c13fbeec2f240e0235e2a82f65ca3f7e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution
Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution
 Warm-Up Questions 1. What is the US Constitution? 2. Why do you feel it is important in your life?
Warm-Up Questions 1. What is the US Constitution? 2. Why do you feel it is important in your life?
 What is the US Constitution? • supreme law of the United States supreme law • foundation and source of the legal authority underlying the existence of the United States of America and the Federal Government of the of America Federal Government United States • framework for the organization of the United States govt
What is the US Constitution? • supreme law of the United States supreme law • foundation and source of the legal authority underlying the existence of the United States of America and the Federal Government of the of America Federal Government United States • framework for the organization of the United States govt
 Who Wrote It? • James Madison is considered “the father of the Constitution” – studied all forms of government before meeting and why they failed – took many notes – proposed many ideas
Who Wrote It? • James Madison is considered “the father of the Constitution” – studied all forms of government before meeting and why they failed – took many notes – proposed many ideas
 When was it written? • May 25 th to September 17 th, 1787 • Philadelphia • Constitutional Convention
When was it written? • May 25 th to September 17 th, 1787 • Philadelphia • Constitutional Convention
 Structure of the Constitution • • three sections beginning – preamble middle – 7 articles ending – 27 amendments – what can be changed making it the “living document”
Structure of the Constitution • • three sections beginning – preamble middle – 7 articles ending – 27 amendments – what can be changed making it the “living document”
 Preamble: introduction – statement of purpose 52 words last part added to the Constitution written by Gouverneur Morris
Preamble: introduction – statement of purpose 52 words last part added to the Constitution written by Gouverneur Morris
 Articles: I: Legislative Branch II: Executive Branch III: Judicial Branch IV: Relations Among the States V: Amendment Process VI: Federal Power VII: Ratification
Articles: I: Legislative Branch II: Executive Branch III: Judicial Branch IV: Relations Among the States V: Amendment Process VI: Federal Power VII: Ratification
 Amendments: 27 Total 1 st ten – Bill of Rights Can be added to with the changing of time/society … the living document
Amendments: 27 Total 1 st ten – Bill of Rights Can be added to with the changing of time/society … the living document
 Article I: Legislative Branch Makes the Laws • Bicameral: – Senate (100) • 2 Senators for each state – House of Representatives (435) • based on population • Reps serve for 2 year terms • Senators serve for 6 year terms • Important Powers: make laws set taxes declare war override Vetoes borrow money regulate international and national trade – print money – – –
Article I: Legislative Branch Makes the Laws • Bicameral: – Senate (100) • 2 Senators for each state – House of Representatives (435) • based on population • Reps serve for 2 year terms • Senators serve for 6 year terms • Important Powers: make laws set taxes declare war override Vetoes borrow money regulate international and national trade – print money – – –
 Article II: Executive Branch Enforces the Laws • President and Vice President are elected to 4 year terms • qualifications: – at least 35 years old – 14 year resident of the US – natural born citizen • elected by the Electoral College • Important powers: – – Commander-in-Chief grant pardons make treaties appoint federal officers
Article II: Executive Branch Enforces the Laws • President and Vice President are elected to 4 year terms • qualifications: – at least 35 years old – 14 year resident of the US – natural born citizen • elected by the Electoral College • Important powers: – – Commander-in-Chief grant pardons make treaties appoint federal officers
 Article III: Judicial Branch Interprets the Laws • Supreme Court judges serve for life • Judicial power rests with U. S. Supreme Court and other courts created by Congress • Important Powers: – decides cases of Constitutional law and federal law – cases involving ambassadors go straight to Supreme Court – Judicial Review (1803 – Marbury v. Madison)
Article III: Judicial Branch Interprets the Laws • Supreme Court judges serve for life • Judicial power rests with U. S. Supreme Court and other courts created by Congress • Important Powers: – decides cases of Constitutional law and federal law – cases involving ambassadors go straight to Supreme Court – Judicial Review (1803 – Marbury v. Madison)
 Other Important Articles: • Article IV: Relations Among the • Article V: Amendments States – amendments are proposed – Each state gives citizens of when 2/3 of House and other states the same Senate deem it necessary rights as there – amendments are proposed – National government will when 2/3 of states deem it protect the states necessary – amendments must be ratified by ¾ of state legislatures or by conventions in ¾ of states
Other Important Articles: • Article IV: Relations Among the • Article V: Amendments States – amendments are proposed – Each state gives citizens of when 2/3 of House and other states the same Senate deem it necessary rights as there – amendments are proposed – National government will when 2/3 of states deem it protect the states necessary – amendments must be ratified by ¾ of state legislatures or by conventions in ¾ of states
 Other Important Articles: • Article VI: Federal Power – Supremacy Clause: federal law is supreme to state law – no religious tests for public office • Article VII: Ratification – How the Constitution becomes the law of the land
Other Important Articles: • Article VI: Federal Power – Supremacy Clause: federal law is supreme to state law – no religious tests for public office • Article VII: Ratification – How the Constitution becomes the law of the land
 BILL OF RIGHTS: Ya gotta know!!! 1. Freedom of religion, speech, assembly, press and the right for people to petition the government 2. States can maintain a militia and citizens rights to bare arms 3. Restricts quartering of troops in private homes 4. Protects against unreasonable search and seizures 5. Assures rights to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness 6. Right to a speedy and public trial 7. Assures right to a jury trial 8. Protects against excessive bail or cruel and unusual punishment 9. Peoples rights are not restricted by the first 8 amendments 10. Restates Constitutions principals of Federalism In Addition: (known as the Reconstruction Amendments) 13. Abolished slavery 14. All persons born in the United States. . . excluding Indians not taxed. . " were citizens and were to be given "full and equal benefit of all laws. " 15. Allows black men the right to vote
BILL OF RIGHTS: Ya gotta know!!! 1. Freedom of religion, speech, assembly, press and the right for people to petition the government 2. States can maintain a militia and citizens rights to bare arms 3. Restricts quartering of troops in private homes 4. Protects against unreasonable search and seizures 5. Assures rights to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness 6. Right to a speedy and public trial 7. Assures right to a jury trial 8. Protects against excessive bail or cruel and unusual punishment 9. Peoples rights are not restricted by the first 8 amendments 10. Restates Constitutions principals of Federalism In Addition: (known as the Reconstruction Amendments) 13. Abolished slavery 14. All persons born in the United States. . . excluding Indians not taxed. . " were citizens and were to be given "full and equal benefit of all laws. " 15. Allows black men the right to vote
 Other Important Amendments: Reconstruction Amendments • 13 th Amendment – abolished slavery • 14 th Amendment – due process and equal protection under the law – all persons born in US are citizens • 15 th Amendment – right to vote regardless of race, color, or previous servitude
Other Important Amendments: Reconstruction Amendments • 13 th Amendment – abolished slavery • 14 th Amendment – due process and equal protection under the law – all persons born in US are citizens • 15 th Amendment – right to vote regardless of race, color, or previous servitude
 Other Important Amendments: • 18 th Amendment – Prohibition of alcohol • 19 th Amendment: – Women’s suffrage • 21 st Amendment: – Repeals prohibition • 22 nd Amendment: – Presidential term limits • 24 th Amendment: – Prohibits poll taxes for voting • 26 th Amendment: – lowers voting age to 18
Other Important Amendments: • 18 th Amendment – Prohibition of alcohol • 19 th Amendment: – Women’s suffrage • 21 st Amendment: – Repeals prohibition • 22 nd Amendment: – Presidential term limits • 24 th Amendment: – Prohibits poll taxes for voting • 26 th Amendment: – lowers voting age to 18
 Seven Principles of the Constitution There is not an order to this… no one principle is more important than the other
Seven Principles of the Constitution There is not an order to this… no one principle is more important than the other
 Popular Sovereignty • Definition – govt in which the people rule by voting; the govt gets its power from the people • Example – people can run for office, campaign for individuals who run, or protest decisions made by others
Popular Sovereignty • Definition – govt in which the people rule by voting; the govt gets its power from the people • Example – people can run for office, campaign for individuals who run, or protest decisions made by others
 Republicanism • Definition – people vote for people to represent their views; representative govt • You can not have the whole population vote on everything, so you vote on people who share similar beliefs and allow them to vote.
Republicanism • Definition – people vote for people to represent their views; representative govt • You can not have the whole population vote on everything, so you vote on people who share similar beliefs and allow them to vote.
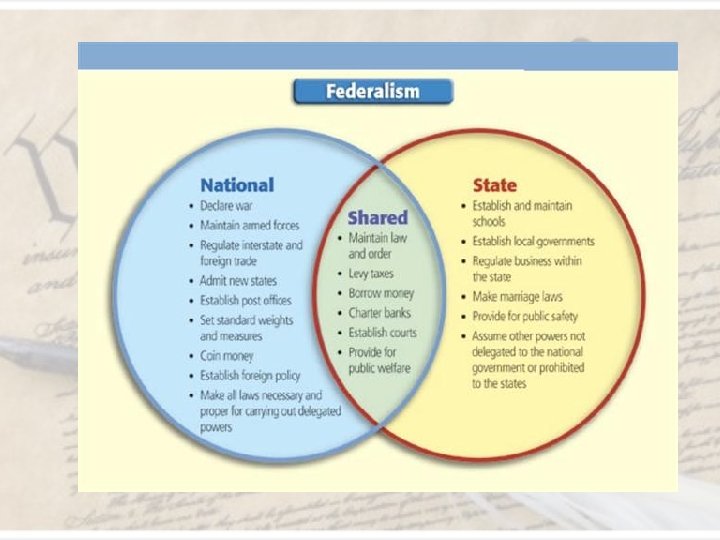
 Federalism • Definition – system of govt in which powers are shared by the state and national government • The national government has ultimate authority, but states have a lot to say in what goes on as well. • national govt = delegated powers • state govt = reserved powers • shared powers national and state govts = concurrent powers
Federalism • Definition – system of govt in which powers are shared by the state and national government • The national government has ultimate authority, but states have a lot to say in what goes on as well. • national govt = delegated powers • state govt = reserved powers • shared powers national and state govts = concurrent powers
 Which government is responsible? • • • Building Roads Certain age to be married Driver’s License Printing Money Get a Passport Arrest a criminal
Which government is responsible? • • • Building Roads Certain age to be married Driver’s License Printing Money Get a Passport Arrest a criminal
 Separation of Power • Definition – divides the govt into 3 branches: Executive, Legislative, and Judicial • Why? So that one person or one group of people do not control everything and become to powerful.
Separation of Power • Definition – divides the govt into 3 branches: Executive, Legislative, and Judicial • Why? So that one person or one group of people do not control everything and become to powerful.
 Individual Rights • Definition – personal liberties and privileges that people are born with and can not be taken away • The Bill of Rights, the first Ten Amendments, was created to list out all of these rights so people know when the governments tries to take them away.
Individual Rights • Definition – personal liberties and privileges that people are born with and can not be taken away • The Bill of Rights, the first Ten Amendments, was created to list out all of these rights so people know when the governments tries to take them away.
 Limited Government • Definition – everyone has to follow the same laws, even members of the govt; limit the power of the government • Example – If a Representative killed a man, he would face a trial just like everybody else.
Limited Government • Definition – everyone has to follow the same laws, even members of the govt; limit the power of the government • Example – If a Representative killed a man, he would face a trial just like everybody else.
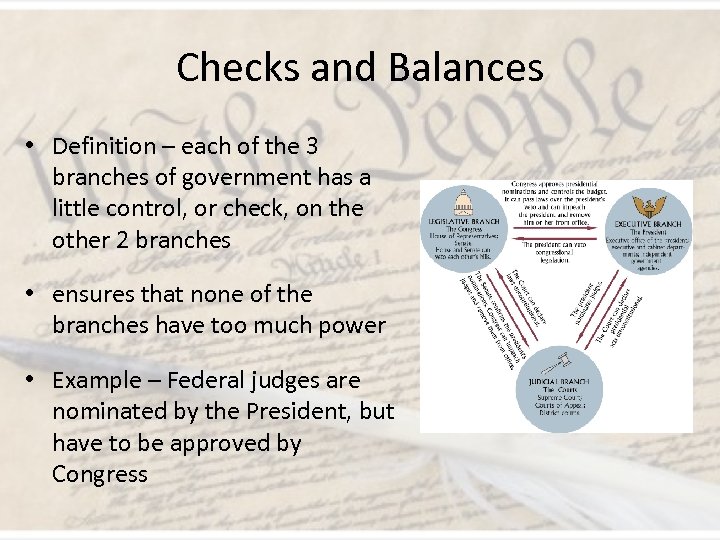 Checks and Balances • Definition – each of the 3 branches of government has a little control, or check, on the other 2 branches • ensures that none of the branches have too much power • Example – Federal judges are nominated by the President, but have to be approved by Congress
Checks and Balances • Definition – each of the 3 branches of government has a little control, or check, on the other 2 branches • ensures that none of the branches have too much power • Example – Federal judges are nominated by the President, but have to be approved by Congress


