5b17c1c9195fdb248de83b5b65e28a06.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 126

Consumer Behavior, Trends & Segmentation Week 3 BA 343

Consumer Behavior & Shopping Patterns: Mental State (Alpha vs. Beta mode), Promo-Tricks (Sales-Limit # items), Use of –lists… n

nce flue at in vior h rs t Beha acto er ess D f sum ü ICon er g Proc Buyakin ine n-M utl sio ü O eci D c & logi ate s lineique tion De hn ü tec enta egm of S
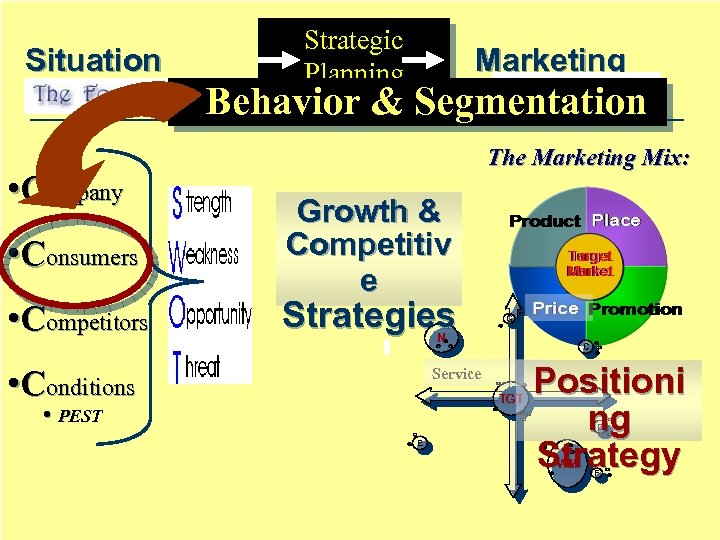
Situation Analysis • Company • Consumers • Competitors Strategic Planning Behavior & Marketing Strategy P’s Segmentation The Marketing Mix: Growth & Competitiv e Strategies G N • Conditions C Service TGT • PEST Positioni ng Strategy D E WM F

How Do You Decide?
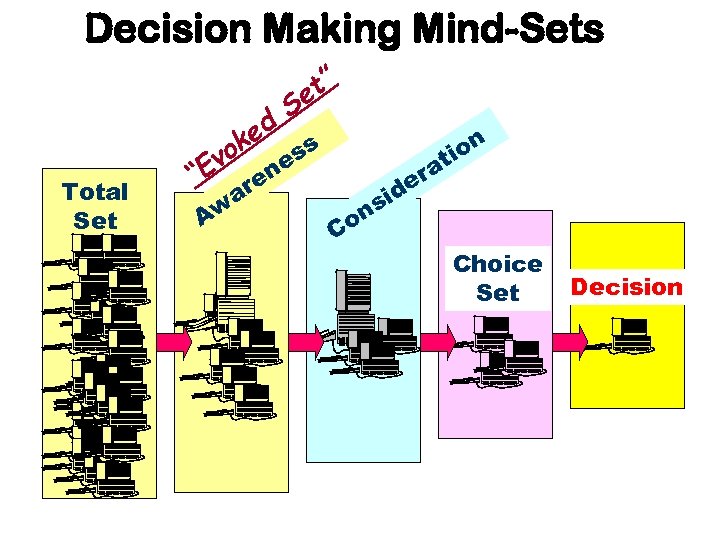
Decision Making Mind-Sets Total Set vo ed k “E t” e S Aw n re a ss e Co si n a er d n io t Choice Set Decision

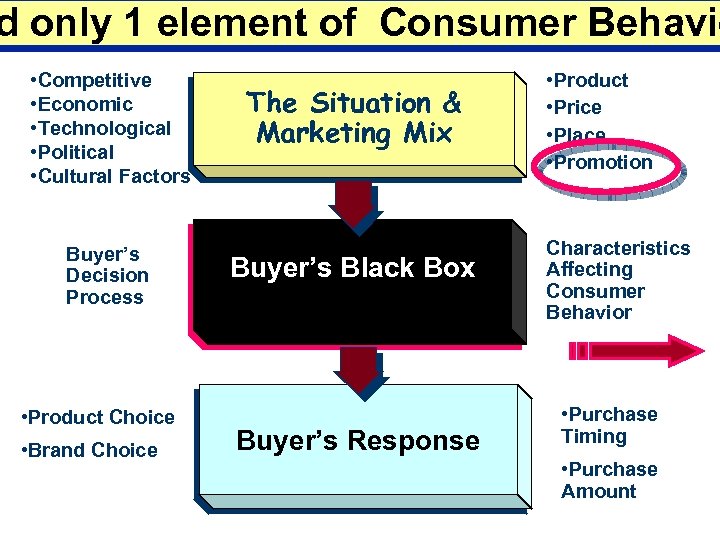
d only 1 element of Consumer Behavio • Competitive • Economic • Technological • Political • Cultural Factors Buyer’s Decision Process • Product Choice • Brand Choice The Situation & Marketing Mix Buyer’s Black Box Buyer’s Response • Product • Price • Place • Promotion Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior • Purchase Timing • Purchase Amount
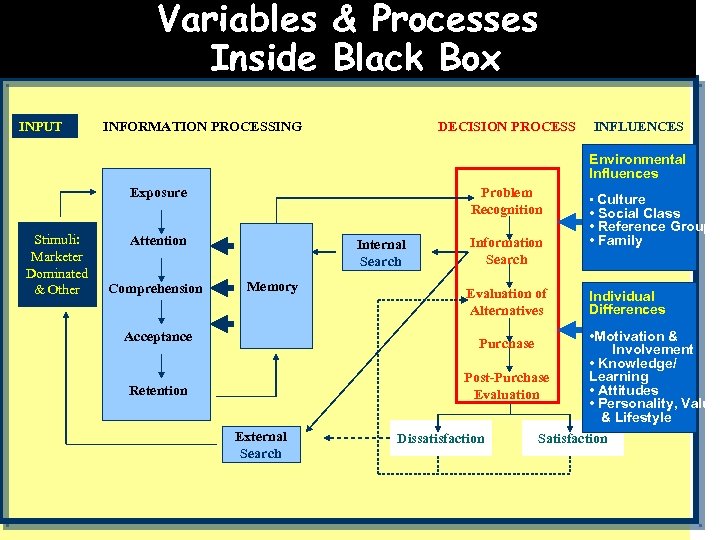
Variables & Processes Inside Black Box INPUT INFORMATION PROCESSING DECISION PROCESS INFLUENCES Environmental Influences Problem Recognition Exposure Stimuli: Marketer Dominated & Other Attention Comprehension Acceptance Information Search • Social Class • Reference Group • Family Evaluation of Alternatives Internal Search Memory Individual Differences • Motivation & Involvement • Knowledge/ Learning Post-Purchase • Attitudes Evaluation • Personality, Values & Lifestyle Dissatisfaction Satisfaction Purchase Retention External Search • Culture
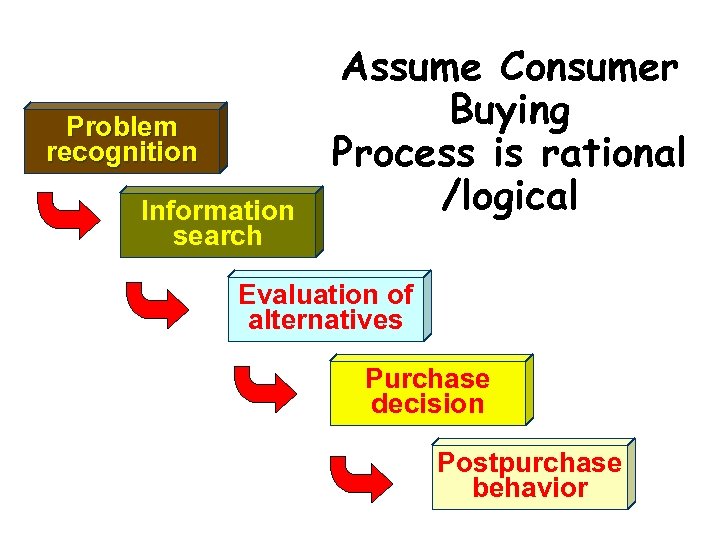
Problem recognition Information search Assume Consumer Buying Process is rational /logical Evaluation of alternatives Purchase decision Postpurchase behavior
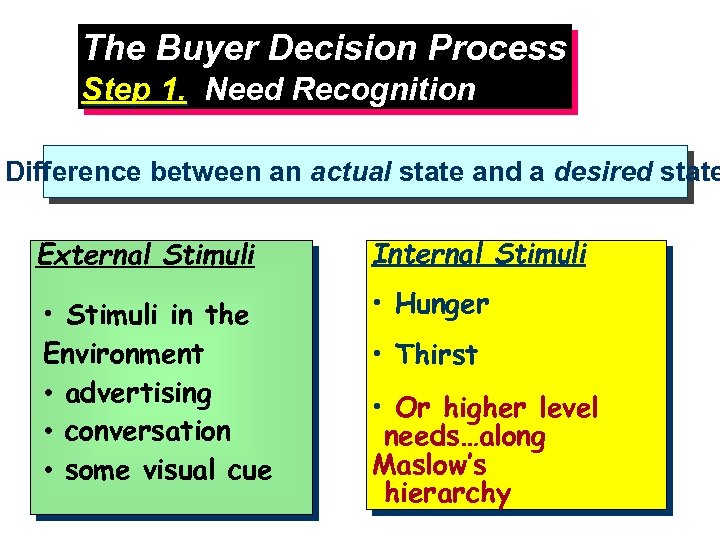
The Buyer Decision Process Step 1. Need Recognition Difference between an actual state and a desired state External Stimuli Internal Stimuli • Stimuli in the Environment • advertising • conversation • some visual cue • Hunger • Thirst • Or higher level needs…along Maslow’s hierarchy
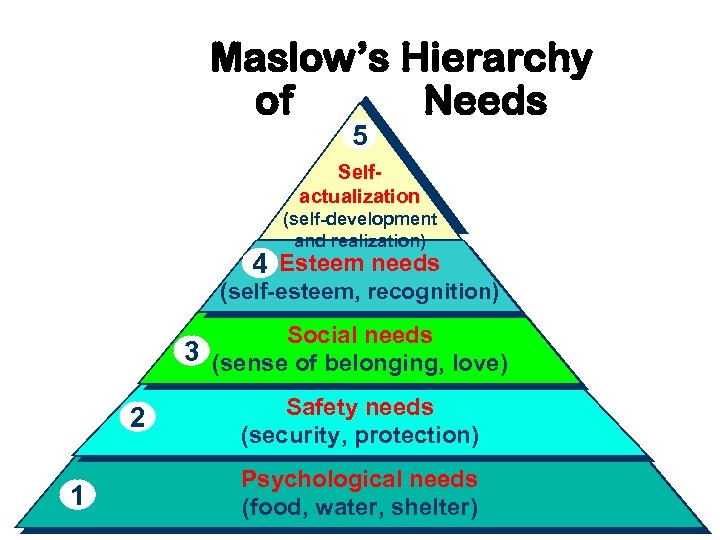
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 5 Selfactualization (self-development and realization) 4 Esteem needs (self-esteem, recognition) Social needs 3 (sense of belonging, love) 2 1 Safety needs (security, protection) Psychological needs (food, water, shelter)
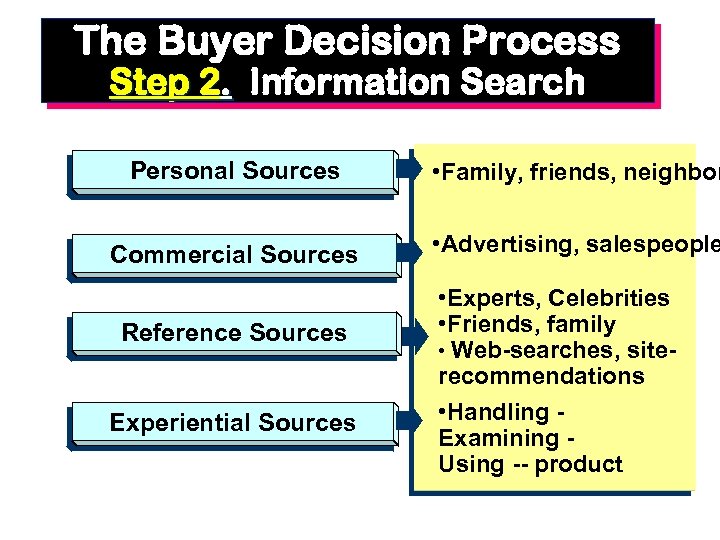
The Buyer Decision Process Step 2. Information Search Personal Sources Commercial Sources Reference Sources Experiential Sources • Family, friends, neighbor • Advertising, salespeople • Experts, Celebrities • Friends, family • Web-searches, site- recommendations • Handling Examining Using -- product
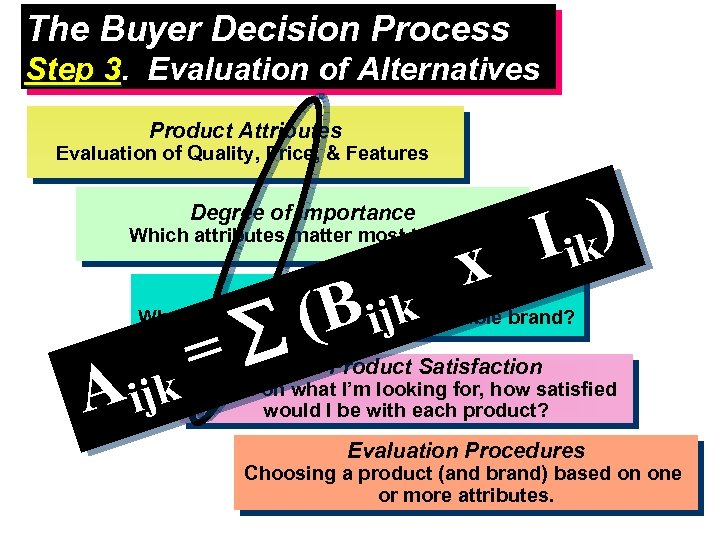
The Buyer Decision Process Step 3. Evaluation of Alternatives 3 Product Attributes Evaluation of Quality, Price, & Features Degree of Importance Which attributes matter most to me? (B ijk Brand Beliefs x ) I ik What do I believe about each available brand? = k A ij Total Product Satisfaction Based on what I’m looking for, how satisfied would I be with each product? Evaluation Procedures Choosing a product (and brand) based on one or more attributes.
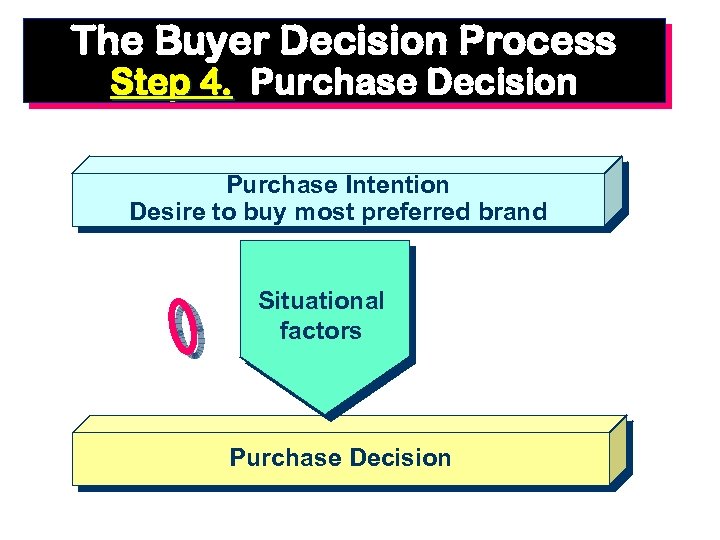
The Buyer Decision Process Step 4. Purchase Decision Purchase Intention Desire to buy most preferred brand Situational factors Purchase Decision

Purchasing Situation l Consumer behavior influenced by: – Physical surroundings – Social surroundings – Temporal perspective – Task & Antecedent

Situational Influences on Consumer Selection 1. Physical surroundings include geographical location, decor, sounds, aromas, lighting, weather 2. Social surroundings influence of other persons present, their characteristics, their apparent roles, & interpersonal interactions occurring. 3. Temporal perspective may be specified in units ranging from time of day to seasons of the year. 4. Task definition includes an intent or requirement to select, shop for, or obtain information about a general or specific purchase. 5. Antecedent states are momentary moods or
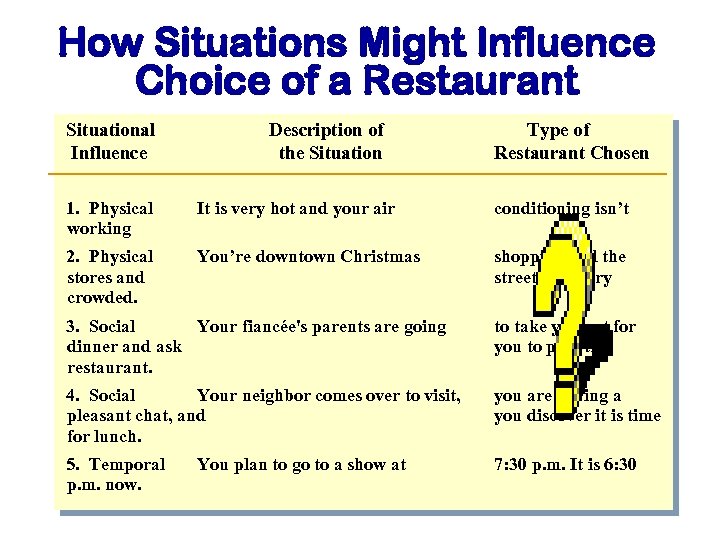
How Situations Might Influence Choice of a Restaurant Situational Influence Description of the Situation Type of Restaurant Chosen 1. Physical working It is very hot and your air conditioning isn’t 2. Physical stores and crowded. You’re downtown Christmas shopping and the streets are very 3. Social Your fiancée's parents are going dinner and ask restaurant. to take you out for you to pick the 4. Social Your neighbor comes over to visit, pleasant chat, and for lunch. you are having a you discover it is time 5. Temporal p. m. now. 7: 30 p. m. It is 6: 30 You plan to go to a show at
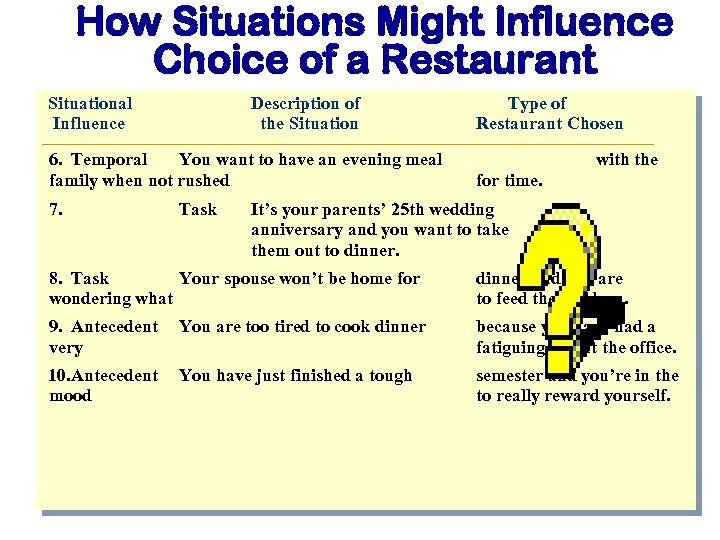
How Situations Might Influence Choice of a Restaurant Situational Influence Description of the Situation 6. Temporal You want to have an evening meal family when not rushed 7. Task Type of Restaurant Chosen with the for time. It’s your parents’ 25 th wedding anniversary and you want to take them out to dinner. 8. Task Your spouse won’t be home for wondering what dinner and you are to feed the children. 9. Antecedent very You are too tired to cook dinner because you have had a fatiguing day at the office. 10. Antecedent mood You have just finished a tough semester and you’re in the to really reward yourself.
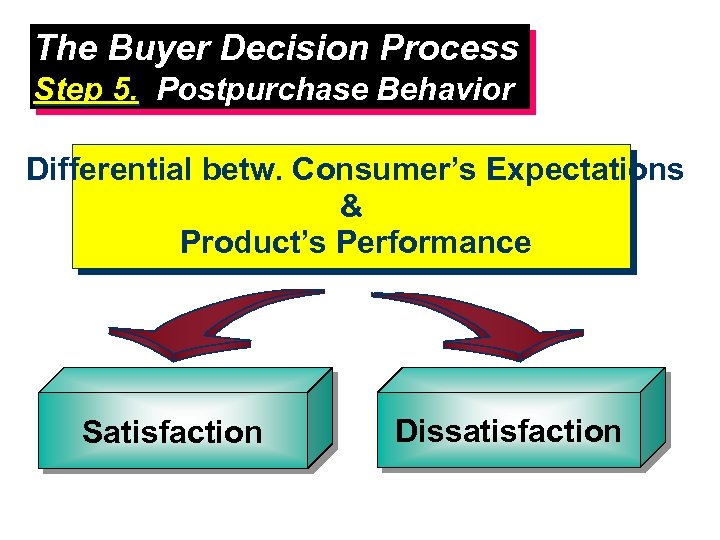
The Buyer Decision Process Step 5. Postpurchase Behavior Differential betw. Consumer’s Expectations & Product’s Performance Satisfaction Dissatisfaction

10, 000+ Studies on every variable influencing Consumer Behavior Problem recognition Information search Evaluation of alternatives Purchase decision Postpurchase behavior
www. business. com/dire ctory/advertising_and_ marketing/market_resea rch/consumer_behavior/

What we know abt Today’s Consumers-
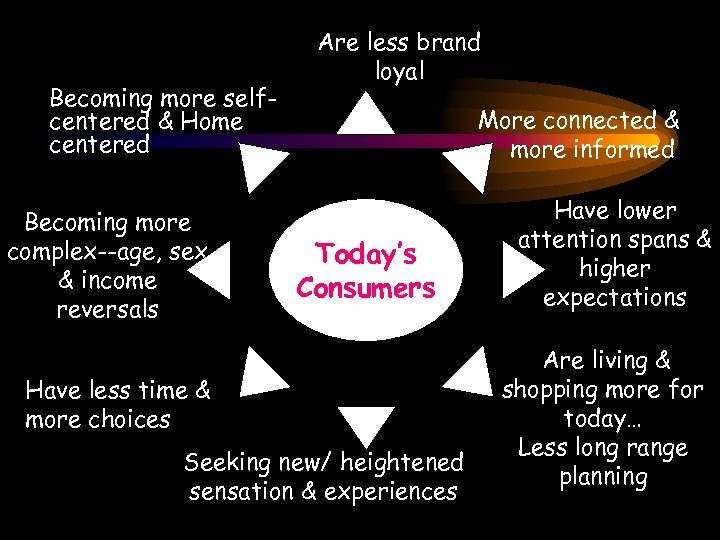
Becoming more selfcentered & Home centered Becoming more complex--age, sex & income reversals Are less brand loyal More connected & more informed Today’s Consumers Have less time & more choices Seeking new/ heightened sensation & experiences Have lower attention spans & higher expectations Are living & shopping more for today… Less long range planning

People are seeking out more intense experiences. Extreme sports, long action -packed weekends, aromatherapy, authentic ethnic foods, even intense flavors of soft drinks

Connectivity • Technology (instant message, mobile phones, email, My. Space, Facebook) are keeping us all connected. • People -have an increased desire for belonging to a greater community. Clanning The growing need to join up with / belong to groups to confront a more chaotic world

Customers spending Less Time & Effort Shopping 1975 vs Today Trips to Mall 3. 1 <1. 4 Stores Visited 7. 0 <3. 0 Hours Spent 10. 0 <2. 9 Source: MAS Marketing/Mc. Millan Doolittle People - eating on the go, frequenting convenience stores- buying products that offer greater convenience. 28
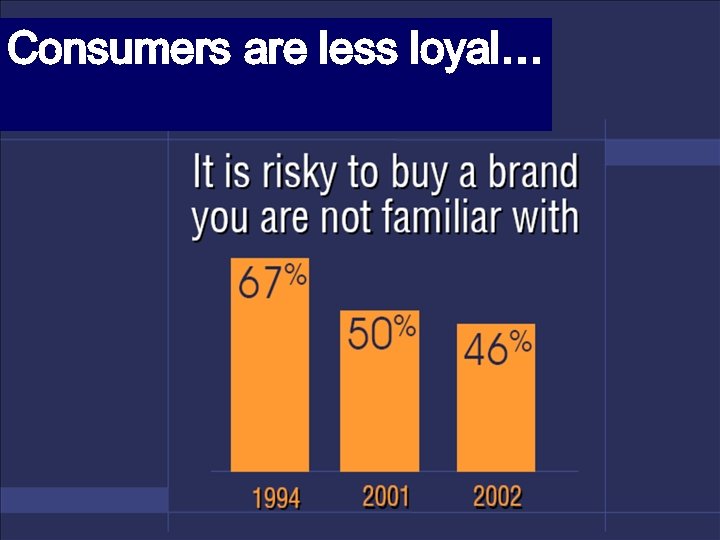
Consumers are less loyal…
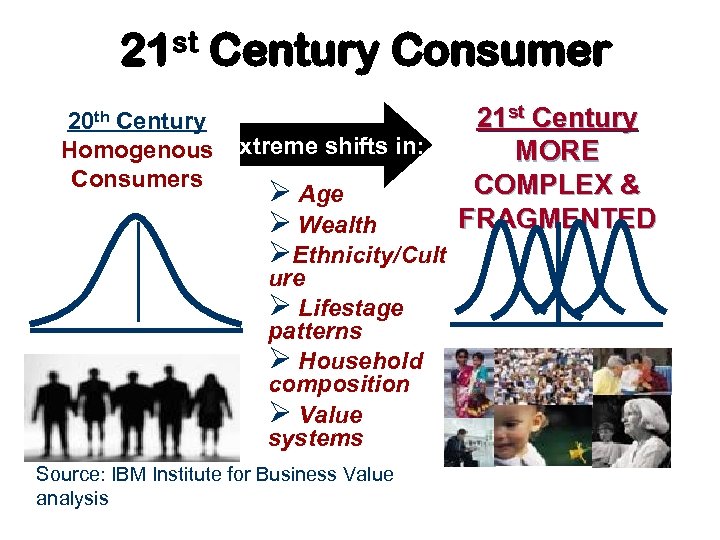
21 st Century Consumer 21 st Century 20 th Century Homogenous Extreme shifts in: MORE Consumers COMPLEX & Ø Age FRAGMENTED Ø Wealth ØEthnicity/Cult ure Ø Lifestage patterns Ø Household composition Ø Value systems Source: IBM Institute for Business Value analysis

Consumers are more Complex • AGE: Children are acting & thinking older. -adults acting more like kids • GENDER: Metrosexuality is in — men behaving more like women-- women behaving more like men • INCOME: High income groups spending on “anti-luxury” --- shopping for discounts-------lower income groups splurging on luxury items
Key to understanding increasingly fickle & fragmented consumer-base…. l Effective market segmentation model that captures complete profile of your actual & potential customer base…

market segmentation= Statistical Procedure clusters cases/consumers so as to maximize homogeneitywithin & heterogeneitybetween groups l on key variables/segmentation dimensions such as: demographic, geographic, socio-graphic, psychographic, technographic l
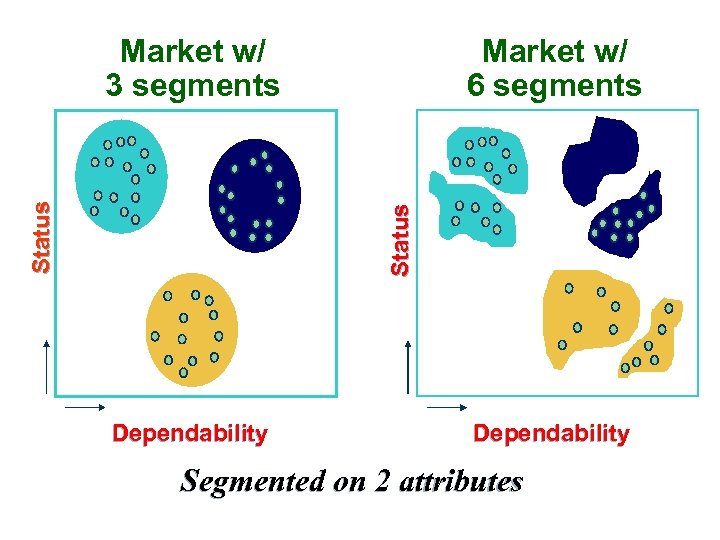
Market w/ 6 segments Status Market w/ 3 segments Dependability Segmented on 2 attributes
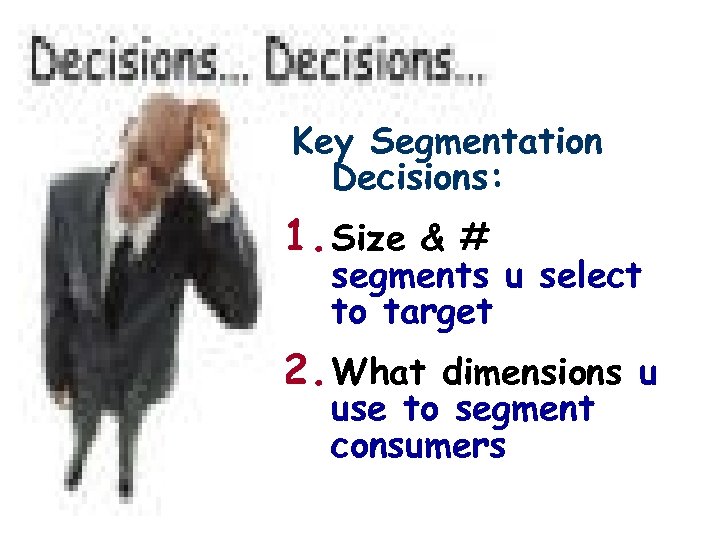
Key Segmentation Decisions: 1. Size & # segments u select to target 2. What dimensions u use to segment consumers
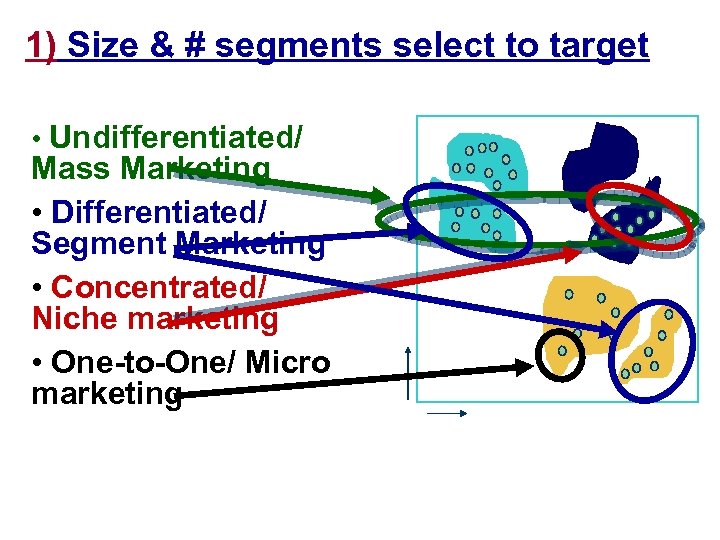
1) Size & # segments select to target Market w/ 3 segments • Undifferentiated/ Status Mass Marketing • Differentiated/ Segment Marketing • Concentrated/ Niche marketing • One-to-One/ Micro marketing Dependability 6 segments

Undifferentiated Strategy – One marketing mix for all members of total market – One mix fits all

Differentiated Strategy – multiple marketing mixes for multiple segments of total market

Concentrated Strategy – One mix focused on one narrowly defined segment of total market

1: 1 Strategy – Marketing Mix customized to meet needs of individual customers – made possible w/ CRM/MRM Systems… http: //www. 1 to 1. com/
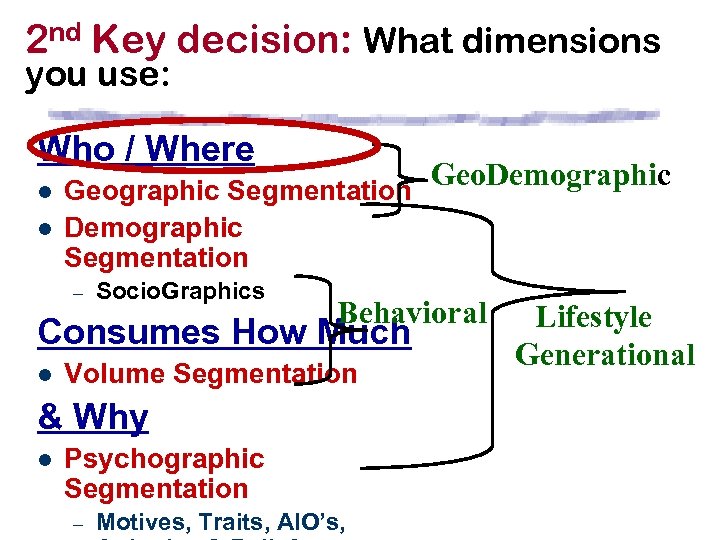
2 nd Key decision: What dimensions you use: Who / Where l l Geographic Segmentation Demographic Segmentation – Socio. Graphics Behavioral Consumes How Much l Volume Segmentation & Why l Psychographic Segmentation – Geo. Demographic Motives, Traits, AIO’s, Lifestyle Generational

Demographics • Age, sex, income, occupation, education, marital status, location, household characteristics, etc…. Socio-Graphic Indexes: • SES- Socio-economic Status (income+ occupation+ education) • FLC- Family Life Cycle (age+ martial status + age/# kids) • TGA’s =target group acronyms (some mix of age/ location/ occupation/income/ or any

• Yuppies- young urban professionals • Chuppies- chinese urban professionals • Dinks- dual income no kids • Poops- persons on one pension • Clumps – computer literate urban metro-sexual professionals • Twits- teens with info technologies • Tweens- 11 -12 year olds

GLAM - Greying, leisured, affluent, middle-aged GUPPY- Green YUPPY NILKY- No income, lots of kids OINK- One income, no kids PANSE- Politically active, not seeking employment RAPPY- Retired, affluent professionals SITCOM- Single income, two children, outrageous mortgage SUPPY- Senior urban professionals WOOPY- Well-off older people YAPPY- Young affluent parents ZUPPY- Zestful upscale person in their prime

SES l Capitalists Class l Upper Class l Middle Class l Working Poor l The Under Class Capitalists 1% Top 1% w/ income from assets earned or inherited l Most Shopping done by personal assistants l
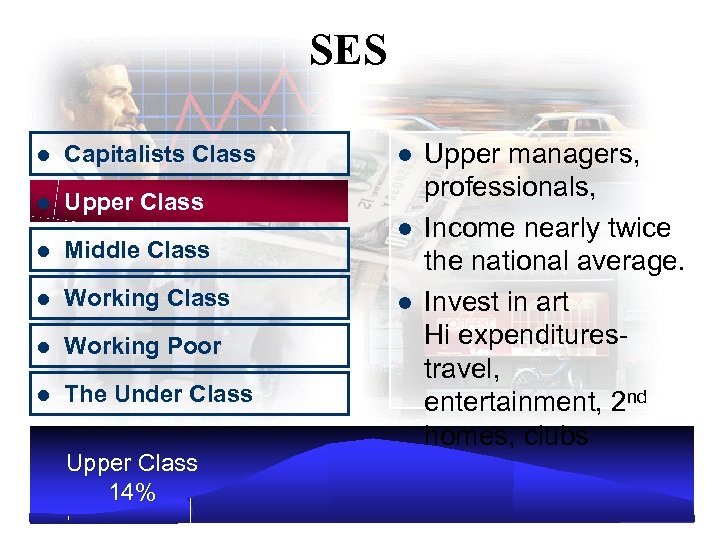
SES l Capitalists Class l Upper Class l Middle Class l Working Poor l The Under Class Upper Class 14% l l l Upper managers, professionals, Income nearly twice the national average. Invest in art Hi expenditurestravel, entertainment, 2 nd homes, clubs
SES l Capitalists Class l Upper Class l Middle Class l Working Poor l The Under Class Middle Class 33% l l l Middle-level whitecollar & top level blue-collar workers. Income somewhat above national average. Mainstream & Mainstay of most marketing efforts
SES l Capitalists Class l Upper Class l Middle Class l Working Poor l The Under Class Middle-level bluecollar & lower-level white-collar workers. l Income & educational level slightly below national level. l Shop for best bargains Working Class prices & 33% discount stores l

SES l Capitalists Class l Upper Class l l Middle Class l Working Poor l The Under Class l l Low paid workers (minimum wage). Income just above the poverty line. Most have some high school education Most products purchased are for Working Poor survival 11 -12%

SES l Capitalists Class l Upper Class l Middle Class l Working Poor l The Under Class l l l Depend primarily on welfare systems Standard of living below poverty line. Lack regular employment and education The Under Class 8 -9%
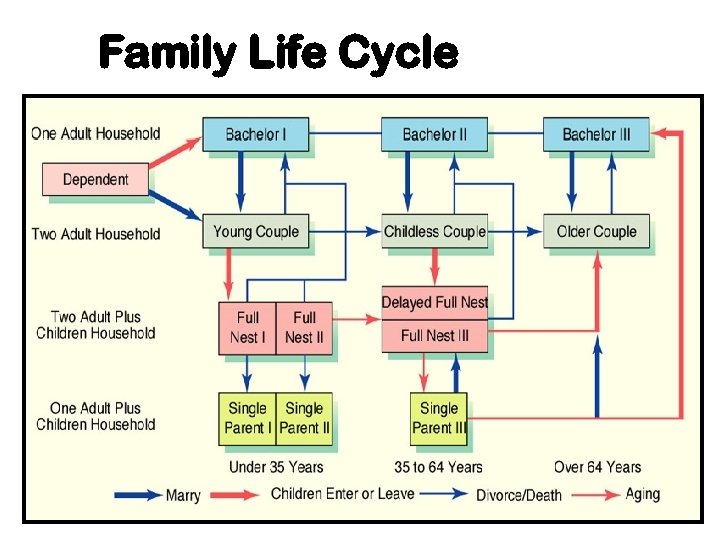
Family Life Cycle

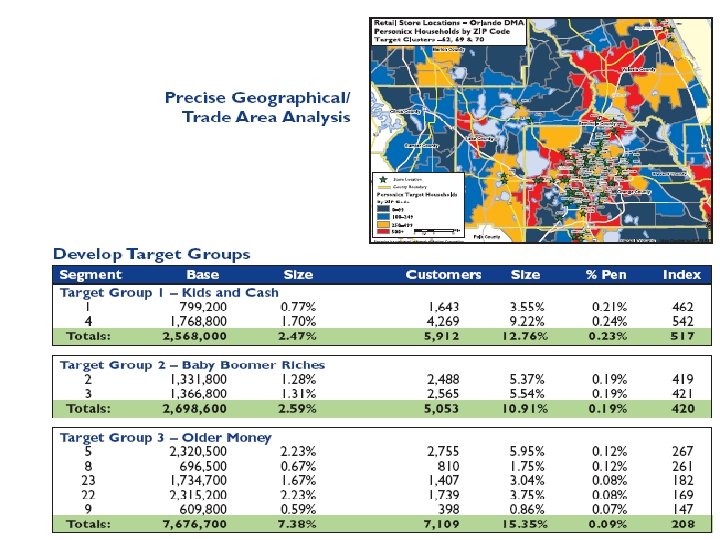
Personicx places each of 112 MM+ U. S. households in its Info. Base into one of 70 segments based on its specific life stage consumer behaviors & demographic characteristics. This enables marketers to see the dramatic difference between consumer behaviors of HHs in same geo-cluster--

Personicx® A household-level segmentation system driven by Info. Base® household data Three Next-Door Neighbors – Three Different Life Stages Taking Hold: Cluster 18 Beginnings: Cluster 39 Aging Upscale: Cluster 23 Same ZIP + 4®, Block Group, Tract and ZIP® Different households with different Personicx Life Stage Clusters *The following trademarks are owned by the United States Postal Service ®: ZIP® and ZIP + 4 ®.
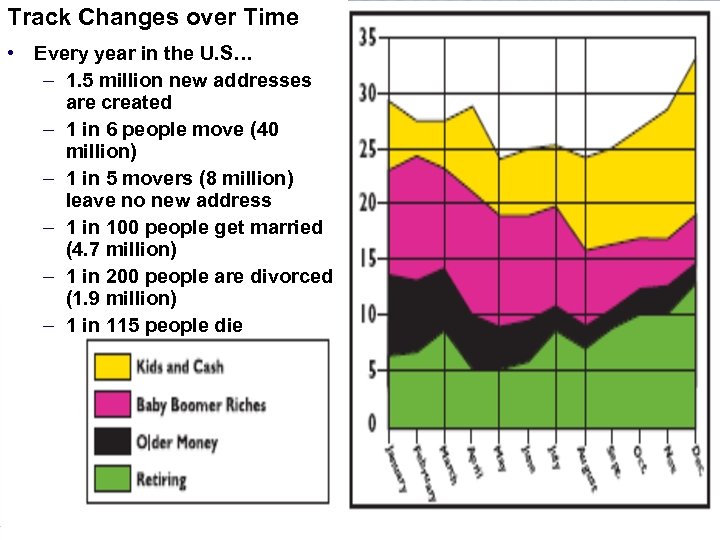
Track Changes over Time • Every year in the U. S… – 1. 5 million new addresses are created – 1 in 6 people move (40 million) – 1 in 5 movers (8 million) leave no new address – 1 in 100 people get married (4. 7 million) – 1 in 200 people are divorced (1. 9 million) – 1 in 115 people die

Video Clip Excerpt Overview of Acxiom Corporation
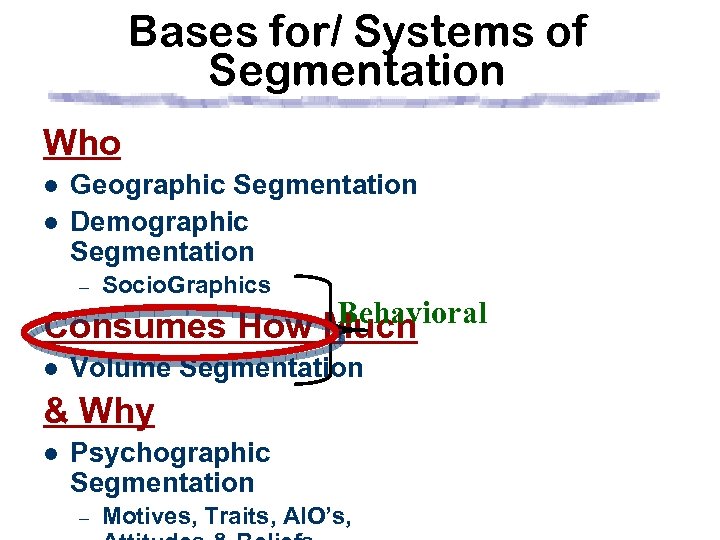
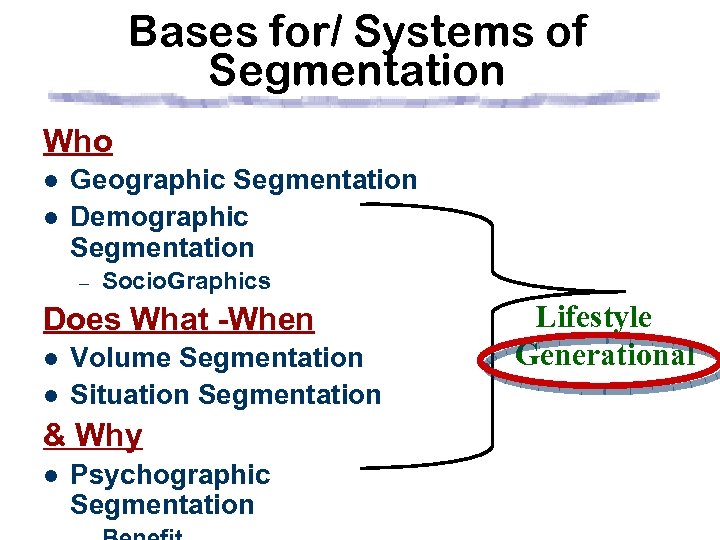
Bases for/ Systems of Segmentation Who l l Geographic Segmentation Demographic Segmentation – Socio. Graphics Behavioral Consumes How Much l Volume Segmentation & Why l Psychographic Segmentation – Motives, Traits, AIO’s,
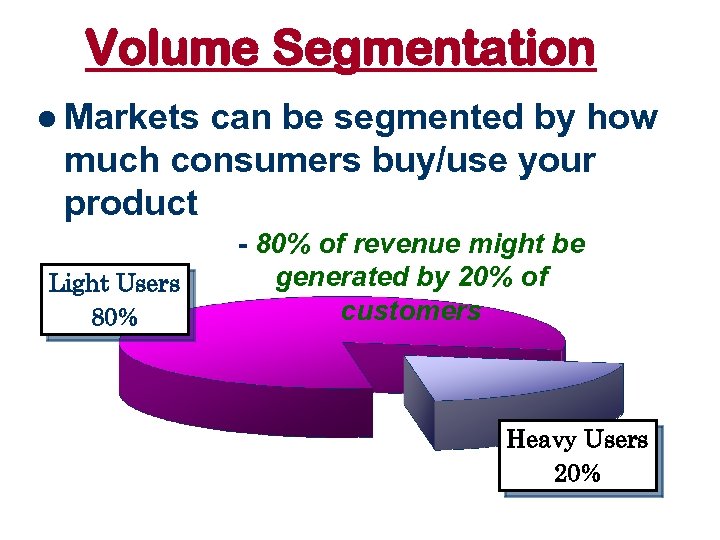
Volume Segmentation l Markets can be segmented by how much consumers buy/use your product Light Users 80% - 80% of revenue might be generated by 20% of customers Heavy Users 20%
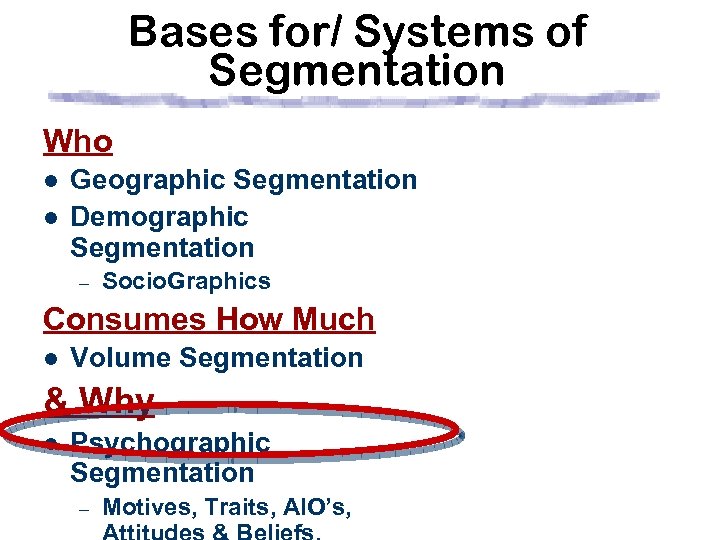
Bases for/ Systems of Segmentation Who l l Geographic Segmentation Demographic Segmentation – Socio. Graphics Consumes How Much l Volume Segmentation & Why l Psychographic Segmentation – Motives, Traits, AIO’s,

Psychographics Measures used to determine what’s going on in the consumer’s head: 1. Motivations 2. Personality Traits & Self-concept 3. Activities, Interests & Opinions 4. Attitudes & Beliefs 5. Benefits sought from product…

Psycho-Factor # 1: Motivational Marketing consumer behavior is result of unconscious motives which can be ascertained thru psychoanalytical research

Motivation Research l l l Motivational marketing emerged shortly after World War II and bloomed in the 1950 s Ernest Dichter founded the Institute of Motivational Research in New York. Defined MR as "qualitative research designed to uncover the consumer's subconscious or hidden motivations that determine purchase behavior. "

Clotaire Rapaille
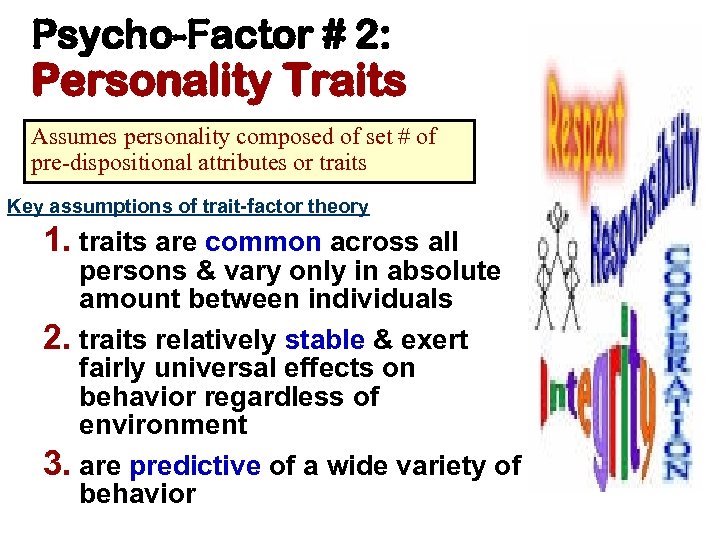
Psycho-Factor # 2: Personality Traits Assumes personality composed of set # of pre-dispositional attributes or traits Key assumptions of trait-factor theory 1. traits are common across all persons & vary only in absolute amount between individuals 2. traits relatively stable & exert fairly universal effects on behavior regardless of environment 3. are predictive of a wide variety of behavior

Some Key Consumer Traits Brand-Loyalty l Style-consciousness l Price-consciousness l Risk-Taking l Innovativeness l Liberal / conservative l Introvert / extrovert l Inner / outer directed l

Self-Concept l l l Ask consumers to describe themselves thru list of adjectives -- Dependable, strong, serious, sensitive aggressive, practical, sociable, confident etc. Also measure discrepancies between real vs. ideal self Image Congruence Research: correlation betw. self-image & brand image – esp. cars, clothes, personal accoutrements, booze….
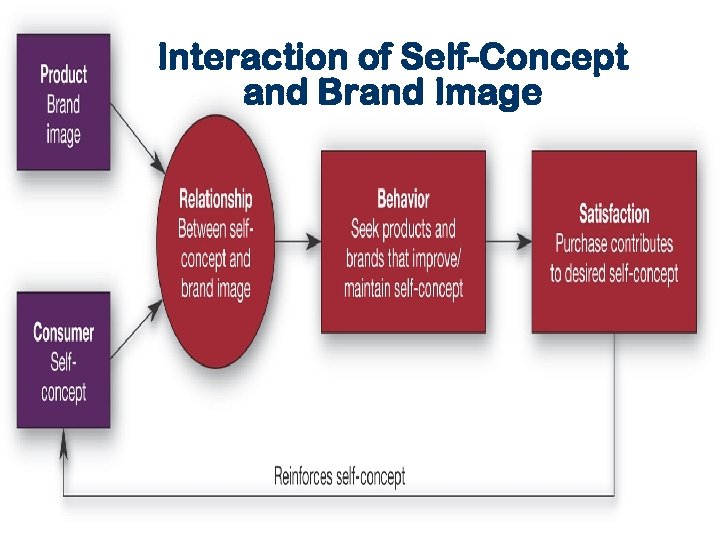
Interaction of Self-Concept and Brand Image
Identity relationships w/ products& brands…. Self-concept attachment – The product helps to establish the user’s identity

Psycho-Factor # 3: AIO’s l Activities – what they do, what they buy, and how they spend their time. l Interests – consumers’ preferences and priorities. l Opinions – views and feelings on such things as world, local, moral, economic, and social affairs.
Psycho-Factor # 4: Attitudes & Beliefs l An attitude= a complex l A belief = a descriptive mental state involving beliefs & feelings & values & dispositions to act in certain ways thought or conviction that a person holds about something, and involves holding an opinion.

The ABC’s of Attitudes 1. The Affective Component (based on feelings or overall evaluation) – I feel good about myself when I drive a BMW 2. The Behavioral Component (likely action toward object- - the consumer’s intention to buy a product) I probably will buy a BMW next time 3. The Cognitive Component (based on beliefs; what you think about product- ideally a result of marketing promotion) – I think BMWs are quality cars

Utilitarian Function of Attitudes Ø consumers seek out products that they believe provide them with benefits that are important to their well-being…
Three factors influence attitude formation: 1. Salient attributes which consumer uses to evaluate a product… 2. Extent to which consumer believes product contains these salient attributes 3. Importance of the attribute to the consumer
Fishbein’s Multi-attribute Theory Fishbein’s model argues that consumers’ attitudes towards a brand derives from: Ø their beliefs about the attributes of the brand Ø and their evaluations of those attributes

Attitude= Belief * Importance Aijk = (Bijk x Iik): i = attribute j = brand k = consumer I = Importance weighting B = Extent to which the brand is believed to possess the attribute

Fishbein’s Multi-attribute Model Ø Step 1: Get consumers’ list of attributes Ø Step 2: Rank each attributes relative importance Ø Step 3: Evaluate each brand with respect to its rating on each attribute. Ø Step 4: Apply Fishbein’s Formula

Example -Application of Multi-attribute Model Evaluating 3 banks: Step One: List of Attributes: Ø quickness in service, office hours, convenience, parking facilities, Step Two: Rank relative importance Ø Quickness=1, Hours= 4, Localization= 3, Parking= 2 Step Three: Evaluate each bank w/respect to each attribute. Ø (6= Excellent, 5=Very Good, 4=Good, 3=Bad, 2=Very Bad, 1=Poor) Step Four: Apply Fishbein’s Formula
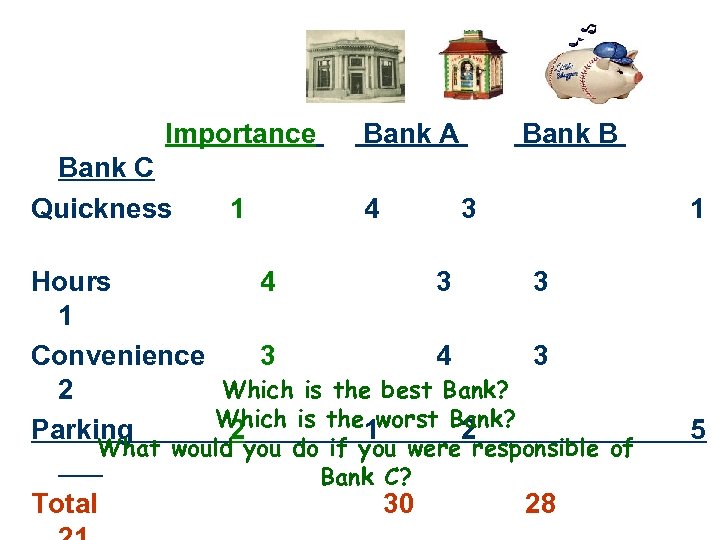
Importance Bank A Bank B Bank C Quickness 1 4 3 1 Hours 4 3 1 Convenience 3 4 3 Which is the best Bank? 2 Which is the Parking 2 1 worst Bank? 5 2 What would you do if you were responsible of Bank C? Total 30 28

Psycho-factor #5: Benefits Segment consumers Based on the benefits that consumers desire from using a specific

Principal benefit sought Flavor & product appearan ce Sensory Segment Colgate Brands favored Demograp hic strengths Special behavioral characterist ics Lifestyle characterist ic Children Users of spearmintflavored toothpaste Hedonist Brighte st of teeth Sociable Macleans, Segment Ultra Brite Decay preventio n Worrier Crest Segment Teens, young people Smokers Active Large Families Heavy users Conservative Price. Figure 5 -3 Independent Cheapest Segment brand Men Heavy users Valueoriented (continued) SOURCE: Adapted from Russell I. Haley, “Benefit Segmentation: A Decision-Oriented Research Tool, “ Journal of Marketing, July 1968, pp. 30 -35.
Bases for/ Systems of Segmentation Who/ Where l l Geographic Segmentation Geo. Demographic Segmentation – Socio. Graphics Does What -When l l Volume Segmentation Situation Segmentation & Why l Psychographic Segmentation
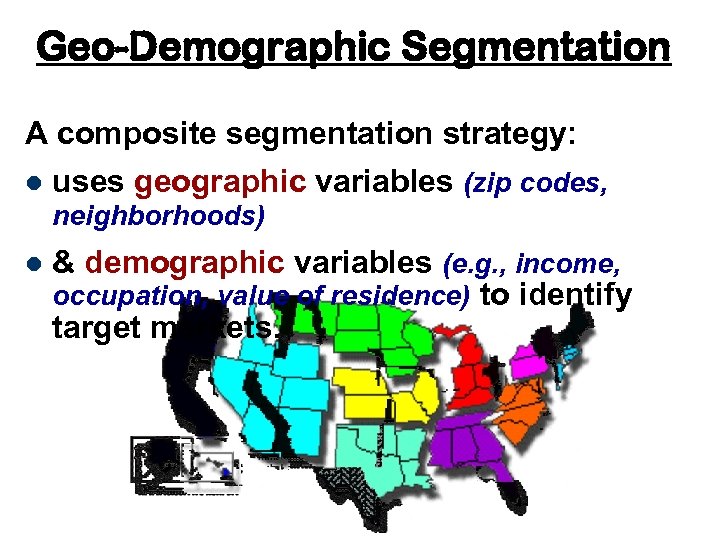
Geo-Demographic Segmentation A composite segmentation strategy: uses geographic variables (zip codes, neighborhoods) l & demographic variables (e. g. , income, occupation, value of residence) to identify target markets. l

The Logic: Birds of a Feather…. Flock Together Ø People w/ similar cultural ways & $ gravitate to one another - form relatively homogeneous communities Ø Once settled in, people emulate their neighbors, adopt similar social values, tastes & expectations Ø And most important of all, share similar patterns of consumer behavior re: product/brand preference & media. . .

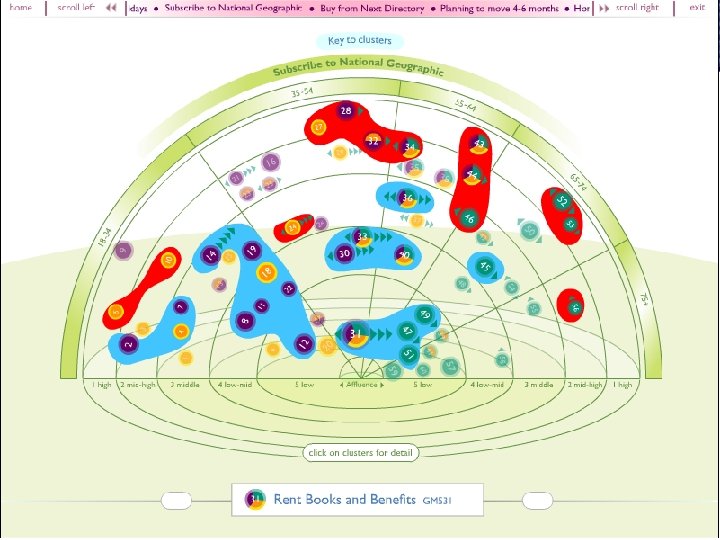
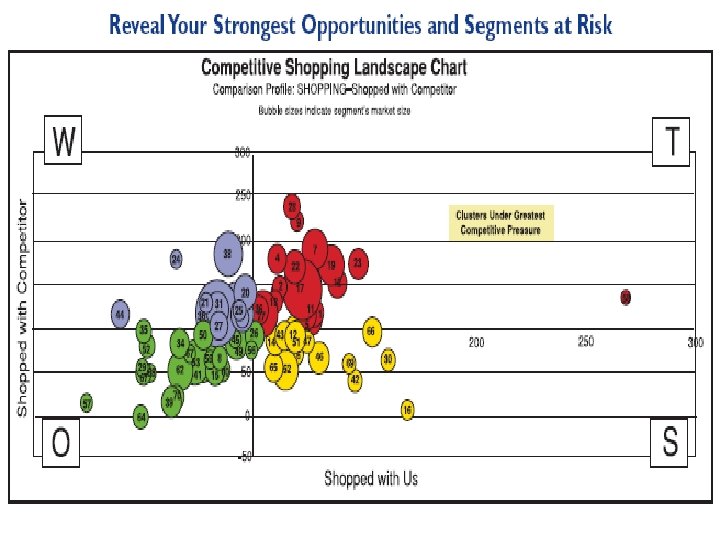
Geo-Demographic Segmentation’s Popularity … 15, 000+ companies in the United States & Canada alone used clusters as part of their marketing information mix last year… Geodemographics: PRIZM, Claritas, and Clusters www. andreas. com/faq-geodemo 3. html Geodemographic. . .
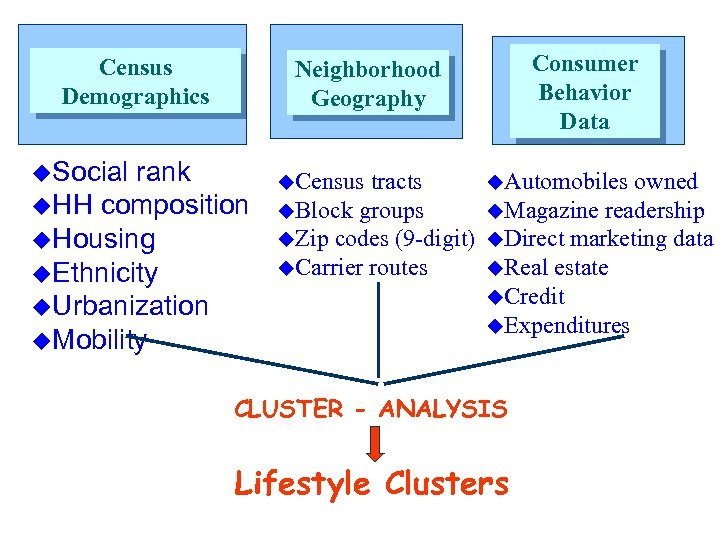
Census Demographics u. Social Consumer Behavior Data Neighborhood Geography rank u. HH composition u. Housing u. Ethnicity u. Urbanization u. Mobility u. Census tracts u. Block groups u. Zip codes (9 -digit) u. Carrier routes u. Automobiles owned u. Magazine readership u. Direct marketing data u. Real estate u. Credit u. Expenditures CLUSTER - ANALYSIS Lifestyle Clusters
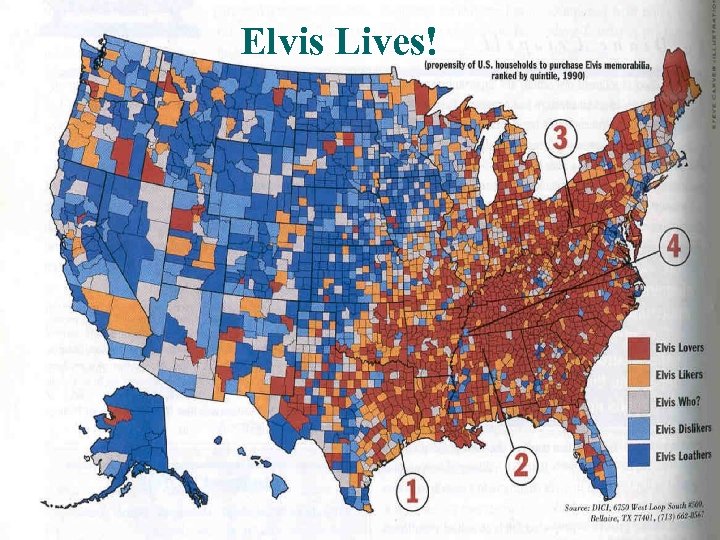
Elvis Lives!

http: //www. claritas. com/target-marketing/market-researchservices/marketing-data/marketing-segmentation/segmentationsystems. jsp
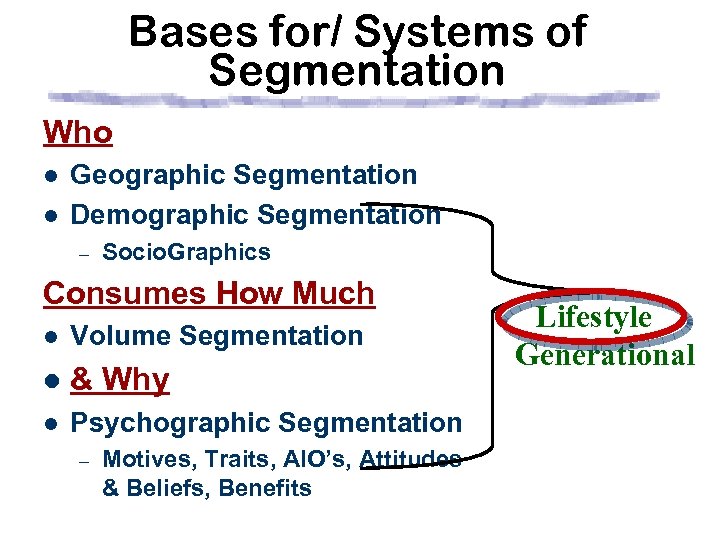
Bases for/ Systems of Segmentation Who l l Geographic Segmentation Demographic Segmentation – Socio. Graphics Consumes How Much l Volume Segmentation l & Why l Psychographic Segmentation – Motives, Traits, AIO’s, Attitudes & Beliefs, Benefits Lifestyle Generational
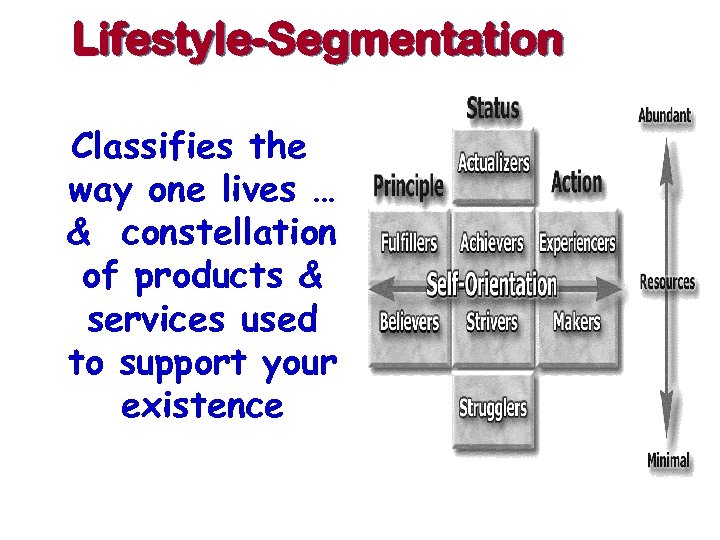
Lifestyle-Segmentation Classifies the way one lives … & constellation of products & services used to support your existence
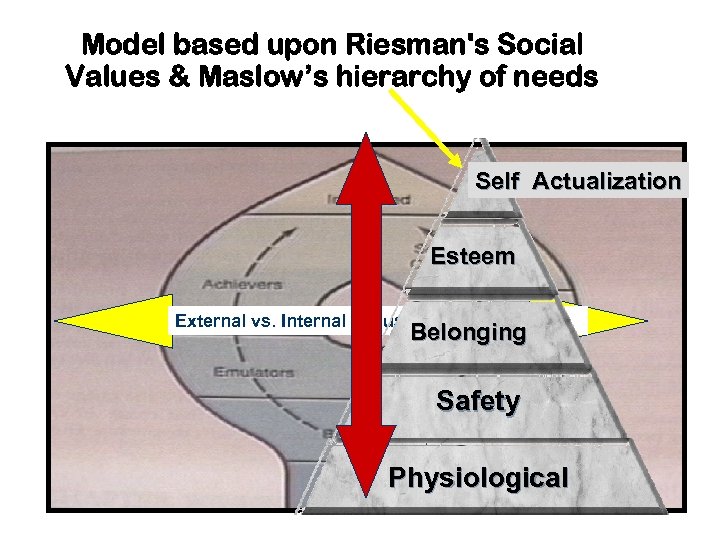
Model based upon Riesman's Social Values & Maslow’s hierarchy of needs Self Actualization Societally Esteem Conscious External vs. Internal Locus of Values/Rewards Belonging Safety Physiological

VALS Logic: Personality traits + key demographics determine an individual's lifestyle 1. A person's tendency to consume goods & services extends beyond age, income, & education. 2. Energy, self-confidence, intellectualism, novelty seeking, innovativeness, impulsiveness, leadership, & vanity…. play critical role 3. Different levels of resources enhance or constrain a person's expression of their primary motivation… Ideals vs. Achievement vs. Self-Expression
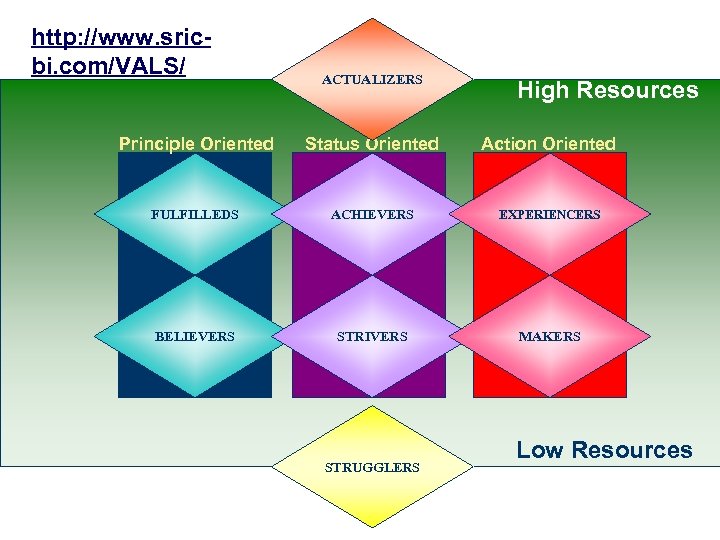
http: //www. sricbi. com/VALS/ ACTUALIZERS High Resources Principle Oriented Status Oriented Action Oriented FULFILLEDS ACHIEVERS EXPERIENCERS BELIEVERS STRIVERS MAKERS STRUGGLERS Low Resources
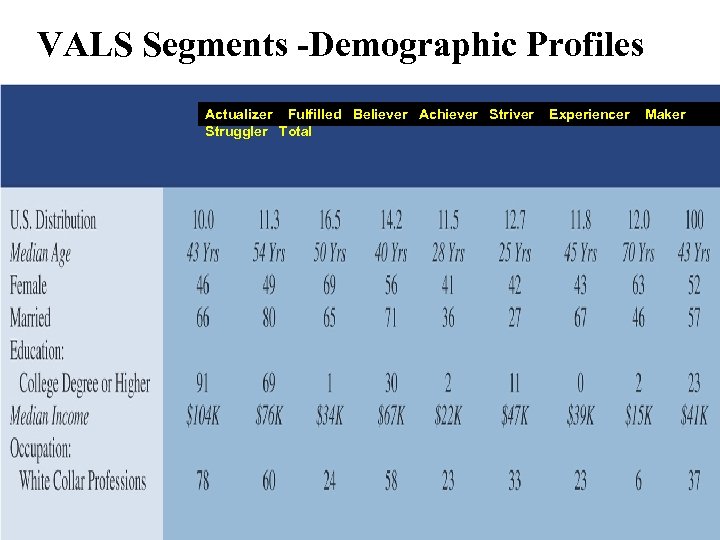
VALS Segments -Demographic Profiles Actualizer Fulfilled Believer Achiever Striver Experiencer Maker Struggler Total
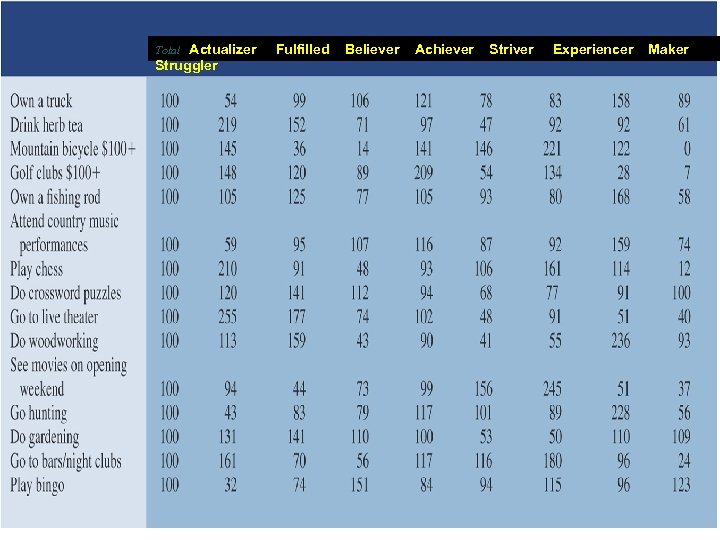
Total Actualizer Fulfilled Believer Achiever Striver Experiencer Maker Struggler
i. Vals

Go Find Your Self Take the VALs Surveyand find what segment you belong to… l http: //www. sricbi. com/VALS/presurvey. shtml

l Val’s with Dr. Pepper example

Lifestyle Clusters- Reflective of Orientation to Technology Lifestyle defined by the Role & Scope that Technology Plays in Peoples Lives

Technographic Segmentation Scheme Define & Segment consumers according to: Ownership l Use Patterns l Motivations (purchase & use) l Attitudes toward Technology l Attitudes toward Media l
![The concept and technique was first introduced in 1985 by Dr. Edward Forrest[1] in The concept and technique was first introduced in 1985 by Dr. Edward Forrest[1] in](https://present5.com/presentation/5b17c1c9195fdb248de83b5b65e28a06/image-102.jpg)
The concept and technique was first introduced in 1985 by Dr. Edward Forrest[1] in a study of VCR users and later elaborated upon in the article, "Segmenting VCR Owners" published in the Journal of Advertising Research. In the article it was suggested that the profiling of technology consumers "should be based on an amalgam of variables which might best be referred to as "technographic". . . which "focuses on the motivations, usage patterns, attitudes about technology. . . as well as measures of a person's
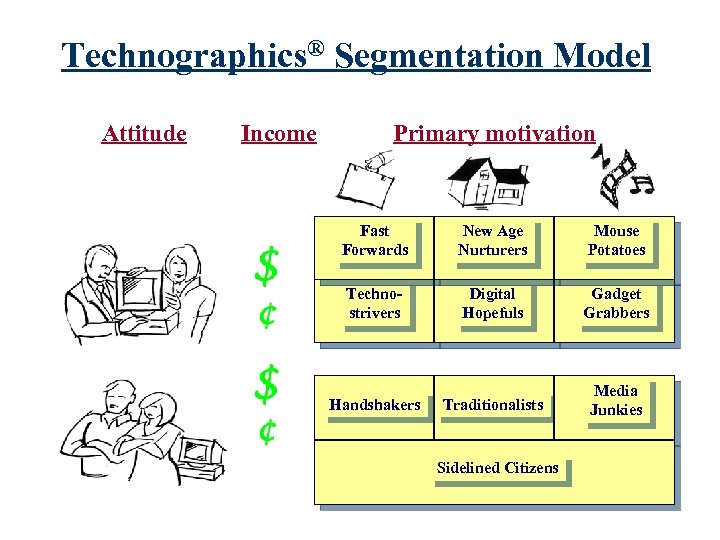
Technographics® Segmentation Model Attitude Income Primary motivation Fast Forwards New Age Nurturers Mouse Potatoes Technostrivers Digital Hopefuls Gadget Grabbers Traditionalists Media Junkies Handshakers Sidelined Citizens
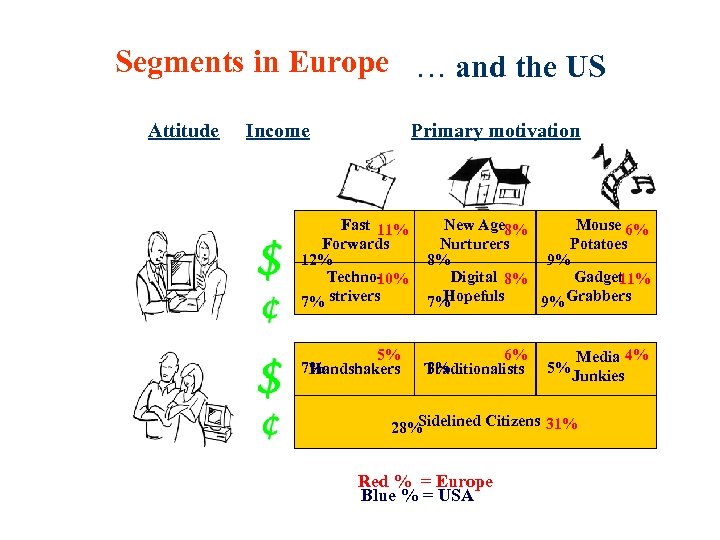
Segments in Europe … and the US Attitude Income Primary motivation Fast 11% Forwards 12% Techno 10% 7% strivers New Age 8% Mouse 6% Nurturers Potatoes 8% 9% Digital 8% Gadget 11% Hopefuls 7% 9% Grabbers 5% 7% Handshakers 6% 8% Traditionalists 5% Media 4% Junkies Sidelined Citizens 31% 28% Red % = Europe Blue % = USA
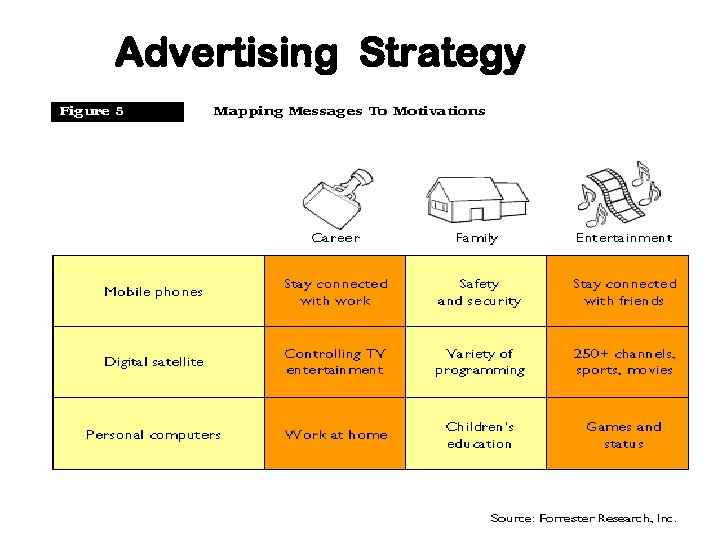
Advertising Strategy
Bases for/ Systems of Segmentation Who l l Geographic Segmentation Demographic Segmentation – Socio. Graphics Does What -When l l Volume Segmentation Situation Segmentation & Why l Psychographic Segmentation Lifestyle Generational

Origins of our identity Our individuality = result of nature & nurture l l l Our commonality = results from our shared culture & experience l l l War; civil unrest; social movements Political persons & events; economic swings Scientific/Technological discoveries & advances Tragedies: Natural & Manmade Entertainment: Movies, TV, Music; artists, celebrities Clothing styles; Lifestyle trends, Fads

Values are shaped by: Generational Life Experiences Called “Markers” l Events l Culture l Politics l Economy l Technology l Personalities

Come of age – Imprint on your WORLD l l Each generation molded by world events that occur during its formative years. … distinct historical experiences create characteristics that stay w/ people thruout rest of their lives
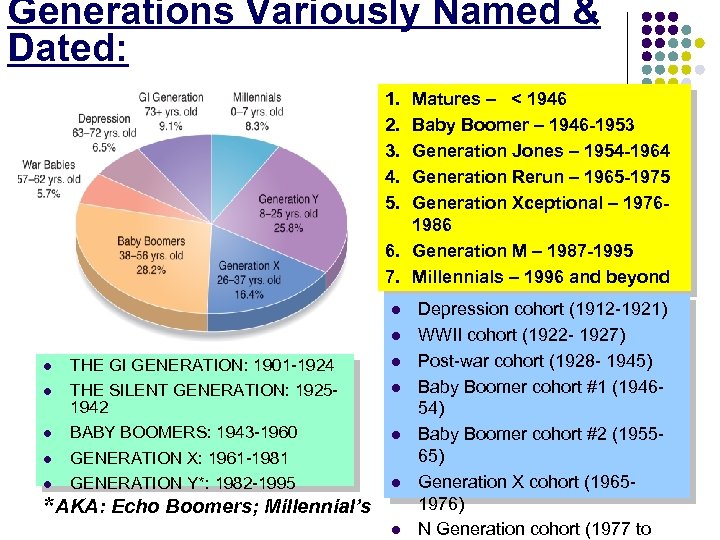
Generations Variously Named & Dated: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Matures – < 1946 Baby Boomer – 1946 -1953 Generation Jones – 1954 -1964 Generation Rerun – 1965 -1975 Generation Xceptional – 19761986 6. Generation M – 1987 -1995 7. Millennials – 1996 and beyond l l l l THE GI GENERATION: 1901 -1924 THE SILENT GENERATION: 19251942 BABY BOOMERS: 1943 -1960 GENERATION X: 1961 -1981 GENERATION Y*: 1982 -1995 l l *AKA: Echo Boomers; Millennial’s l Depression cohort (1912 -1921) WWII cohort (1922 - 1927) Post-war cohort (1928 - 1945) Baby Boomer cohort #1 (194654) Baby Boomer cohort #2 (195565) Generation X cohort (19651976) N Generation cohort (1977 to

Some Defining Events. Senior Generations Born: <1945 Depression cohort (born from 1912 to 1921) l Lived thru- The Great Depression, high levels unemployment, poverty, lack of creature comforts, financial uncertainty WWII cohort/ GI Gen. (born from 1922 to 1927) l Lived thru- : men leaving to war - many not returning, -- women working in factories, focus on defeating a common enemy Post-war cohort/ Silent Gen. (born from 1928 to 1945) l Lived thru- : sustained economic growth, social tranquility, The Cold War,

Born: 1945 ~1964 78 million Baby Boomer cohort #1 (born 1946 to 1954) Lived thru- : assassination of JFK, RFK, and MLK, political unrest, walk on moon, Vietnam War, anti-war protests, sexual freedom, civil rights – environmental- hippie & women’s movement, protests and riots, experimentation w/ drugs Baby Boomer cohort #2 (born 1955 to 1964) Lived thru- : Watergate, defeat in Vietnam, the oil embargo, raging inflation, gasoline shortages Cultural Icons & Memorabilia “The Ed Sullivan Show”, Fallout Shelters, Poodle Skirts and Pop Beads, Slinkies, TV Dinners, Hula Hoops, The Peace Sign, “Laugh In”, Clinton, Midler, Leno, IDEALIST – Prophet: Innerdriven, moralistic generation - Streisand, Gates comes of age during a period of spiritual awakening

Gen X cohort Initial Impact Events: • Challenger explosion • Iran-Contra • social malaise • Reaganomics • AIDs • fall of Berlin Wall • Predom. of single parent families Born: 1965~1983 48 million Cultural Memorabilia “The Brady Bunch”, Pet Rocks, Platform Shoes, “The Simpsons”, “Dynasty”, ET, Cabbage Patch Dolls, Brad Pitt, Cameron Diaz, Carrot Top, TV-Friends, Brady Bunch, Ninja turtles ADAPTIVE- Nomad: A hypocritical generation- coasts along on accomplishments of civics, lay the groundwork for new idealist era.

Born: 1984 ~2002 first wired gen… Initial Impact Events: : Cultural Icons? • Xena Warrior Princess • Buffy The Vampire Slayer • cell phones laptops/ CIVIC– Hero: Outer-driven, morally complacent generation -institutionalizes ipods ideals of previous generations. . • Rise of the Internet • 9 -11 • Cultural diversity • 2 wars in Iraq

The New generation. Ferals? Born: after ~1990 Age today: <17 Predicted to be. Alienated, cynical generationchallenge ideals of parents & develop into pragmatic, risktaking adults. .
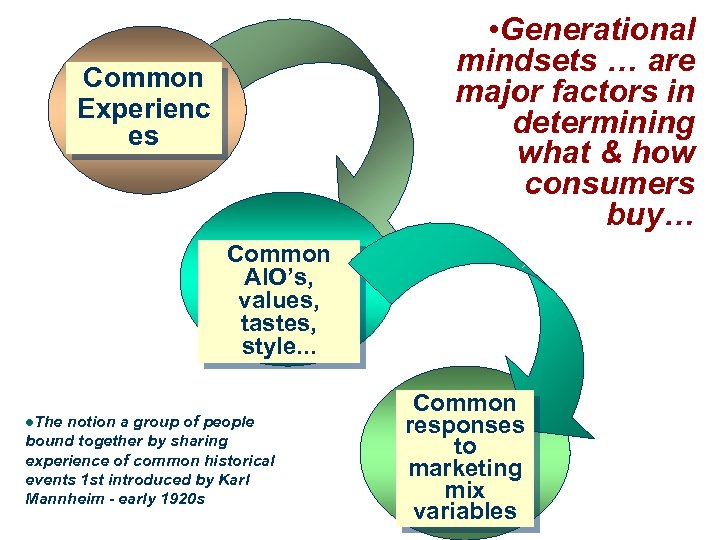
• Generational mindsets … are major factors in determining what & how consumers buy… Common Experienc es Common AIO’s, values, tastes, style. . . l. The notion a group of people bound together by sharing experience of common historical events 1 st introduced by Karl Mannheim - early 1920 s Common responses to marketing mix variables

Generational Marketing Key Considerations not a key behavior driver for all product categories- but is particularly appropriate for: l Food l Music l Apparel l Automotive l Financial & Insurance l as well as entertainment products.
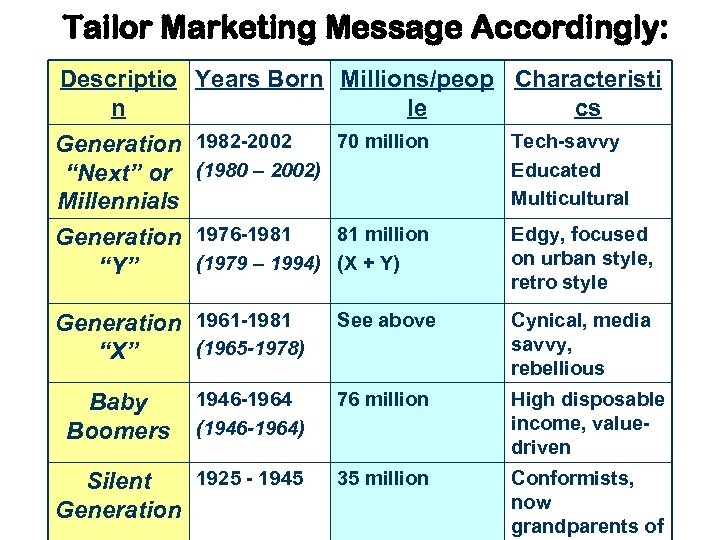
Tailor Marketing Message Accordingly: Descriptio Years Born Millions/peop n le 70 million Generation 1982 -2002 “Next” or (1980 – 2002) Millennials Characteristi cs Tech-savvy Educated Multicultural 81 million Generation 1976 -1981 (1979 – 1994) (X + Y) “Y” Edgy, focused on urban style, retro style Generation 1961 -1981 (1965 -1978) “X” See above Cynical, media savvy, rebellious 1946 -1964 (1946 -1964) 76 million High disposable income, valuedriven 1925 - 1945 Silent Generation 35 million Conformists, now grandparents of Baby Boomers

Marketing to Seniors The Classic

Marketing to Boomers “The generation that dropped acid to escape reality… is generation that drops antacid to cope w/ it” The Music The Values
For X+ generations… it’s all about the rate of change every month = new technology every day = new product / service every minute = new blog & website Change you now experience in one year… Your Grandparents experienced in one lifetime.


Marketing to Gen X -- "The Street-Savvy Generation" • Divorce • one-parent families, step families • working parents, latch-key lives • violence on television, violence in the streets l& breaking down of traditional values & sources of

How to Market to Gen-Yer’s

5b17c1c9195fdb248de83b5b65e28a06.ppt