ab15548947ae54ed369cebb698544ced.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Consumers Rule Chapter 1
Consumers Rule Chapter 1
 Factors in Consumer Behavior • The story of Gail in the marketplace… – Demographics – Psychographics – Opinions and behaviors of others • Market segmentation – Targeting a brand only to specific groups of consumers rather than to everybody 2
Factors in Consumer Behavior • The story of Gail in the marketplace… – Demographics – Psychographics – Opinions and behaviors of others • Market segmentation – Targeting a brand only to specific groups of consumers rather than to everybody 2
 What is Consumer Behavior? • The study of the processes involved when individuals or groups select, purchase, use, or dispose of products, services, ideas, or experiences to satisfy needs and desires 3
What is Consumer Behavior? • The study of the processes involved when individuals or groups select, purchase, use, or dispose of products, services, ideas, or experiences to satisfy needs and desires 3
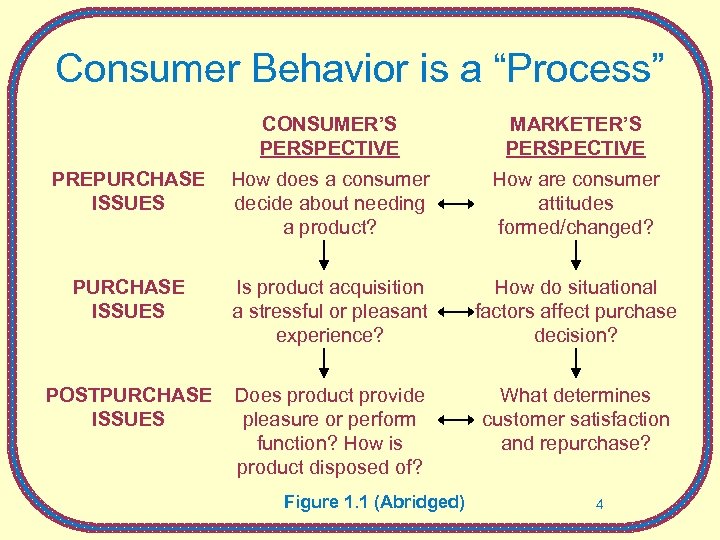 Consumer Behavior is a “Process” CONSUMER’S PERSPECTIVE MARKETER’S PERSPECTIVE PREPURCHASE ISSUES How does a consumer decide about needing a product? How are consumer attitudes formed/changed? PURCHASE ISSUES Is product acquisition a stressful or pleasant experience? How do situational factors affect purchase decision? POSTPURCHASE ISSUES Does product provide pleasure or perform function? How is product disposed of? What determines customer satisfaction and repurchase? Figure 1. 1 (Abridged) 4
Consumer Behavior is a “Process” CONSUMER’S PERSPECTIVE MARKETER’S PERSPECTIVE PREPURCHASE ISSUES How does a consumer decide about needing a product? How are consumer attitudes formed/changed? PURCHASE ISSUES Is product acquisition a stressful or pleasant experience? How do situational factors affect purchase decision? POSTPURCHASE ISSUES Does product provide pleasure or perform function? How is product disposed of? What determines customer satisfaction and repurchase? Figure 1. 1 (Abridged) 4
 Actors in Consumer Behavior • Consumer: A person who identifies a need or desire, makes a purchase, and then disposes of the product – Purchaser vs. user vs. influencer – Organization/group as consumer 5
Actors in Consumer Behavior • Consumer: A person who identifies a need or desire, makes a purchase, and then disposes of the product – Purchaser vs. user vs. influencer – Organization/group as consumer 5
 Segmenting Consumers • Market Segmentation – Similar consumers • Example: “Heavy Users” of fast-food industry 6
Segmenting Consumers • Market Segmentation – Similar consumers • Example: “Heavy Users” of fast-food industry 6
 Market Segmentation Finely-tuned marketing segmentation strategies allow marketers to reach only those consumers likely to be interested in buying their products. 7
Market Segmentation Finely-tuned marketing segmentation strategies allow marketers to reach only those consumers likely to be interested in buying their products. 7
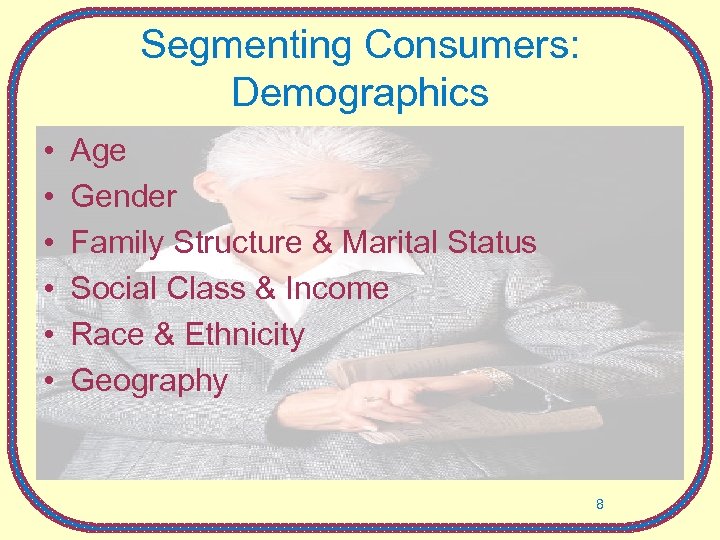 Segmenting Consumers: Demographics • • • Age Gender Family Structure & Marital Status Social Class & Income Race & Ethnicity Geography 8
Segmenting Consumers: Demographics • • • Age Gender Family Structure & Marital Status Social Class & Income Race & Ethnicity Geography 8
 A Lesson Learned • Nike was forced to pull this advertisement for a running shoe after disabilities rights groups claimed the ads were offensive. • How could Nike have done a better job of getting its message across without offending a powerful demographic? 9
A Lesson Learned • Nike was forced to pull this advertisement for a running shoe after disabilities rights groups claimed the ads were offensive. • How could Nike have done a better job of getting its message across without offending a powerful demographic? 9
 Segmenting Consumers: Lifestyles • Psychographics – The way we feel about ourselves – The things we value – The things we do in our spare time 10
Segmenting Consumers: Lifestyles • Psychographics – The way we feel about ourselves – The things we value – The things we do in our spare time 10
 Relationship Marketing • Success = building lifetime relationships between brands and customers – Regular interaction with customers – Database Marketing 11
Relationship Marketing • Success = building lifetime relationships between brands and customers – Regular interaction with customers – Database Marketing 11
 Marketing’s Impact on Consumers • Marketers significantly influence the world and the information we learn! – Advertisements, stores, and products communicate and persuade 12
Marketing’s Impact on Consumers • Marketers significantly influence the world and the information we learn! – Advertisements, stores, and products communicate and persuade 12
 The Meaning of Consumption • People often buy products not for what they do, but for what they mean – Brands… • …Convey image/personality • …Define our place in modern society • …Help us to form bonds with others who share similar preferences 13
The Meaning of Consumption • People often buy products not for what they do, but for what they mean – Brands… • …Convey image/personality • …Define our place in modern society • …Help us to form bonds with others who share similar preferences 13
 Brand Relationship Types • • Self-Concept Attachment Nostalgic Attachment Interdependence Love CLICK ON LOGO TO SEE VIDEO ABOUT CONSUMERS’ LOVE OF HARLEY DAVIDSON 14
Brand Relationship Types • • Self-Concept Attachment Nostalgic Attachment Interdependence Love CLICK ON LOGO TO SEE VIDEO ABOUT CONSUMERS’ LOVE OF HARLEY DAVIDSON 14
 The Global Consumer • Global Consumer Culture – People united by common devotion to: • Brand name consumer goods • Movie stars • Celebrities • Leisure activities – Pressure to understand similarities and differences of customers in various countries 15
The Global Consumer • Global Consumer Culture – People united by common devotion to: • Brand name consumer goods • Movie stars • Celebrities • Leisure activities – Pressure to understand similarities and differences of customers in various countries 15
 Virtual Consumption • Impact of the Web on consumer behavior – 24/7 shopping without leaving home – Instantaneous access to news – Handheld devices & wireless communications • C 2 C e-commerce – Virtual brand communities. – Consumer chat rooms AMAZON. COM 16
Virtual Consumption • Impact of the Web on consumer behavior – 24/7 shopping without leaving home – Instantaneous access to news – Handheld devices & wireless communications • C 2 C e-commerce – Virtual brand communities. – Consumer chat rooms AMAZON. COM 16
 Virtual Consumption (Cont’d) • “Wired” Americans spend… – …Less time with friends/family – …Less time shopping in stores – …More time working at home after hours • But, many report that e-mail strengthens family ties 17
Virtual Consumption (Cont’d) • “Wired” Americans spend… – …Less time with friends/family – …Less time shopping in stores – …More time working at home after hours • But, many report that e-mail strengthens family ties 17
 Marketing and Reality • “Blurred boundaries” between marketing efforts and “the real world” – Popular culture shaped by marketers 18
Marketing and Reality • “Blurred boundaries” between marketing efforts and “the real world” – Popular culture shaped by marketers 18
 Marketing Ethics and Public Policy • Business Ethics: rules of conduct that guide actions in the marketplace – What is “Right vs. Wrong” • Differs among people, organizations, and cultures 19
Marketing Ethics and Public Policy • Business Ethics: rules of conduct that guide actions in the marketplace – What is “Right vs. Wrong” • Differs among people, organizations, and cultures 19
 Discussion • There is a computer game called JFK Reloaded that lets players reenact President Kennedy’s assassination. – Have the game’s developers gone too far, or is any historical event “fair game” to be adapted into an entertainment vehicle? 20
Discussion • There is a computer game called JFK Reloaded that lets players reenact President Kennedy’s assassination. – Have the game’s developers gone too far, or is any historical event “fair game” to be adapted into an entertainment vehicle? 20
 Marketing Ethics and Public Policy (cont’d) • Consumers think better of products made by firms they feel behave ethically – Marketing “violators” • Mislabeling package contents • “Bait-and-switch” selling strategy • Alcohol/tobacco billboards in low-income neighborhoods RJRT. COM 21
Marketing Ethics and Public Policy (cont’d) • Consumers think better of products made by firms they feel behave ethically – Marketing “violators” • Mislabeling package contents • “Bait-and-switch” selling strategy • Alcohol/tobacco billboards in low-income neighborhoods RJRT. COM 21
 Needs and Wants: Do Marketers Manipulate Consumers? • Consumerspace • Do marketers create artificial needs? – Need: A basic biological motive – Want: One way that society has taught us that need can be satisfied • Are advertising and marketing necessary? – Economics of information perspective: Advertising is an important source of consumer information. • Do marketers promise miracles? – Advertisers simply don’t know enough to manipulate people. 22
Needs and Wants: Do Marketers Manipulate Consumers? • Consumerspace • Do marketers create artificial needs? – Need: A basic biological motive – Want: One way that society has taught us that need can be satisfied • Are advertising and marketing necessary? – Economics of information perspective: Advertising is an important source of consumer information. • Do marketers promise miracles? – Advertisers simply don’t know enough to manipulate people. 22
 Manipulating Needs & Wants • Marketers tell people what they should want – Marketerspace vs. Consumerspace – Response: Marketers recommend ways to satisfy basic biological needs 23
Manipulating Needs & Wants • Marketers tell people what they should want – Marketerspace vs. Consumerspace – Response: Marketers recommend ways to satisfy basic biological needs 23
 Public Policy & Consumerism • Concern for the welfare of consumers – Department of Agriculture – Federal Trade Commission – Food and Drug Administration – Securities and Exchange Commission – Environmental Protection Agency CPSC. GOV 24
Public Policy & Consumerism • Concern for the welfare of consumers – Department of Agriculture – Federal Trade Commission – Food and Drug Administration – Securities and Exchange Commission – Environmental Protection Agency CPSC. GOV 24
 Consumer Activism • Adbusters: America = Corporate Brand – Buy Nothing Day & TV Turnoff Week • Culture Jamming – Disrupt corporate efforts in cultural landscape 25
Consumer Activism • Adbusters: America = Corporate Brand – Buy Nothing Day & TV Turnoff Week • Culture Jamming – Disrupt corporate efforts in cultural landscape 25
 Adbusters’ Blackspot sneakers in response to Nike’s unfair labor practices ADBUSTERS. ORG 26
Adbusters’ Blackspot sneakers in response to Nike’s unfair labor practices ADBUSTERS. ORG 26
 Consumer Related Issues • UNICEF sponsored this advertising campaign against child labor. The field of consumer behavior plays a role in addressing important consumer issues such as child 27 exploitation.
Consumer Related Issues • UNICEF sponsored this advertising campaign against child labor. The field of consumer behavior plays a role in addressing important consumer issues such as child 27 exploitation.
 The Dark Side of Consumer Behavior • Consumer Terrorism: – An example: Susceptibility of the nation’s food supply to bioterrorism • Addictive Consumption: – Consumer addiction: • A physiological and/or psychological dependency on products or services • Compulsive Consumption: – Repetitive shopping as an antidote to tension, anxiety, depression, or boredom 28
The Dark Side of Consumer Behavior • Consumer Terrorism: – An example: Susceptibility of the nation’s food supply to bioterrorism • Addictive Consumption: – Consumer addiction: • A physiological and/or psychological dependency on products or services • Compulsive Consumption: – Repetitive shopping as an antidote to tension, anxiety, depression, or boredom 28
 The Dark Side of Consumer Behavior (cont. ) • Consumed Consumers: – People who are used or exploited, willingly or not, for commercial gain in the marketplace • Illegal Activities: – Consumer Theft: • Shrinkage: The industry term for inventory and cash losses from shoplifting and employee theft – Anticonsumption: • Events in which products and services are deliberately defaced or mutilated 29
The Dark Side of Consumer Behavior (cont. ) • Consumed Consumers: – People who are used or exploited, willingly or not, for commercial gain in the marketplace • Illegal Activities: – Consumer Theft: • Shrinkage: The industry term for inventory and cash losses from shoplifting and employee theft – Anticonsumption: • Events in which products and services are deliberately defaced or mutilated 29
 Study of Consumer Behavior • Interdisciplinary Influences – Many different perspectives/fields • Consumer Behavior Employers – Universities, manufacturers, museums, advertising agencies, and governments 30
Study of Consumer Behavior • Interdisciplinary Influences – Many different perspectives/fields • Consumer Behavior Employers – Universities, manufacturers, museums, advertising agencies, and governments 30
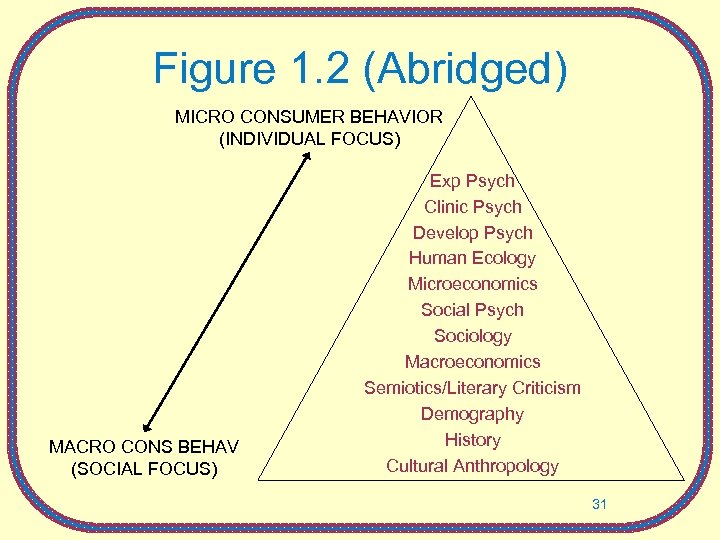 Figure 1. 2 (Abridged) MICRO CONSUMER BEHAVIOR (INDIVIDUAL FOCUS) MACRO CONS BEHAV (SOCIAL FOCUS) Exp Psych Clinic Psych Develop Psych Human Ecology Microeconomics Social Psych Sociology Macroeconomics Semiotics/Literary Criticism Demography History Cultural Anthropology 31
Figure 1. 2 (Abridged) MICRO CONSUMER BEHAVIOR (INDIVIDUAL FOCUS) MACRO CONS BEHAV (SOCIAL FOCUS) Exp Psych Clinic Psych Develop Psych Human Ecology Microeconomics Social Psych Sociology Macroeconomics Semiotics/Literary Criticism Demography History Cultural Anthropology 31
 Journal of Consumer Research 32
Journal of Consumer Research 32
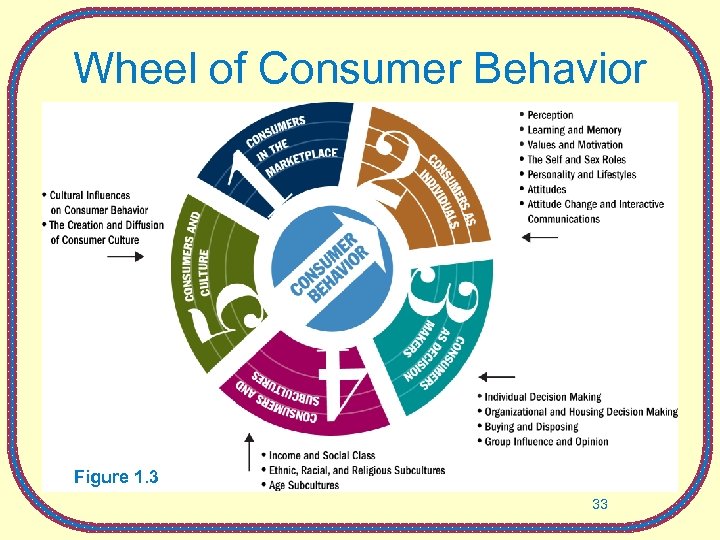 Wheel of Consumer Behavior Figure 1. 3 33
Wheel of Consumer Behavior Figure 1. 3 33


