 Consequences of Regional-Scale Nuclear Conflicts: Understanding and Avoiding Nuclear Catastrophe
Consequences of Regional-Scale Nuclear Conflicts: Understanding and Avoiding Nuclear Catastrophe
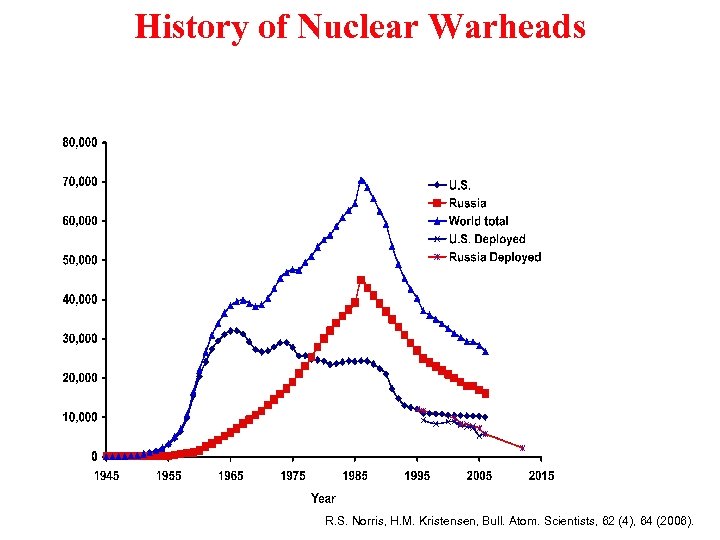 History of Nuclear Warheads R. S. Norris, H. M. Kristensen, Bull. Atom. Scientists, 62 (4), 64 (2006).
History of Nuclear Warheads R. S. Norris, H. M. Kristensen, Bull. Atom. Scientists, 62 (4), 64 (2006).
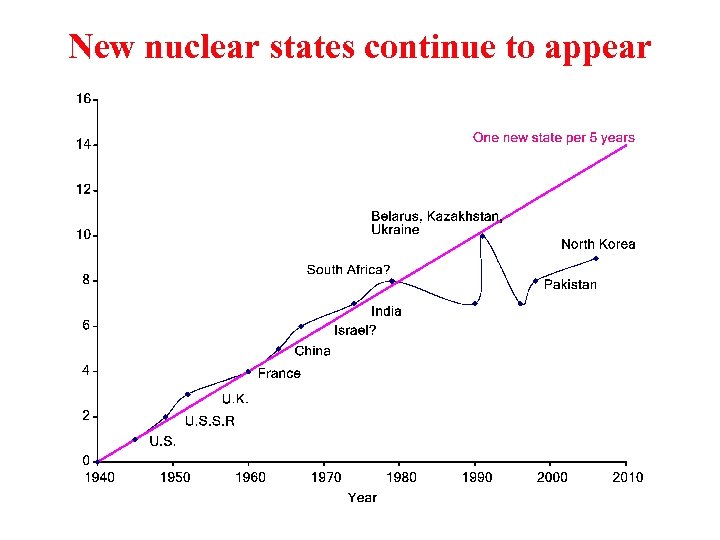 New nuclear states continue to appear
New nuclear states continue to appear
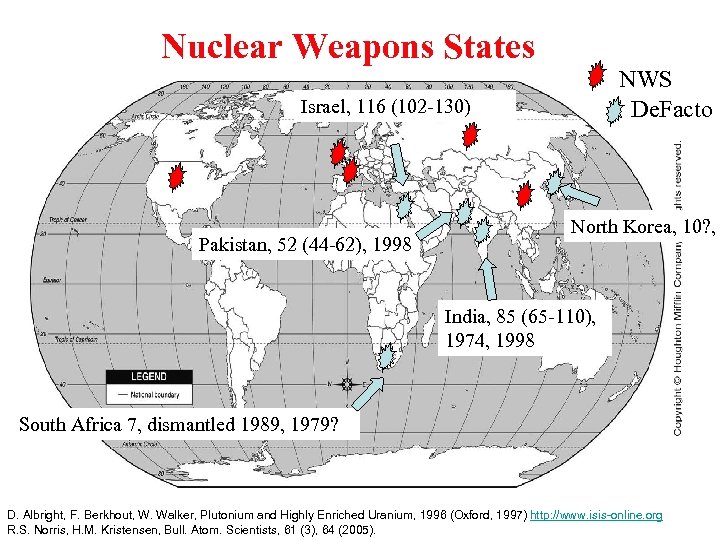 Nuclear Weapons States NWS De. Facto Israel, 116 (102 -130) Pakistan, 52 (44 -62), 1998 North Korea, 10? , India, 85 (65 -110), 1974, 1998 South Africa 7, dismantled 1989, 1979? D. Albright, F. Berkhout, W. Walker, Plutonium and Highly Enriched Uranium, 1996 (Oxford, 1997) http: //www. isis-online. org R. S. Norris, H. M. Kristensen, Bull. Atom. Scientists, 61 (3), 64 (2005).
Nuclear Weapons States NWS De. Facto Israel, 116 (102 -130) Pakistan, 52 (44 -62), 1998 North Korea, 10? , India, 85 (65 -110), 1974, 1998 South Africa 7, dismantled 1989, 1979? D. Albright, F. Berkhout, W. Walker, Plutonium and Highly Enriched Uranium, 1996 (Oxford, 1997) http: //www. isis-online. org R. S. Norris, H. M. Kristensen, Bull. Atom. Scientists, 61 (3), 64 (2005).
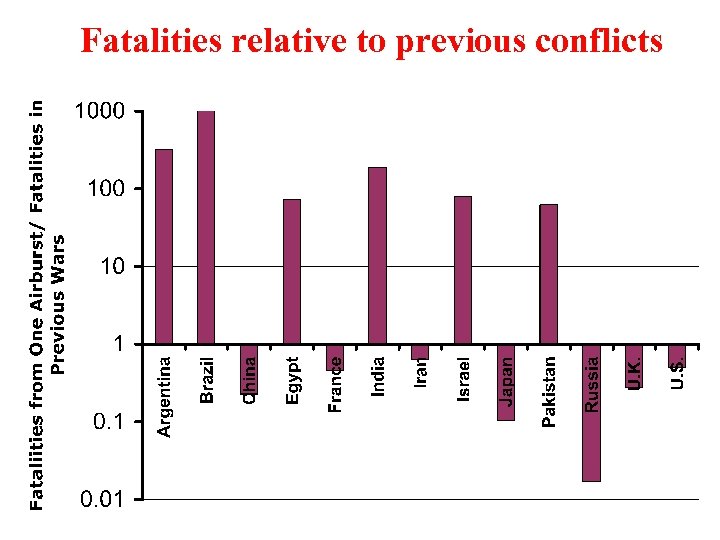 Fatalities relative to previous conflicts
Fatalities relative to previous conflicts
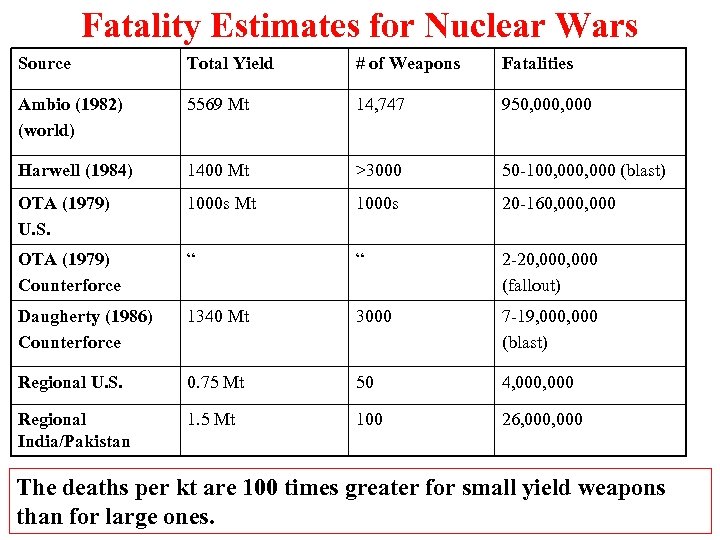 Fatality Estimates for Nuclear Wars Source Total Yield # of Weapons Fatalities Ambio (1982) (world) 5569 Mt 14, 747 950, 000 Harwell (1984) 1400 Mt >3000 50 -100, 000 (blast) OTA (1979) U. S. 1000 s Mt 1000 s 20 -160, 000 OTA (1979) Counterforce “ “ 2 -20, 000 (fallout) Daugherty (1986) Counterforce 1340 Mt 3000 7 -19, 000 (blast) Regional U. S. 0. 75 Mt 50 4, 000 Regional India/Pakistan 1. 5 Mt 100 26, 000 The deaths per kt are 100 times greater for small yield weapons than for large ones.
Fatality Estimates for Nuclear Wars Source Total Yield # of Weapons Fatalities Ambio (1982) (world) 5569 Mt 14, 747 950, 000 Harwell (1984) 1400 Mt >3000 50 -100, 000 (blast) OTA (1979) U. S. 1000 s Mt 1000 s 20 -160, 000 OTA (1979) Counterforce “ “ 2 -20, 000 (fallout) Daugherty (1986) Counterforce 1340 Mt 3000 7 -19, 000 (blast) Regional U. S. 0. 75 Mt 50 4, 000 Regional India/Pakistan 1. 5 Mt 100 26, 000 The deaths per kt are 100 times greater for small yield weapons than for large ones.
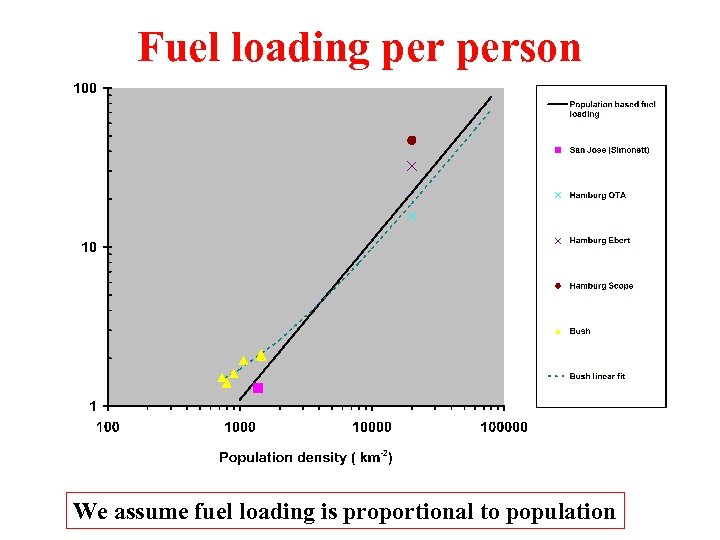 Fuel loading person We assume fuel loading is proportional to population
Fuel loading person We assume fuel loading is proportional to population
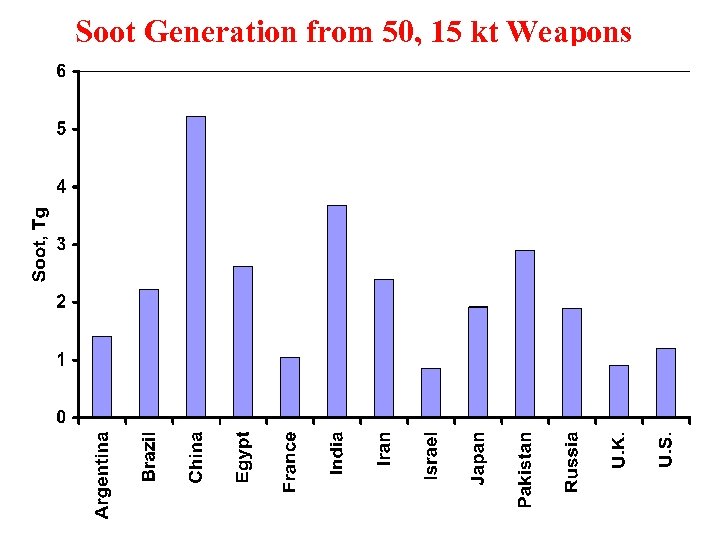 Soot Generation from 50, 15 kt Weapons
Soot Generation from 50, 15 kt Weapons
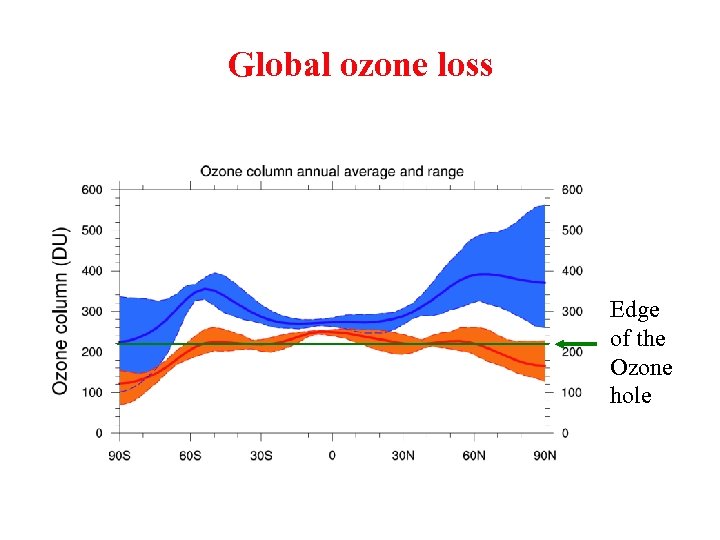 Global ozone loss Edge of the Ozone hole
Global ozone loss Edge of the Ozone hole
 Summary • The number of nuclear states is growing • 40 countries have enough fissionable materials for 1104 weapons. • Modern nuclear weapons are small and lightweight. One weapon detonated by a terrorist could cause a million casualties. • 50 nuclear explosions of 15 kt yield can cause as many fatalities as once projected for a full scale “counterforce” war between the superpowers. • Large amounts of smoke can be generated from a regional war that could trigger global climate change and ozone loss affecting non-combatant countries.
Summary • The number of nuclear states is growing • 40 countries have enough fissionable materials for 1104 weapons. • Modern nuclear weapons are small and lightweight. One weapon detonated by a terrorist could cause a million casualties. • 50 nuclear explosions of 15 kt yield can cause as many fatalities as once projected for a full scale “counterforce” war between the superpowers. • Large amounts of smoke can be generated from a regional war that could trigger global climate change and ozone loss affecting non-combatant countries.
 Based on the Papers: ATMOSPHERIC EFFECTS AND SOCIETAL CONSEQUENCES OF REGIONAL SCALE NUCLEAR CONFLICTS AND ACTS OF INDIVIDUAL NUCLEAR TERRORISM Owen B. Toon, Richard P. Turco, Alan Robock, Charles Bardeen, Luke Oman, Georgiy L. Stenchikov Atmos. Chem. Phys. . 7, 2003 -2012, 2007 and CLIMATIC CONSEQUENCES OF REGIONAL SCALE NUCLEAR CONFLICTS Alan Robock, Luke Oman, Georgiy L. Stenchikov, Owen B. Toon, Charles Bardeen, Richard P. Turco Atmos. Chem. Phys. , 7, 1973 -2002, 2007
Based on the Papers: ATMOSPHERIC EFFECTS AND SOCIETAL CONSEQUENCES OF REGIONAL SCALE NUCLEAR CONFLICTS AND ACTS OF INDIVIDUAL NUCLEAR TERRORISM Owen B. Toon, Richard P. Turco, Alan Robock, Charles Bardeen, Luke Oman, Georgiy L. Stenchikov Atmos. Chem. Phys. . 7, 2003 -2012, 2007 and CLIMATIC CONSEQUENCES OF REGIONAL SCALE NUCLEAR CONFLICTS Alan Robock, Luke Oman, Georgiy L. Stenchikov, Owen B. Toon, Charles Bardeen, Richard P. Turco Atmos. Chem. Phys. , 7, 1973 -2002, 2007
 End of talk the following are spare slides
End of talk the following are spare slides
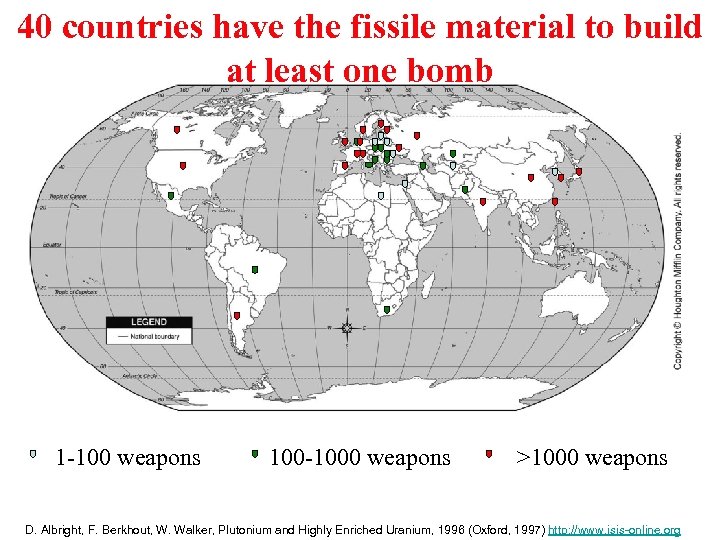 40 countries have the fissile material to build at least one bomb 1 -100 weapons 100 -1000 weapons >1000 weapons D. Albright, F. Berkhout, W. Walker, Plutonium and Highly Enriched Uranium, 1996 (Oxford, 1997) http: //www. isis-online. org
40 countries have the fissile material to build at least one bomb 1 -100 weapons 100 -1000 weapons >1000 weapons D. Albright, F. Berkhout, W. Walker, Plutonium and Highly Enriched Uranium, 1996 (Oxford, 1997) http: //www. isis-online. org
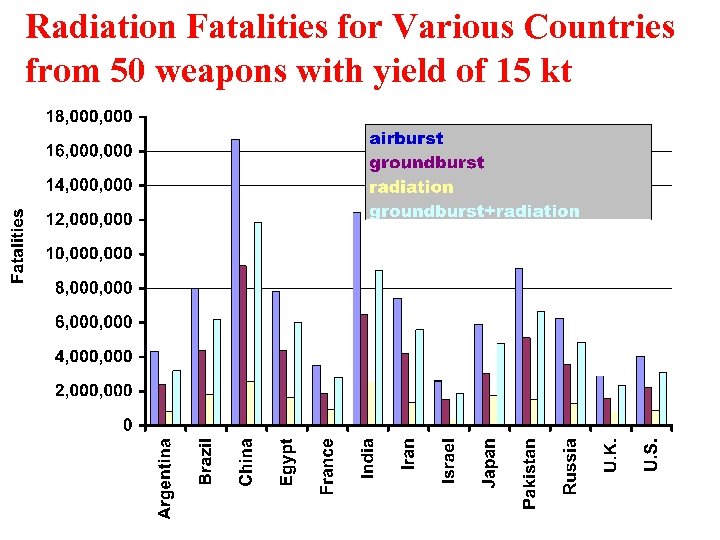 Radiation Fatalities for Various Countries from 50 weapons with yield of 15 kt
Radiation Fatalities for Various Countries from 50 weapons with yield of 15 kt