 Construction Planning and Prerequisite Measure Twice, Cut Once Chapter 3 1
Construction Planning and Prerequisite Measure Twice, Cut Once Chapter 3 1
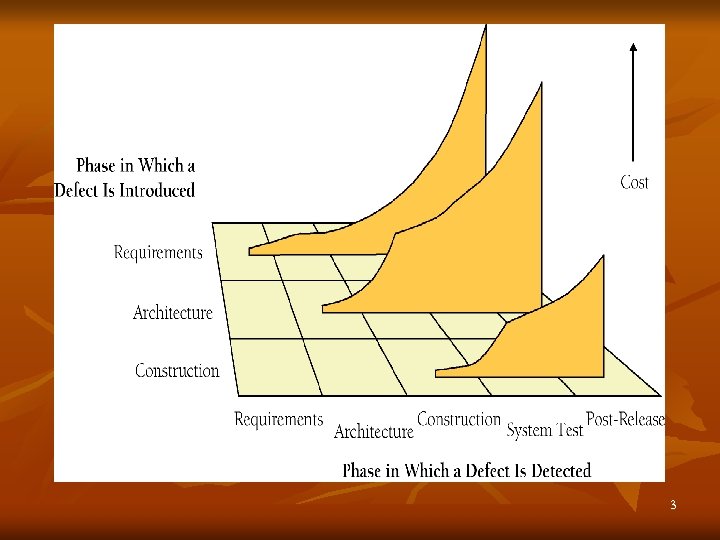
 Importance of Prerequisite Earlier parts of projects are “Prerequisite”. Projects run best if appropriate preparation activities are done before construction Removing an error by the beginning of construction allows rework to be done 10 to 100 times less expensively 2
Importance of Prerequisite Earlier parts of projects are “Prerequisite”. Projects run best if appropriate preparation activities are done before construction Removing an error by the beginning of construction allows rework to be done 10 to 100 times less expensively 2
 3
3
 4
4
 Problem-Definition Prerequisite n n Is clear statement of the problem Does Not indicate to any possible solution One or two pages and sounds like problem Should be in user language and described from user’s point of view 5
Problem-Definition Prerequisite n n Is clear statement of the problem Does Not indicate to any possible solution One or two pages and sounds like problem Should be in user language and described from user’s point of view 5
 n n Good Example: “We can’t keep up with orders for Giant” Bad Example “We need to optimize our automated dataentry system to keep up with orders for the Giant“ 6
n n Good Example: “We can’t keep up with orders for Giant” Bad Example “We need to optimize our automated dataentry system to keep up with orders for the Giant“ 6
 Requirements Prerequisite n n n Contains what a software system is supposed to do The first step toward a solution Helps user derive system’s functionalities User can review and agree on requirements Keep programmer of guessing what the user wants 7
Requirements Prerequisite n n n Contains what a software system is supposed to do The first step toward a solution Helps user derive system’s functionalities User can review and agree on requirements Keep programmer of guessing what the user wants 7
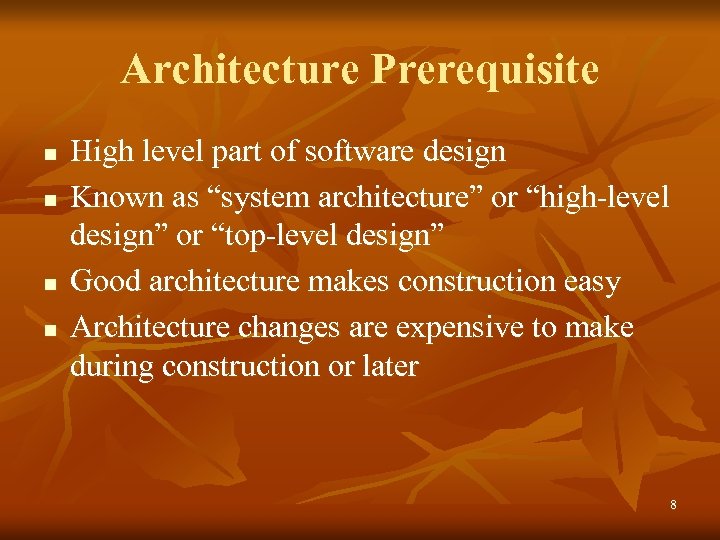 Architecture Prerequisite n n High level part of software design Known as “system architecture” or “high-level design” or “top-level design” Good architecture makes construction easy Architecture changes are expensive to make during construction or later 8
Architecture Prerequisite n n High level part of software design Known as “system architecture” or “high-level design” or “top-level design” Good architecture makes construction easy Architecture changes are expensive to make during construction or later 8
 Typical architecture components n Program Organization n n Major Classes n n Responsibilities of major classes and interaction with other classes Data Design n Defining major building blocks Might be class, group of classes (subsystem) Includes communication rules with other blocks, High level of file and table design Specify if single or multiple database to be used Business Rules n Must be mentioned and describe the impact of the rules on system design 9
Typical architecture components n Program Organization n n Major Classes n n Responsibilities of major classes and interaction with other classes Data Design n Defining major building blocks Might be class, group of classes (subsystem) Includes communication rules with other blocks, High level of file and table design Specify if single or multiple database to be used Business Rules n Must be mentioned and describe the impact of the rules on system design 9
 n Typical architecture components. . continue User Interface Design n Recourse Management n n Usually specified at requirements time Major elements of web page format, GUIs, command line interface. . How managing resources such as database connections, threads, memory. . Security n n n High level and code level security Handling un-trusted data (such as user data, cookies, configuration data), encryption, detail in error messages. Protecting secret data in memory 10
n Typical architecture components. . continue User Interface Design n Recourse Management n n Usually specified at requirements time Major elements of web page format, GUIs, command line interface. . How managing resources such as database connections, threads, memory. . Security n n n High level and code level security Handling un-trusted data (such as user data, cookies, configuration data), encryption, detail in error messages. Protecting secret data in memory 10
 Typical architecture components. . continue n Scalability n n n The ability of a system to grow to meet future demands Plan to handle growth of users, servers, number and size of database records, transaction volume Interoperability n How data or resources will be shared with other software or hardware 11
Typical architecture components. . continue n Scalability n n n The ability of a system to grow to meet future demands Plan to handle growth of users, servers, number and size of database records, transaction volume Interoperability n How data or resources will be shared with other software or hardware 11