c049e603158b675e3df1a25537021505.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 Consumer’s Attitude and Perception of Fresh Seafood Products : Cognitive Effects on Behaviour buying Stéphane Gouin - Lucile Mesnildrey – Lesueur Marie Agrocampus Ouest CFR Rennes, Pôle halieutique 65 rue de Saint Brieuc - CS 84215 – 35042 Rennes Cedex, France EAFE, 1 st-2 nd June 2010 - University of Helsinki, Finland
Consumer’s Attitude and Perception of Fresh Seafood Products : Cognitive Effects on Behaviour buying Stéphane Gouin - Lucile Mesnildrey – Lesueur Marie Agrocampus Ouest CFR Rennes, Pôle halieutique 65 rue de Saint Brieuc - CS 84215 – 35042 Rennes Cedex, France EAFE, 1 st-2 nd June 2010 - University of Helsinki, Finland
 PLAN 1. Consumer’s behaviours 1. 1. Attitudes and habits 2. 2. Perceptions and motivations 3. 3. Expectations and needs 2. Strategic consequences in french food retailing
PLAN 1. Consumer’s behaviours 1. 1. Attitudes and habits 2. 2. Perceptions and motivations 3. 3. Expectations and needs 2. Strategic consequences in french food retailing
 1. Consumer’s behaviours
1. Consumer’s behaviours
 Cogépêche Research Project Goals : • Assess consumer’s expectations and purchasing habits depending on the way of distribution. • Propose new trails of valorisation for fresh seafood products.
Cogépêche Research Project Goals : • Assess consumer’s expectations and purchasing habits depending on the way of distribution. • Propose new trails of valorisation for fresh seafood products.
 Context • Evolution of the fresh seafood products markets partly due to the globalization of the market. • Evolution of the consumer’s taste and behaviour face to the fresh seafood products • Evolution of the fresh seafood products perception • Occurrence of the industrialised fishing production • Development of the medium and large grocery stores
Context • Evolution of the fresh seafood products markets partly due to the globalization of the market. • Evolution of the consumer’s taste and behaviour face to the fresh seafood products • Evolution of the fresh seafood products perception • Occurrence of the industrialised fishing production • Development of the medium and large grocery stores
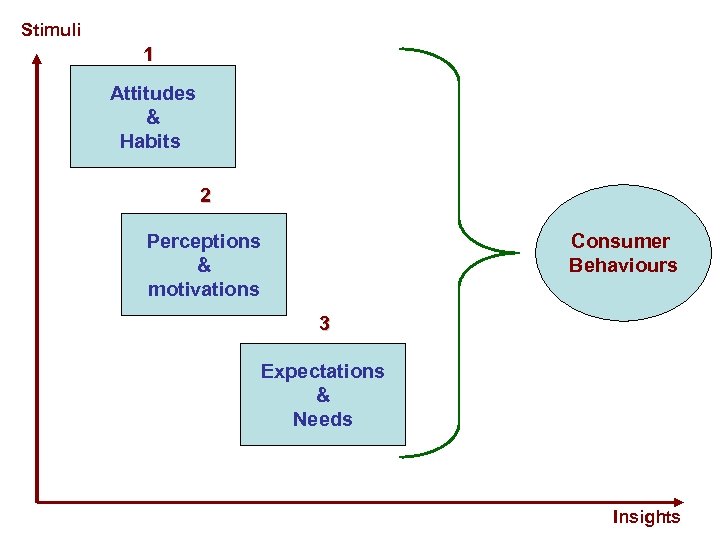 Stimuli 1 Attitudes & Habits 2 Perceptions & motivations Consumer Behaviours 3 Expectations & Needs Insights
Stimuli 1 Attitudes & Habits 2 Perceptions & motivations Consumer Behaviours 3 Expectations & Needs Insights
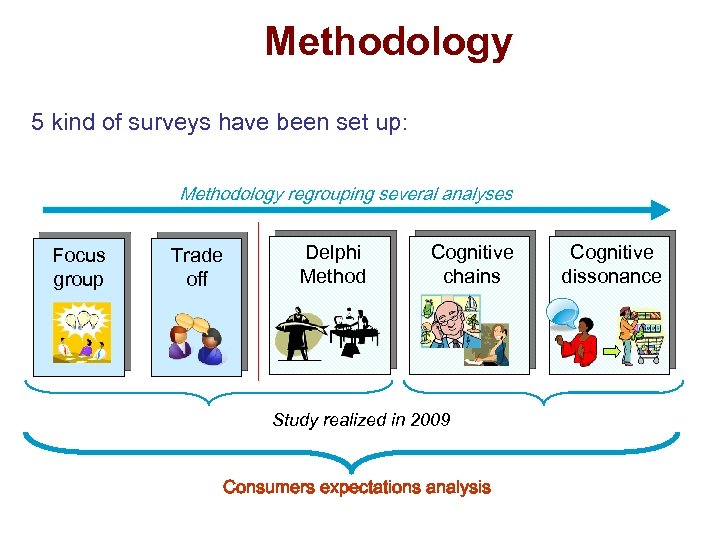 Methodology 5 kind of surveys have been set up: Methodology regrouping several analyses Focus group Trade off Delphi Method Cognitive chains Study realized in 2009 Consumers expectations analysis Cognitive dissonance
Methodology 5 kind of surveys have been set up: Methodology regrouping several analyses Focus group Trade off Delphi Method Cognitive chains Study realized in 2009 Consumers expectations analysis Cognitive dissonance
 Focus group • 18 focus group have been realised during the last month with 6 to 10 people each time Trade off • 850 people have been interviewed in order to specify the ideal seafood product for consumers Delphi Method • 50 interviews to confirm (or to invalidate) expectations, needs and behaviour of seafood products consumers according to professional’s viewpoint chains • 100 analysis of seafood products characteristics and determination of their importance in the decision of purchasing act Cognitive dissonance • 150 analysis of consumer’s habits, conviction, belief, behaviour about seafood products and the contradiction between them Cognitive
Focus group • 18 focus group have been realised during the last month with 6 to 10 people each time Trade off • 850 people have been interviewed in order to specify the ideal seafood product for consumers Delphi Method • 50 interviews to confirm (or to invalidate) expectations, needs and behaviour of seafood products consumers according to professional’s viewpoint chains • 100 analysis of seafood products characteristics and determination of their importance in the decision of purchasing act Cognitive dissonance • 150 analysis of consumer’s habits, conviction, belief, behaviour about seafood products and the contradiction between them Cognitive
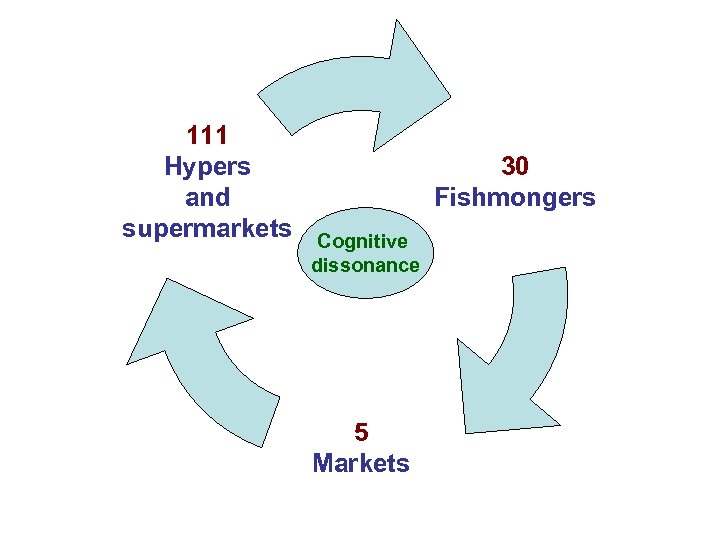 111 Hypers and supermarkets 30 Fishmongers Cognitive dissonance 5 Markets
111 Hypers and supermarkets 30 Fishmongers Cognitive dissonance 5 Markets
 1. 1. Attitudes and habits
1. 1. Attitudes and habits
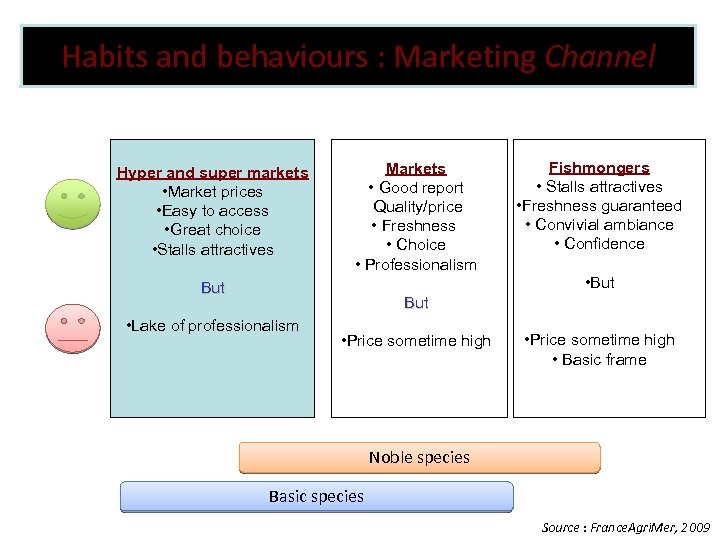 Habits and behaviours : Marketing Channel Hyper and super markets • Market prices • Easy to access • Great choice • Stalls attractives Markets • Good report Quality/price • Freshness • Choice • Professionalism But Fishmongers • Stalls attractives • Freshness guaranteed • Convivial ambiance • Confidence • But • Lake of professionalism • Price sometime high • Basic frame Noble species Basic species Source : France. Agri. Mer, 2009
Habits and behaviours : Marketing Channel Hyper and super markets • Market prices • Easy to access • Great choice • Stalls attractives Markets • Good report Quality/price • Freshness • Choice • Professionalism But Fishmongers • Stalls attractives • Freshness guaranteed • Convivial ambiance • Confidence • But • Lake of professionalism • Price sometime high • Basic frame Noble species Basic species Source : France. Agri. Mer, 2009
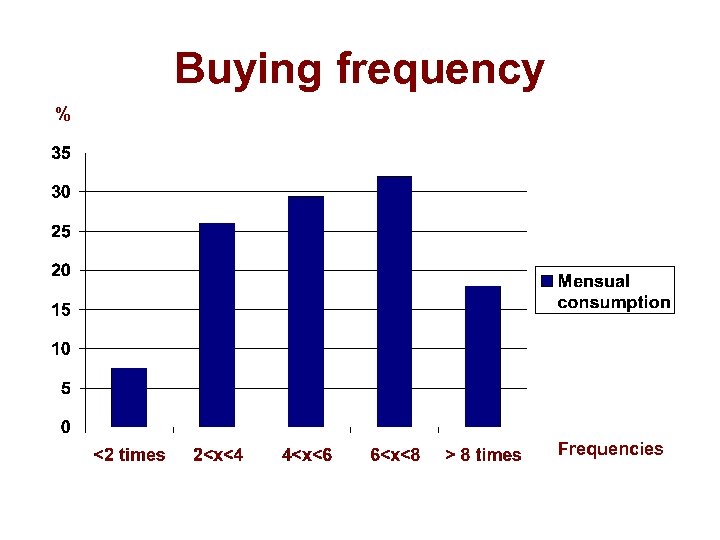 Buying frequency % Frequencies
Buying frequency % Frequencies
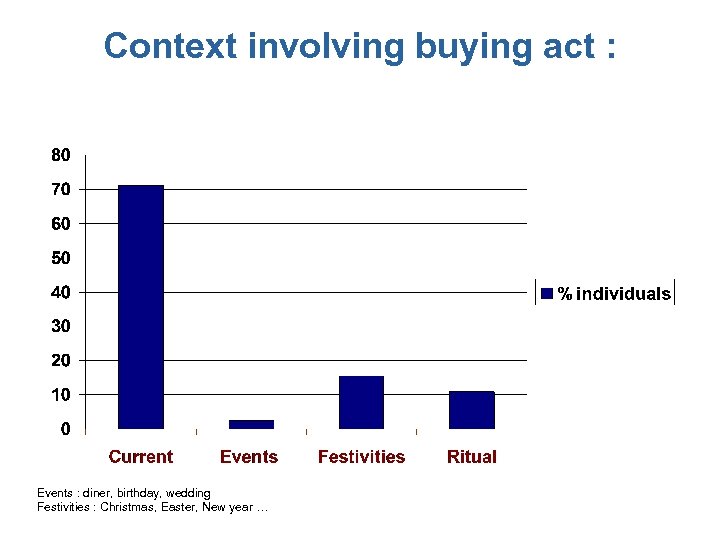 Context involving buying act : Events : diner, birthday, wedding Festivities : Christmas, Easter, New year …
Context involving buying act : Events : diner, birthday, wedding Festivities : Christmas, Easter, New year …
 2. 2. Perceptions and motivations
2. 2. Perceptions and motivations
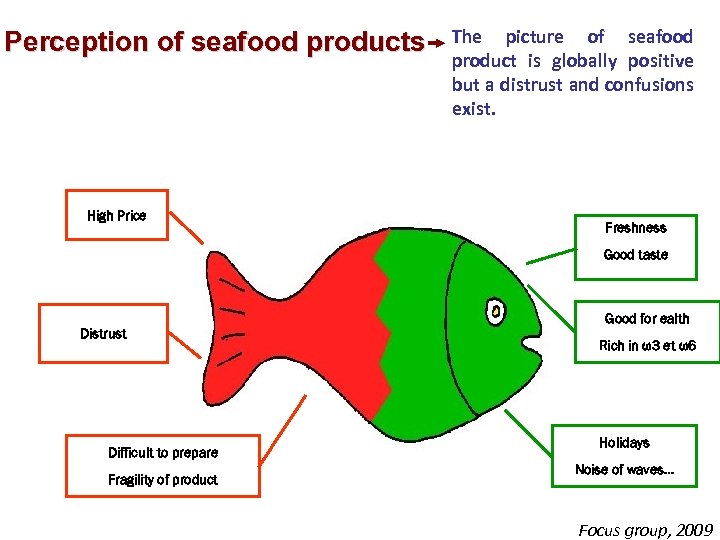 Perception of seafood products High Price The picture of seafood product is globally positive but a distrust and confusions exist. Freshness Good taste Distrust Difficult to prepare Fragility of product Good for ealth Rich in ω3 et ω6 Holidays Noise of waves… Focus group, 2009
Perception of seafood products High Price The picture of seafood product is globally positive but a distrust and confusions exist. Freshness Good taste Distrust Difficult to prepare Fragility of product Good for ealth Rich in ω3 et ω6 Holidays Noise of waves… Focus group, 2009
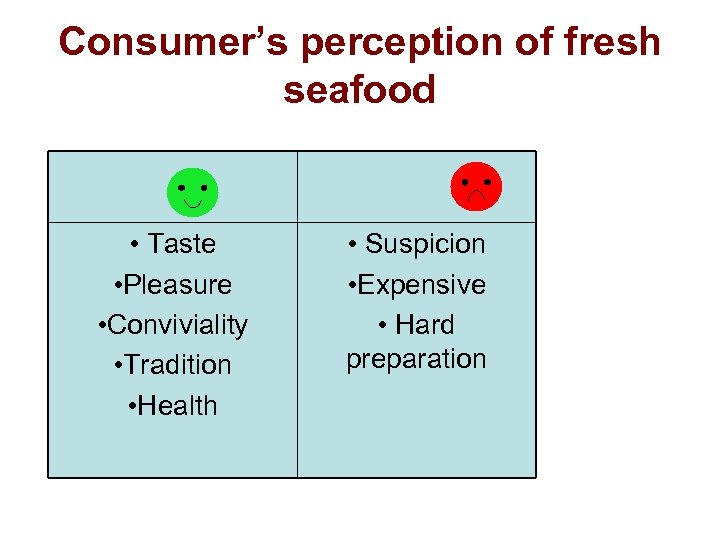 Consumer’s perception of fresh seafood • Taste • Pleasure • Conviviality • Tradition • Health • Suspicion • Expensive • Hard preparation
Consumer’s perception of fresh seafood • Taste • Pleasure • Conviviality • Tradition • Health • Suspicion • Expensive • Hard preparation
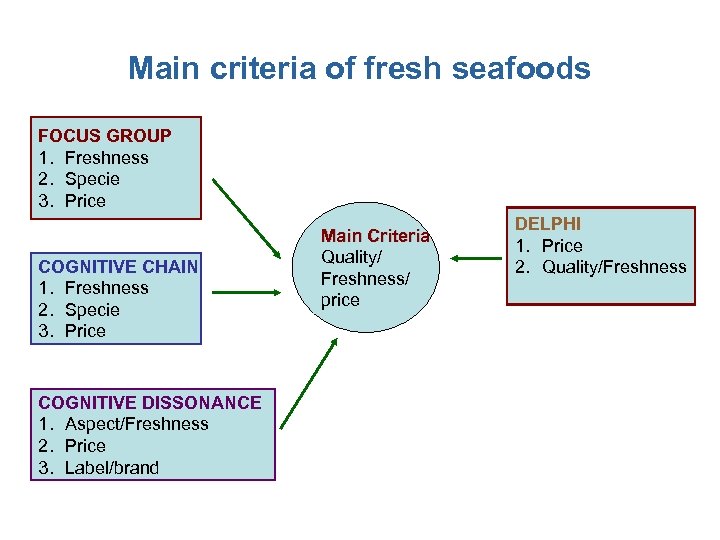 Main criteria of fresh seafoods FOCUS GROUP 1. Freshness 2. Specie 3. Price COGNITIVE CHAIN 1. Freshness 2. Specie 3. Price COGNITIVE DISSONANCE 1. Aspect/Freshness 2. Price 3. Label/brand Main Criteria Quality/ Freshness/ price DELPHI 1. Price 2. Quality/Freshness
Main criteria of fresh seafoods FOCUS GROUP 1. Freshness 2. Specie 3. Price COGNITIVE CHAIN 1. Freshness 2. Specie 3. Price COGNITIVE DISSONANCE 1. Aspect/Freshness 2. Price 3. Label/brand Main Criteria Quality/ Freshness/ price DELPHI 1. Price 2. Quality/Freshness
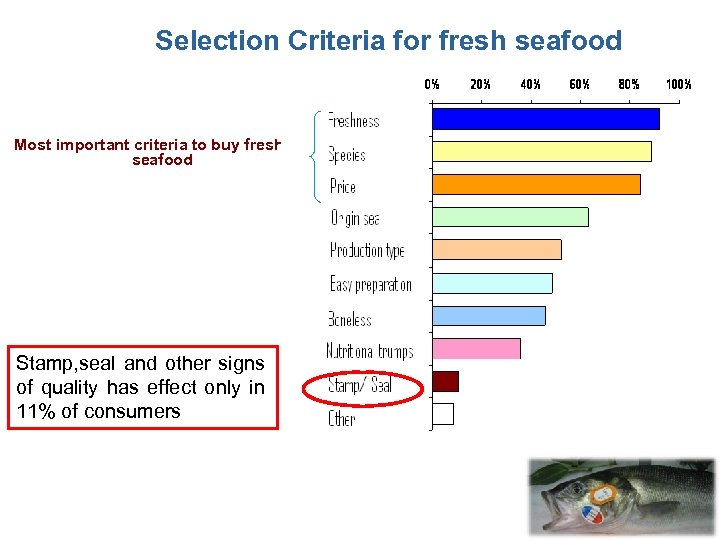 Selection Criteria for fresh seafood Most important criteria to buy fresh seafood Stamp, seal and other signs of quality has effect only in 11% of consumers
Selection Criteria for fresh seafood Most important criteria to buy fresh seafood Stamp, seal and other signs of quality has effect only in 11% of consumers
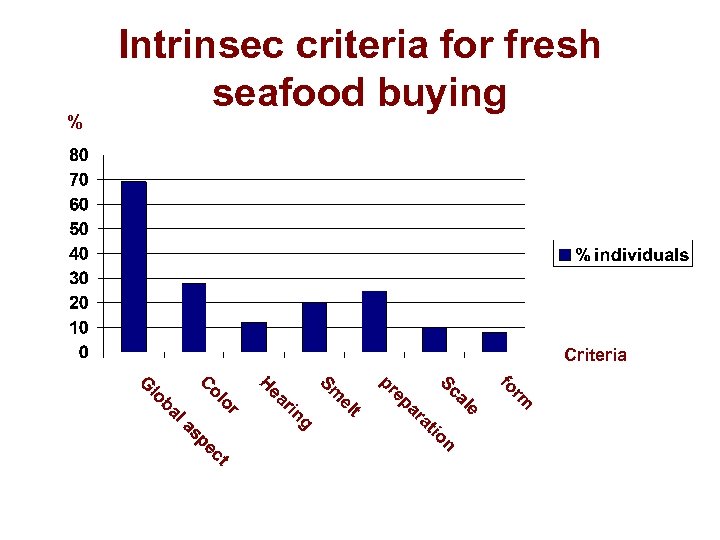 % Intrinsec criteria for fresh seafood buying Criteria
% Intrinsec criteria for fresh seafood buying Criteria
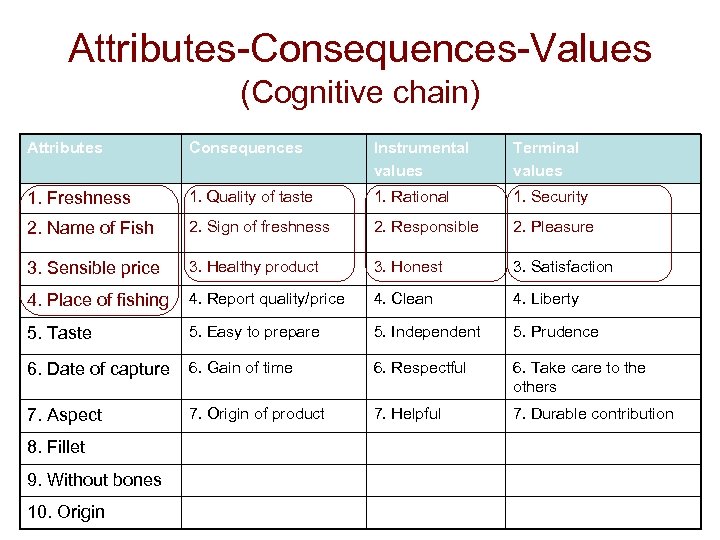 Attributes-Consequences-Values (Cognitive chain) Attributes Consequences Instrumental values Terminal values 1. Freshness 1. Quality of taste 1. Rational 1. Security 2. Name of Fish 2. Sign of freshness 2. Responsible 2. Pleasure 3. Sensible price 3. Healthy product 3. Honest 3. Satisfaction 4. Place of fishing 4. Report quality/price 4. Clean 4. Liberty 5. Taste 5. Easy to prepare 5. Independent 5. Prudence 6. Date of capture 6. Gain of time 6. Respectful 6. Take care to the others 7. Aspect 7. Origin of product 7. Helpful 7. Durable contribution 8. Fillet 9. Without bones 10. Origin
Attributes-Consequences-Values (Cognitive chain) Attributes Consequences Instrumental values Terminal values 1. Freshness 1. Quality of taste 1. Rational 1. Security 2. Name of Fish 2. Sign of freshness 2. Responsible 2. Pleasure 3. Sensible price 3. Healthy product 3. Honest 3. Satisfaction 4. Place of fishing 4. Report quality/price 4. Clean 4. Liberty 5. Taste 5. Easy to prepare 5. Independent 5. Prudence 6. Date of capture 6. Gain of time 6. Respectful 6. Take care to the others 7. Aspect 7. Origin of product 7. Helpful 7. Durable contribution 8. Fillet 9. Without bones 10. Origin
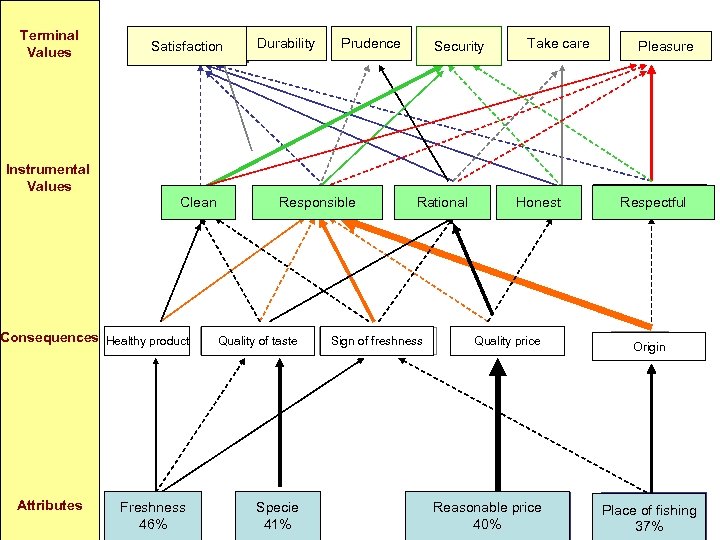 Terminal Values Instrumental Values Satisfaction Propre Clean Produit sain Consequences Healthy product Attributes Fraîcheur Freshness 46% Durable Sagesse Durability Prudence Responsable Responsible Qualité gustative Quality of taste Espèce Specie 41% Gage de fraicheur Sécurité Prendre soin Take care Security Rationnel Rational Sign of freshness Honnête Honest Qualité/prix Quality price Prix raisonnable Reasonable price 40% Pleasure Respectueux Respectful Origine Origin Lieu de pêche Place of fishing 37%
Terminal Values Instrumental Values Satisfaction Propre Clean Produit sain Consequences Healthy product Attributes Fraîcheur Freshness 46% Durable Sagesse Durability Prudence Responsable Responsible Qualité gustative Quality of taste Espèce Specie 41% Gage de fraicheur Sécurité Prendre soin Take care Security Rationnel Rational Sign of freshness Honnête Honest Qualité/prix Quality price Prix raisonnable Reasonable price 40% Pleasure Respectueux Respectful Origine Origin Lieu de pêche Place of fishing 37%
 Customer behaviour concerning fresh seafood buying Sample : 109 persons 100% Persons having realized their buying intention Persons having not realized their buying intention 65 persons 60% 44 persons 40% Persons having left off their fresh seafood buying Persons having bought another seafood product that they wanted 5 persons 11%% 39 persons 89%
Customer behaviour concerning fresh seafood buying Sample : 109 persons 100% Persons having realized their buying intention Persons having not realized their buying intention 65 persons 60% 44 persons 40% Persons having left off their fresh seafood buying Persons having bought another seafood product that they wanted 5 persons 11%% 39 persons 89%
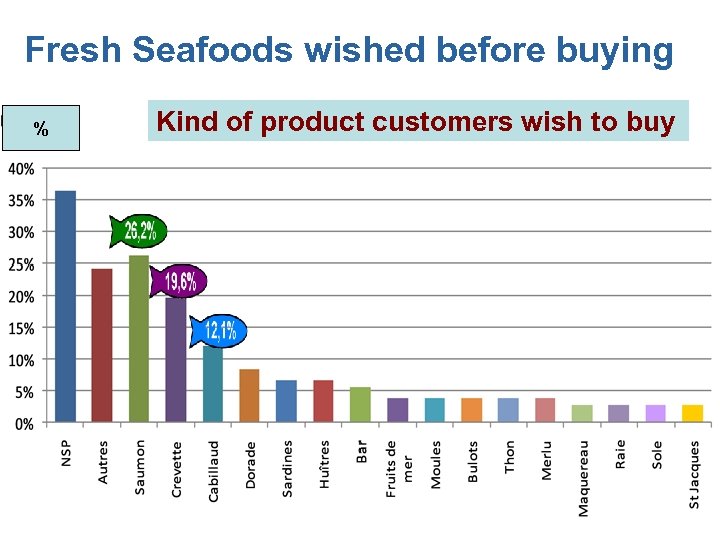 Fresh Seafoods wished before buying % Kind of product customers wish to buy
Fresh Seafoods wished before buying % Kind of product customers wish to buy
 Attributes influencing consumers’ buying act
Attributes influencing consumers’ buying act
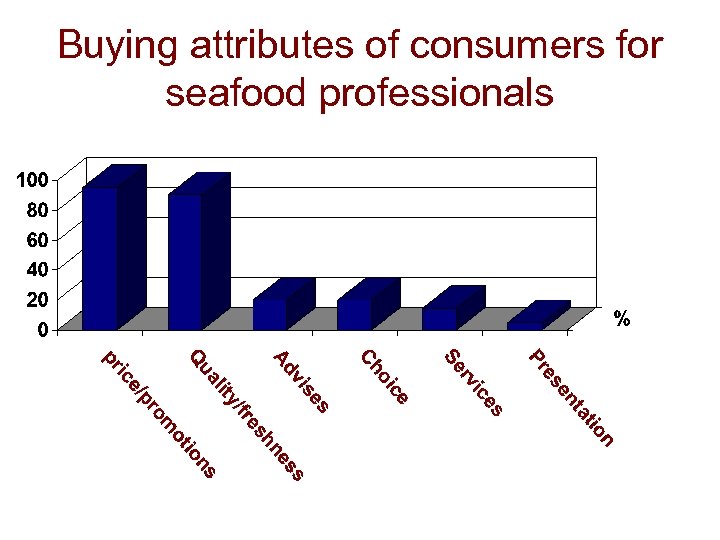 Buying attributes of consumers for seafood professionals
Buying attributes of consumers for seafood professionals
 Ideal product of fresh seafood: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Wild fish Low level of lipid Jagged Boneless Fresh
Ideal product of fresh seafood: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Wild fish Low level of lipid Jagged Boneless Fresh
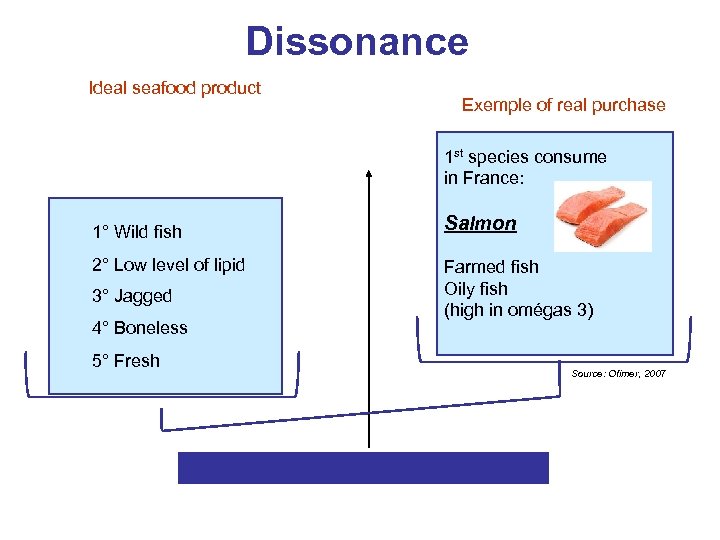 Dissonance Ideal seafood product Exemple of real purchase 1 st species consume in France: 1° Wild fish 2° Low level of lipid 3° Jagged 4° Boneless 5° Fresh Salmon Farmed fish Oily fish (high in omégas 3) Source: Ofimer, 2007
Dissonance Ideal seafood product Exemple of real purchase 1 st species consume in France: 1° Wild fish 2° Low level of lipid 3° Jagged 4° Boneless 5° Fresh Salmon Farmed fish Oily fish (high in omégas 3) Source: Ofimer, 2007
 3. 3. Expectations and needs
3. 3. Expectations and needs
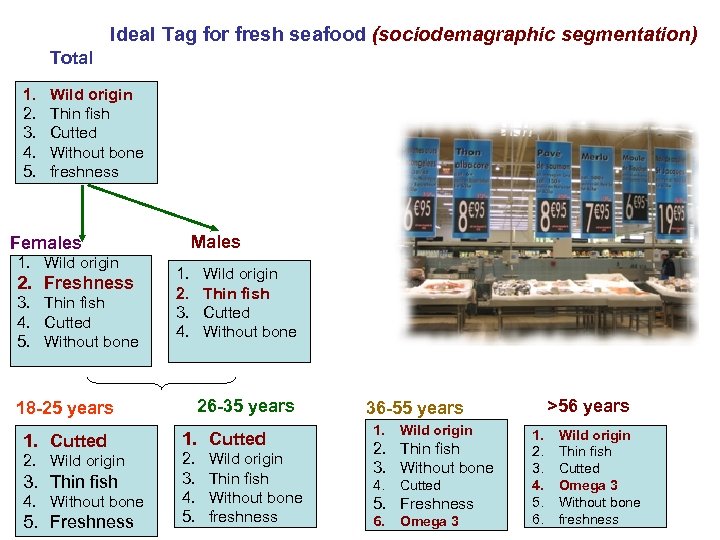 Ideal Tag for fresh seafood (sociodemagraphic segmentation) Total 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Wild origin Thin fish Cutted Without bone freshness Males Females 1. Wild origin 2. Freshness 3. Thin fish 4. Cutted 5. Without bone 1. 2. 3. 4. 26 -35 years 18 -25 years 1. Cutted 2. Wild origin 3. Thin fish 4. Without bone 5. Freshness Wild origin Thin fish Cutted Without bone 1. Cutted 2. 3. 4. 5. Wild origin Thin fish Without bone freshness >56 years 36 -55 years 1. Wild origin 2. Thin fish 3. Without bone 4. Cutted 5. Freshness 6. Omega 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Wild origin Thin fish Cutted Omega 3 Without bone freshness
Ideal Tag for fresh seafood (sociodemagraphic segmentation) Total 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Wild origin Thin fish Cutted Without bone freshness Males Females 1. Wild origin 2. Freshness 3. Thin fish 4. Cutted 5. Without bone 1. 2. 3. 4. 26 -35 years 18 -25 years 1. Cutted 2. Wild origin 3. Thin fish 4. Without bone 5. Freshness Wild origin Thin fish Cutted Without bone 1. Cutted 2. 3. 4. 5. Wild origin Thin fish Without bone freshness >56 years 36 -55 years 1. Wild origin 2. Thin fish 3. Without bone 4. Cutted 5. Freshness 6. Omega 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Wild origin Thin fish Cutted Omega 3 Without bone freshness
 • Unawareness of fresh seafood products: main obstacle to the consumption of fresh seafood products. • Gap between expectations, needs and purchasing habits… Which consent to pay? • Seal of approval, eco-label, signs of quality… Is there a real interest for consumers?
• Unawareness of fresh seafood products: main obstacle to the consumption of fresh seafood products. • Gap between expectations, needs and purchasing habits… Which consent to pay? • Seal of approval, eco-label, signs of quality… Is there a real interest for consumers?
 Consumer’s needs ü More information about origin, place of fishing, ü More transparency ü Proposition from salesmen to discover fresh seafood : recipes and advices about preparation, accompanying vegetables… ü Fresh seafood ready to cook, boneless ü Stall more exotic and original ü Cheaper
Consumer’s needs ü More information about origin, place of fishing, ü More transparency ü Proposition from salesmen to discover fresh seafood : recipes and advices about preparation, accompanying vegetables… ü Fresh seafood ready to cook, boneless ü Stall more exotic and original ü Cheaper
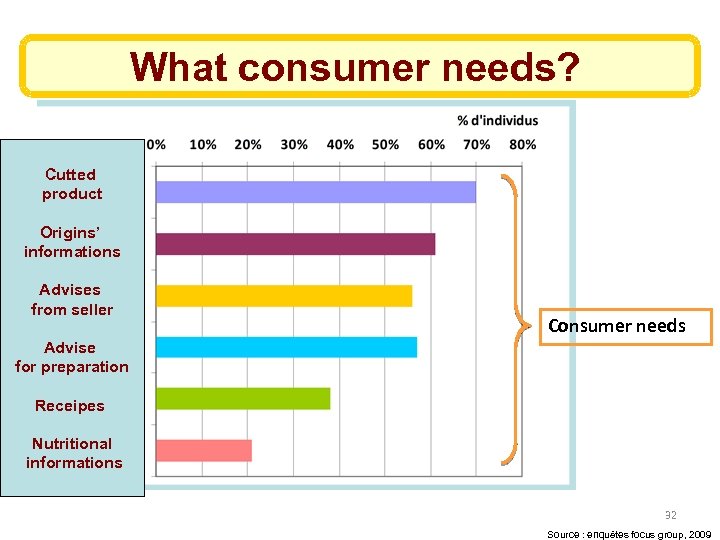 What consumer needs? Cutted product Origins’ informations Advises from seller Consumer needs Advise for preparation Receipes Nutritional informations 32 Source : enquêtes focus group, 2009
What consumer needs? Cutted product Origins’ informations Advises from seller Consumer needs Advise for preparation Receipes Nutritional informations 32 Source : enquêtes focus group, 2009
 The consumer of tomorrow…. …. wants to consume ethical products …. wants clear information (needs facts to support his emotional choices) …. wants to improve the quality of life (demand for natural and original products) …. wants to experience different cultures (demand for ethnic products) …. wants convenience (offered in the way he wants it)
The consumer of tomorrow…. …. wants to consume ethical products …. wants clear information (needs facts to support his emotional choices) …. wants to improve the quality of life (demand for natural and original products) …. wants to experience different cultures (demand for ethnic products) …. wants convenience (offered in the way he wants it)
 2. Strategies in french food retailing
2. Strategies in french food retailing
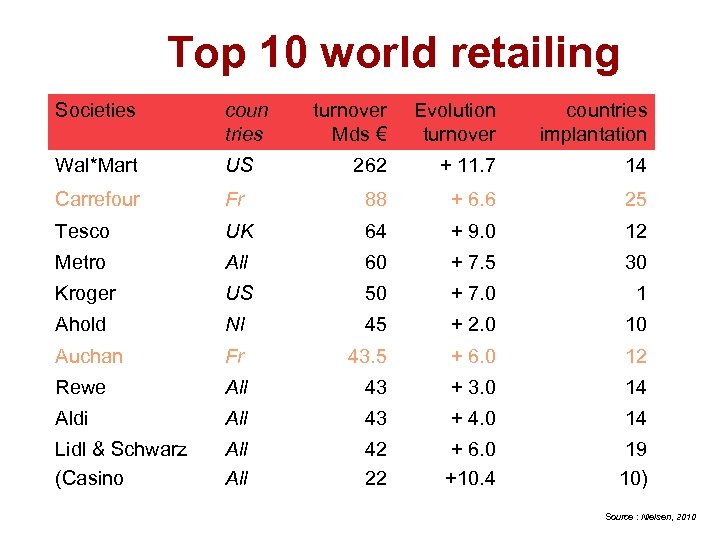 Top 10 world retailing Societies coun tries turnover Mds € Evolution turnover countries implantation Wal*Mart US 262 + 11. 7 14 Carrefour Fr 88 + 6. 6 25 Tesco UK 64 + 9. 0 12 Metro All 60 + 7. 5 30 Kroger US 50 + 7. 0 1 Ahold Nl 45 + 2. 0 10 Auchan Fr 43. 5 + 6. 0 12 Rewe All 43 + 3. 0 14 Aldi All 43 + 4. 0 14 Lidl & Schwarz (Casino All 42 22 + 6. 0 +10. 4 19 10) Source : Nielsen, 2010
Top 10 world retailing Societies coun tries turnover Mds € Evolution turnover countries implantation Wal*Mart US 262 + 11. 7 14 Carrefour Fr 88 + 6. 6 25 Tesco UK 64 + 9. 0 12 Metro All 60 + 7. 5 30 Kroger US 50 + 7. 0 1 Ahold Nl 45 + 2. 0 10 Auchan Fr 43. 5 + 6. 0 12 Rewe All 43 + 3. 0 14 Aldi All 43 + 4. 0 14 Lidl & Schwarz (Casino All 42 22 + 6. 0 +10. 4 19 10) Source : Nielsen, 2010
 FRENCH RETAILER’S POSITIONING Centralised Carrefour (Carrefour, Carrefour Market, Carrefour Contact, Carrefour City Ed, DIA) Intermarché (Intermarché, Ecomarché, Netto) Auchan (Auchan, Simply Market) Casino (Géant, Casino, Leader Price) Monoprix (Monoprix, Inno, Daily Monop) Independent Système U (Hyper U, Super U, Marché U, Utile) (Cora, Match) Leclerc (Leclerc) Decentralised Source : S. Gouin Cora Integrated
FRENCH RETAILER’S POSITIONING Centralised Carrefour (Carrefour, Carrefour Market, Carrefour Contact, Carrefour City Ed, DIA) Intermarché (Intermarché, Ecomarché, Netto) Auchan (Auchan, Simply Market) Casino (Géant, Casino, Leader Price) Monoprix (Monoprix, Inno, Daily Monop) Independent Système U (Hyper U, Super U, Marché U, Utile) (Cora, Match) Leclerc (Leclerc) Decentralised Source : S. Gouin Cora Integrated
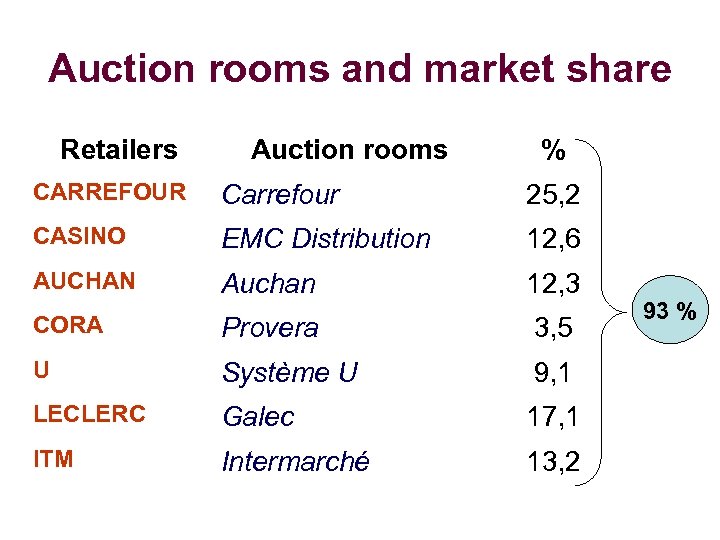 Auction rooms and market share Retailers Auction rooms % CARREFOUR Carrefour 25, 2 CASINO EMC Distribution 12, 6 AUCHAN Auchan 12, 3 CORA Provera 3, 5 U Système U 9, 1 LECLERC Galec 17, 1 ITM Intermarché 13, 2 93 %
Auction rooms and market share Retailers Auction rooms % CARREFOUR Carrefour 25, 2 CASINO EMC Distribution 12, 6 AUCHAN Auchan 12, 3 CORA Provera 3, 5 U Système U 9, 1 LECLERC Galec 17, 1 ITM Intermarché 13, 2 93 %
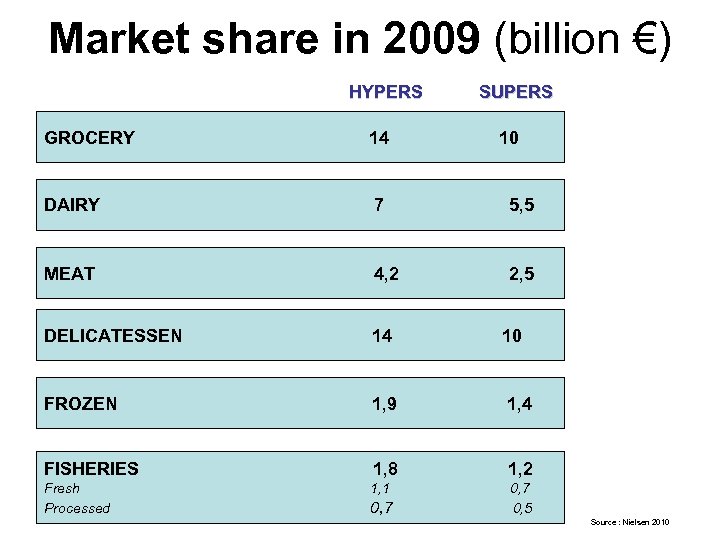 Market share in 2009 (billion €) HYPERS SUPERS GROCERY 14 10 DAIRY 7 5, 5 MEAT 4, 2 2, 5 DELICATESSEN 14 10 FROZEN 1, 9 1, 4 FISHERIES 1, 8 1, 2 Fresh Processed 1, 1 0, 7 0, 5 Source : Nielsen 2010
Market share in 2009 (billion €) HYPERS SUPERS GROCERY 14 10 DAIRY 7 5, 5 MEAT 4, 2 2, 5 DELICATESSEN 14 10 FROZEN 1, 9 1, 4 FISHERIES 1, 8 1, 2 Fresh Processed 1, 1 0, 7 0, 5 Source : Nielsen 2010
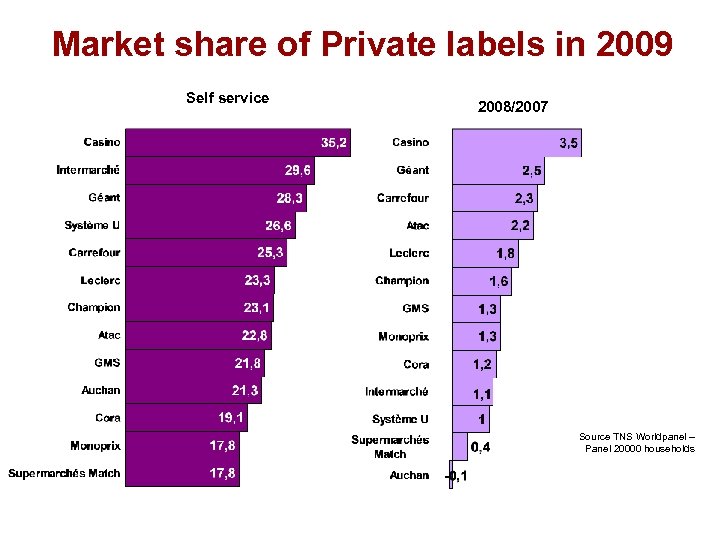 Market share of Private labels in 2009 Self service 2008/2007 Source TNS Worldpanel – Panel 20000 households
Market share of Private labels in 2009 Self service 2008/2007 Source TNS Worldpanel – Panel 20000 households
 French consumption/kg /year Bread Potatoes Fresh vegetables Beef Poultries Eggs Seafood (freh, frozen) Cheese Yogurts 1970 80, 6 95, 6 70, 4 1980 70, 6 89, 0 88, 4 1990 61, 7 60, 8 86, 0 2008 53, 7 71, 3 85, 9 15, 6 14, 2 11, 5 9, 9 19, 2 19, 3 14, 2 12, 8 17, 1 21, 7 14, 0 14, 4 13, 8 19, 7 13, 6 11, 8 13, 8 8, 6 15, 2 8, 7 16, 6 15, 9 18, 4 22, 2
French consumption/kg /year Bread Potatoes Fresh vegetables Beef Poultries Eggs Seafood (freh, frozen) Cheese Yogurts 1970 80, 6 95, 6 70, 4 1980 70, 6 89, 0 88, 4 1990 61, 7 60, 8 86, 0 2008 53, 7 71, 3 85, 9 15, 6 14, 2 11, 5 9, 9 19, 2 19, 3 14, 2 12, 8 17, 1 21, 7 14, 0 14, 4 13, 8 19, 7 13, 6 11, 8 13, 8 8, 6 15, 2 8, 7 16, 6 15, 9 18, 4 22, 2
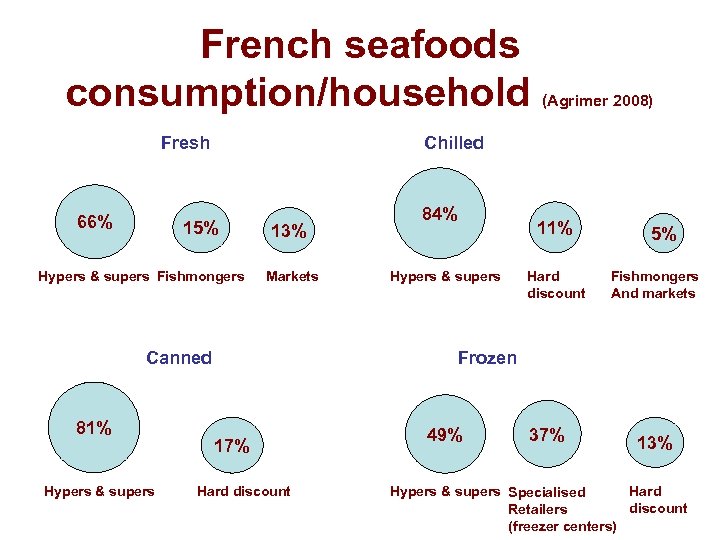 French seafoods consumption/household Fresh 66% Chilled 15% Hypers & supers Fishmongers 13% Markets Canned 81% Hypers & supers (Agrimer 2008) 17% Hard discount 84% 11% Hypers & supers Hard discount 5% Fishmongers And markets Frozen 49% 37% 13% Hypers & supers Specialised Hard discount Retailers (freezer centers)
French seafoods consumption/household Fresh 66% Chilled 15% Hypers & supers Fishmongers 13% Markets Canned 81% Hypers & supers (Agrimer 2008) 17% Hard discount 84% 11% Hypers & supers Hard discount 5% Fishmongers And markets Frozen 49% 37% 13% Hypers & supers Specialised Hard discount Retailers (freezer centers)
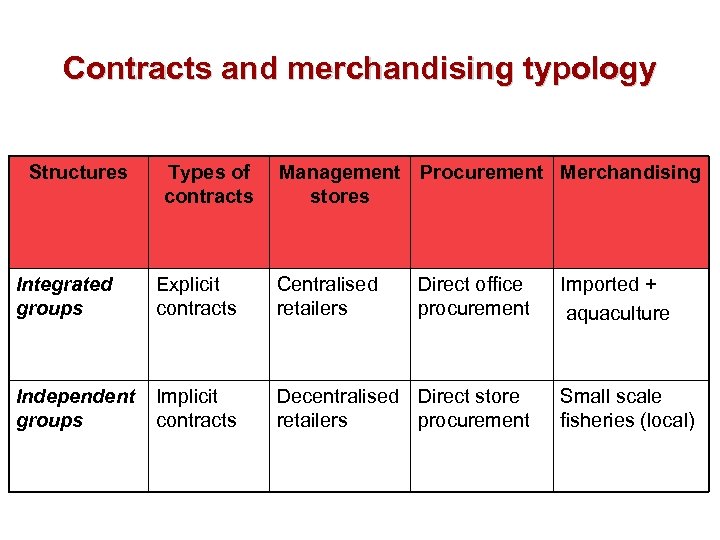 Contracts and merchandising typology Structures Types of contracts Management Procurement Merchandising stores Integrated groups Explicit contracts Centralised retailers Direct office procurement Independent groups Implicit contracts Decentralised Direct store retailers procurement Imported + aquaculture Small scale fisheries (local)
Contracts and merchandising typology Structures Types of contracts Management Procurement Merchandising stores Integrated groups Explicit contracts Centralised retailers Direct office procurement Independent groups Implicit contracts Decentralised Direct store retailers procurement Imported + aquaculture Small scale fisheries (local)
 Insufficient visibility on unloadings – Lack of information in real time to organise the sale of fresh seafoods – Adequation fresh seafood/sale in store • Difficulty to anticipate the price variations – Lack of reliable information contributes to the difficulties to organise the selling stores
Insufficient visibility on unloadings – Lack of information in real time to organise the sale of fresh seafoods – Adequation fresh seafood/sale in store • Difficulty to anticipate the price variations – Lack of reliable information contributes to the difficulties to organise the selling stores
 Promotion policies • National promotion : 2 months before selling (to ensure supplying) – Difficult to supply 10 tons of brittany lobster • Increase NIP (New Instrument Publicity) – Theatralisation, animation, testing • Answer to situation/function – Category management
Promotion policies • National promotion : 2 months before selling (to ensure supplying) – Difficult to supply 10 tons of brittany lobster • Increase NIP (New Instrument Publicity) – Theatralisation, animation, testing • Answer to situation/function – Category management
 Merchandising expectations • New concept of merchandising based on situation/function – – Singularisation (ITM) Meal solution (carry out) – (Carrefour) Packaged (Leclerc, U…) Eat on place (Casino) • New target of cunsumers : generational typology • New communication : origin, tracability, carbon print…
Merchandising expectations • New concept of merchandising based on situation/function – – Singularisation (ITM) Meal solution (carry out) – (Carrefour) Packaged (Leclerc, U…) Eat on place (Casino) • New target of cunsumers : generational typology • New communication : origin, tracability, carbon print…
 Equipment « singularisation type » : Exemple of supermarket üDefine a shopper segmentation üRespect the logic of customer : fishing choice, product range, consumption mode ü respect the preparation degree : ready to cook, to grill, to broil, to assemble üCreate a product group : whole, filleted, sliced, thin or thick steak…
Equipment « singularisation type » : Exemple of supermarket üDefine a shopper segmentation üRespect the logic of customer : fishing choice, product range, consumption mode ü respect the preparation degree : ready to cook, to grill, to broil, to assemble üCreate a product group : whole, filleted, sliced, thin or thick steak…
 Tomorrow : what attempts and needs? Theatralisation : an answer of evasion needs? → Point of sale atmosphere is able to influence the shopper → Fishing display in supermarkets and fishmongers have to stimulate buying customers 47
Tomorrow : what attempts and needs? Theatralisation : an answer of evasion needs? → Point of sale atmosphere is able to influence the shopper → Fishing display in supermarkets and fishmongers have to stimulate buying customers 47
 Conclusion
Conclusion
 In the future Private lebel increasing Fresh space development New concepts Shelves re positioning
In the future Private lebel increasing Fresh space development New concepts Shelves re positioning
 The end of fresh seafood products? • Fresh seafood stall will decrease • Fresh seafood in packaging will increase including new concept : ready to cook, ready to eat, to mix with something, with sauce… • Only several fresh seafood species will be available • New merchandising concept will be necessary to extend the consumer generations
The end of fresh seafood products? • Fresh seafood stall will decrease • Fresh seafood in packaging will increase including new concept : ready to cook, ready to eat, to mix with something, with sauce… • Only several fresh seafood species will be available • New merchandising concept will be necessary to extend the consumer generations
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!


