fd85df168a636803b3127298bdca3376.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
Conquer unprecedented complexity by making better use of your engineering data © 2013 IBM Corporation

Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Smarter products rising complexity § Product innovation enables companies to: – Leapfrog their competition – Grow demand – Increase revenues – Raise profits § The next generation of innovative, smarter products requires more: – Instrumentation – Intelligence – Interconnection § This is driving increasing complexity in: – Collaboration across engineering disciplines – Engineering artifacts and their relationships 2 © 2013 IBM Corporation
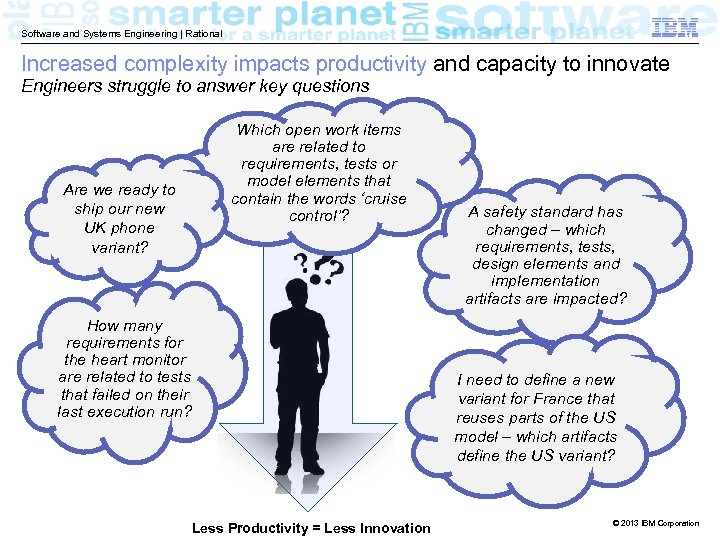
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Increased complexity impacts productivity and capacity to innovate Engineers struggle to answer key questions Are we ready to ship our new UK phone variant? Which open work items are related to requirements, tests or model elements that contain the words ‘cruise control’? How many requirements for the heart monitor are related to tests that failed on their last execution run? A safety standard has changed – which requirements, tests, design elements and implementation artifacts are impacted? I need to define a new variant for France that reuses parts of the US model – which artifacts define the US variant? Less Productivity = Less Innovation © 2013 IBM Corporation

Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Workers across the enterprise, including engineering, spend a lot of time (not) finding information § Knowledge workers spend 15% to 35% of their time searching for information § 40% of corporate users report that they cannot find the information they need to do their jobs § 50% of most intranet searches are abandoned § 90% of the time that knowledge workers spend in creating new reports is recreating information that already exists § More than 50% of knowledge workers report they spend more than 1 hour a week to look for a specific piece of information § Some find themselves looking for data at least 10 times a week, spending more than 10 minutes in each request § Overall, we estimate that knowledge workers spend a day a week searching for data and reformatting data Sources : http: //www. kmworld. com/Articles/Editorial/Features/The-high-cost-of-not-finding-information-9534. aspx Information Gathering in the Electronic Age: The Hidden Cost of the Hunt, The Ridge Group © 2013 IBM Corporation
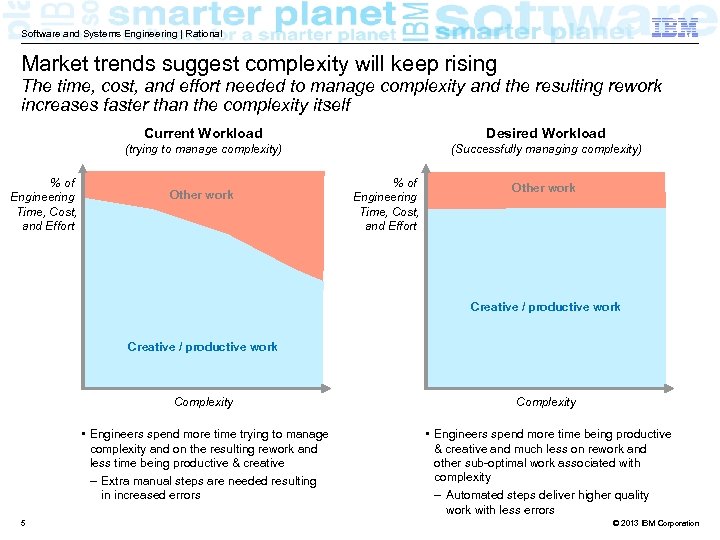
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Market trends suggest complexity will keep rising The time, cost, and effort needed to manage complexity and the resulting rework increases faster than the complexity itself Current Workload (trying to manage complexity) % of Engineering Time, Cost, and Effort Desired Workload (Successfully managing complexity) Other work % of Engineering Time, Cost, and Effort Other work Creative / productive work Complexity • Engineers spend more time trying to manage complexity and on the resulting rework and less time being productive & creative – Extra manual steps are needed resulting in increased errors 5 Complexity • Engineers spend more time being productive & creative and much less on rework and other sub-optimal work associated with complexity – Automated steps deliver higher quality work with less errors © 2013 IBM Corporation
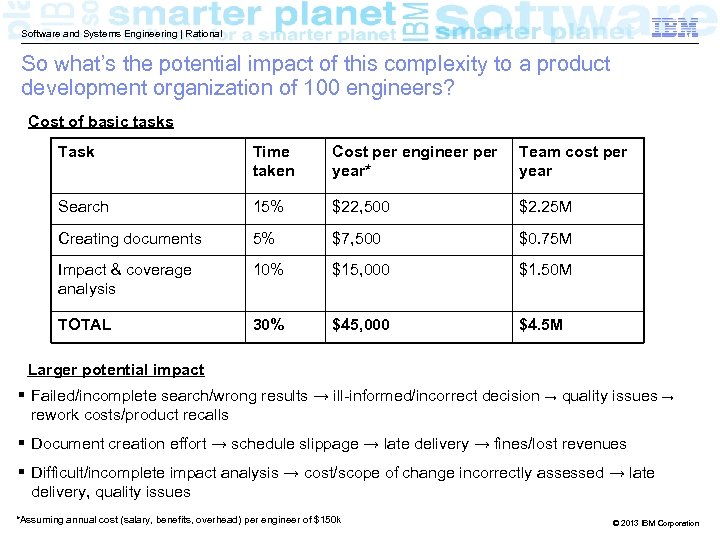
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational So what’s the potential impact of this complexity to a product development organization of 100 engineers? Cost of basic tasks Task Time taken Cost per engineer per year* Team cost per year Search 15% $22, 500 $2. 25 M Creating documents 5% $7, 500 $0. 75 M Impact & coverage analysis 10% $15, 000 $1. 50 M TOTAL 30% $45, 000 $4. 5 M Larger potential impact § Failed/incomplete search/wrong results → ill-informed/incorrect decision → quality issues → rework costs/product recalls § Document creation effort → schedule slippage → late delivery → fines/lost revenues § Difficult/incomplete impact analysis → cost/scope of change incorrectly assessed → late delivery, quality issues *Assuming annual cost (salary, benefits, overhead) per engineer of $150 k © 2013 IBM Corporation
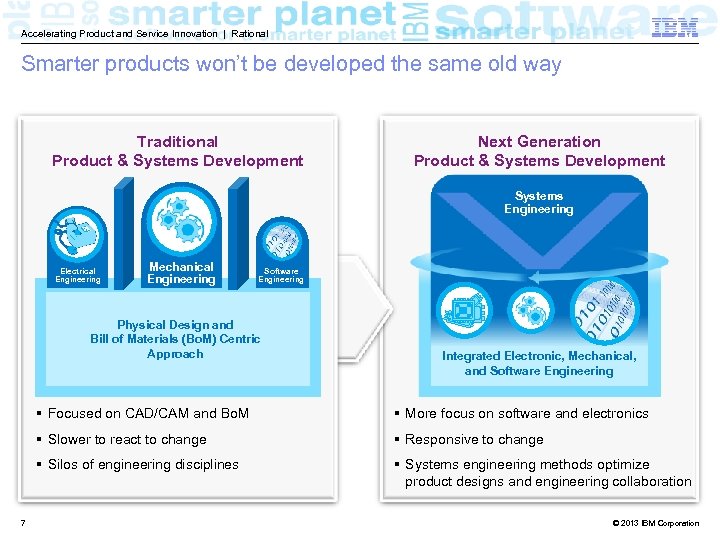
Accelerating Product and Service Innovation | Rational Smarter products won’t be developed the same old way Traditional Product & Systems Development Next Generation Product & Systems Development Systems Engineering Electrical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Software Engineering Physical Design and Bill of Materials (Bo. M) Centric Approach Integrated Electronic, Mechanical, and Software Engineering § Focused on CAD/CAM and Bo. M § Slower to react to change § Responsive to change § Silos of engineering disciplines 7 § More focus on software and electronics § Systems engineering methods optimize product designs and engineering collaboration © 2013 IBM Corporation
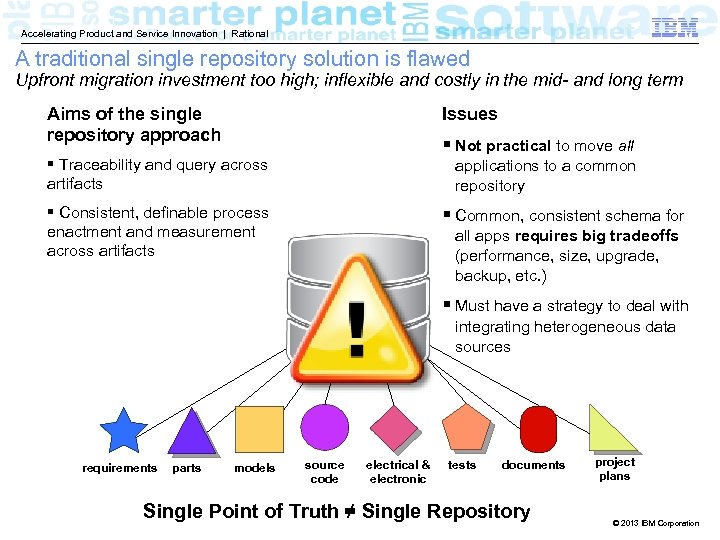
Accelerating Product and Service Innovation | Rational A traditional single repository solution is flawed Upfront migration investment too high; inflexible and costly in the mid- and long term Issues Aims of the single repository approach § Not practical to move all § Traceability and query across artifacts applications to a common repository § Consistent, definable process enactment and measurement across artifacts § Common, consistent schema for all apps requires big tradeoffs (performance, size, upgrade, backup, etc. ) § Must have a strategy to deal with integrating heterogeneous data sources requirements parts models source code electrical & electronic tests documents Single Point of Truth ≠ Single Repository project plans © 2013 IBM Corporation
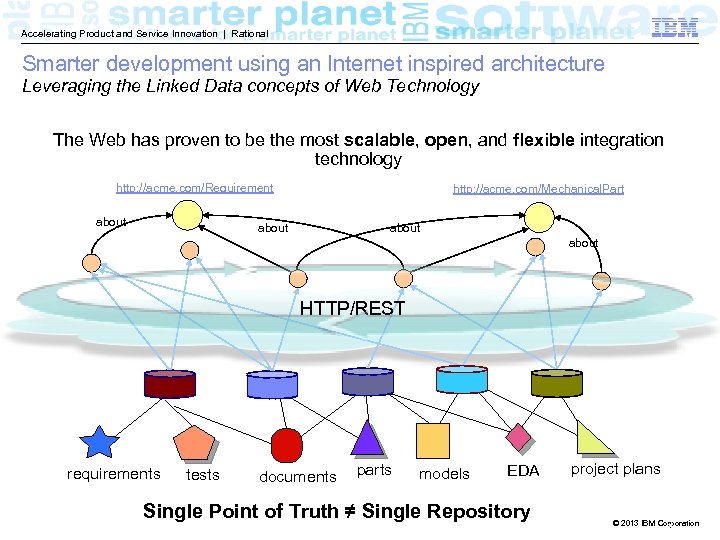
Accelerating Product and Service Innovation | Rational Smarter development using an Internet inspired architecture Leveraging the Linked Data concepts of Web Technology The Web has proven to be the most scalable, open, and flexible integration technology http: //acme. com/Requirement about http: //acme. com/Mechanical. Part about HTTP/REST requirements tests documents parts models EDA Single Point of Truth ≠ Single Repository project plans © 2013 IBM Corporation 9
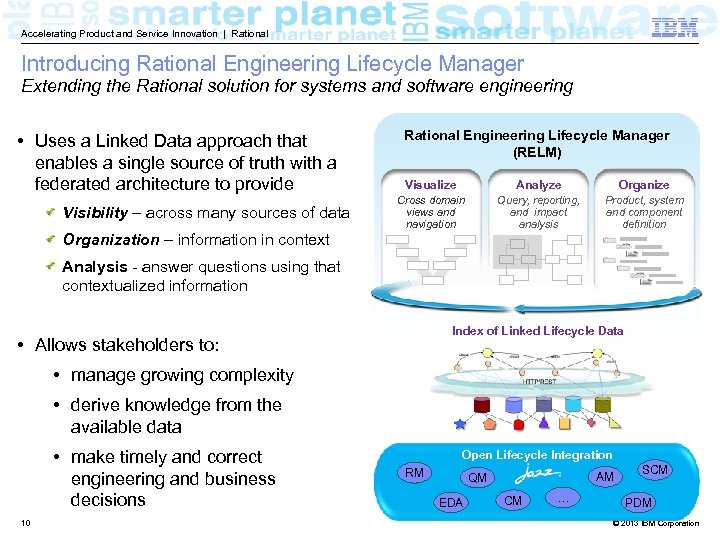
Accelerating Product and Service Innovation | Rational Introducing Rational Engineering Lifecycle Manager Extending the Rational solution for systems and software engineering • Uses a Linked Data approach that enables a single source of truth with a federated architecture to provide Visibility – across many sources of data Organization – information in context Rational Engineering Lifecycle Manager (RELM) Visualize Analyze Organize Cross domain views and navigation Query, reporting, and impact analysis Product, system and component definition Analysis - answer questions using that contextualized information Index of Linked Lifecycle Data • Allows stakeholders to: • manage growing complexity • derive knowledge from the available data • make timely and correct engineering and business decisions 10 Open Lifecycle Integration RM AM QM EDA CM … SCM PDM © 2013 IBM Corporation

Software and Systems Engineering | Rational EADS sees value for engineering teams in RELM Beta Provides visibility, impact analysis and document generation across the product lifecycle “The beta version of Rational Engineering Lifecycle Manager showed us that it has potential to be a very valuable tool and approach to solving challenges in the engineering of complex products. ” Simon Bradley, Vice President, Head of Global Innovation Network, Systems & Products Architecture, EADS 11 Image courtesy of Tim Beach / freedigitalphotos. net About EADS Innovation Works The Software and Systems Engineering team of EADS Innovation Works, the corporate research and development department of EADS, is responsible not only for developing future technologies and solutions bringing value to the different business units of EADS, but also evaluating state of the art or new technologies such as tools, which may improve how engineers at EADS develop and manage their products. © 2013 IBM Corporation
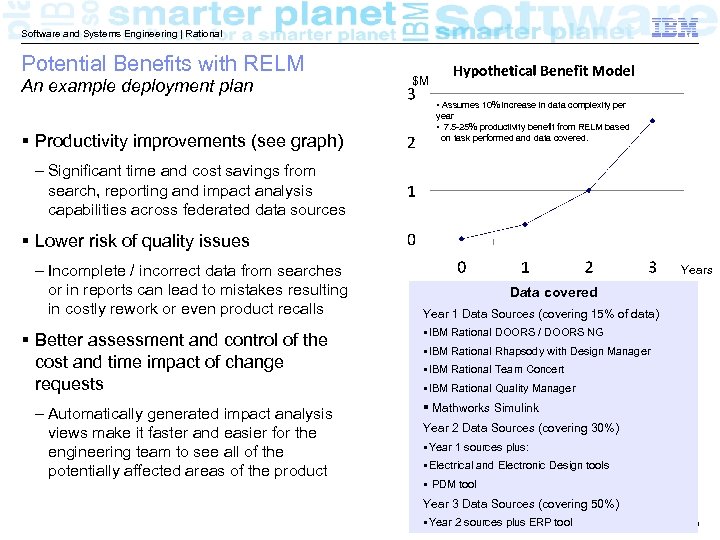
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Potential Benefits with RELM An example deployment plan $M • Assumes 10% increase in data complexity per § Productivity improvements (see graph) year • 7. 5 -25% productivity benefit from RELM based on task performed and data covered. – Significant time and cost savings from search, reporting and impact analysis capabilities across federated data sources § Lower risk of quality issues – Incomplete / incorrect data from searches or in reports can lead to mistakes resulting in costly rework or even product recalls § Better assessment and control of the cost and time impact of change requests – Automatically generated impact analysis views make it faster and easier for the engineering team to see all of the potentially affected areas of the product Years Data covered Year 1 Data Sources (covering 15% of data) §IBM Rational DOORS / DOORS NG §IBM Rational Rhapsody with Design Manager §IBM Rational Team Concert §IBM Rational Quality Manager § Mathworks Simulink Year 2 Data Sources (covering 30%) §Year 1 sources plus: §Electrical and Electronic Design tools § PDM tool Year 3 Data Sources (covering 50%) §Year 2 sources plus ERP tool © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Take the next step with RELM Conquer unprecedented complexity by making better use of your engineering data § Increase your innovative capacity – By making better use of your engineering data § Improve efficiency and productivity – By managing complexity of data and relationships § Increase agility to reduce costs – By understanding impact of change across engineering disciplines § Enhance collaboration and visibility – By understanding interaction and dependencies between development disciplines § Leverage your existing tools and infrastructure with – A federated, linked-data architecture based on open standards – Tight integration with Rational systems and software solutions – Extensibility to integrate data from other disciples (e. g. electrical, electronic, mechanical) 13 © 2013 IBM Corporation

Software and Systems Engineering | Rational www. ibm. com/software/rational © Copyright IBM Corporation 2011. All rights reserved. The information contained in these materials is provided for informational purposes only, and is provided AS IS without warranty of any kind, express or implied. IBM shall not be responsible for any damages arising out of the use of, or otherwise related to, these materials. Nothing contained in these materials is intended to, nor shall have the effect of, creating any warranties or representations from IBM or its suppliers or licensors, or altering the terms and conditions of the applicable license agreement governing the use of IBM software. References in these materials to IBM products, programs, or services do not imply that they will be available in all countries in which IBM operates. Product release dates and/or capabilities referenced in these materials may change at any time at IBM’s sole discretion based on market opportunities or other factors, and are not intended to be a commitment to future product or feature availability in any way. IBM, the IBM logo, Rational, the Rational logo, Telelogic, the Telelogic logo, and other IBM products and services are trademarks of the International Business Machines Corporation, in the United States, other countries or both. Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others. 14 © 2013 IBM Corporation

Software and Systems Engineering | Rational www. ibm. com/software/rational 15 © 2013 IBM Corporation

Software and Systems Engineering | Rational NOTE TO PRESENTER § After presenting the main flow above you may want to show a demo or do a deeper dive in charts. § The following section provides a deeper dive into RELM capabilities; move them into the main flow if appropriate for your audience. © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Visualize: Navigation and Exploration § Structured and traceable views of engineering data across the development lifecycle § Views are ‘live’ and dynamic § Interactively explore and interrogate development lifecycle data and relationships § Predefined views to support specific industries (e. g. ISO 26262) § Ability to create new views or customize predefined views § Save and share views Example User Story “So that I can more easily achieve, maintain and monitor compliance to ISO 26262, as a Safety Manager I need a view that shows me the different process tasks, their status and related tasks” © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Analyze: Search and Query Example User Story “So that I can perform ‘Where Used’ analysis, as a Systems Engineer I need to be able to construct a query that shows me which products, systems, subsystems, capabilities, components and their versions and variants are associated with a given requirement, logical design element, or E/E artifact. ” Example User Story § Perform plaintext searches across development lifecycle data § “So that I can understand overall implementation status for a specific product variant for a new market, as a Product Manager I need to be able to construct a query that shows me which requirements are associated with tests that failed on their last execution run within the context of my specific product variant. ” Construct powerful queries to answer specific questions about products or systems under development © 2013 IBM Corporation
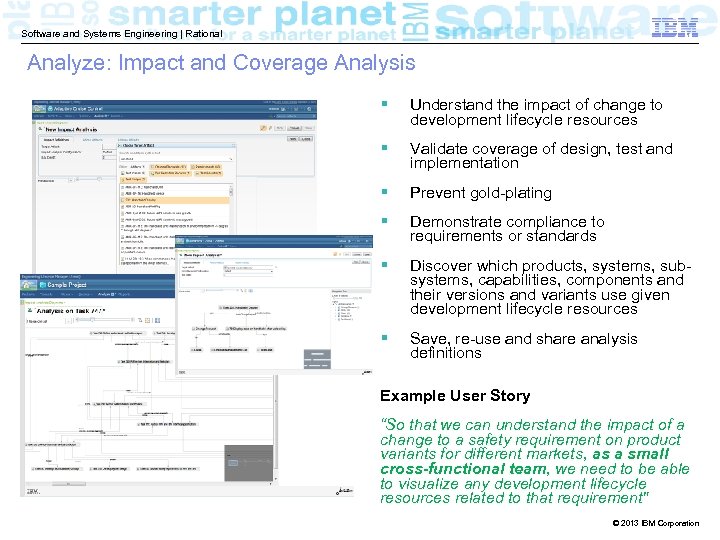
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Analyze: Impact and Coverage Analysis § Understand the impact of change to development lifecycle resources § Validate coverage of design, test and implementation § Prevent gold-plating § Demonstrate compliance to requirements or standards § Discover which products, systems, subsystems, capabilities, components and their versions and variants use given development lifecycle resources § Save, re-use and share analysis definitions Example User Story “So that we can understand the impact of a change to a safety requirement on product variants for different markets, as a small cross-functional team, we need to be able to visualize any development lifecycle resources related to that requirement" © 2013 IBM Corporation
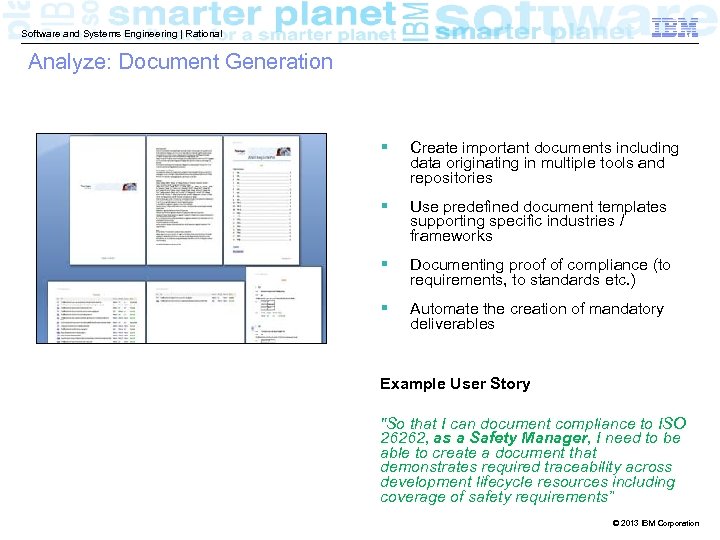
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Analyze: Document Generation § Create important documents including data originating in multiple tools and repositories § Use predefined document templates supporting specific industries / frameworks § Documenting proof of compliance (to requirements, to standards etc. ) § Automate the creation of mandatory deliverables Example User Story "So that I can document compliance to ISO 26262, as a Safety Manager, I need to be able to create a document that demonstrates required traceability across development lifecycle resources including coverage of safety requirements” © 2013 IBM Corporation
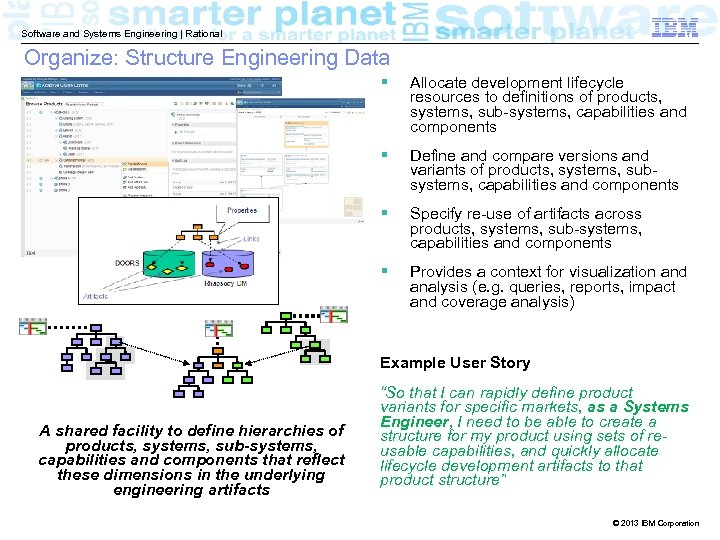
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Organize: Structure Engineering Data § Allocate development lifecycle resources to definitions of products, systems, sub-systems, capabilities and components § Define and compare versions and variants of products, systems, subsystems, capabilities and components § Specify re-use of artifacts across products, systems, sub-systems, capabilities and components § Provides a context for visualization and analysis (e. g. queries, reports, impact and coverage analysis) Example User Story A shared facility to define hierarchies of products, systems, sub-systems, capabilities and components that reflect these dimensions in the underlying engineering artifacts “So that I can rapidly define product variants for specific markets, as a Systems Engineer, I need to be able to create a structure for my product using sets of reusable capabilities, and quickly allocate lifecycle development artifacts to that product structure” © 2013 IBM Corporation

Software and Systems Engineering | Rational BACKUP 22 © 2013 IBM Corporation
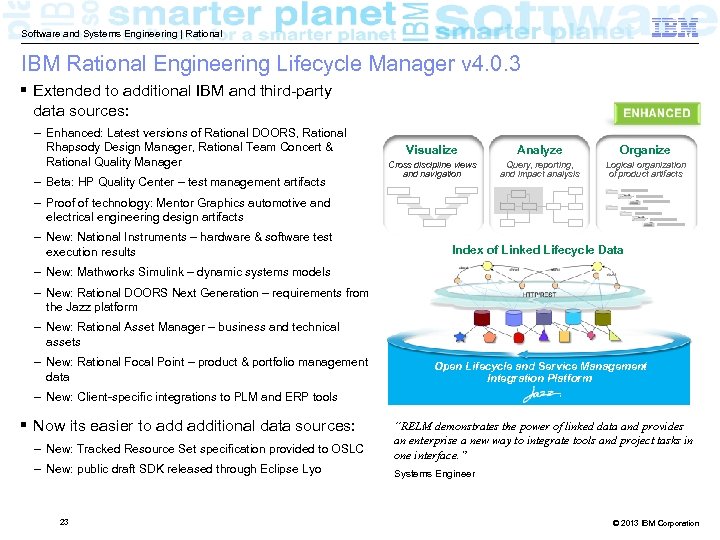
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational IBM Rational Engineering Lifecycle Manager v 4. 0. 3 § Extended to additional IBM and third-party data sources: – Enhanced: Latest versions of Rational DOORS, Rational Rhapsody Design Manager, Rational Team Concert & Rational Quality Manager – Beta: HP Quality Center – test management artifacts Visualize Analyze Organize Cross discipline views and navigation Query, reporting, and impact analysis Logical organization of product artifacts – Proof of technology: Mentor Graphics automotive and electrical engineering design artifacts – New: National Instruments – hardware & software test execution results Index of Linked Lifecycle Data – New: Mathworks Simulink – dynamic systems models – New: Rational DOORS Next Generation – requirements from the Jazz platform – New: Rational Asset Manager – business and technical assets – New: Rational Focal Point – product & portfolio management data Open Lifecycle and Service Management Integration Platform – New: Client-specific integrations to PLM and ERP tools § Now its easier to additional data sources: – New: Tracked Resource Set specification provided to OSLC – New: public draft SDK released through Eclipse Lyo 23 “RELM demonstrates the power of linked data and provides an enterprise a new way to integrate tools and project tasks in one interface. ” Systems Engineer © 2013 IBM Corporation

Software and Systems Engineering | Rational 321 Gang on RELM: the next step in managing complex systems development “IBM Rational Engineering Lifecycle Manager is the first tool of its kind. RELM fills a large gap to help manage complexity in fast-paced, multi-team, multi-disciplined complex systems development. ” About 321 Gang Works with clients in A&D, automotive, telecom, & medical devices sectors who are tackling the many challenges of these industries. —Harry Koehnemann, Director of Technology, 321 Gang 24 © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Manageware: RELM delivers development lifecycle oversight “RELM rounds out a systems & software engineering environment with visual, contextual views of data, relationships & status across the development lifecycle” —Shirley Jhirad, Manageware 25 About Manageware help their clients maximize the value of their investment in development teams and tools. Manageware’s “THINK” implementation framework and IBM solutions enable fast time-to-value. Combined with RELM, Manageware will enable clients to further improve development performance through cross-lifecycle visibility and team collaboration. © 2013 IBM Corporation
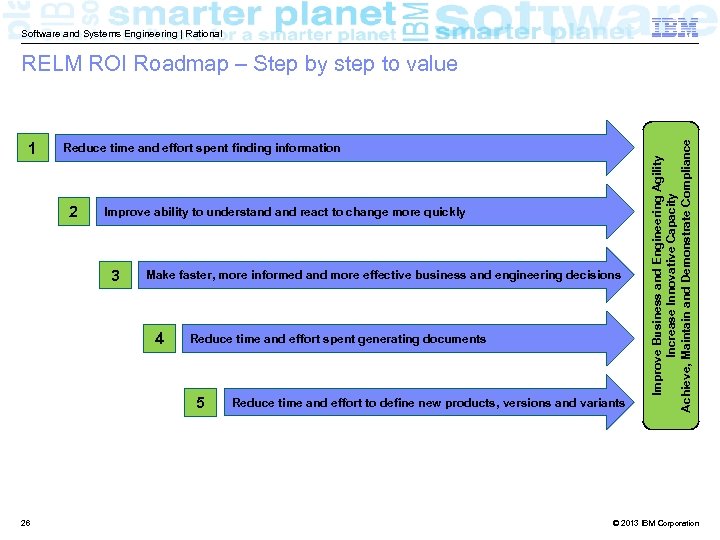
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational 1 Reduce time and effort spent finding information 2 Improve ability to understand react to change more quickly 3 Make faster, more informed and more effective business and engineering decisions 4 Reduce time and effort spent generating documents 5 26 Reduce time and effort to define new products, versions and variants Improve Business and Engineering Agility Increase Innovative Capacity Achieve, Maintain and Demonstrate Compliance RELM ROI Roadmap – Step by step to value © 2013 IBM Corporation
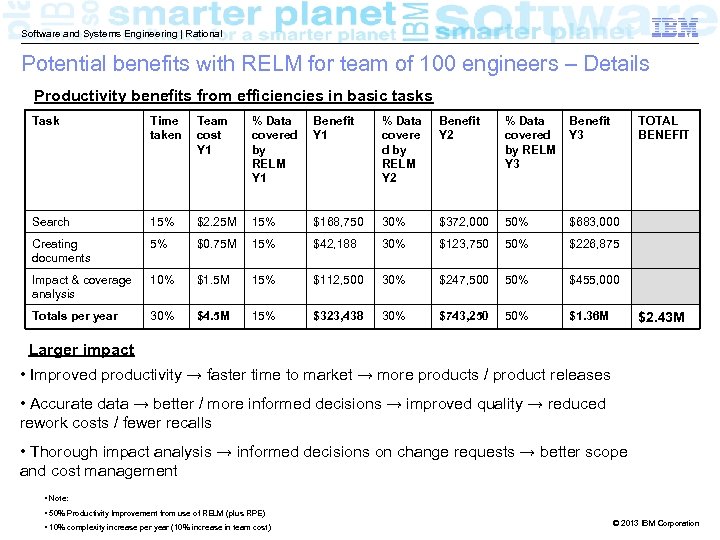
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Potential benefits with RELM for team of 100 engineers – Details Productivity benefits from efficiencies in basic tasks Task Time taken Team cost Y 1 % Data covered by RELM Y 1 Benefit Y 1 % Data covere d by RELM Y 2 Benefit Y 2 % Data covered by RELM Y 3 Benefit Y 3 TOTAL BENEFIT Search 15% $2. 25 M 15% $168, 750 30% $372, 000 50% $683, 000 Creating documents 5% $0. 75 M 15% $42, 188 30% $123, 750 50% $226, 875 Impact & coverage analysis 10% $1. 5 M 15% $112, 500 30% $247, 500 50% $455, 000 Totals per year 30% $4. 5 M 15% $323, 438 30% $743, 250 50% $1. 36 M $2. 43 M Larger impact • Improved productivity → faster time to market → more products / product releases • Accurate data → better / more informed decisions → improved quality → reduced rework costs / fewer recalls • Thorough impact analysis → informed decisions on change requests → better scope and cost management • Note: • 50% Productivity Improvement from use of RELM (plus RPE) • 10% complexity increase per year (10% increase in team cost) © 2013 IBM Corporation

Accelerating Product and Service Innovation | Rational The product development landscape is evolving From Focusing on Cost - to Focusing on Innovation Reengineering Tool-Assisted Design 1970 – 1980’s Product Engineering 1980’s - Present & Beyond § 2 D CAD § Ad-hoc data management § No organization / process change § 3 D CAD § PDM focus on mechanical BOM § Organization & process improvement § Increased focus on software engineering § Full traceability of requirements throughout product lifecycle § Holistic system design and interaction A smarter planet begins with smarter products © 2013 IBM Corporation 28
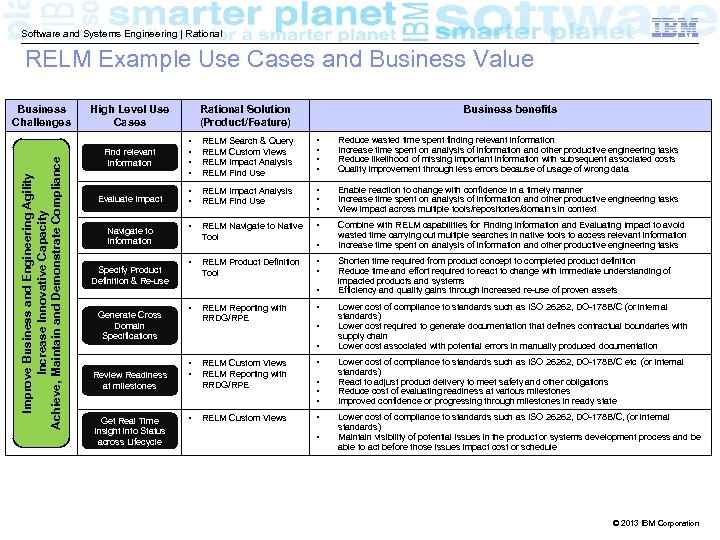
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational RELM Example Use Cases and Business Value Improve Business and Engineering Agility Increase Innovative Capacity Achieve, Maintain and Demonstrate Compliance Business Challenges 29 High Level Use Cases Rational Solution (Product/Feature) Business benefits Find relevant Information • • RELM Search & Query RELM Custom Views RELM Impact Analysis RELM Find Use • • Reduce wasted time spent finding relevant information Increase time spent on analysis of information and other productive engineering tasks Reduce likelihood of missing important information with subsequent associated costs Quality improvement through less errors because of usage of wrong data Evaluate Impact • • RELM Impact Analysis RELM Find Use • • • Enable reaction to change with confidence in a timely manner Increase time spent on analysis of information and other productive engineering tasks View impact across multiple tools/repositories/domains in context • RELM Navigate to Native Tool • Combine with RELM capabilities for Finding Information and Evaluating Impact to avoid wasted time carrying out multiple searches in native tools to access relevant information Increase time spent on analysis of information and other productive engineering tasks RELM Product Definition Tool • • Navigate to information Specify Product Definition & Re-use Generate Cross Domain Specifications Review Readiness at milestones Get Real Time Insight into Status across Lifecycle • • RELM Reporting with RRDG/RPE • • • RELM Custom Views RELM Reporting with RRDG/RPE • • RELM Custom Views • • • Shorten time required from product concept to completed product definition Reduce time and effort required to react to change with immediate understanding of impacted products and systems Efficiency and quality gains through increased re-use of proven assets Lower cost of compliance to standards such as ISO 26262, DO-178 B/C (or internal standards) Lower cost required to generate documentation that defines contractual boundaries with supply chain Lower cost associated with potential errors in manually produced documentation Lower cost of compliance to standards such as ISO 26262, DO-178 B/C etc (or internal standards) React to adjust product delivery to meet safety and other obligations Reduce cost of evaluating readiness at various milestones Improved confidence or progressing through milestones in ready state Lower cost of compliance to standards such as ISO 26262, DO-178 B/C, (or internal standards) Maintain visibility of potential issues in the product or systems development process and be able to act before those issues impact cost or schedule © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Use Case 1: Find Relevant Information § Description – Systems Engineer (or other user) accesses RELM and performs a plain-text search to discover information relevant to his/her current task. § Actors/Roles – Systems Engineer, Project Manager, Product Manager, Safety Manager, Requirements Engineer, Quality Manager, Test Engineer, Software Engineer Customer pain points with current solution • • 30 Need to log in to multiple tools/repositories to find relevant information Inconsistent or non-existent search mechanisms provided in each tool Easy to miss important information Difficult to see discovered information in context RELM will provide the ability to • Quickly search for relevant information from a single interface, regardless of where the information is stored and managed • View discovered information from multiple tools/repositories/domains in context Key Benefits • Reduce wasted time spent finding relevant information • Increase time spent on analysis of information and other productive engineering tasks • Reduce likelihood of missing important information with subsequent associated costs • Quality improvement through less errors because of usage of wrong data © 2013 IBM Corporation

Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Use Case 2: Evaluate Impact of Change § Description – Systems Engineer (or other user) is made aware of a potential change (example: parameters of a safety requirement for a specific market are revised) and accesses RELM and performs an impact analysis to determine which lifecycle resources might be impacted by that change § Actors/Roles – Systems Engineer, Project Manager, Product Manager, Safety Manager, Requirements Engineer, Quality Manager, Test Engineer, Software Engineer Customer pain points with current solution RELM will provide the ability to • • • 31 Need to log in to multiple tools/repositories to perform impact analysis across multiple levels/tools/domains Inconsistent impact analysis capabilities provided in each tool Static reports are the only mechanism that can be used to visualize traceability and impact across multiple levels and don’t provide the interactive capabilities necessary to organize and filter the results on demand Reports are slow to generate (against live data sources), or have a higher than acceptable latency (against a data warehouse) • Perform impact analysis across the entire lifecycle, regardless of where the information is stored and managed Interact with impact analysis results to filter and hide irrelevant information and organize displayed results to focus on information most important and relevant to the task at hand Key Benefits • • Enable reaction to change with confidence in a timely manner Increase time spent on analysis of information and other productive engineering tasks © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Use Case 3: Navigate to information from a single point of entry § Description – Systems Engineer (or other user) accesses RELM and finds some information relevant to his/her task (e. g. via ‘Find Information - UC 1’ or ‘Evaluate Impact – UC 2’) and then navigates directly to the information in the tool that stores and manages the information for editing § Actors/Roles – Systems Engineer, Project Manager, Product Manager, Safety Manager, Requirements Engineer, Quality Manager, Test Engineer, Software Engineer Customer pain points with current solution • Need manually open multiple tools/repositories and use potentially inconsistent mechanisms to locate and access information in each RELM will provide the ability to • Quickly and easily access relevant information in the tool in which the data is stored and managed Key Benefits • Combine with RELM capabilities for Finding Information and Evaluating Impact to avoid wasted time carrying out multiple searches in native tools to access relevant information • Increase time spent on analysis of information and other productive engineering tasks 32 © 2013 IBM Corporation
Market Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Use Case 4: Specify Product Definition and Re-use § Description – Systems Engineer (or other user) accesses RELM and specifies and characterizes a product by allocating lifecycle resources that define that product. The Systems Engineer may re-use existing product definitions by allocating them as components or sub-systems. § Actors/Roles – Systems Engineer Customer pain points with current solution • No central mechanism available to define products or systems No central mechanism available to specify re-use of lifecycle artifacts Forced to use ad-hoc solutions in existing tooling to represent product definition (e. g. DOORS formal module structure, Rhapsody Sys. ML models) which are not visible from other tools No means to easily discover which lifecycle artifacts define a product or system No means to easily discover which products or systems use a lifecycle artifact No central mechanism to tie product definition to product workflow activities • • • RELM will provide the ability to • • Key Benefits • • • 33 Combine with RELM capabilities for Finding Information to quickly define products, components, capabilities, systems, and subsystems Easily discover the set of lifecycle artifacts that define a product or system Easily discover which products and systems use a given lifecycle artifact Associate product definition to workflow and state Shorten time required from product concept to completed product definition Reduce time and effort required to react to change with immediate understanding of impacted products and systems Efficiency and quality gains through increased reuse of proven assets © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Use Case 5: Generate Cross Domain Specifications § Description – Systems Engineer (or other user) accesses RELM and generates required specifications/documentation containing data from multiple domains/tools § Actors/Roles – Systems Engineer, Project Manager, Product Manager, Safety Manager, Requirements Engineer, Quality Manager, Test Engineer, Software Engineer Customer pain points with current solution • • • Unable to generate complex cross-domain specifications in an acceptable time Difficult to create specifications/documentation required to demonstrate compliance to standards (internal or external) Difficult to create specifications/documentation required to cross contractual boundaries RELM will provide the ability to • • Key Benefits • • • 34 Generate cross-domain specifications/documents in an acceptable time Create custom documents when combined with RPE for template authoring. Lower cost of compliance to standards such as ISO 26262, DO-178 B/C etc (or internal standards) Lower cost associated with potential errors in manually produced documentation Lower cost required to generate documentation that defines contractual boundaries with supply chain © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Use Case 6: Review Readiness at Milestones § Description – Systems Engineer (or other user) accesses RELM and assesses whether the product or system will fulfill its functional and non-functional obligations. § Actors/Roles – Product Manager, Systems Engineer, Quality Manager Customer pain points with current solution • Difficult to maintain visibility throughout the product delivery lifecycle whether the product will fulfill its functional and nonfunctional obligations RELM will provide the ability to • Visualize summary product and component testing and validation status with detail drill down • Validate test results are mapped to product functional and non-functional obligations • For product validation gaps, provide initiation and tracking of work items Key Benefits • Lower cost of compliance to standards such as ISO 26262, DO-178 B/C etc (or internal standards) • React to adjust product delivery to meet safety and other obligations • Reduce cost of evaluating readiness at various milestones • Improved confidence or progressing through milestones in ready state 35 © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Use Case 7: Get Real Time Insight into Status across the Lifecycle § Description – Systems Engineer (or other user) accesses RELM and uses one or more custom views to discover near real-time status of various aspects of the product and systems development lifecycle § Actors/Roles – Systems Engineer, Project Manager, Product Manager, Safety Manager, Requirements Engineer, Quality Manager, Test Engineer, Software Engineer Customer pain points with current solution • No means available to access lifecycle wide views of real-time product and system development status (data warehouse solutions have associated latency) RELM will provide the ability to • Monitor and visualize status of multiple aspects of the product and systems development lifecycle • Get a big picture view of the entire product or system including sub-systems • Maintain awareness of changes throughout the product or systems development process and communicate these changes to appropriate stakeholders Key Benefits • Lower cost of compliance to standards such as ISO 26262, DO-178 B/C, IEC 880, Cenelec. • Maintain visibility of potential issues in the product or systems development process and be able to react before those issues impact cost or schedule 36 © 2013 IBM Corporation
Software and Systems Engineering | Rational Maximize the value of your software investments with IBM Rational Lab Services § Provides best practices from lessons learned to maximize ROI – Identifying key traceability and data relationships which should be visualized in RELM § Becomes your trusted advisors based on years of experience and industry knowledge – Improving business and delivery process efficiency through transparency provided by RELM § Offers a clearer understanding of how the toolset applies to your unique environment, processes and industry – Integrating your environment and implementing your use cases in RELM Tailored services to address your unique needs Fast. Tracks Used to accelerate installation and migrations. Quick. Starts Rapidly implement tools using pre-defined activities and deployment templates. Assessments Proven methodologies to gather customer requirements and environment context. Delivers guidance on best practices for the customer’s context. Deployment Packages Deployment options based on proven practices are tailored to support the customer’s context and usage model. Commercial Assets Packaged tools and services providing solutions to specific customer environments; tool integrations, extensions and other automation. Training Instructor Led education with options for Classroom & Online environments “Reduced 75% testing time/test cycle by automating creation and execution of tests from the design model or target platform. ” - A Defense Research and Development Organization 37 © 2013 IBM Corporation
fd85df168a636803b3127298bdca3376.ppt