80907859ec39e9d7e5f0305d1a9fa0d6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

Content Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • • • Accounting Authentication Authorization Convenience Wrappers Data Key Management Delegation Dynamic Connectivity Service Job Repository Policy Site access control User Key Management INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 1

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Accounting www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

WS-Agreement and security Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • An effort is underway in Italy to implement WSAgreement as part of JRA 1 activities. • Secure SLA negotiation and establishment is often mentioned as a critical requirement, but there are currently no standard solutions or even best practices available • Phase 1: Team up with the Italian effort to investigate and identify security related issues. INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 3

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Authentication www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

OCSP support Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • OCSP is on the revocation roadmap. We need to provide modules that – make the necessary callouts – caches responses – works in line with the GGF CAOPS document (in progress). • Phase 1: Clarify requirements (GGF CAOPS work) and a gap analysis w. r. t. support in certificate validation routines currently used in g. Lite (C, Java). – What about LCG-2? • Phase 2: implement the OCSP functionality where necessary INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 5

Another way to do it. . . Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Central revocation checking – Another policy enforcement module • Phase 1: static central CRL checking – Similar to SAZ at Fermilab • Phase 2: OCSP INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 6

Pseudonymity service Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • We have covered the necessity for this before. . . • Phase 1: System design document – Collaboration with Grid. Shib to better understand pseudonymity issues • Phase 2: implementation • Phase 3: test bed deployment • NOTE: necessary mods to a few other security infrastructure modules (VOMS, others? ) will be required as well INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 7

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Authorization www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

Local Authorization Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Roadmap – – – all assertions carried as SAML statements all local (and global) policies expressed in XACML separate authorization service using standard protocols site policy, AND-ed with user and VO policy, evaluated together policy evaluation never requires special local privs (‘root’) • EGEE Architecture – Authorization Framework (Java) and LCAS (C/C++ world) – both provide set of PDPs (but slightly more PDPs will be there for the Auth. Z FW) – Authorization Service via OGSA-Auth. Z-WG spec – PDPs: user white/blacklist, VOMS-ACL, Proxy-lifetime, OID checks, peer-system name validation, central CRL checking INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 9

Local Authorization - PDPs Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Policy Decision Points (PDPs): § ban/allow and VOMS-ACL: Java + § proxy lifetime check: C + Java • SAAARG requirement 1. 4. 1. 1 for proxies § central revocation checking: • If not easily switched on in Open. SSL, make it a PDP • phase 1: static central CRL checking (similar to SAZ at Fermilab) • phase 2: OCSP § OID- (of generic extension) check: C + Java • SAAARG requirement 1. 3. 4 • ‘Strength’ of user key storage contained in policy-OID extension to be checked against a pre-defined (site-approved) list. • Coordination required with identity certificate providers § peer hostname check for certs: Java • Limit the use of agent credentials to domain-name of originating system by linking it to authentication data: o Subject. Alt. Name or d. NSName extension. INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 10
Authorization – standards Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Move towards standard auth. Z interfaces: – globus auth. Z interface (LCAS) – Credential mapping and setuid interface (LCMAPS) § Definition underway (GGF) – Authorization Service via OGSA-Auth. Z-WG spec • Start using XACML for policy expression – How about the plans to define of a minimal set of XACML and have a C implementation of that? INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 11

Workspace Service and LCMAPS Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Workspace Service is part of GT 4 -core (Kate Keahey et al. ) – DAS: Account mgmt interface – DAF: Creation of accounts • Policy configurable • Provides lifetime management and will provide quota management • Account clean-up mechanism: – Possibility to put account in quarantine first – Example clean-up script provided • Access control to Workspace Service based on DN and VOMS attr. • Access control to account – Currently based on DN – Will provide ACLs on VOMS attributes (based on call-out ? ) • Support of poolaccounts – Clean-up of poolaccounts – Uses as a back-end LCMAPS to manage gridmapdir (poolindex) INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 12
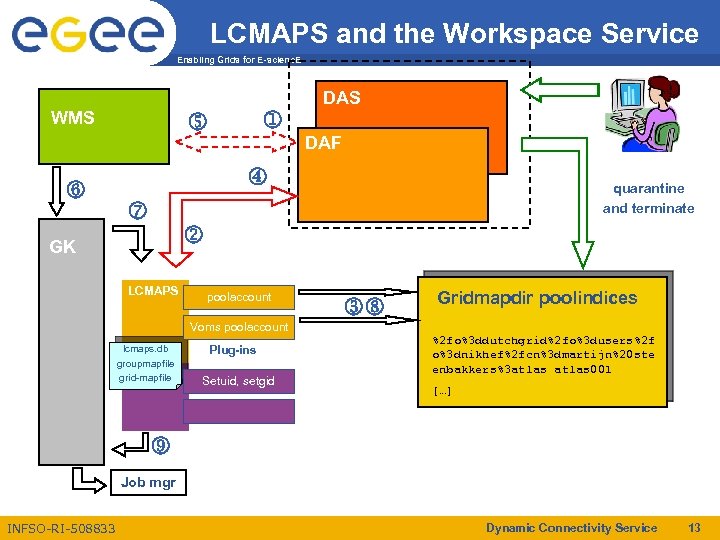
LCMAPS and the Service Workspace Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E DAS WMS o j n DAF m p quarantine and terminate k GK LCMAPS poolaccount Voms poolaccount lcmaps. db groupmapfile grid-mapfile Plug-ins Setuid, setgid lq Gridmapdir poolindices %2 fo%3 ddutchgrid%2 fo%3 dusers%2 f o%3 dnikhef%2 fcn%3 dmartijn%20 ste enbakkers%3 atlas 001 […] r Job mgr INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 13

Workspace Service - issues Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • How does it fit in the Workload Management System? – Release 1: WSS not used by WMS, only by end-users – Following releases: § Condor-G requests accounts from Workspace Service. § Condor schedd (one per user/VO) manages the accounts (lifetime extension) • Condor-G will allocate set of accounts with – service credentials? § Shifts trust to condor (sysadmins have to trust a possibly remote service? ) – user credentials? § Harder to implement for Condor • • Is it ok if schedd does account lifetime extension with server credential? – Can be set by ACL on user account resource. – Easier to implement for condor, but – Requires that su-exec wrapper has “execute-as” functionality Allocate one account per job: – In addition to DN+attributes (or proxy) also a job counter should be passed to Workspace Service, LCMAPS and su-exec wrapper. • Issues should be sorted out in design team meeting (22 March) INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 14

GAAA integration-1 Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Remote/central GAAA auth. Z service • flexible combination of pull, push, agent access control models • Auth. Z assertions/tickets and/or tokens for performance optimisation • Integration with EGEE/GT Auth. Z framework and other EGEE services based on SAML, XACML, WS-Security industry standards and GT Auth. Z interface. • Pilot: callout from gridftp to GAAA Auth. Z service – LCAS a java auth. Z FW a GAAA auth. Z service or – LCAS a GAAA auth. Z service • EGEE Requirement #100375 (PTF Savannah): “Authorization for network resources access” – Gap to fill for GAAA? Multidomain auth. Z? • More info: http: //staff. science. uva. nl/~demch/worksinprogress/draft-ocesecurity-architecture-authz-02. pdf INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 15

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E GAAA integration: motivation and benefits • GAAA and g. Lite/GT in general – AIRG is experimenting with using Grid for Optical network management and resource reservation using currently GT 3. 3 – Resource management and policy is based on GAAA Az F/w • GAAA and grid. FTP – The same as above + grid. FTP is used for bulk file/data transfer to generate above Gigabit datastreams • GAAA/GAAAPI + g. Lite/GT 4 Auth. Z framework – GAAAPI implements generic RBAC and GAAA Authz f/w functionality flexibly configurable for agent, pull and push models – Uses SAML for Auth. Z assertions and XACML for Auth. Z messaging and policy exchange – Provides functionality for handling Auth. Z and Auth. N tickets and tokens both in proprietary and SAML format – Configurable for different distributed access control scenarios § Single domain PEP-PDP, different domains PEP-PDP and PDP-PEP § All context handlers and ticket/token handling modules can work at both PEP and PDP side INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 16

GAAA integration-2 Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • remote invocation C client – As a plugin for LCAS – Callout to java auth. Z FW and/or GAAA server by GGF OGSAauth. Z WG standards – What should be passed from client to auth. Z service? § Complete: Subject Attributes/Roles, Resource, Actions • All what is required for policy evaluation § Minimum: Subject. ID, Resource, Actions • All remaining information must be added by PEP-PDP context handler o This functionality is available in GAAAPI • Subject. ID must be provided with Subject confirmation data cryptographically (Signature or Encryption) proving Subject’s identity – Communication: XML security, gsoap, MLS? – Performance? INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 17
VOMS Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • VOMS unit test certificates • VOMS PDP module for Java – Incorporate Globus impl into the g. Lite build system INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 18

Mutual Authorization Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Phase 1: System design • Phase 2: Implementation INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 19

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Data key management www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

Data key management Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Phase 1: System design document – ongoing – JRA 1/DM involvement? – NA 4 involvement? • Phase 2: Implementation – Convenience libraries for applications (based on input from NA 4 representatives) • Phase 3: Test bed deployment INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 21

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Delegation www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

WS-Delegation Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • EGEE adopted a interim solution for doing delegation, based on Grid. Site work. • OSG, and the Globus Alliance has approached us to work on a common definition of a delegation interface "done proper", to be used by all parties. – Strawman document in progress, joint by OSG, EGEE, GA, PPDG, and WSRF. NET – will be distributed within a week • Phase 1: Design document (ongoing) • Phase 2: (Re-)implementation – could most likely be based on current delegation solution INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 23

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Convenience wrappers www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

Message-level security wrappers Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • The "raw" WS-Security libraries are complex to use and not particularly user friendsly. • JRA 1 (CERN) has requested convenience wrappers that will do the necessary encryption/signing and decryption/validation of SOAP payloads. • Phase 1: Implementation. Work closely with JRA 1 to ensure that the result has adequate support and an appropriate API signature. INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 25

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Dynamic Connectivity Service Oscar Koeroo JRA 3 www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

Content Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • • What’s the problem? What do we need? How do we want to solve it Our prototype – and how does it work INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 27

What’s the problem? Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Most to all WNs (in LCG-2) can make outbound connection to almost any machine on the Internet – No Firewalls that limits a user § A few possibilities are: • WN publicly addressable • Inbound is prohibited and outbound is still free to use o NAT box o Firewall rules • WNs are locked up for any Internet traffic – VOs request ability for their users to connect to there own servers § Pulling VO specific data on a WN • Packages • Data § Push result on to VO specific machines § Interactive • Database access • This means that every (rogue) user can do harmful things like: – Launch DDo. S - Grid Jobs can aid or start a DDo. S on a (web-)server – Share Warez - Compromised machines can serve as Warez servers – Make a pass-through for Worms & Viruses INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 28

What we need… Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Network containment – We need to keep a user primarily in the fabric – If users have a connectivity wish they can request it at the (concerning) resource centers – RCs need to be in full control of their (network) domain INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 29

How do we want to solve it Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Lockup a site tight – Let the Grid services be connectable and let them connect to others – Grid services mutual authenticate themselves to other services with some kind of access control so they can be regarded as safe(r) connections – For the WNs and the jobs: § No (direct) inbound connectivity • Achieved by setting up a router, NAT box or Firewall (or some combination) prohibiting these connections § No outbound connectivity • The router, NAT box or firewall (or a combi. ) prohibit these connections • Only when needed open-up a port to make a (controlled) connection available INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 30

The prototype called: “Lasa” Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • “Proxy” has a (overloaded) meaning in: – The database world • A kind of cache for queries – The networking world • HTTP • FTP – The security world • X 509 – RFC 3820 • Radius • Can we throw ‘Site Proxy’ to /dev/null and use ‘Dynamic Connectivity Service’ ? • The name of our prototype will be ‘Lasa’ INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 31
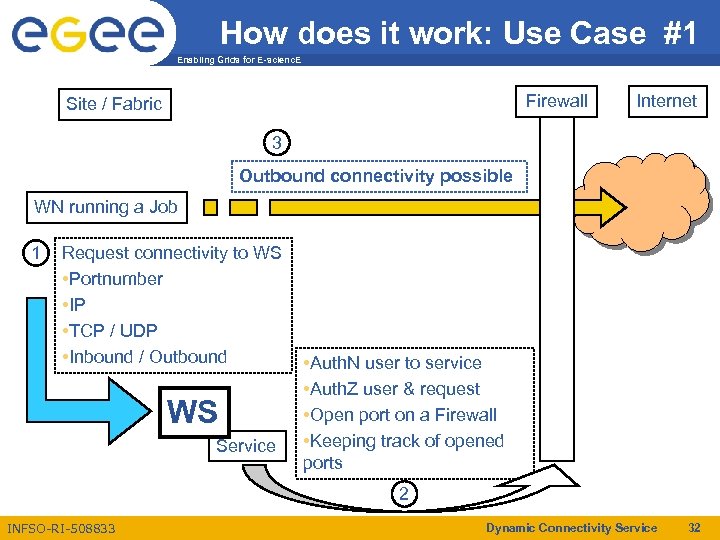
How does it work: Use Case #1 Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Firewall Site / Fabric Internet 3 Outbound connectivity possible WN running a Job 1 Request connectivity to WS • Portnumber • IP • TCP / UDP • Inbound / Outbound WS Service • Auth. N user to service • Auth. Z user & request • Open port on a Firewall • Keeping track of opened ports 2 INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 32
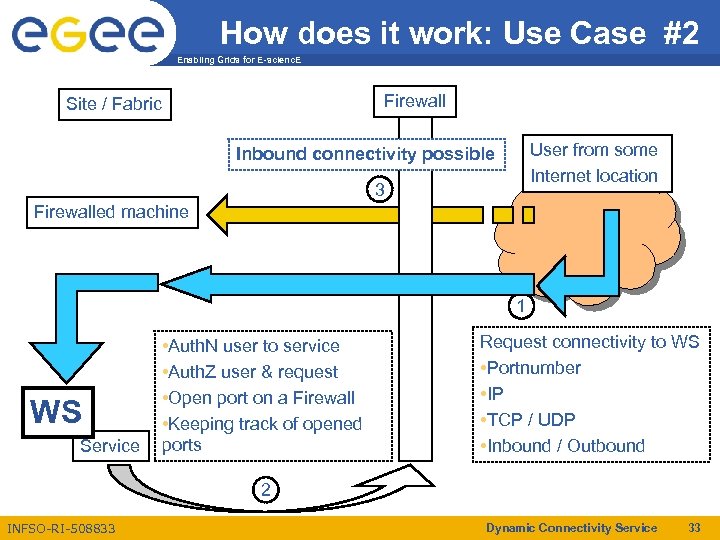
How does it work: Use Case #2 Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Firewall Site / Fabric User from some Internet location Inbound connectivity possible 3 Firewalled machine 1 WS Service • Auth. N user to service • Auth. Z user & request • Open port on a Firewall • Keeping track of opened ports Request connectivity to WS • Portnumber • IP • TCP / UDP • Inbound / Outbound 2 INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 33
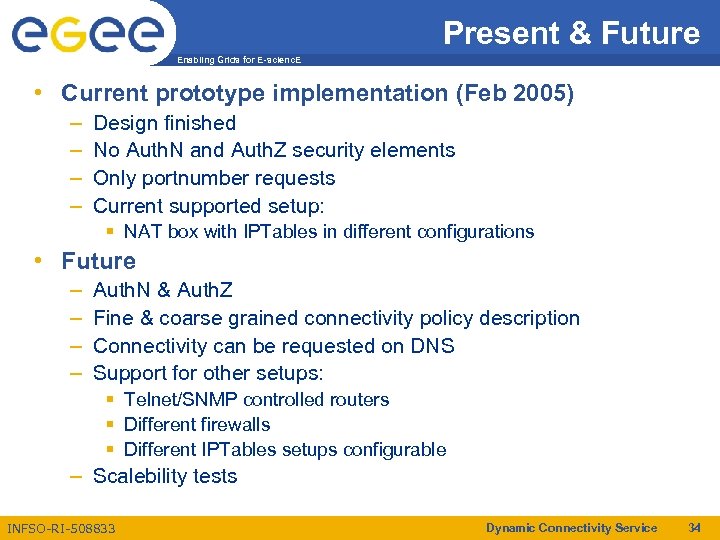
Present & Future Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Current prototype implementation (Feb 2005) – – Design finished No Auth. N and Auth. Z security elements Only portnumber requests Current supported setup: § NAT box with IPTables in different configurations • Future – – Auth. N & Auth. Z Fine & coarse grained connectivity policy description Connectivity can be requested on DNS Support for other setups: § Telnet/SNMP controlled routers § Different firewalls § Different IPTables setups configurable – Scalebility tests INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 34

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Job Repository Oscar Koeroo JRA 3 www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

Content Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • • Where does it do what? Goal of Job Repository How does it work (database schema) To Be Done… INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 36

Where does it do what? Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • The glite-gatekeeper uses the LCMAPS framework for it’s enhanced usermapping capabilities – The LCMAPS framework provides usermapping from DN + VOMS attributes to Unix UIDs and GIDs • Job Repository is primarily a LCMAPS plug-in # LCMAPS Policies: voms: localaccount -> posix_enf | vomsextract -> vomslocalgroup -> vomspoolgroup -> vomspoolaccount -> jobrep -> posix_enf standaard: localaccount -> jobrep | poolaccount -> jobrep -> posix_enf | posix_enf INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 37

Goal of Job Repository Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • It’s goal is to log all the mapping information into a relational database – Which user (identified with a DN) submitted what kind of job (based on the RSL) – Which certificate chain has been used per job (linked to this user) – Which set of VOMS Attributes did the user use this time and which jobs have been executed with them – Which VOMS attribute mapped into which primary GID – Which VOMS attributes mapped into which secundary GIDs – Keep hold of the job status through the batch system’s unique identifier (batch system independent) • Using any kind of database with the same code – Done though ‘iodbc’ (starting with a My. SQL database) INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 38
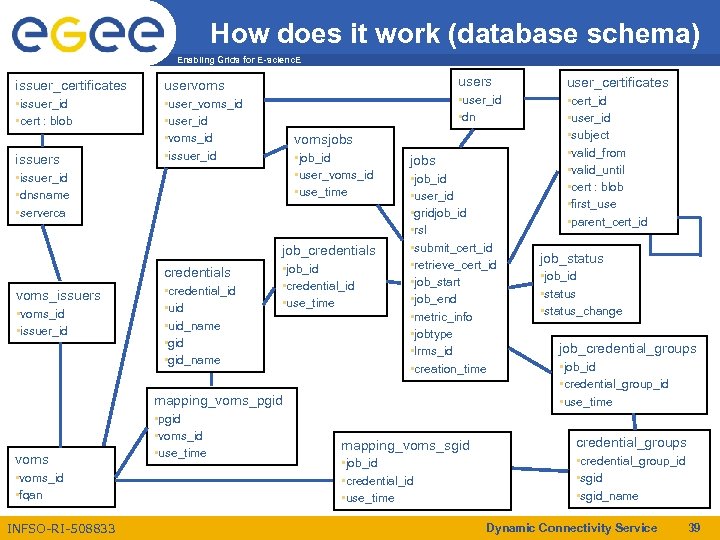
How does it work (database schema) Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E issuer_certificates • issuer_id • cert : blob users • user_voms_id • user_id • voms_id • issuer_id issuers • job_id • user_voms_id • use_time job_credentials voms_issuers • voms_id • issuer_id • credential_id • uid_name • gid_name • cert_id • user_id • subject • valid_from • valid_until • cert : blob • first_use • parent_cert_id vomsjobs • issuer_id • dnsname • serverca credentials user_certificates • user_id • dn uservoms • job_id • credential_id • use_time jobs • job_id • user_id • gridjob_id • rsl • submit_cert_id • retrieve_cert_id • job_start • job_end • metric_info • jobtype • lrms_id • creation_time mapping_voms_pgid voms • voms_id • fqan INFSO-RI-508833 • pgid • voms_id • use_time job_status • job_id • status_change job_credential_groups • job_id • credential_group_id • use_time mapping_voms_sgid credential_groups • job_id • credential_id • use_time • credential_group_id • sgid_name Dynamic Connectivity Service 39

TBD Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Performance upgrade – Perhaps a slight change on the schema can speed up the total proces – Current performance with globus-job-runs: 20 jobs per second sustained or 100 jobs burst per second (burst lasting max 3 seconds, needing a cooldown of 20 seconds) Note: globus-job-runs can exceed 100 jobs per second with success without the Job Repository • Using ‘iodbc 3. 52. 2’ – Slight interface change • Code reorganization INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 40

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Policy www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

Operational policy enforcement Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • We need to provide methods that enforce operational policy in the runtime • Phase 1: design, figure out how to best do this – part of the certificate path validation routines? – a separate higher-level check? • Phase 2: implementation of necessary software modules (C and Java). – and instructions on how to configure/integrate/enable it! INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 42

Policy enforcement checks: Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Proxy certificate validity: The JSPG defines maximum validity constraints in line with the GGF SAAA recommendations. • Peer hostname check: The abuse of agent credentials can be limited by linking the authentication data of the agent to the domain-name of the originating system. • Certification Policy OID check INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 43

Policy evaluation Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Several policy reasoning efforts are underway • G-PBox, Uv. A GAAA, Grid. Site XACML support, . . . • Phase 1: We need a better understanding of commonalities and differences, and where there are still gaps • Actually deploying something within a year? INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 44

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Site access control and integration www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833
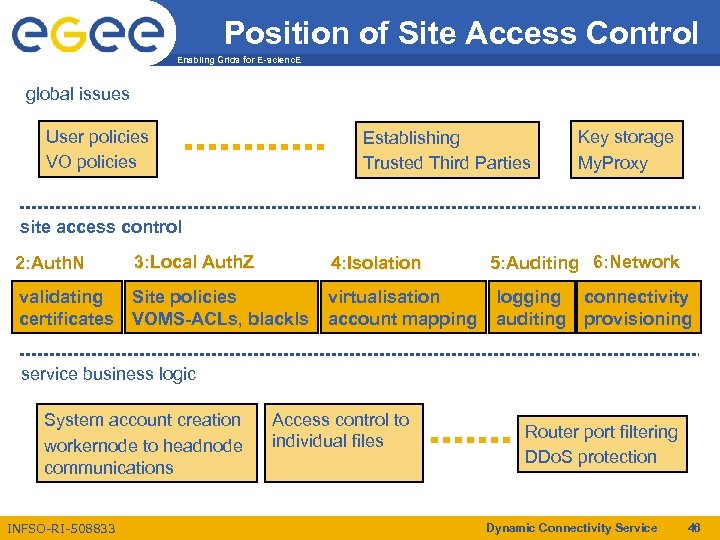
Position of Site Access Control Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E global issues User policies VO policies Establishing Trusted Third Parties Key storage My. Proxy site access control 2: Auth. N 3: Local Auth. Z 4: Isolation validating certificates Site policies VOMS-ACLs, blackls virtualisation account mapping 5: Auditing 6: Network logging auditing connectivity provisioning service business logic System account creation workernode to headnode communications INFSO-RI-508833 Access control to individual files Router port filtering DDo. S protection Dynamic Connectivity Service 46

Goals Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Generic access control to services – Authentication – Authorization – for legacy applications & file access, networks, … • • • Sites are always in control of their resources Flexibility, scalability Allow for central control in a site Converge to a single policy format Standardization of configuration Address requirements from NA 4, SAAA-RG, and others (incorporated in MJRA 3. 1 “user requirements”) INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 47

Isolation Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Roadmap – virtualization of resources (VM) or assigning of local credentials – should be indistinguishable from ‘outside’ • EGEE Architecture – – – only based on credential mapping do as little as possible with ‘root’ privileges: su-exec minimizing local management: poolaccounts & poolgroups credential mapping and manipulation: LCMAPS management capabilities on these accounts: Work. Space Service INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 48

Su-exec wrapper Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Thin layer with root privileges will replace gatekeeper • Internals – – Use a standard credential mapping call-out interface LCMAPS implements this interface Call-out to auth. Z FW? ? ? Execute the requested command • External interface – CGI-bin interface to insert into apache server (gridsite) – CLI to be used for perl, java? – How to pass the security context? (gss_export_sec_context() etc. ) § Involves environment variables: insecure? – Do we want to have “execute as” functionality? • Requires coordination with condor, gridsite, globus – Design team, GGF? INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 49
System Integration components Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Additional options for system integration • NSS-grid – make regular commands (ls, top) show grid DNs – Example: $ ls –l file_from_atlas -rw-r--r-1 /O=dutchgrid/O=users/O=nikhef/CN=Martijn Steenbakkers /ATLAS/user/Role=Admin • 1 Nov 13 17: 22 file_from_atlas – linked to credential mapping and auditing system (Job. Repository) – Could replace ldap mechanism as distributed source of authorization information. grid-PAM – retrofit existing services with grid security – gsi-ssh, gsi-cvs, … • No explicit requirements within the project • highly popular outside, with smaller installations • no effort assigned until real requirement is there INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 50

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E User key management www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E My. Proxy deployment recommendations • JRA 3 involvement? INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 52

PURSE Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E • Portal / web frontend for user registration – Credentials stored in My. Proxy • Existing product exists (KTH, ANL, NCSA) – A revised version is planned • Phase 1: Requirements gathering and system design document • Phase 2: Implementation INFSO-RI-508833 Dynamic Connectivity Service 53

Enabling Grids for E-scienc. E Summary www. eu-egee. org INFSO-RI-508833
80907859ec39e9d7e5f0305d1a9fa0d6.ppt