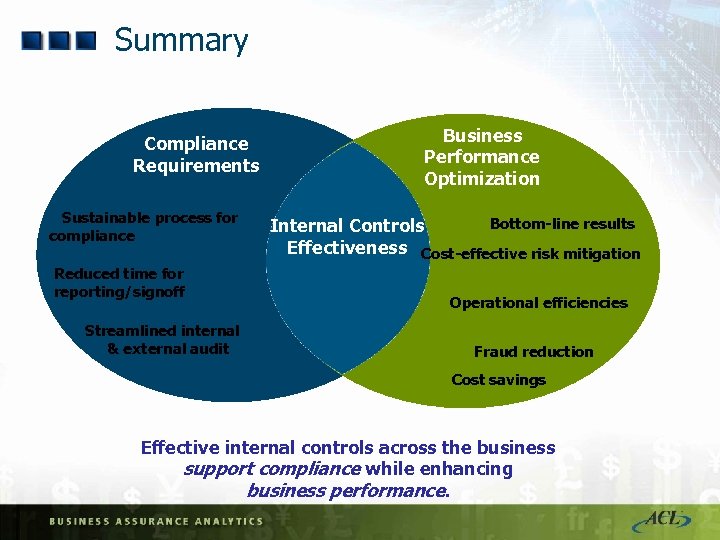 Summary Compliance Requirements Sustainable process for compliance Reduced time for reporting/signoff Streamlined internal & external audit Business Performance Optimization Bottom-line results Internal Controls Effectiveness Cost-effective risk mitigation Operational efficiencies Fraud reduction Cost savings Effective internal controls across the business support compliance while enhancing business performance.
Summary Compliance Requirements Sustainable process for compliance Reduced time for reporting/signoff Streamlined internal & external audit Business Performance Optimization Bottom-line results Internal Controls Effectiveness Cost-effective risk mitigation Operational efficiencies Fraud reduction Cost savings Effective internal controls across the business support compliance while enhancing business performance.
 Questions? Sabino Ramos Regional Director ACL Services Ltd +1 -604 -646 -4265 Sabino_ramos@acl. com www. acl. com
Questions? Sabino Ramos Regional Director ACL Services Ltd +1 -604 -646 -4265 Sabino_ramos@acl. com www. acl. com



