88f37d88633d10613b367684e19033be.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Content Management Interoperability Services An Introduction

Outline ‣ What we are announcing ‣ Why is this important to customers? (I. e. the business case) ‣ The current standards landscape ‣ What is CMIS? o o Goals Target scenarios Workshop Timeline

What are we announcing Content Management Interoperability Services Proposed Standard ‣ Starting in October 2006, EMC, IBM and Microsoft joined forces to propose the first Web services standard for exchanging content with and between ECM systems. ‣ Additional collaborators now include: Alfresco, Open. Text, Oracle and SAP ‣ We are now announcing that the proposed standard is called the Content Management Interoperability Services (CMIS) and will be registered for public comment with OASIS starting 9/10 ‣ What we are releasing: ‣ ‣ Common Domain Model for CM (Data Model, Capabilities) Bindings: SOAP for System to System, REST/Atom for System to Application
Why Customers Want Interoperability Tech Pubs Engineering Sales Challenges Multiple content repositories and vendor specific systems ‣ Discrete business units ‣ Application specific ECM solutions ‣ Mergers and acquisitions Results ‣ ‣ ‣ Stove-piped information Discrete environments Multiple investments Added costs Loss of business flexibility Increased complexity for developers
Benefits of Interoperability Tech Pubs Engineering Sales Benefits Improved user access to content Increases enterprise effectiveness ‣ Easier for users to get access to the right information at the right time from their application Reduces application development costs and grows ISV’s addressable market ‣ Develop application once to access CMIScompliant repositories Protects customer’s investment in applications and repositories ‣ Developed applications can run against multiple repositories Propels ECM industry to the next level of growth ‣ Defines a set of standards, technology and interface, that works across multiple vendor and technology providers.
Current options for integrating ECM systems Migrate content from one system to another. Build/buy one-off connectors to enable interoperability in limited scenarios. Federation Current standards are not inclusive of all major ECM vendors We need an open standard that works across heterogeneous systems

Existing Standards Content Management Related Standards ‣ Java Content Repository (JSR 170/283) ‣ Atom / Atom Publishing Protocol: (APP) ‣ Java Portlet Specification (JSR 168), ASP. Net Webparts, ‣ Web Services for Remote Portlets (WSRP) Web. DAV ‣ Other industry standards-related activities ‣ i. ECM Consortium ‣ ECM Publicly Available Specification (PAS) through British Standards Institution (BSI)

CMIS Goals ‣ A standard for sharing information stored in disparate repositories that is designed to: Ensure interoperability for people and for applications among multiple content repositories across all platforms o Enable applications to target one or more ECM repositories uniformly for core content services ‣ Easy mapping to existing ECM systems ‣ Provide several protocol bindings using the common domain model: ‣ Exploit web technologies o Expose standard set of APIs for existing capabilities of CM repositories o Leverage existing content o Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) o Representational State Transfer (REST) / ATOM o o Web 2. 0 Internet Scale Service-orientation Resource-orientation
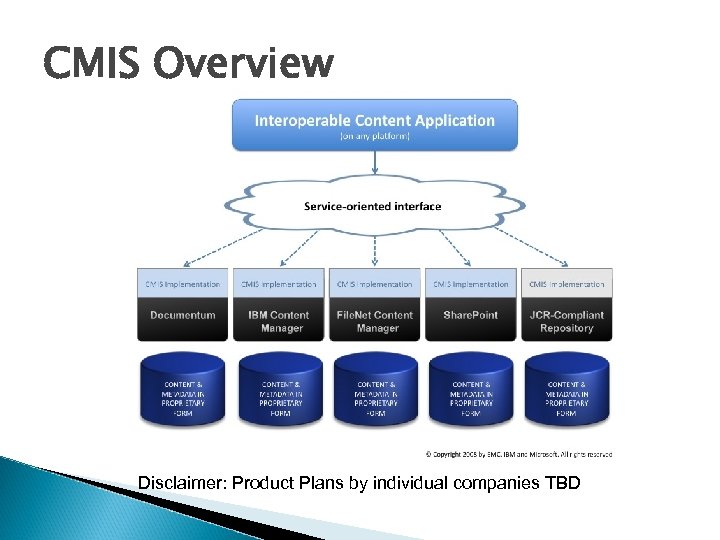
CMIS Overview Disclaimer: Product Plans by individual companies TBD

CMIS Non-Goals What CMIS is not intended to do ‣ ‣ Expose ALL capabilities of an ECM repository or application o Integrated ECM suites may still use proprietary interfaces for “better together” functionality where appropriate. Standardize designer/admin-type operations, e. g. : o Defining object types o Controlling security

Target Scenarios ‣ Content Collaboration/ Aggregation: o Allow integration of content from different repositories, not just presentation/views. o E. g. “My Assigned Tasks/Documents” from multiple systems. o Allow customers to use the user interface of one application for the content of another. o Support Mashups and Web 2. 0 Technologies Content Centric Applications (e. g. BPM, multichannel publishing) o Enable applications that can read or publish content to any repository as part of a business process, without needing specific connectors for each repository.

Target Scenarios ‣ E-Discovery: o Enable e-Discovery applications that can work against any repository, while still leveraging key ECM concepts like object types & metadata, relationships and versioning. ‣ Archival: o Enable consistent archiving of information from business systems to CMIS-compliant repositories ‣ Compound / Virtual Document: o Enable consistent modeling, discovery and persistence of compound document relationships for CMIS-compliant repositories

Interoperability Workshop All seven vendors participated: Alfresco, EMC, IBM, Microsoft, Open. Text, Oracle and SAP Achieved Interoperability among the companies, including: ◦ IBM Lotus and Microsoft Share. Point clients on CMIS Providers ◦ SAP client on CMIS Providers
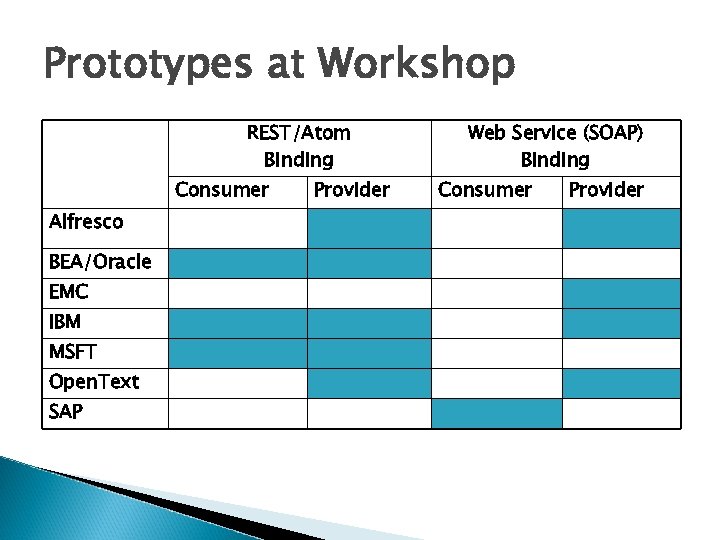
Prototypes at Workshop REST/Atom Binding Consumer Alfresco BEA/Oracle EMC IBM MSFT Open. Text SAP Provider Web Service (SOAP) Binding Consumer Provider
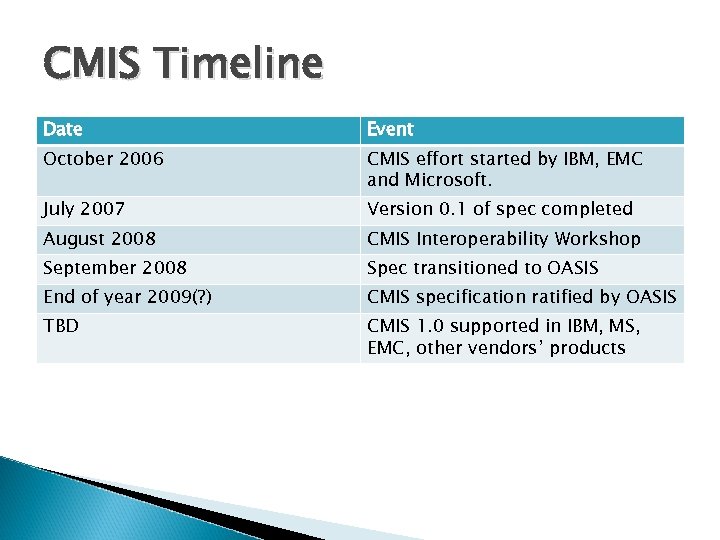
CMIS Timeline Date Event October 2006 CMIS effort started by IBM, EMC and Microsoft. July 2007 Version 0. 1 of spec completed August 2008 CMIS Interoperability Workshop September 2008 Spec transitioned to OASIS End of year 2009(? ) CMIS specification ratified by OASIS TBD CMIS 1. 0 supported in IBM, MS, EMC, other vendors’ products

Appendix: CMIS Technical Overview
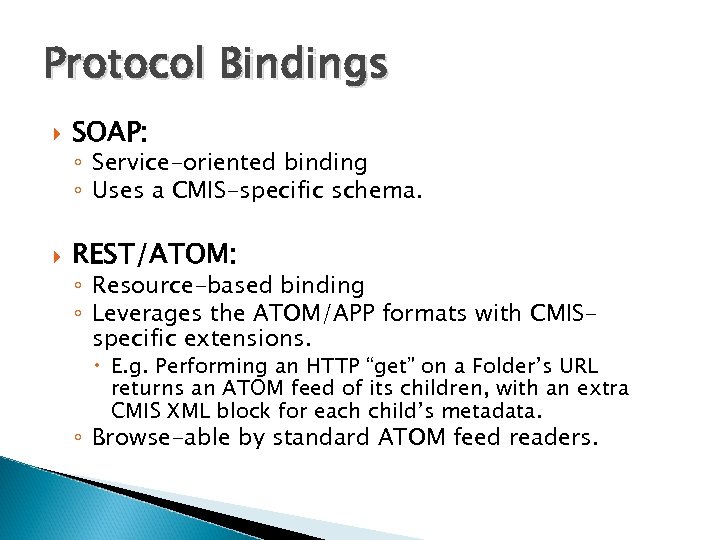
Protocol Bindings SOAP: ◦ Service-oriented binding ◦ Uses a CMIS-specific schema. REST/ATOM: ◦ Resource-based binding ◦ Leverages the ATOM/APP formats with CMISspecific extensions. E. g. Performing an HTTP “get” on a Folder’s URL returns an ATOM feed of its children, with an extra CMIS XML block for each child’s metadata. ◦ Browse-able by standard ATOM feed readers.
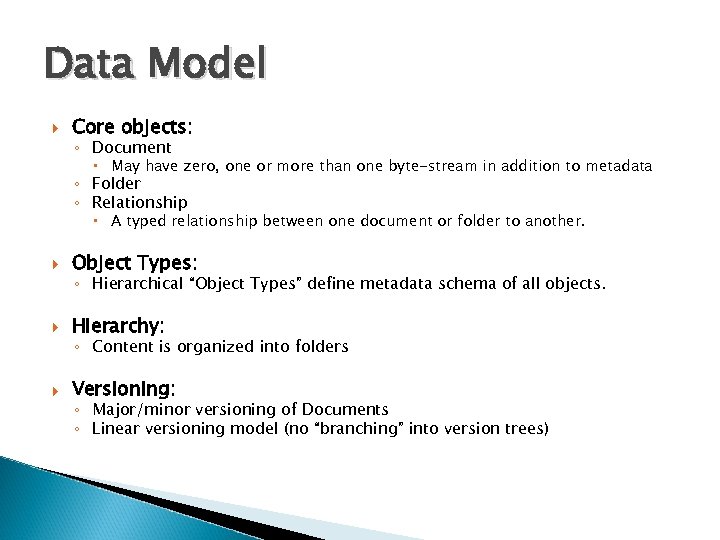
Data Model Core objects: ◦ Document May have zero, one or more than one byte-stream in addition to metadata ◦ Folder ◦ Relationship A typed relationship between one document or folder to another. Object Types: Hierarchy: Versioning: ◦ Hierarchical “Object Types” define metadata schema of all objects. ◦ Content is organized into folders ◦ Major/minor versioning of Documents ◦ Linear versioning model (no “branching” into version trees)
Query Model SQL-based query syntax Includes: ◦ Full-text indexing (optional) ◦ Returning relevancy scores ◦ Property-specific queries (e. g. where Modified. Date > 6/11/2007) ◦ Wildcards

Security Model Authentication is handled by each protocol Authorization context is exposed via an “Allowable. Action” collection on every object ◦ Identifies what actions a user can perform, given their permissions & the object state.

Optional Capabilities CMIS Repositories can optionally support the following capabilities: ◦ Multi-filing/un-filing: Allows documents to be filed in >1 folder concurrently, or un-filed. Used in applications like case management (where a single document may be relevant to multiple cases). ◦ Full-text Query support: Allows repositories to support property-only queries. ◦ “SQL Join” Query Support: Allowed repositories to specify whether they support “joining” of query results.

CMIS Services Repository Services ◦ get. Repositories ◦ get. Repository. Info ◦ get. Type. Definition ◦ get. Types Navigation Services ◦ get. Checked. Out. Docs ◦ get. Children ◦ get. Descendants ◦ get. Folder. Parents ◦ get. Object. Parents Policy Services ◦ apply. Policy ◦ get. Applied. Policies ◦ remove. Policy Versioning Services ◦ cancel. Checkout ◦ checkin ◦ checkout ◦ delete. All. Versions ◦ get. Propertiesof. Latest. Version Object Services ◦ create. Document ◦ create. Folder ◦ create. Policy ◦ create. Relationship ◦ delete. Content. Stream ◦ delete. Object ◦ delete. Tree ◦ get. Allowable. Actions ◦ get. Content. Stream ◦ get. Properties ◦ move. Object ◦ set. Content. Stream ◦ update. Properties Discovery Services ◦ Query Multi-Filing Services ◦ add. Object. To. Folder ◦ remove. Object. From. Folder Relationship Services ◦ get. Relationships
EMC Client on CMIS Providers Do not distribute
Lotus Client on CMIS Providers Do not distribute
Share. Point Client on CMIS Providers Do not distribute
88f37d88633d10613b367684e19033be.ppt