78753c2dc0ea3e400b8a84eb334b0aab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Consumer-specified Service License Selection and Composition G. R. Gangadharan 1, Hong-Linh Truong 2, Martin Treiber 2, Vincenzo D‘Andrea 1, Schahram Dustdar 2, Renato Iannella 3, Michael Weiss 4 truong@infosys. tuwien. ac. at 1 University of Trento, Italy 2 Vienna University of Technology, Austria 3 National ICT Australia, Austrilia 4 Carleton University, Canada 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 1
Consumer-specified Service License Selection and Composition G. R. Gangadharan 1, Hong-Linh Truong 2, Martin Treiber 2, Vincenzo D‘Andrea 1, Schahram Dustdar 2, Renato Iannella 3, Michael Weiss 4 truong@infosys. tuwien. ac. at 1 University of Trento, Italy 2 Vienna University of Technology, Austria 3 National ICT Australia, Austrilia 4 Carleton University, Canada 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 1
 Talk outline § Motivation § ODRL-S license overview § License-aware service selection and composition framework § License composition for composite service § Directional Matchmaking Algorithm § Illustrating scenario § Conclusion and next steps 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 2
Talk outline § Motivation § ODRL-S license overview § License-aware service selection and composition framework § License composition for composite service § Directional Matchmaking Algorithm § Illustrating scenario § Conclusion and next steps 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 2
 Software as a Service/Utility & License § Web service, Saa. S and Service Utility § Can be composed and used by different consumers § Different usage modes (e. g. , subscription, pay per use) § etc. § Some questions § How to deal with legal „terms“? Such as noncommercial use § How to associate licenses with a service utility? § How to search, select and compose service utility, taking into account the license? 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 3
Software as a Service/Utility & License § Web service, Saa. S and Service Utility § Can be composed and used by different consumers § Different usage modes (e. g. , subscription, pay per use) § etc. § Some questions § How to deal with legal „terms“? Such as noncommercial use § How to associate licenses with a service utility? § How to search, select and compose service utility, taking into account the license? 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 3
 What is a Service License? • A license between a service provider (as the licensor) with (could be) many service consumers (the licensees). • Describes the use of and access to services in machine interpretable form. • A complementary concept for completeness of service usage description. • Can be viewed as a superset including SLAs and Policies. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 4
What is a Service License? • A license between a service provider (as the licensor) with (could be) many service consumers (the licensees). • Describes the use of and access to services in machine interpretable form. • A complementary concept for completeness of service usage description. • Can be viewed as a superset including SLAs and Policies. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 4
 Existing work in Service License? • Though there are few examples of service licenses (by Amazon, Google, Yahoo!), to the best of our knowledge, there is no conceptualization of service licensing. • These licenses are not machine interpretable. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 5
Existing work in Service License? • Though there are few examples of service licenses (by Amazon, Google, Yahoo!), to the best of our knowledge, there is no conceptualization of service licensing. • These licenses are not machine interpretable. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 5
 Why Not a Software License for Services? • Services are also software fragments! • Services are not targeted as standalone applications. • Consumers do not require to download them for local use. • Services support composition and reuse. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 6
Why Not a Software License for Services? • Services are also software fragments! • Services are not targeted as standalone applications. • Consumers do not require to download them for local use. • Services support composition and reuse. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 6
 What is this paper about • This paper: • Uses ODRL-S to describe service license • Proposes composition and selection of services based on licenses • We do not discuss • The comparison between ODRL-S with other specifications (e. g. , WS-Policy, WSPL, WSOL, WSLA, Slang, etc. ) • Specifying license is not the focus of this paper • See http: //dit. unitn. it/~gr/pubs. html • Selecting a service based on functional parameters • Contribution: Consumer-specified license-based service selection 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 7
What is this paper about • This paper: • Uses ODRL-S to describe service license • Proposes composition and selection of services based on licenses • We do not discuss • The comparison between ODRL-S with other specifications (e. g. , WS-Policy, WSPL, WSOL, WSLA, Slang, etc. ) • Specifying license is not the focus of this paper • See http: //dit. unitn. it/~gr/pubs. html • Selecting a service based on functional parameters • Contribution: Consumer-specified license-based service selection 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 7
 Background: Anatomy of a Service License • ODRL-S (Open Digital Rights Language for Services) • Based on ODRL-S (http: //odrl. net/) • Subject • define the service being licensed • Scope of Rights • adaptation, composition, attribution, derivation, sharealike, non-commercial use • Financial Terms • Warranty, Indemnity, and Limitation of liability (WIL) • Evolution • deal with software evolution/versioning 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 8
Background: Anatomy of a Service License • ODRL-S (Open Digital Rights Language for Services) • Based on ODRL-S (http: //odrl. net/) • Subject • define the service being licensed • Scope of Rights • adaptation, composition, attribution, derivation, sharealike, non-commercial use • Financial Terms • Warranty, Indemnity, and Limitation of liability (WIL) • Evolution • deal with software evolution/versioning 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 8
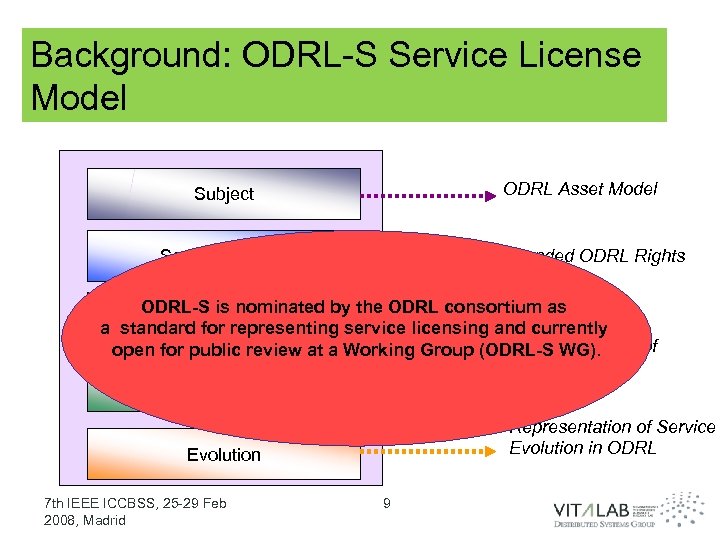 Background: ODRL-S Service License Model ODRL Asset Model Subject Extended ODRL Rights Model Scope of Rights ODRL-S is nominated by the ODRL consortium as Financial Terms a standard for representing service licensing and currently Representation of open for public review at a Working Group (ODRL-S WG). SLA in ODRL Warranties, Indemnities, Limitation of Liabilities Representation of Service Evolution in ODRL Evolution 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 9
Background: ODRL-S Service License Model ODRL Asset Model Subject Extended ODRL Rights Model Scope of Rights ODRL-S is nominated by the ODRL consortium as Financial Terms a standard for representing service licensing and currently Representation of open for public review at a Working Group (ODRL-S WG). SLA in ODRL Warranties, Indemnities, Limitation of Liabilities Representation of Service Evolution in ODRL Evolution 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 9
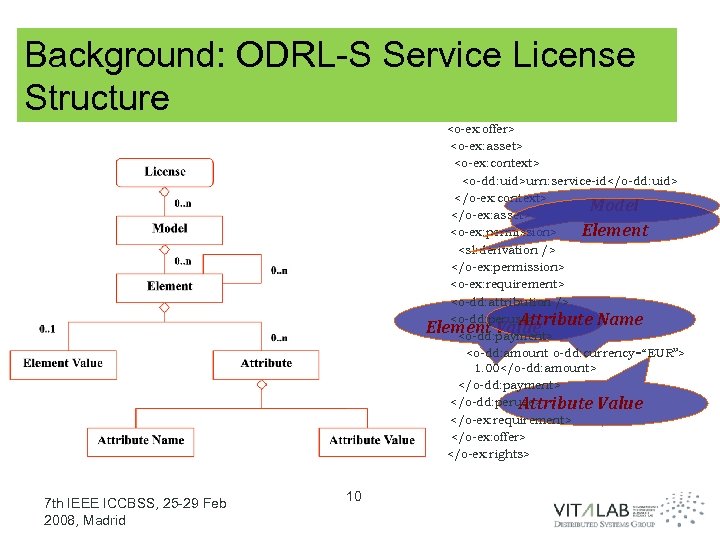 Background: ODRL-S Service License Structure
Background: ODRL-S Service License Structure
![Previous and background work for this paper § License Compatibility analysis [ICSOC’ 07]. § Previous and background work for this paper § License Compatibility analysis [ICSOC’ 07]. §](https://present5.com/presentation/78753c2dc0ea3e400b8a84eb334b0aab/image-11.jpg) Previous and background work for this paper § License Compatibility analysis [ICSOC’ 07]. § Service selection based on functional parameters § Vector space-based web services search (http: //www. vitalab. tuwien. ac. at/projects/search/) § Web Services Evolution Management Framework (SEMF) § Managing licenses and other services information § https: //www. vitalab. tuwien. ac. at/autocompwiki [ICSOC’ 07] G. R. Gangadharan, M. Weiss, V. D’Andrea, R. Iannella “Service License Composition and Compatibility Analysis”, Proc. of the Intl. Conf. on Service Oriented Computing (ICSOC’ 07), Vienna, Austria, Sept. 2007. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 11
Previous and background work for this paper § License Compatibility analysis [ICSOC’ 07]. § Service selection based on functional parameters § Vector space-based web services search (http: //www. vitalab. tuwien. ac. at/projects/search/) § Web Services Evolution Management Framework (SEMF) § Managing licenses and other services information § https: //www. vitalab. tuwien. ac. at/autocompwiki [ICSOC’ 07] G. R. Gangadharan, M. Weiss, V. D’Andrea, R. Iannella “Service License Composition and Compatibility Analysis”, Proc. of the Intl. Conf. on Service Oriented Computing (ICSOC’ 07), Vienna, Austria, Sept. 2007. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 11
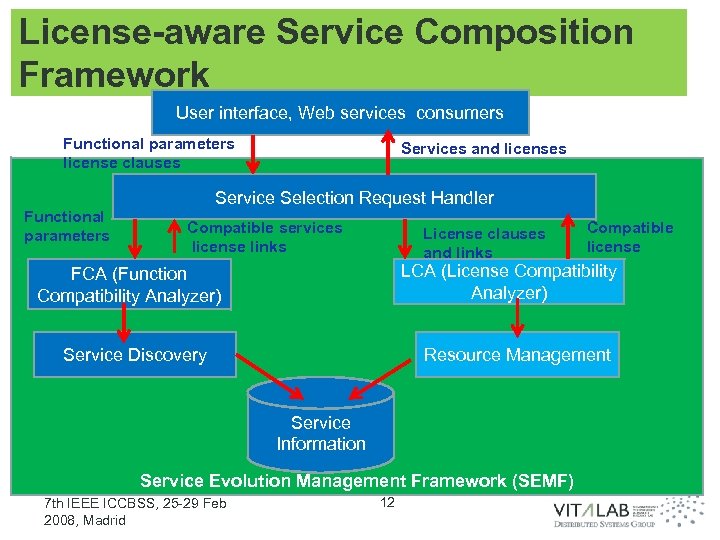 License-aware Service Composition Framework User interface, Web services consumers Functional parameters license clauses Functional parameters Services and licenses Service Selection Request Handler Compatible services license links License clauses and links LCA (License Compatibility Analyzer) FCA (Function Compatibility Analyzer) Service Discovery Resource Management Service Information Service Evolution Management Framework (SEMF) 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid Compatible license 12
License-aware Service Composition Framework User interface, Web services consumers Functional parameters license clauses Functional parameters Services and licenses Service Selection Request Handler Compatible services license links License clauses and links LCA (License Compatibility Analyzer) FCA (Function Compatibility Analyzer) Service Discovery Resource Management Service Information Service Evolution Management Framework (SEMF) 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid Compatible license 12
 Managing Service License using SEMF (cont. ) 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 15
Managing Service License using SEMF (cont. ) 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 15
 Consumer-specified Licenses • A service provider defines a license for the service and publishes the service with the license. • Service consumers are often interested in selecting a service with a particular type of license. Consumer-specified license: A set of license clauses specified by a consumer to be used in the selection of services. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 16
Consumer-specified Licenses • A service provider defines a license for the service and publishes the service with the license. • Service consumers are often interested in selecting a service with a particular type of license. Consumer-specified license: A set of license clauses specified by a consumer to be used in the selection of services. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 16
 Consumer-specified License-based Service Selection and Composition § Consumers specify licenses for a service to be composed § Our framework § Finds suitable services § Checks if licenses allow services to be composed § Proposes composite service license § Applies Directional Matching Algorithm for consumerspecified and provider-specific licenses in license composition 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 17
Consumer-specified License-based Service Selection and Composition § Consumers specify licenses for a service to be composed § Our framework § Finds suitable services § Checks if licenses allow services to be composed § Proposes composite service license § Applies Directional Matching Algorithm for consumerspecified and provider-specific licenses in license composition 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 17
 Service License Composition • Objective • To propose a service license for composite service • Composite license associated with composite service • Approach • Two licenses are compared using our algorithm presented in [ICSOC’ 07]. • A composite service license is generated by • Extracting elements of each license and put them together in a single license. • Removing redundant clauses. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 18
Service License Composition • Objective • To propose a service license for composite service • Composite license associated with composite service • Approach • Two licenses are compared using our algorithm presented in [ICSOC’ 07]. • A composite service license is generated by • Extracting elements of each license and put them together in a single license. • Removing redundant clauses. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 18
 Service License Composition • A set of functionalities and the requested license clauses are provided by a consumer as inputs. • Services matching the functionality specified by a consumer is retrieved. • LCA searches in the Service Information for the information about licenses of each service being selected by FCA • The license of the selected service is compared with the consumer-specified license. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 19
Service License Composition • A set of functionalities and the requested license clauses are provided by a consumer as inputs. • Services matching the functionality specified by a consumer is retrieved. • LCA searches in the Service Information for the information about licenses of each service being selected by FCA • The license of the selected service is compared with the consumer-specified license. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 19
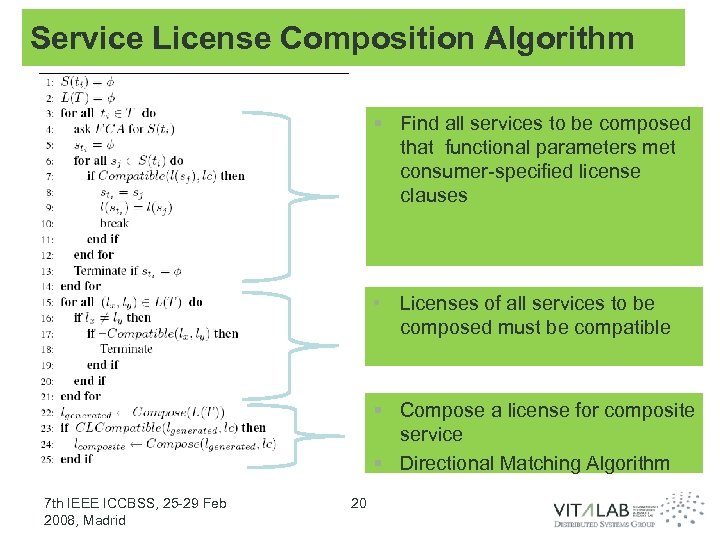 Service License Composition Algorithm § Find all services to be composed that functional parameters met consumer-specified license clauses • Licenses of all services to be composed must be compatible § Compose a license for composite service § Directional Matching Algorithm 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 20
Service License Composition Algorithm § Find all services to be composed that functional parameters met consumer-specified license clauses • Licenses of all services to be composed must be compatible § Compose a license for composite service § Directional Matching Algorithm 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 20
 Directional Matchmaking Algorithm (DMA) • Analyzing the compatibility between a consumer specified license and a provider specified service license. • Compatibility is directional • Based on a set of rules for compatibility between • consumer-specified license clauses against unspecified Scope of Rights and Financial Terms in providerspecified license clauses. • unspecified Scope of Rights and Financial Terms in consumer-specified license clauses against providerspecified license clauses. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 21
Directional Matchmaking Algorithm (DMA) • Analyzing the compatibility between a consumer specified license and a provider specified service license. • Compatibility is directional • Based on a set of rules for compatibility between • consumer-specified license clauses against unspecified Scope of Rights and Financial Terms in providerspecified license clauses. • unspecified Scope of Rights and Financial Terms in consumer-specified license clauses against providerspecified license clauses. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 21
 Directional Matchmaking Algorithm (DMA) (cont. ) • Two licenses are compatible, if all the respective models in both the licenses are compatible. • A model is compatible with another model, if the model types are same and their elements are compatible. • An element e 1 is compatible with another element e 2, if: • e 1 and e 2 have same type or using redefinition or unspecification [use tables] • e 1 and e 2 have equal value. • for all nested elements, corresponding elements are compatible. • all attributes of e 1 and e 2 are compatible. • An attribute a 1 is compatible with another attribute a 2, if the attributes are of same type and the associated values of attributes are equal. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 22
Directional Matchmaking Algorithm (DMA) (cont. ) • Two licenses are compatible, if all the respective models in both the licenses are compatible. • A model is compatible with another model, if the model types are same and their elements are compatible. • An element e 1 is compatible with another element e 2, if: • e 1 and e 2 have same type or using redefinition or unspecification [use tables] • e 1 and e 2 have equal value. • for all nested elements, corresponding elements are compatible. • all attributes of e 1 and e 2 are compatible. • An attribute a 1 is compatible with another attribute a 2, if the attributes are of same type and the associated values of attributes are equal. 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 22
 Illustrating scenario § Current implementation § Not all features have been implemented § Java-based algorithms § Tested in house § Simple scenario § Restaurance. Service to be composed from § Location. Service: provides map/location information § Reservation. Service: provides table reservations § We need to find possible Location. Service and Reservation. Service suitable to consumer-specified license 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 23
Illustrating scenario § Current implementation § Not all features have been implemented § Java-based algorithms § Tested in house § Simple scenario § Restaurance. Service to be composed from § Location. Service: provides map/location information § Reservation. Service: provides table reservations § We need to find possible Location. Service and Reservation. Service suitable to consumer-specified license 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 23
 Illustrating scenario: examples of licenses Reservation. Service License Location. Service License 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid Consumer-specified license 24
Illustrating scenario: examples of licenses Reservation. Service License Location. Service License 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid Consumer-specified license 24
 Illustrating scenario: Consumer Specified SL Composition Location. Service License
Illustrating scenario: Consumer Specified SL Composition Location. Service License
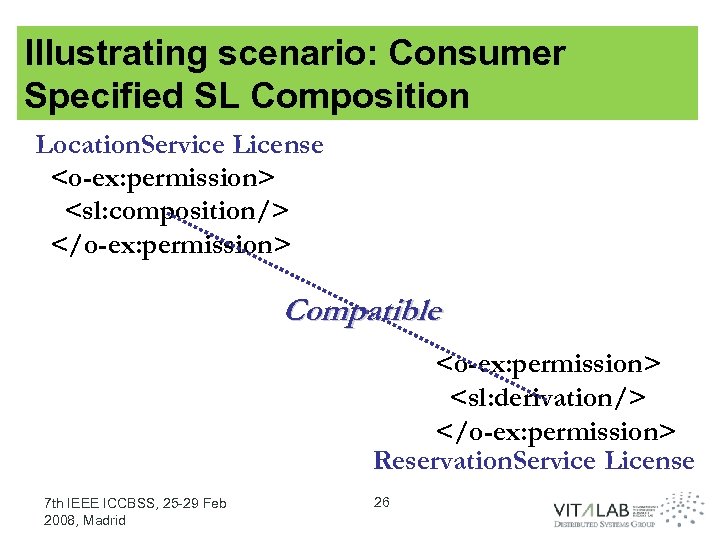 Illustrating scenario: Consumer Specified SL Composition Location. Service License
Illustrating scenario: Consumer Specified SL Composition Location. Service License
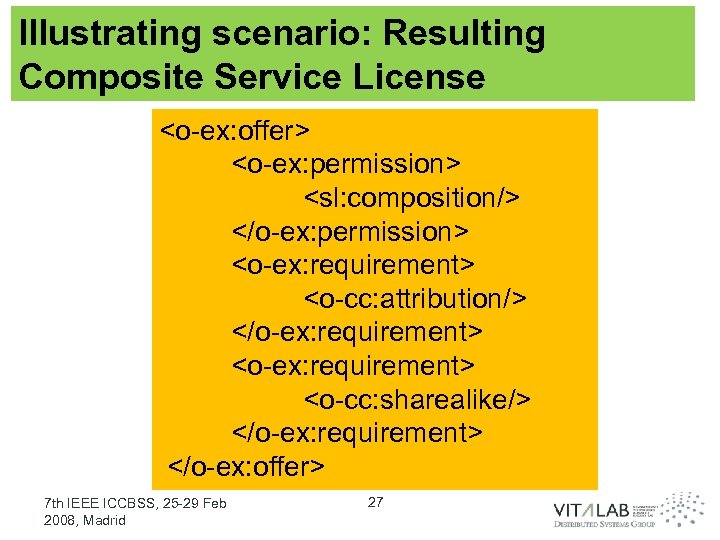 Illustrating scenario: Resulting Composite Service License
Illustrating scenario: Resulting Composite Service License
 Summary and next challenges § Mechanism to specify and associate licenses with services § To support consumer-specified, license-aware service selection and composition, motivated by Saa. S and service utility models § Foundation study for our next steps: àHow to realize and provide a full implementation of service license model for Saa. S/service utility àValidation of a real system with license-aware selection and composition àLicense enforcement for services 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 28
Summary and next challenges § Mechanism to specify and associate licenses with services § To support consumer-specified, license-aware service selection and composition, motivated by Saa. S and service utility models § Foundation study for our next steps: àHow to realize and provide a full implementation of service license model for Saa. S/service utility àValidation of a real system with license-aware selection and composition àLicense enforcement for services 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 28
 Thanks for your attention! Feedback, suggestion, research collaboration are more than welcome! Hong-Linh Truong Distributed Systems Group Vienna University of Technology truong@infosys. tuwien. ac. at https: //www. vitalab. tuwien. ac. at/autocompwiki 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 29
Thanks for your attention! Feedback, suggestion, research collaboration are more than welcome! Hong-Linh Truong Distributed Systems Group Vienna University of Technology truong@infosys. tuwien. ac. at https: //www. vitalab. tuwien. ac. at/autocompwiki 7 th IEEE ICCBSS, 25 -29 Feb 2008, Madrid 29


