ceba9d7b88db95efb8a75722106f330e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45

Consumer Behavior, 9 th Edition SCHIFFMAN & KANUK Chapter 6 Consumer Perception
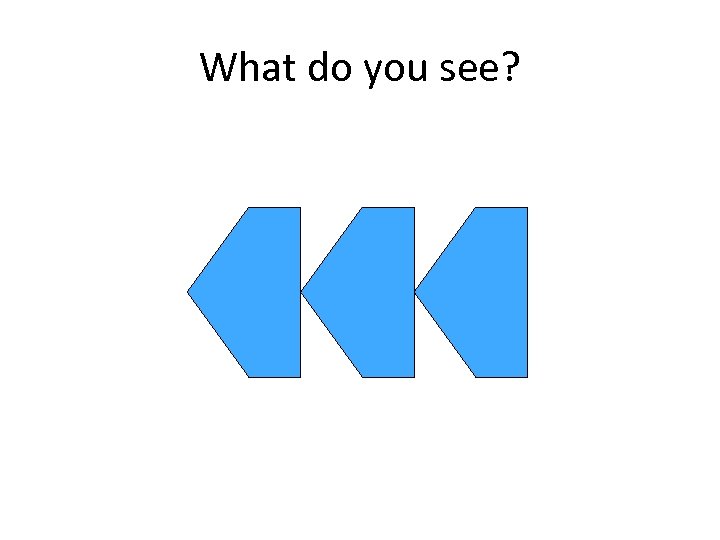
What do you see?
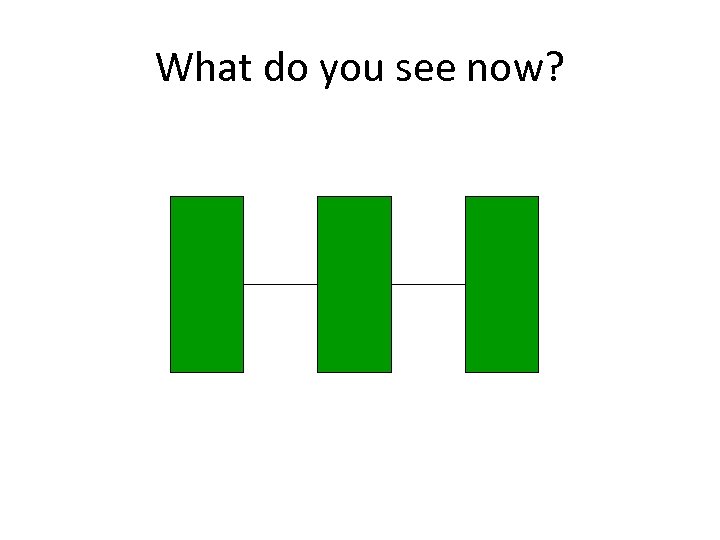
What do you see now?

What colour comes to mind?
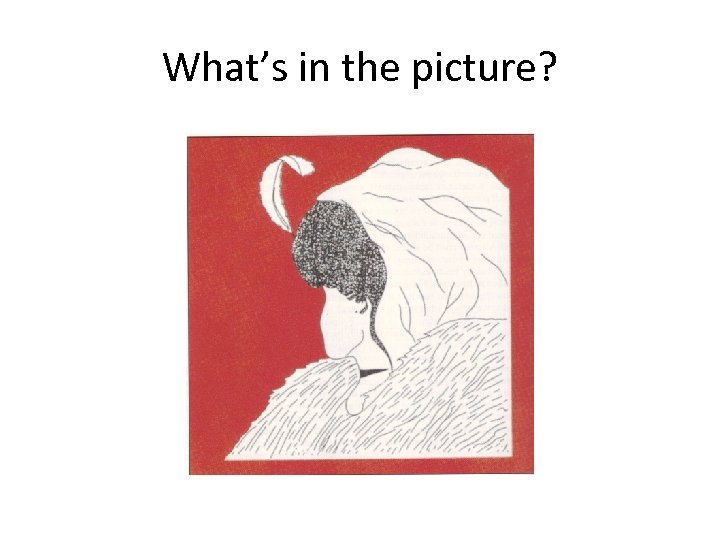

What’s in the picture?

So…. what then is perception? • The process by which an individual selects, organizes, and interprets stimuli into a meaningful and coherent picture of the world • How we see the world around us
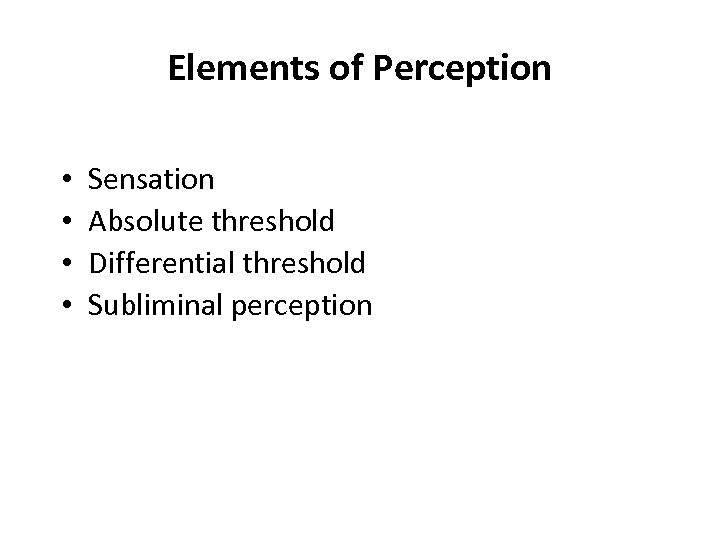
Elements of Perception • • Sensation Absolute threshold Differential threshold Subliminal perception
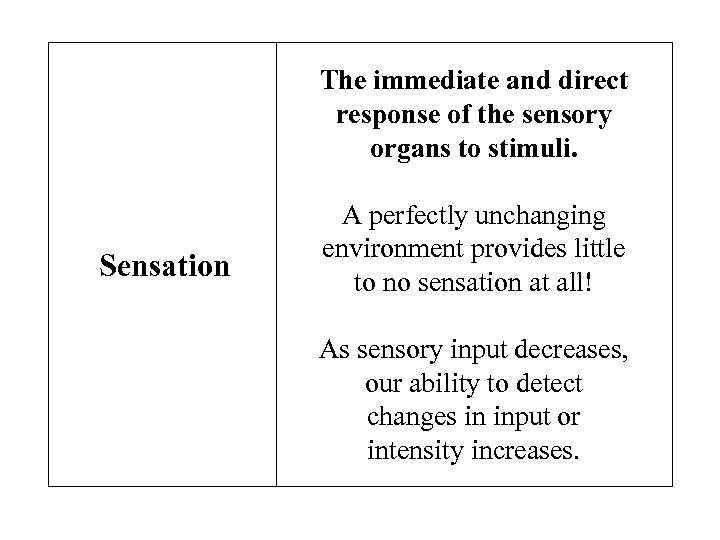
The immediate and direct response of the sensory organs to stimuli. Sensation A perfectly unchanging environment provides little to no sensation at all! As sensory input decreases, our ability to detect changes in input or intensity increases.
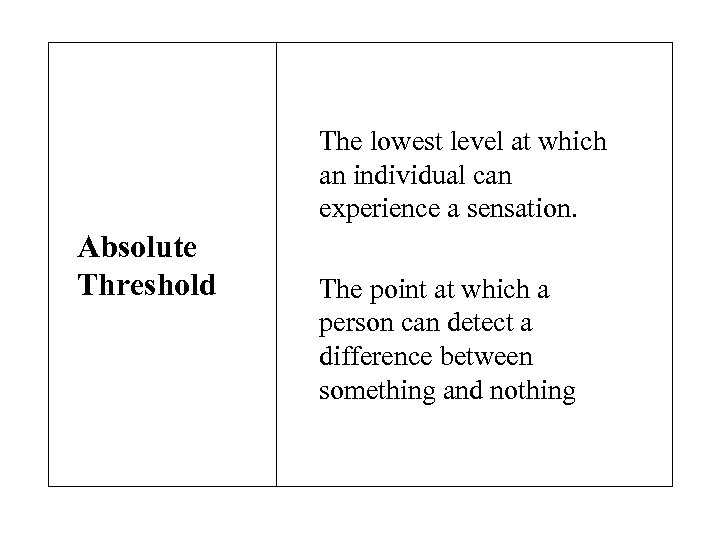
The lowest level at which an individual can experience a sensation. Absolute Threshold The point at which a person can detect a difference between something and nothing

Sensory Adaptation • As our exposure to stimulus increases, we notice it less. • Factors leading to adaptation: – Intensity, duration, discrimination, exposure, relevance • Promotional methods aimed at increasing sensory input: – Experiential marketing, Sophisticated scented ads, inserts and pop-ups, ambush advertising, Product placement

Increased Sensory Input increased intensity

Increased Sensory Input 3 D/digital billboard
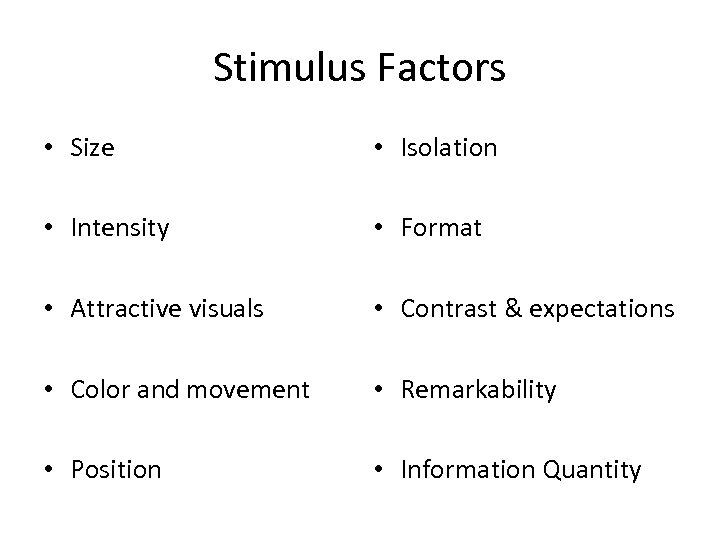
Stimulus Factors • Size • Isolation • Intensity • Format • Attractive visuals • Contrast & expectations • Color and movement • Remarkability • Position • Information Quantity

Differential Threshold The minimal differences that can be detected between two similar stimuli
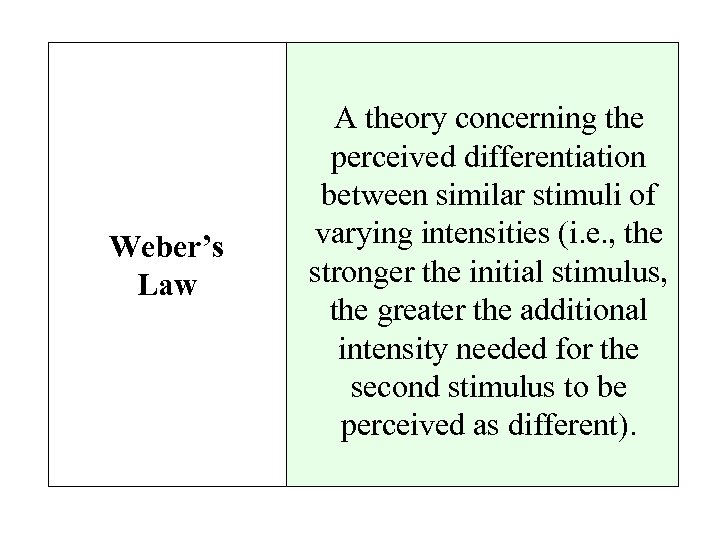
Weber’s Law A theory concerning the perceived differentiation between similar stimuli of varying intensities (i. e. , the stronger the initial stimulus, the greater the additional intensity needed for the second stimulus to be perceived as different).

Marketing Applications of the JND • Need to determine the relevant j. n. d. for their products – so that negative changes are not readily discernible to the public – so that product improvements are very apparent to consumers

Betty Crocker Changes Fall Below the J. N. D.

Changes in Brand Name Fall Below the J. N. D.

Subliminal Perception of very weak or rapid stimuli received below the level of conscious awareness.

Subliminal Perception • 1957: Drive-In Movie Theater • 1974: Publication of Subliminal Seduction • 1990 s: Allegations against Disney

Is Subliminal Persuasion Effective? • Extensive research has shown no evidence that subliminal advertising can cause behavior changes • Some evidence that subliminal stimuli may influence affective reactions
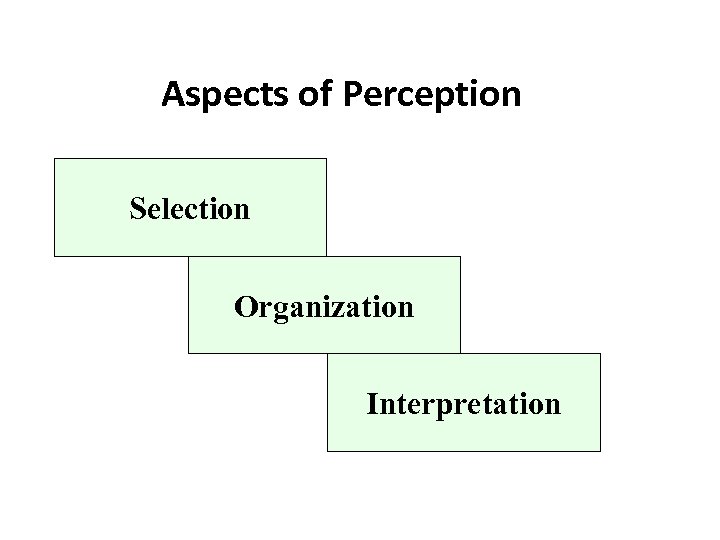
Aspects of Perception Selection Organization Interpretation

Perceptual Selection • People receive only a small fraction of the stimuli to which they are exposed. • Depends on two major factors – Consumers’ previous experience – Consumers’ motives

Concepts Concerning Selective Perception • • Selective Exposure Selective Attention Perceptual Defense Perceptual Blocking

Principles of Perceptual Organization • Figure and ground – Definition of figure depends on the background • Grouping – Information is organized into chunks • Closure – Incomplete stimuli create tension

Influences of Perceptual Distortion • Stereotypes – Physical Appearances – Descriptive Terms – First Impressions – Jumping to Conclusions – Halo Effect……………. The i. Pod has had positive effects on perceptions of Apple's other products

“Safed Teeka” Use of cultural habits to formulate imagery involving steriotypes associated with product category

Issues In Consumer Imagery • • Product Positioning and Repositioning Positioning of Services Perceived Price Perceived Quality Retail Store Image Manufacturer Image Perceived Risk

Using Imagery

Positioning & Repositioning Positioning Repositioning • Establishing a specific image for a brand in relation to competing brands. • Involves changing the identity of the product relative to the identity of the competing brands in the collective minds of the target market • If a brand does not reposition at the right time , it may not get a second chance

Repositioning of Cadbury Dairy Milk • “Kid in all of us” • “Spontaneous Joy”– (girl dancing in the cricket field) • “Real Taste of Life”– A girl is shown breaking the security barriers and entering thecricket field to celebrate the victory of the country in the crickedmatch under the tag line “Kuch Khaas Hai Zindagi mein”. Thiscampaign went on to be awarded The Campaign of the. Century, in India at the Abby (Ad Club, Mumbai) awards.

Different Ad Campaigns by Cadbury Dairy Milk • • • “Khaane Waalon Ko Khaane Ka Bahana Chahiye” “Kuch Meetha Ho jaye” “Pappu Paas Ho gaya” “Radha Miss Palampur ban gaye “ “Meetha hai Khaana aaj pehli tarrekh hai” “Is Diwali aap kise khush kar rahe hain” – Sister tying rakhi to her brother and receiving a box of chocolates in return • “Shubh Aaarambh”
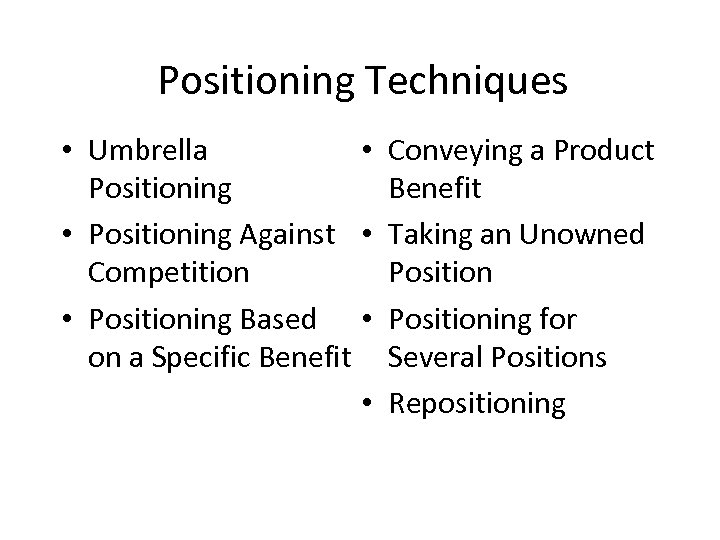
Positioning Techniques • Umbrella • Positioning Against • Competition • Positioning Based • on a Specific Benefit • Conveying a Product Benefit Taking an Unowned Positioning for Several Positions Repositioning

Apple’s 1984 Ad Positions Against the Competition Click icon to reach ad
Perceptual Mapping A research technique that enables marketers to plot graphically consumers’ perceptions concerning product attributes of specific brands.
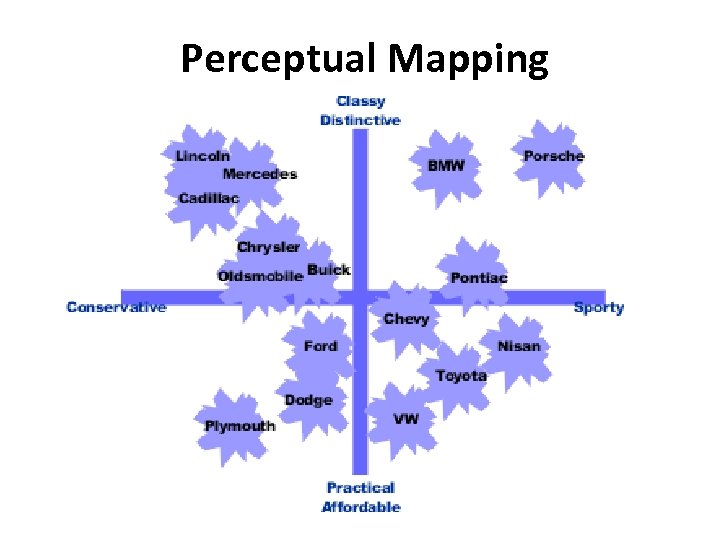
Perceptual Mapping
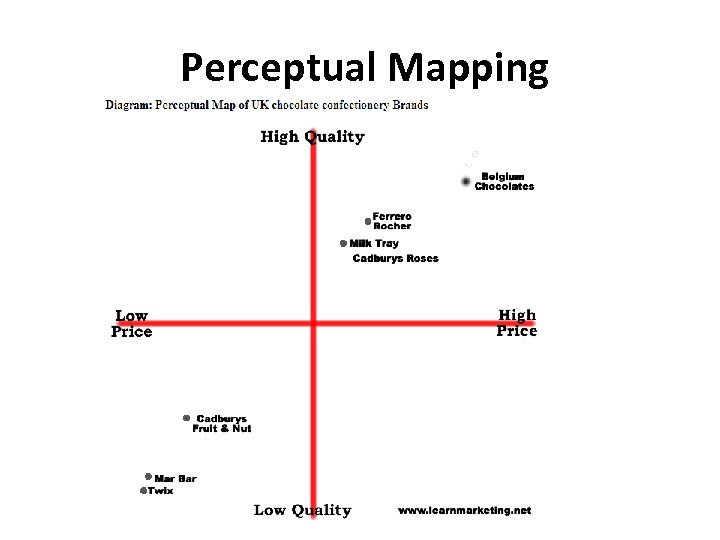
Perceptual Mapping

Pricing Strategies Focused on Perceived Value • Satisfaction-based Pricing • Relationship Pricing • Efficiency Pricing

Issues in Perceived Price • Reference prices – Internal – External • Tensile and objective price claims
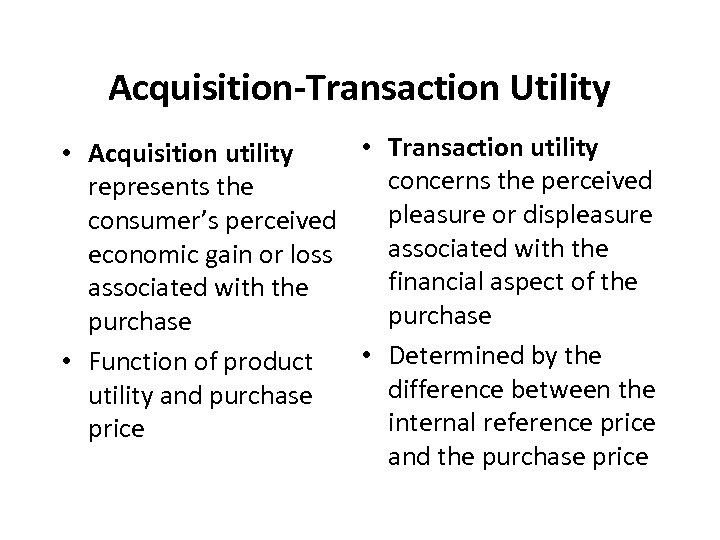
Acquisition-Transaction Utility • Transaction utility • Acquisition utility concerns the perceived represents the pleasure or displeasure consumer’s perceived associated with the economic gain or loss financial aspect of the associated with the purchase • Determined by the • Function of product difference between the utility and purchase internal reference price and the purchase price

Tensile and Objective Price Claims • Evaluations least favorable for ads stating the minimum discount level • Ads stating maximum discount levels are better than stating a range

Perceived Quality • Perceived Quality of Products – Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Cues • Perceived Quality of Services • Price/Quality Relationship
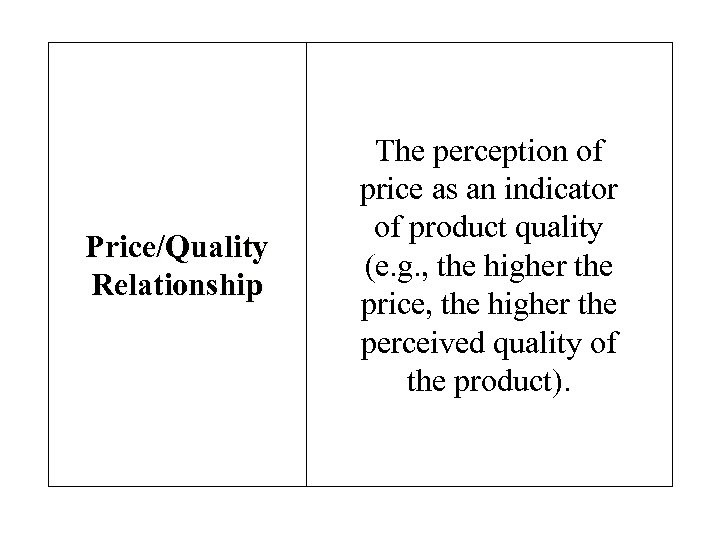
Price/Quality Relationship The perception of price as an indicator of product quality (e. g. , the higher the price, the higher the perceived quality of the product).
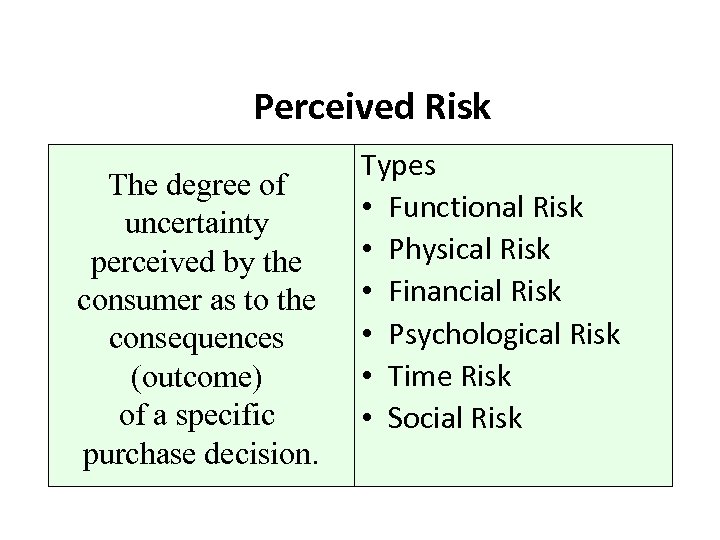
Perceived Risk The degree of uncertainty perceived by the consumer as to the consequences (outcome) of a specific purchase decision. Types • Functional Risk • Physical Risk • Financial Risk • Psychological Risk • Time Risk • Social Risk

How Consumers Handle Risk • • • Seek Information Stay Brand Loyal Select by Brand Image Rely on Store Image Buy the Most Expensive Model Seek Reassurance
ceba9d7b88db95efb8a75722106f330e.ppt