Consumer buying behaviour The buying behaviour of final


Consumer buying behaviour The buying behaviour of final consumers who buy goods and services for personal consumption
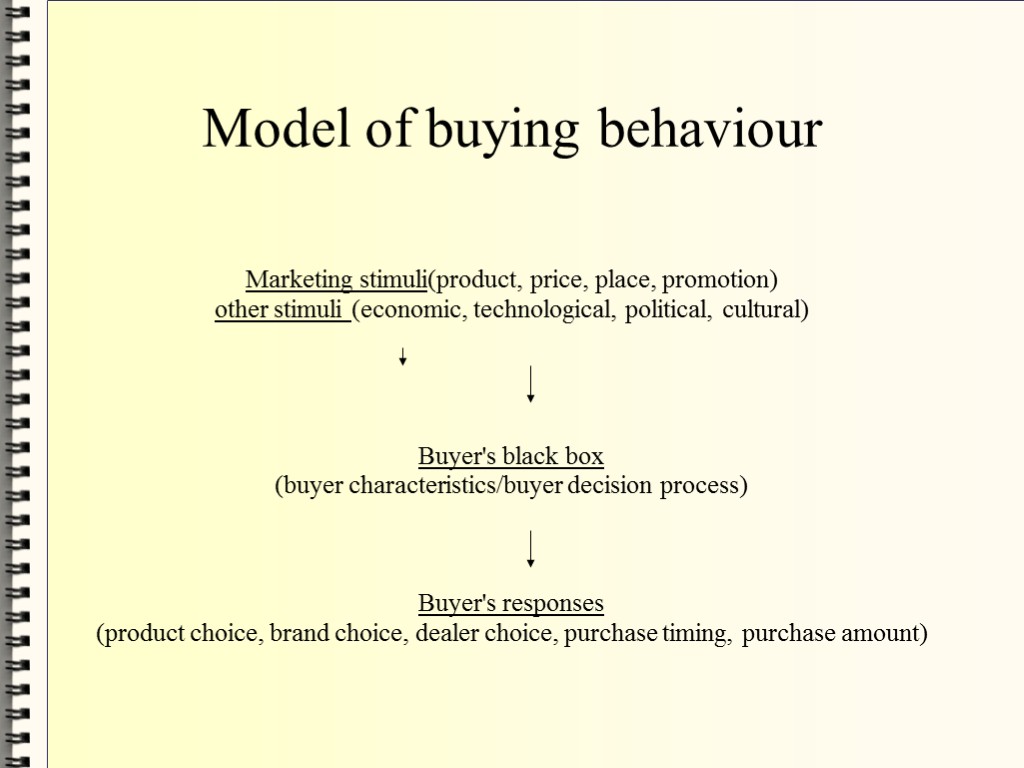
Model of buying behaviour Marketing stimuli(product, price, place, promotion) other stimuli (economic, technological, political, cultural) Buyer's black box (buyer characteristics/buyer decision process) Buyer's responses (product choice, brand choice, dealer choice, purchase timing, purchase amount)

Marketing and other stimuli enter the consumer's «black box» and produce certain responses. The company that really understands how consumers will respond to different product features, prices and advertising appeal has a great advantage over its competitors.

Characteristics affecting consumer behaviour 1.Cultural factors ( culture, subculture, social class) 2. Social factors (reference groups, family, roles and status) 3. Personal factors (age, occupation, economic circumstances, lifestyle, personality, self-concept) 4. Psychological factors (motivation, perception, learning, beliefs and attitudes)

Consumer purchases are influenced strongly by these factors. Marketers cannot control them , but they must take them into account.

Maslow's theory of motivation 5. Self-development and realisation needs – потребности в саморазвитии и самоутверждении 4. Esteem needs (потребности в уважении) self-esteem - самоуважение, recognition – признание окружающих, status 3. Social needs (sense of belonging – чувство духовной близости, love) 2. Safety needs (security - безопасность, protection - защищенность) 1. Physiological needs (hunger, thirst)

Types of buying decision behaviour Complex Dissonance-reducing (неуверенное) Variety-seeking (поисковое) Habitual (привычное)
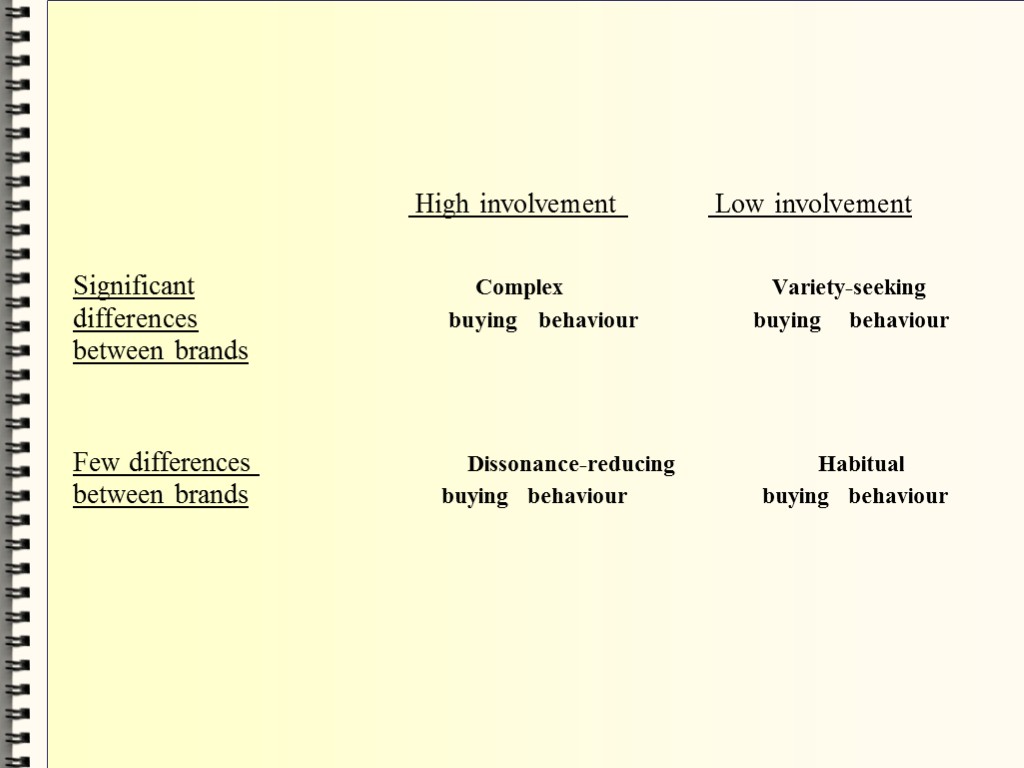
High involvement Low involvement Significant Complex Variety-seeking differences buying behaviour buying behaviour between brands Few differences Dissonance-reducing Habitual between brands buying behaviour buying behaviour

Consumers undertake complex buying behaviour when they are higly involved in a purchase and perceive significant differences among brands, or when the product is expensive, risky, purchased infrequently (e.g. buying a personal computer)

Dissonance-reducing buying behaviour occurs when consumers are highly involved with an expensive, infrequent or risky purchase, but see little difference among brands (e.g. buying a carpet)

Habitual buying behaviour occurs when consumers are not highly involved in a purchase and see little significant brand difference. (salt)

Variety-seeking buying behaviour occurs when consumers are not highly involved in a purchase but perceive significant differences among brands ( e.g. confectionery)
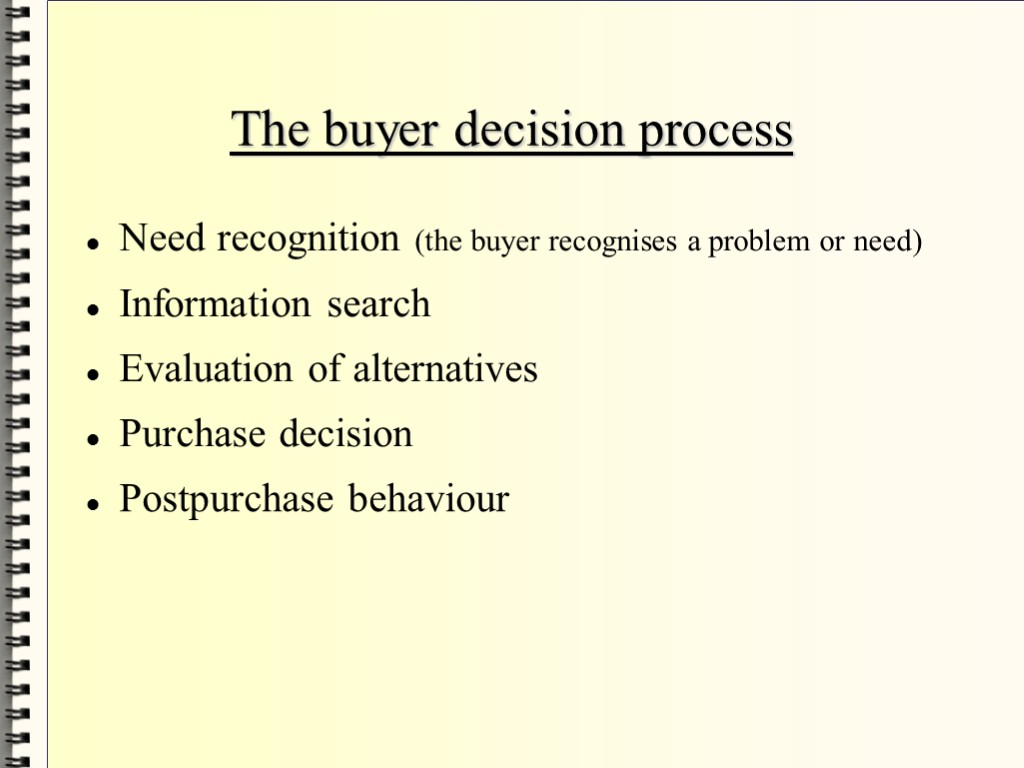
The buyer decision process Need recognition (the buyer recognises a problem or need) Information search Evaluation of alternatives Purchase decision Postpurchase behaviour
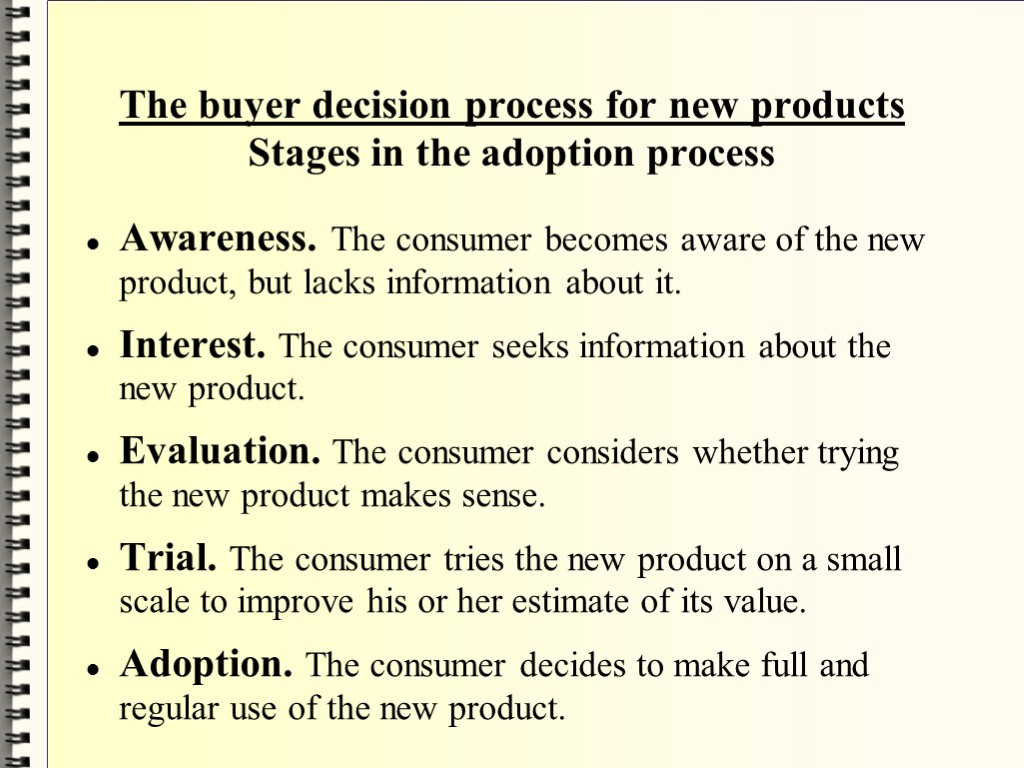
The buyer decision process for new products Stages in the adoption process Awareness. The consumer becomes aware of the new product, but lacks information about it. Interest. The consumer seeks information about the new product. Evaluation. The consumer considers whether trying the new product makes sense. Trial. The consumer tries the new product on a small scale to improve his or her estimate of its value. Adoption. The consumer decides to make full and regular use of the new product.
consumer_behaviour.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

