2a967c97b5037d416eeb9c00ff7c896f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78

Constipation & Diarrhea March 4, 2010

Objectives 1. 2. 3. Learn an approach to treating constipation in the Emergency Room and on discharge Discuss when “constipation” needs further workup Diarrhea-discuss the common and important ED presentations

True or False 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Correction of constipation has been shown to diminish enuresis Correction of constipation has been shown to decrease the frequency of UTI’s Fecal soiling is associated with severe functional constipation Constipation can be a cause of rectal prolapse On digital rectal exam, no stool in the rectal vault is consistent with functional constipation

True or False 6) 7) 8) 9) Vomiting can be a sign of Hirshsprung’s Vomiting can be a sign of functional constipation Celiac disease can present as constipation Constipation is the first symptom of botulism

Few more quick facts 1) 2) When is the 1 st stool of a neonate normally passed? Which chemotherapy agent causes constipation?

Definitions n Constipation n Functional Constipation

Definitions n Constipation ¨ Delay or difficulty in defecation, present for >2 weeks n Functional Constipation ¨ Constipation without objective evidence of a pathologic condition

Case 1 2 month baby, term, formula fed n Having 4 -5 bowel movements/week n Grandma thinks something is seriously wrong because her other grandchild has 45 bowel movements/day n What do you do? n

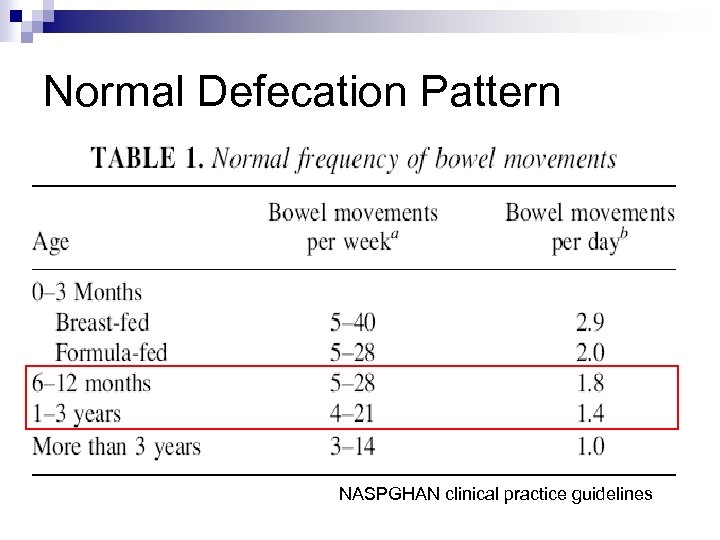
Normal Defecation Pattern
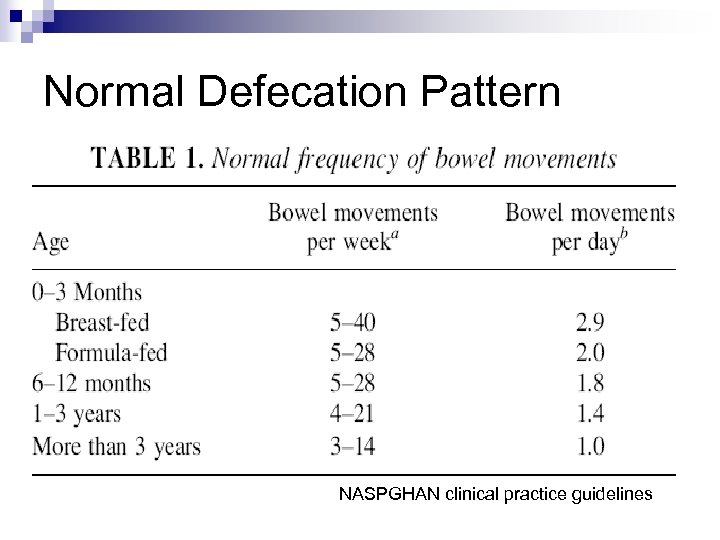
Normal Defecation Pattern NASPGHAN clinical practice guidelines
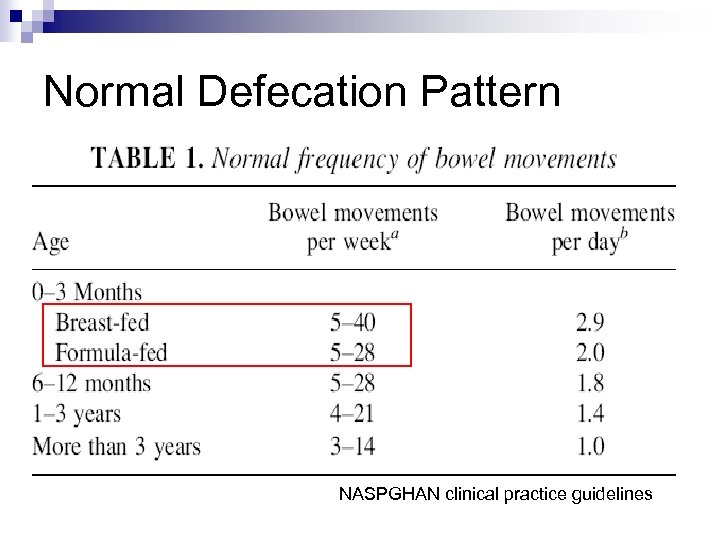
Normal Defecation Pattern NASPGHAN clinical practice guidelines

Approach to Constipation n What is your approach? ? ?

Approach to Constipation n Are there any red flags?

Approach to Constipation n Red flags ¨ Fever ¨ Emesis ¨ Bloody diarrhea ¨ FTT ¨ Anal stenosis ¨ Tight empty rectum ¨ Delayed passage of meconium n If yes…. need to investigate further

Approach to Constipation No red flags=functional constipation n Is there fecal impaction? n ¨ Yes: disimpact Oral or rectal meds n Usually 2 -3 days required n ¨ No: n Treat as outpatient Education, diet, oral meds

Approach to constipation n Treatment effective ¨ Yes: maintence therapy 4 -6 months ¨ No: Bloodwork T 4, TSH n Celiac screen n Lead n Calcium n n If above workup is negative, and child still constipated, refer to GI n But may want to refer for sweat chloride & rectal bx
What about abdominal x-rays? n Not needed if rectal exam reveals large amounts of stool ¨ Sens & PPV >80% If child is obese or refuses the rectal exam, the AXR is reliable in determining fecal retention n If used in combination with DRE n ¨ sens 92% & PPV 94% NASPGHAN clinical practice guidelines

Case 2 n n n n 1 month asian male, term, with 12 h hx of constipation Prior to presentation, had 4 -5 BM/day Breastfed, feeding less well at last 2 feeds No emesis Had passed meconium within first 24 h Neonatal screen Neg for CF and hypothyroid O/E: alert, slightly fussy, vitals stable ¨ distended abdo, +BS ¨ No anal fissure ¨ Palpable firm stool in rectum ¨
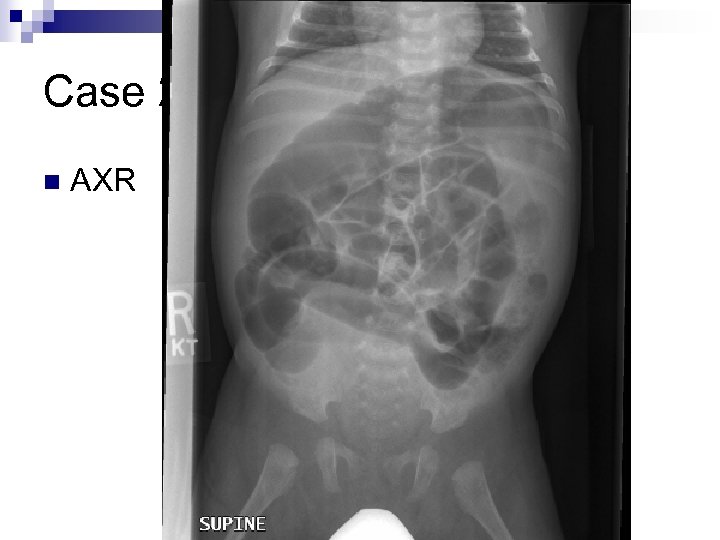
Case 2 n AXR
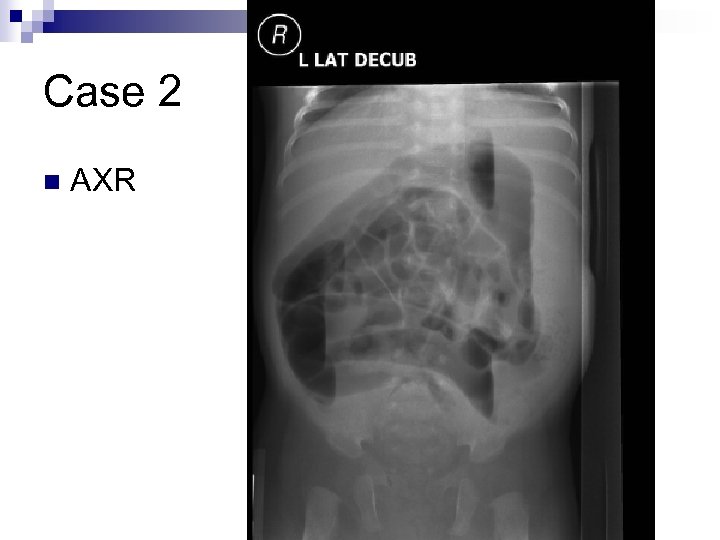
Case 2 n AXR

Case 2 n n n Glycerin supp-resulted in dry, crumbly stool in diaper Attempted enema-came out immediately Manual disimpaction-able to remove dry hard stool, with overflow liquid seepage After disimpaction, fed well, abdomen softer Arranged for F/U in Urgent Peds for further W/U (hirshsprung, CF, hypothyroid)

Case 2 Returned to ED the following afternoon n Tachypnic n Repeat AXR n
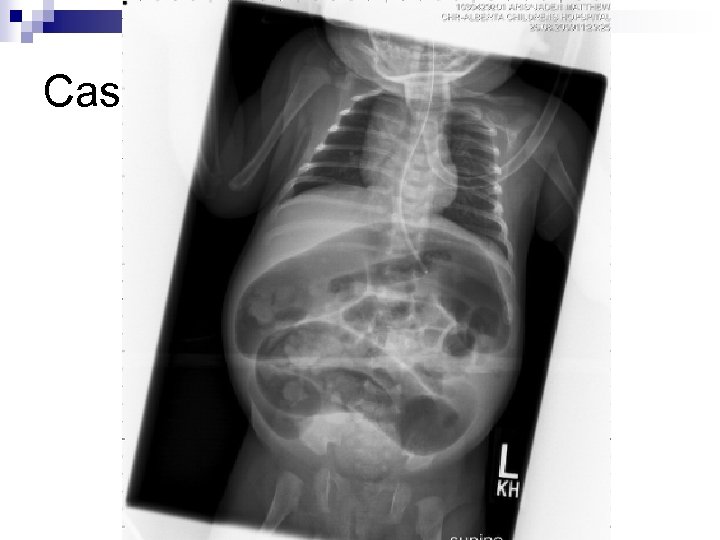
Case 2
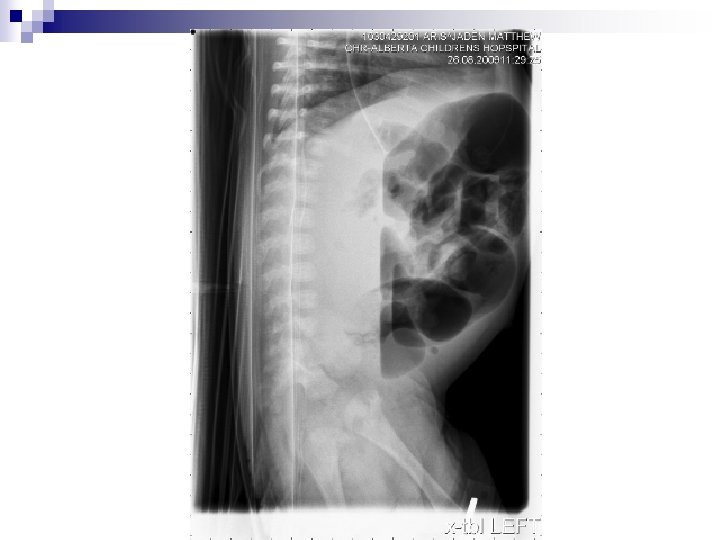

Case 2 n Intubated due to respiratory distress Went up to OR for laparotomy…. . with pre-op suspicion of volvulus n Post op dx: Inspissated stool n Workup all negative n ¨ Sweat chloride, Hirshsprung’s, thyroid

Case 2: Take home message n Be cautious in diagnosing and discharging a 1 month old with constipation!

Case 3 n n n n 3 month male with distended abdomen & poor feeding No emesis Passing stool 2 -3 times/day Febrile in ED (38. 8) What do you want to do? NB question on history: is the stool liquid? (ie overflow incontinence) NB finding on exam: tight anal sphincter with no stool in rectum

Hirshsprung Disease Most common cause of lower intestinal obstruction in neonates n Rare cause of intractable constipation in toddlers & school age children n ¨ Diagnosed n after age 3 in 8 -20% of pts Absence of ganglion cells in the myenteric & submucous plexuses of the distal colon ¨ Sustained segment contraction of the aganglionic

Hirshsprung Disease n Enterocolitis ¨ Fever, abdo distension, explosive bloody diarrhea ¨ Occurs at age 2 -3 months ¨ 20% mortality ¨ Greatest risk factor is delayed diagnosis of Hirshsprung’s

The “don’t want to miss” causes of constipation Hirshsprung Disease n Cystic Fibrosis n Botulism n Hypothyroid n Imperforate anus n Sacral teratoma n Sexual abuse n Celiac Disease n
Botulism n n n Initial symptom of botulism is constipation Lethargy and feeding difficulties follow P/E: ¨ Decreased DTR, decreased suck & gag ¨ Poorly reactive pupils & Ptosis ¨ Oculomotor palsies ¨ Facial weakness n n Dx: Identify C. botulinum spores & toxin in stool* Tx: Admit! 50 -77% require intubation ¨ Baby BIG

Treatment of Constipation n Depends on age ¨ If <3 months, should have F/U with a Pediatrician n Consists of ¨ “rescue therapy” ¨ maintenance therapy

Acute treatment (>1 year) n Fleet Enema ¨ Pediatric 66 m. L, Adult 133 m. L n Once >2 yrs, use adult enema ¨ Onset 2 -5 minutes ¨ Side effects: Hyperphosphatemia n Use with caution in renal failure n ¨ Osmotic effect in the small intestine n draws water into the gut lumen, produces distension, promotes peristalsis and evacuation

Maintenance Treatment (>1 year) n PEG 3350 ¨ Osmotic Laxative ¨ Dose 1 g/kg/d (Max 17 g) ¨ Onset in 1 -3 days ¨ Side effects (minimal): n bloating, cramping, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea ¨ Contraindications n GI obstruction, ileus, bowel perforation, toxic colitis, megacolon

Evidence for PEG 3350 RCT, double blind n 100 patients (aged 6 months-15 years) n After fecal disimpaction, received either PEG or Lactulose n Primary outcomes: n ¨ defecation and encopresis frequency/week ¨ successful treatment after eight weeks n Secondary outcomes: ¨ Side effects after 8 weeks Gut. 2004 Nov; 53(11): 1590 -4.

Evidence for PEG 3350 n Success defined as: ¨ defecation frequency > 3/week ¨ encopresis < once every 2 weeks n Results ¨ Success was significantly higher in the PEG group (56%) compared with the lactulose group (29%) ¨ PEG 3350 patients reported less abdominal pain, straining, and pain at defecation than children using lactulose

Evidence for PEG 3350 CONCLUSIONS: n PEG 3350 compared with lactulose provided a higher success rate with fewer side effects n PEG 3350 should be the laxative of first choice in childhood constipation

Treatments to avoid n Mineral oil (if <1 yr, use with caution if <3) ¨ Lipoid n Phosphate enemas (if <1 year) ¨ Can n pneumonia if aspirated use glycerine suppository Stimulant laxatives (long term) ¨ Senekot ¨ Dulcolax

Case 4 2 year female with 4 day hx of constipation & 8 cm rectal prolapse n Has just started toilet training n What are you going to do? n

Case 4 n Other history ¨ Has 2 -3 BM/week with ++straining ¨ Fecal soiling present ¨ Term, passed meconium on day 2 of life ¨ Was admitted to hospital at 18 months with pneumonia n O/E ¨ Weight & height at 5 th percentile

Case 4 n Other history ¨ Has 2 -3 BM/week with ++straining ¨ Fecal soiling present ¨ Term, passed meconium on day 2 of life ¨ Was admitted to hospital at 18 months with pneumonia n O/E ¨ Weight & height at 5 th percentile

Case 4 n What is your immediate treatment? n What is the diagnosis? (top 3)

Case 4 n What is your immediate treatment ¨ Reduce protrusion (pressure with warm compress) ¨ Start pt on stool softeners ¨ Surgery in refractive cases n What is the diagnosis? (top 3) ¨ Cystic Fibrosis ¨ Chronic constipation ¨ Meningocoele

True or False n n Correction of constipation has been shown to diminish enuresis TRUE

True or False n n Correction of constipation has been shown to decrease the frequency of UTI’s TRUE

True or False n n Fecal soiling is associated with severe functional constipation TRUE

True or False n n Constipation can be a cause of rectal prolapse TRUE but…. need to also consider other etiologies ¨ ¨ ¨ Cystic Fibrosis Meningocoele Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) Ehlers-Danlos Ulcerative colitis Pertussis

True or False n n On digital rectal exam, no stool in the rectal vault is consistent with functional constipation FALSE

True or False Vomiting can be a sign of Hirshsprung’s n TRUE n

True or False Vomiting can be a sign of functional constipation n FALSE n

True or False n n Constipation is the first symptom of botulism TRUE

Quick Facts When is the 1 st stool of a neonate normally passed? n 99% pass stool within 24 hours and 100% pass stool within 48 hours n ¨ Prems may be a little delayed (76% pass within 24 hours and 98. 8% pass within 48 h)

Quick Facts Which chemotherapy agent causes constipation? n Vincristine n

Diarrhea

True or False 1) Salmonella enteritis can be safely treated as an outpatient 2) 40% of infants are colonized with C. diff 3) Amoxicillin is responsible for most cases of pseudomembranous colitis in children 4) Switching to a lactose free formula is helpful during an acute diarrheal illness 5) Toddlers diarrhea is the most common cause of chronic diarrhea in children between the ages of 12 -36 months

Diarrhea n Definition n The “not to miss” diagnoses (4)

Diarrhea n Definition ¨ Softening in the consistency of the stool with or without an increase in the number of stools n The not to miss diagnoses (5) ¨ Intussusception ¨ Pseudomembranous Colitis ¨ Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome ¨ Appendicits ¨ Salmonella enteritis with bacteremia

Diarrhea & Gastroenteritis n Usually no investigations are required ¨ watery n Once diarrhea is bloody…. do the tests ¨ Blood n and stool cultures, U/A, CBC, BUN/Cr Risk factors for bacteremia from gastro ¨ Fever n diarrhea in previously healthy children >5 days and child <12 months Remember to ask about reptiles in the house

HUS Initially mild gastroenteritis n Hematochezia n Pallor(microangiopathic hemolytic anemia) n Purpura (Thrombocytopenia) n Hematuria n Renal Failure n ¨ If parents tell you that the kid hasn’t peed in 24 hours, take them seriously

HUS Most often in kids <4 years n E. coli 0157: H 7 n ¨ Avoid antibiotics in patients with acute enteritis presumed secondary to E. coli 0157 n Take home point ¨ Do CBC, Cr, urinalysis in kids with bloody diarrhea (as well as stool & blood cultures)

Salmonella enteritis n Salmonella gastroenteritis is usually self-limited ¨ Fever generally resolves within 48 to 72 hours ¨ Diarrhea resolves within 4 to 10 days n n BUT…in infants 5 -40% will have +blood culture So…. children <3 months (some say 1 year) with symptomatic salmonellosis should be treated with antibiotics until blood cultures are negative ¨ Cefotax 100 -200 mg/kg/d div q 6 h ¨ Ceftriaxone 75 mg/kg/d OD
Pseudomembranous colitis n n Despite high carrier rates, illness is uncommon in neonates & infants Abdominal distension, fever and bloody stools are the key physical findings May occur several weeks after antibiotics Tx: ¨ Discontinue current antibiotic ¨ Metronidazole 20 -40 mg/kg/d div q 6 h PO ¨ 2 nd line Vanco (if really severe, combine flagyl vanco) ¨ Admit to monitor for toxic megacolon &

Case 5 4 month male with daily diarrhea (6 x/d) n Pretty bad eczema n Admitted to hospital at 3 months of age with pneumonia n O/E: weight 4. 5 kg n What are you going to do before sending this child home? n

Case 5 4 month male with daily diarrhea (6 x/d) n Pretty bad eczema n Admitted to hospital at 3 months of age with pneumonia n O/E: weight 4. 5 kg (Failure to thrive) n What are you going to do before sending this child home? n

Case 6 n n n n 12 month female 5 loose stools/day Mom thinks that occasionally she is bloated Thriving No history of eczema 2 previous URTI’s What do you think the diagnosis is? Mom asks if this could be lactose intolerance…. what do you think?
Normal Defecation Pattern NASPGHAN clinical practice guidelines

Toddler’s Diarrhea n n n Occurs at age 1 -3 years History of excessive carbohydrate containing beverages (specifically sorbital- found in apple, pear & prune juice) Stools occur during the day (not at night) ¨ May n n contain undigested food particles Limit sugar containing drinks and increase fat in the diet to 40% Fluid restriction to <90 ml/kg/d

Lactase Deficiency n Congenital lactase deficiency is RARE! ¨ <50 cases worldwide ¨ So…. when a parent is worried that their infant is lactose intolerant and this is causing diarrhea…. reassure that this is not the cause of their diarrhea (unless their child is #51 in the world)

Secondary Lactose Intolerance Common n Follows small bowel mucosal damage n ¨ Ie. Rotavirus, Celiac disease Transient & resolves with mucosal healing n Treatment (classically) n ¨ Milk free diet or lactose-free formula ¨ But clinical trials haven't shown a benefit in acute infectious diarrhea for the majority of infants

Use of Probiotics Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Saccharomyces n There are RCT’s supporting their use in acute infectious diarrhea and C. diff n ¨ In n rotavirus-diarrhea is briefer and milder However, therapy is not yet standardized and the most effective organism has not been identified

True or False Salmonella enteritis can be safely treated as an outpatient n TRUE IF >12 months (possible if >3 mo) n

True or False 40% of infants are colonized with C. diff n TRUE n

True or False Amoxicillin is responsible for most cases of pseudomembranous colitis in children n TRUE n ¨ Because of the frequency it is prescribed

True or False Switching to a lactose free formula is helpful during an acute diarrheal illness n FALSE n

True or False Toddlers diarrhea is the most common cause of chronic diarrhea in children between the ages of 12 -36 months n TRUE n

Objectives 1. 2. 3. Learn an approach to treating constipation in the Emergency Room and on discharge Discuss when “constipation” needs further workup Diarrhea-discuss the common and important ED presentations

Questions?
2a967c97b5037d416eeb9c00ff7c896f.ppt