b374edc25aded2ece0aa6bcbb17162d8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Contents of the presentation 1. Introduction: Water and waste water situation in Germany 2. Procedures, contents of the waste water statistics in Germany 3. International Reporting on waste water (e. g. Joint Questionnaire) 4. Problems to fulfill the requirements © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 1 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
Contents of the presentation 1. Introduction: Water and waste water situation in Germany 2. Procedures, contents of the waste water statistics in Germany 3. International Reporting on waste water (e. g. Joint Questionnaire) 4. Problems to fulfill the requirements © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 1 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
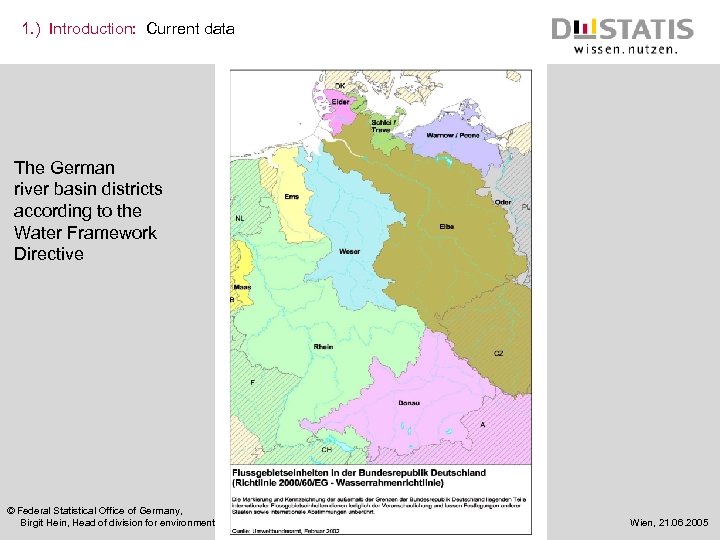 1. ) Introduction: Current data The German river basin districts according to the Water Framework Directive © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 2 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
1. ) Introduction: Current data The German river basin districts according to the Water Framework Directive © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 2 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
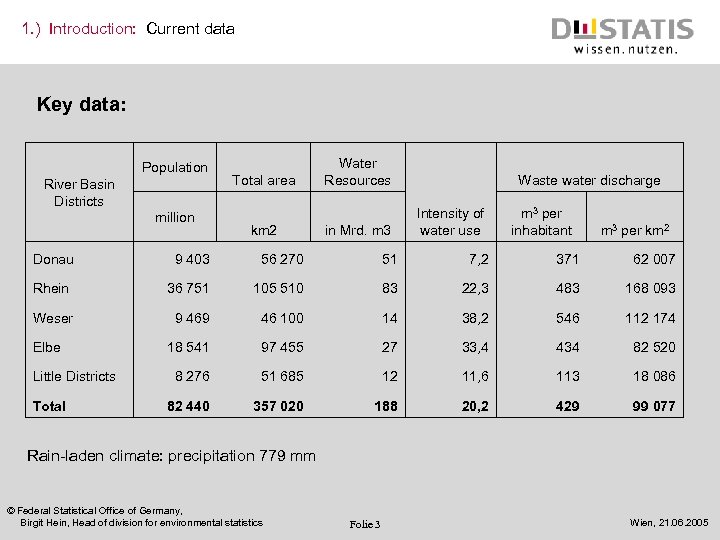 1. ) Introduction: Current data Key data: Population River Basin Districts million Total area km 2 Water Resources in Mrd. m 3 Waste water discharge Intensity of water use m 3 per inhabitant m 3 per km 2 Donau 9 403 56 270 51 7, 2 371 62 007 Rhein 36 751 105 510 83 22, 3 483 168 093 Weser 9 46 100 14 38, 2 546 112 174 18 541 97 455 27 33, 4 434 82 520 Little Districts 8 276 51 685 12 11, 6 113 18 086 Total 82 440 357 020 188 20, 2 429 99 077 Elbe Rain-laden climate: precipitation 779 mm © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 3 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
1. ) Introduction: Current data Key data: Population River Basin Districts million Total area km 2 Water Resources in Mrd. m 3 Waste water discharge Intensity of water use m 3 per inhabitant m 3 per km 2 Donau 9 403 56 270 51 7, 2 371 62 007 Rhein 36 751 105 510 83 22, 3 483 168 093 Weser 9 46 100 14 38, 2 546 112 174 18 541 97 455 27 33, 4 434 82 520 Little Districts 8 276 51 685 12 11, 6 113 18 086 Total 82 440 357 020 188 20, 2 429 99 077 Elbe Rain-laden climate: precipitation 779 mm © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 3 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
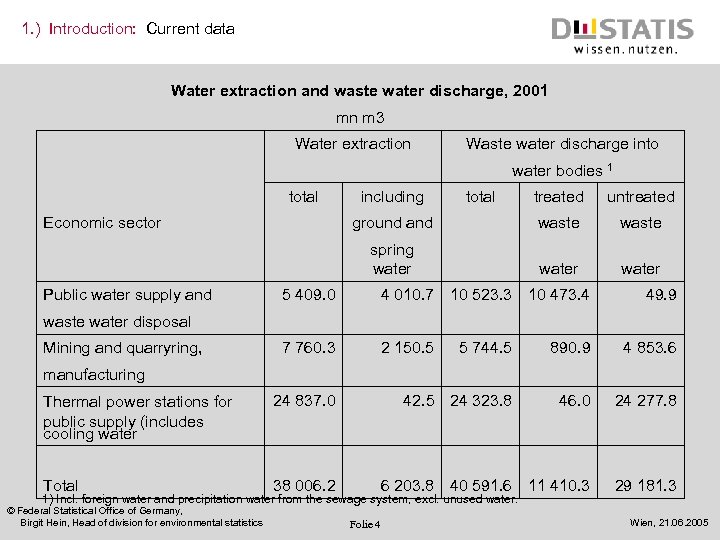 1. ) Introduction: Current data Water extraction and waste water discharge, 2001 mn m 3 Water extraction Public water supply and waste water disposal Mining and quarryring, manufacturing Thermal power stations for public supply (includes cooling water Total water bodies 1 Economic sector Waste water discharge into total including total treated ground and waste spring water 5 409. 0 4 010. 7 10 523. 3 10 473. 4 49. 9 7 760. 3 2 150. 5 5 744. 5 890. 9 4 853. 6 42. 5 24 323. 8 46. 0 24 277. 8 24 837. 0 6 203. 8 40 591. 6 11 410. 3 29 181. 3 38 006. 2 1) Incl. foreign water and precipitation water from the sewage system, excl. unused water. © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics untreated Folie 4 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
1. ) Introduction: Current data Water extraction and waste water discharge, 2001 mn m 3 Water extraction Public water supply and waste water disposal Mining and quarryring, manufacturing Thermal power stations for public supply (includes cooling water Total water bodies 1 Economic sector Waste water discharge into total including total treated ground and waste spring water 5 409. 0 4 010. 7 10 523. 3 10 473. 4 49. 9 7 760. 3 2 150. 5 5 744. 5 890. 9 4 853. 6 42. 5 24 323. 8 46. 0 24 277. 8 24 837. 0 6 203. 8 40 591. 6 11 410. 3 29 181. 3 38 006. 2 1) Incl. foreign water and precipitation water from the sewage system, excl. unused water. © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics untreated Folie 4 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
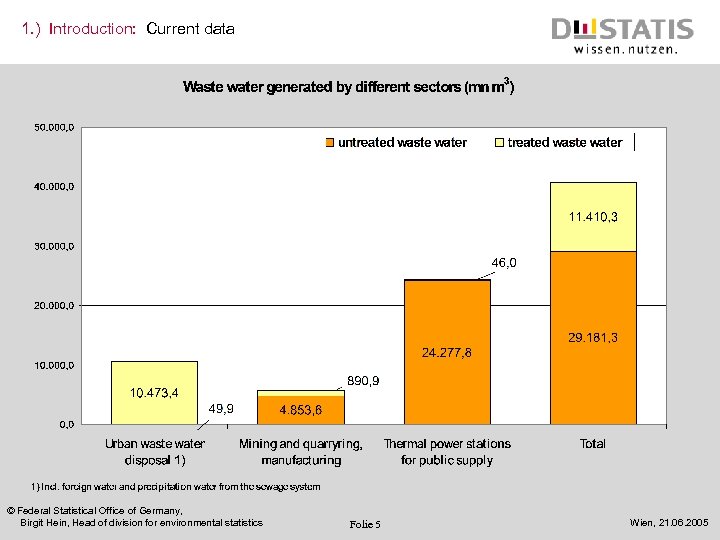 1. ) Introduction: Current data © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 5 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
1. ) Introduction: Current data © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 5 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
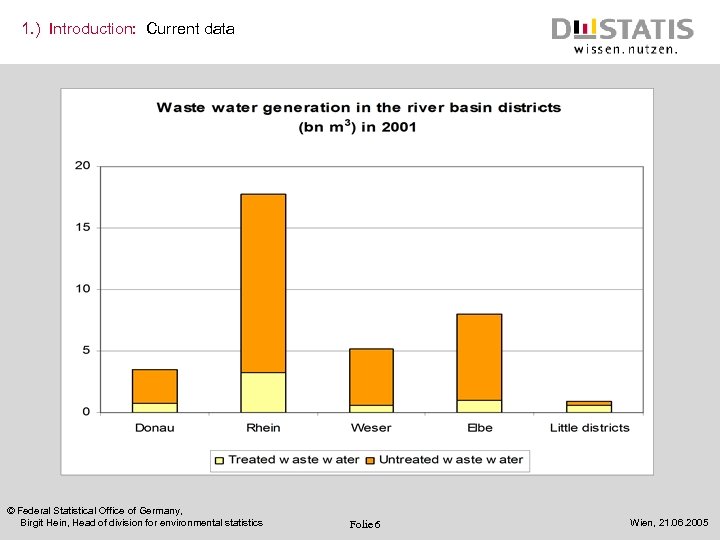 1. ) Introduction: Current data © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 6 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
1. ) Introduction: Current data © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 6 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
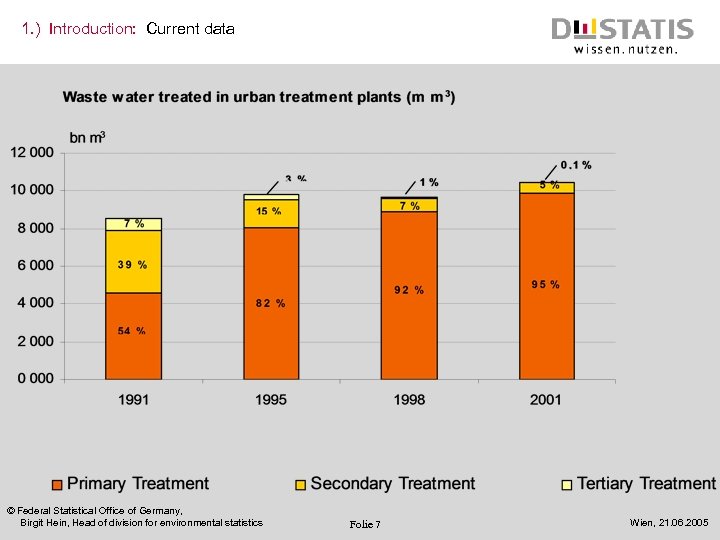 1. ) Introduction: Current data © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 7 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
1. ) Introduction: Current data © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 7 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
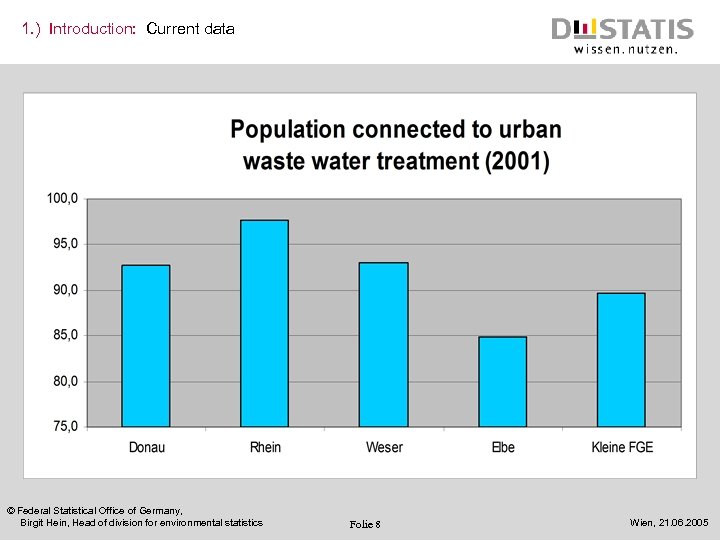 1. ) Introduction: Current data © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 8 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
1. ) Introduction: Current data © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 8 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
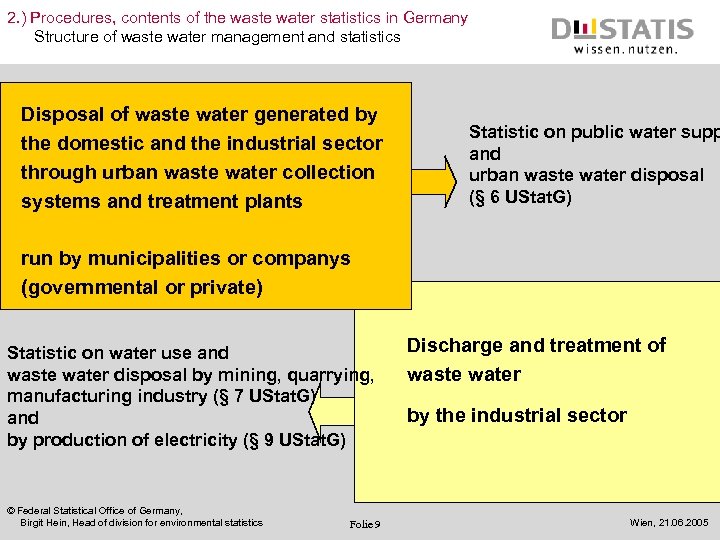 2. ) Procedures, contents of the waste water statistics in Germany Structure of waste water management and statistics Disposal of waste water generated by the domestic and the industrial sector through urban waste water collection systems and treatment plants Statistic on public water supp and urban waste water disposal (§ 6 UStat. G) run by municipalities or companys (governmental or private) Statistic on water use and waste water disposal by mining, quarrying, manufacturing industry (§ 7 UStat. G) and by production of electricity (§ 9 UStat. G) © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 9 Discharge and treatment of waste water by the industrial sector Wien, 21. 06. 2005
2. ) Procedures, contents of the waste water statistics in Germany Structure of waste water management and statistics Disposal of waste water generated by the domestic and the industrial sector through urban waste water collection systems and treatment plants Statistic on public water supp and urban waste water disposal (§ 6 UStat. G) run by municipalities or companys (governmental or private) Statistic on water use and waste water disposal by mining, quarrying, manufacturing industry (§ 7 UStat. G) and by production of electricity (§ 9 UStat. G) © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 9 Discharge and treatment of waste water by the industrial sector Wien, 21. 06. 2005
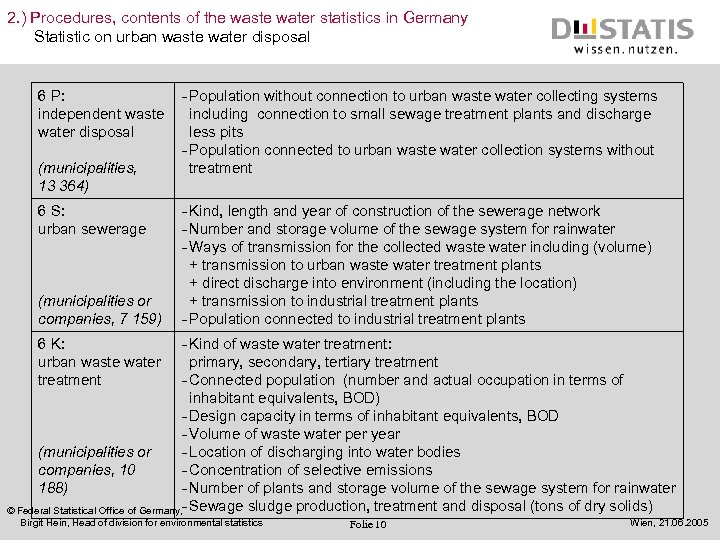 2. ) Procedures, contents of the waste water statistics in Germany Statistic on urban waste water disposal 6 P: - Population without connection to urban waste water collecting systems independent waste including connection to small sewage treatment plants and discharge water disposal less pits - Population connected to urban waste water collection systems without (municipalities, treatment 13 364) 6 S: urban sewerage (municipalities or companies, 7 159) - Kind, length and year of construction of the sewerage network - Number and storage volume of the sewage system for rainwater - Ways of transmission for the collected waste water including (volume) + transmission to urban waste water treatment plants + direct discharge into environment (including the location) + transmission to industrial treatment plants - Population connected to industrial treatment plants - Kind of waste water treatment: primary, secondary, tertiary treatment - Connected population (number and actual occupation in terms of inhabitant equivalents, BOD) - Design capacity in terms of inhabitant equivalents, BOD - Volume of waste water per year (municipalities or - Location of discharging into water bodies companies, 10 - Concentration of selective emissions 188) - Number of plants and storage volume of the sewage system for rainwater © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, - Sewage sludge production, treatment and disposal (tons of dry solids) 6 K: urban waste water treatment Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 10 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
2. ) Procedures, contents of the waste water statistics in Germany Statistic on urban waste water disposal 6 P: - Population without connection to urban waste water collecting systems independent waste including connection to small sewage treatment plants and discharge water disposal less pits - Population connected to urban waste water collection systems without (municipalities, treatment 13 364) 6 S: urban sewerage (municipalities or companies, 7 159) - Kind, length and year of construction of the sewerage network - Number and storage volume of the sewage system for rainwater - Ways of transmission for the collected waste water including (volume) + transmission to urban waste water treatment plants + direct discharge into environment (including the location) + transmission to industrial treatment plants - Population connected to industrial treatment plants - Kind of waste water treatment: primary, secondary, tertiary treatment - Connected population (number and actual occupation in terms of inhabitant equivalents, BOD) - Design capacity in terms of inhabitant equivalents, BOD - Volume of waste water per year (municipalities or - Location of discharging into water bodies companies, 10 - Concentration of selective emissions 188) - Number of plants and storage volume of the sewage system for rainwater © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, - Sewage sludge production, treatment and disposal (tons of dry solids) 6 K: urban waste water treatment Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 10 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
 2. ) Procedures, contents of the waste water statistics in Germany Statistic on industrial waste water disposal Respondents: units of mining, quarrying, manufacturing and production of electricity (2001: 1 7 A / 9 A: - Origin of waste water (cooling or production processes) Part IV - Transmission to Waste water + urban waste water collecting systems and treatment plants generation + own industrial treatment plants and + other external industrial treatment plants discharge - direct discharge into environment (including the location) and concentration of selective emissions 7 B / 9 B: - Kind of waste water treatment Waste water primary, secondary, tertiary treatment and special procedures treatment - Transmission to + urban waste water collecting systems and treatment plants + other external industrial treatment plants - Transmission to another own industrial treatment plant - direct discharge into environment (including the location) and concentration of selective emissions - Sewage sludge production, treatment and disposal (tons of dry solids) © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 11 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
2. ) Procedures, contents of the waste water statistics in Germany Statistic on industrial waste water disposal Respondents: units of mining, quarrying, manufacturing and production of electricity (2001: 1 7 A / 9 A: - Origin of waste water (cooling or production processes) Part IV - Transmission to Waste water + urban waste water collecting systems and treatment plants generation + own industrial treatment plants and + other external industrial treatment plants discharge - direct discharge into environment (including the location) and concentration of selective emissions 7 B / 9 B: - Kind of waste water treatment Waste water primary, secondary, tertiary treatment and special procedures treatment - Transmission to + urban waste water collecting systems and treatment plants + other external industrial treatment plants - Transmission to another own industrial treatment plant - direct discharge into environment (including the location) and concentration of selective emissions - Sewage sludge production, treatment and disposal (tons of dry solids) © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 11 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
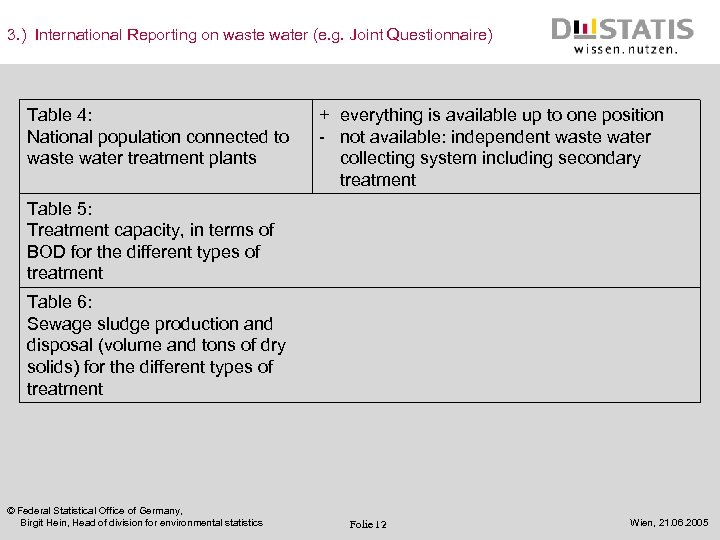 3. ) International Reporting on waste water (e. g. Joint Questionnaire) Table 4: National population connected to waste water treatment plants + everything is available up to one position - not available: independent waste water collecting system including secondary treatment Table 5: Treatment capacity, in terms of BOD for the different types of treatment Table 6: Sewage sludge production and disposal (volume and tons of dry solids) for the different types of treatment © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 12 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
3. ) International Reporting on waste water (e. g. Joint Questionnaire) Table 4: National population connected to waste water treatment plants + everything is available up to one position - not available: independent waste water collecting system including secondary treatment Table 5: Treatment capacity, in terms of BOD for the different types of treatment Table 6: Sewage sludge production and disposal (volume and tons of dry solids) for the different types of treatment © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 12 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
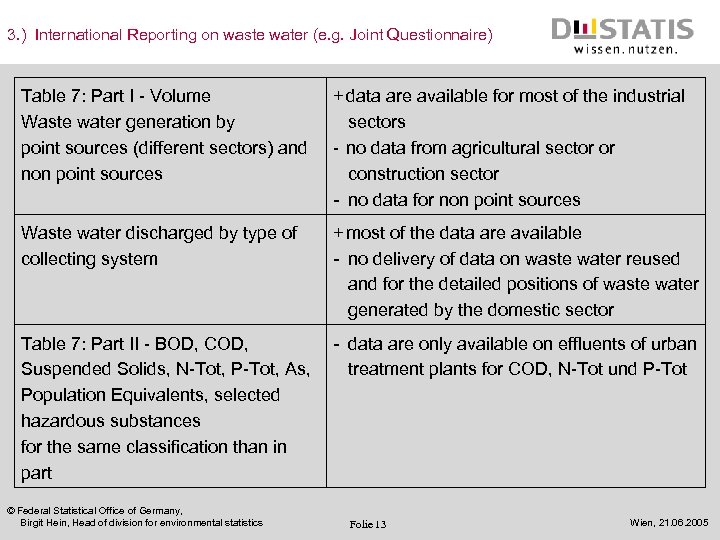 3. ) International Reporting on waste water (e. g. Joint Questionnaire) Table 7: Part I - Volume Waste water generation by point sources (different sectors) and non point sources + data are available for most of the industrial sectors - no data from agricultural sector or construction sector - no data for non point sources Waste water discharged by type of collecting system + most of the data are available - no delivery of data on waste water reused and for the detailed positions of waste water generated by the domestic sector Table 7: Part II - BOD, COD, - data are only available on effluents of urban Suspended Solids, N-Tot, P-Tot, As, treatment plants for COD, N-Tot und P-Tot Population Equivalents, selected hazardous substances for the same classification than in part © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 13 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
3. ) International Reporting on waste water (e. g. Joint Questionnaire) Table 7: Part I - Volume Waste water generation by point sources (different sectors) and non point sources + data are available for most of the industrial sectors - no data from agricultural sector or construction sector - no data for non point sources Waste water discharged by type of collecting system + most of the data are available - no delivery of data on waste water reused and for the detailed positions of waste water generated by the domestic sector Table 7: Part II - BOD, COD, - data are only available on effluents of urban Suspended Solids, N-Tot, P-Tot, As, treatment plants for COD, N-Tot und P-Tot Population Equivalents, selected hazardous substances for the same classification than in part © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 13 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
 4. Problems to fulfill the requirements General reasons: • • • For collecting new data a modification of the law is necessary • „ Länder“ also collect data, this results in double surveys parallel to the statistics The long tradition hinders modification Actually the politics plan to reduce the „statistical burden“ for enterprises - Water politics are primarily in their hand - The European Commission requires data, e. g. Urban Waste Water Directive“ • Other additonal data collection: Environmental agency; EPER • • • Data collection is conducted only every three years Some sectors are not included (services, contstruction, agriculture) Overlapping parts are difficult to report while the statistics are subdivided in two parts © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 14 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
4. Problems to fulfill the requirements General reasons: • • • For collecting new data a modification of the law is necessary • „ Länder“ also collect data, this results in double surveys parallel to the statistics The long tradition hinders modification Actually the politics plan to reduce the „statistical burden“ for enterprises - Water politics are primarily in their hand - The European Commission requires data, e. g. Urban Waste Water Directive“ • Other additonal data collection: Environmental agency; EPER • • • Data collection is conducted only every three years Some sectors are not included (services, contstruction, agriculture) Overlapping parts are difficult to report while the statistics are subdivided in two parts © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 14 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
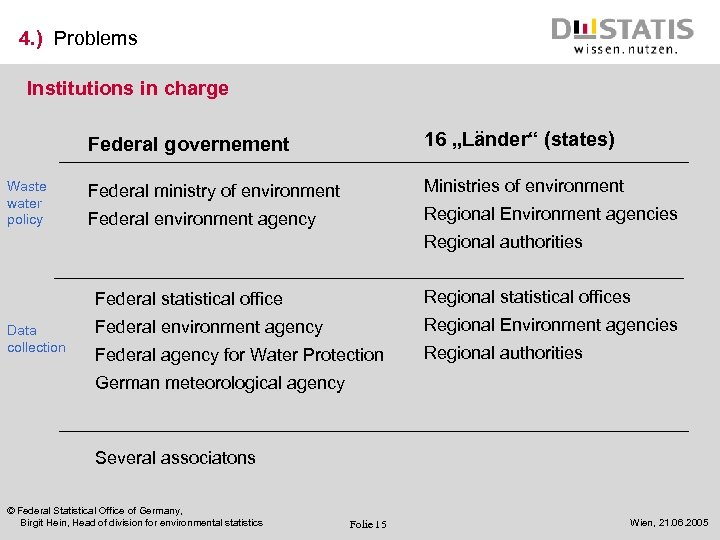 4. ) Problems Institutions in charge Federal governement Waste water policy 16 „Länder“ (states) Federal ministry of environment Ministries of environment Federal environment agency Regional Environment agencies Regional authorities Federal statistical office Data collection Regional statistical offices Federal environment agency Regional Environment agencies Federal agency for Water Protection Regional authorities German meteorological agency Several associatons © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 15 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
4. ) Problems Institutions in charge Federal governement Waste water policy 16 „Länder“ (states) Federal ministry of environment Ministries of environment Federal environment agency Regional Environment agencies Regional authorities Federal statistical office Data collection Regional statistical offices Federal environment agency Regional Environment agencies Federal agency for Water Protection Regional authorities German meteorological agency Several associatons © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 15 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
 4. Problems to fulfill the requirements Specific reasons • • Degree of detailing is particular very high, but the political need is not clear the tables are often organized from a more theoretical point of view Deviation of definitions Conclusion • • • Concentration of the priority data Extension of the use of other databases (UGR, EPER) Improvement of coordination between the different requirements (primarily within the EU) © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 16 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
4. Problems to fulfill the requirements Specific reasons • • Degree of detailing is particular very high, but the political need is not clear the tables are often organized from a more theoretical point of view Deviation of definitions Conclusion • • • Concentration of the priority data Extension of the use of other databases (UGR, EPER) Improvement of coordination between the different requirements (primarily within the EU) © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 16 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
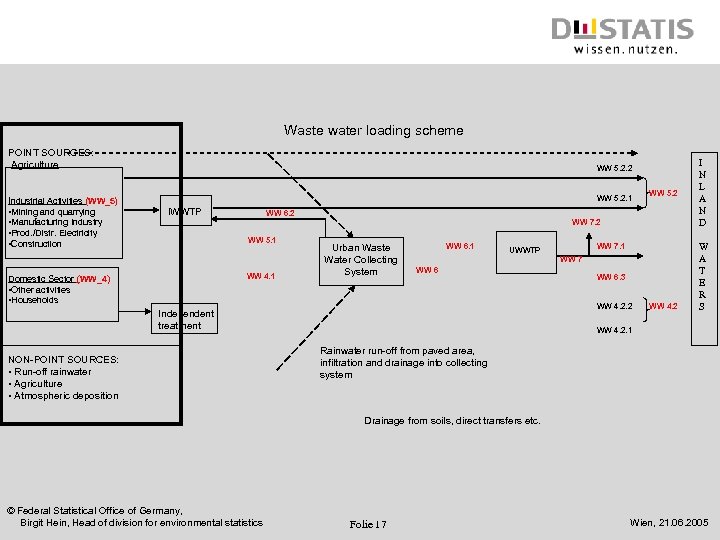 Waste water loading scheme POINT SOURCES: Agriculture WW 5. 2. 2 Industrial Activities (WW_5) WW 5. 2. 1 • Mining and quarrying • Manufacturing Industry • Prod. /Distr. Electricity • Construction IWWTP WW 5. 2 WW 6. 2 WW 7. 2 WW 5. 1 WW 4. 1 Domestic Sector (WW_4) • Other activities • Households Urban Waste Water Collecting System WW 6. 1 WW 7 WW 6. 3 WW 4. 2. 2 Independent treatment NON-POINT SOURCES: • Run-off rainwater • Agriculture • Atmospheric deposition WW 7. 1 UWWTP WW 4. 2 I N L A N D W A T E R S WW 4. 2. 1 Rainwater run-off from paved area, infiltration and drainage into collecting system Drainage from soils, direct transfers etc. © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 17 Wien, 21. 06. 2005
Waste water loading scheme POINT SOURCES: Agriculture WW 5. 2. 2 Industrial Activities (WW_5) WW 5. 2. 1 • Mining and quarrying • Manufacturing Industry • Prod. /Distr. Electricity • Construction IWWTP WW 5. 2 WW 6. 2 WW 7. 2 WW 5. 1 WW 4. 1 Domestic Sector (WW_4) • Other activities • Households Urban Waste Water Collecting System WW 6. 1 WW 7 WW 6. 3 WW 4. 2. 2 Independent treatment NON-POINT SOURCES: • Run-off rainwater • Agriculture • Atmospheric deposition WW 7. 1 UWWTP WW 4. 2 I N L A N D W A T E R S WW 4. 2. 1 Rainwater run-off from paved area, infiltration and drainage into collecting system Drainage from soils, direct transfers etc. © Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Birgit Hein, Head of division for environmental statistics Folie 17 Wien, 21. 06. 2005


