f1c0be07da308ddb210a569dfb20b340.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Connect. Communicate. Collaborate Interdomain SLAs Enforcement Framework in Real Qo. S-Enabled Networks C. Marinos, A. Polyrakis, V. Pouli, M. Grammatikou, V. Maglaris {cmarinos, apolyr, vpouli, mary, maglaris}@netmode. ntua. gr NTUA/GRNET TNC 08, Bruges, 21 May 2008 NTUA/GRNET

Outline • • • Connect. Communicate. Collaborate Introduction Multi-domain SLAs SLA Enforcement Framework Current work Future work NTUA/GRNET
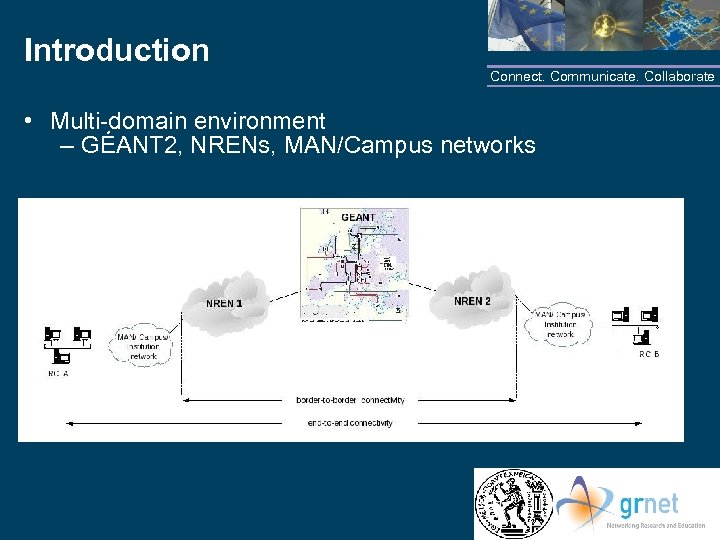
Introduction Connect. Communicate. Collaborate • Multi-domain environment – GÉANT 2, NRENs, MAN/Campus networks NTUA/GRNET
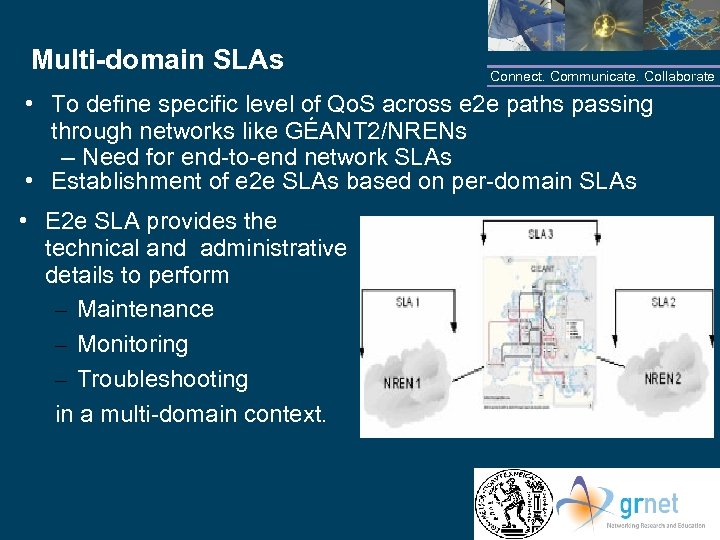
Multi-domain SLAs Connect. Communicate. Collaborate • To define specific level of Qo. S across e 2 e paths passing through networks like GÉANT 2/NRENs – Need for end-to-end network SLAs • Establishment of e 2 e SLAs based on per-domain SLAs • E 2 e SLA provides the technical and administrative details to perform – Maintenance – Monitoring – Troubleshooting in a multi-domain context. NTUA/GRNET

SLA: template SLA template can be divided in two objects: 1. Legal Part - Administrative Level Object (ALO) 2. Service Level Object (SLO) - ALO: set of administrative-legal parameters – – – Contacts Duration Availability Response times Fault handling procedures - SLO: set of technical parameters – – – Service instance scope Flow description Performance guarantees Monitoring infrastructure Reliability guarantees: max downtime (MDT), time to repair (TTR) NTUA/GRNET Connect. Communicate. Collaborate

Merging rules for e 2 e SLA Connect. Communicate. Collaborate E 2 e SLA derived from the merging of the per-domain SLAs. Most of the metrics are the union of per-domain metric values. While for the e 2 e performance metrics apply the following rules: - C(e 2 e) <= min{Ci} - MTU(e 2 e) <= min{MTUi} - OWD(e 2 e) => Σ{OWDi} - IPDV(e 2 e) = we treat IPDV as an RMS value and use its square as an additive parameter - Packet loss: will be the sum of all the packet losses across the individual domains: PLe 2 e ≥ ∑{PLi} NTUA/GRNET

SLA Framework Connect. Communicate. Collaborate • Introduce SLA Framework for automated SLA management, creation, publication in an inter-domain environment • Adopted by AMPS (Advanced Multi-domain Provisioning System) of GÉANT 2 NTUA/GRNET
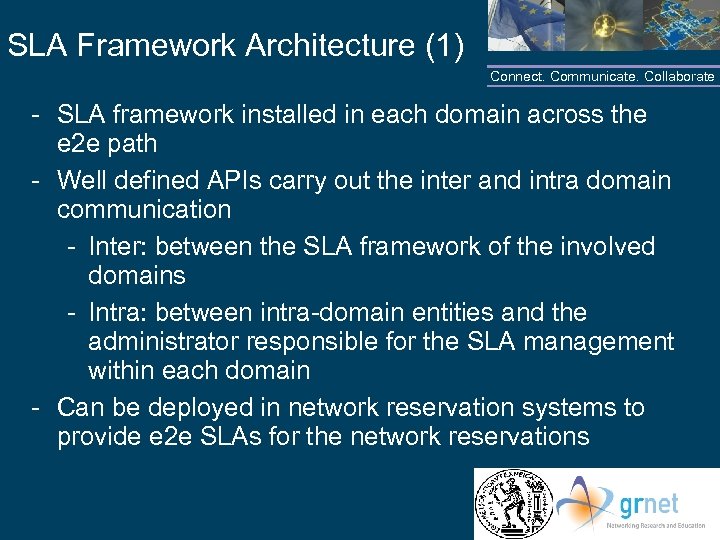
SLA Framework Architecture (1) Connect. Communicate. Collaborate - SLA framework installed in each domain across the e 2 e path - Well defined APIs carry out the inter and intra domain communication - Inter: between the SLA framework of the involved domains - Intra: between intra-domain entities and the administrator responsible for the SLA management within each domain - Can be deployed in network reservation systems to provide e 2 e SLAs for the network reservations NTUA/GRNET
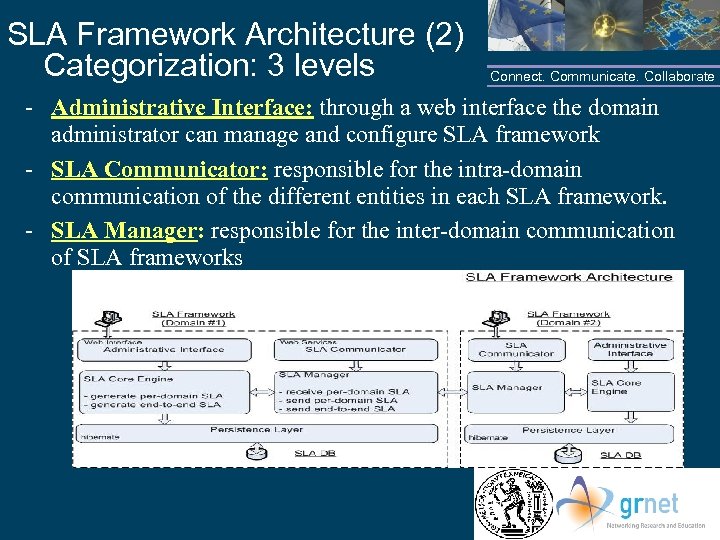
SLA Framework Architecture (2) Categorization: 3 levels Connect. Communicate. Collaborate - Administrative Interface: through a web interface the domain administrator can manage and configure SLA framework - SLA Communicator: responsible for the intra-domain communication of the different entities in each SLA framework. - SLA Manager: responsible for the inter-domain communication of SLA frameworks NTUA/GRNET

SLA Service Lifecycle – 3 phases 1. Creation phase 2. Publication phase 3. Delivery phase NTUA/GRNET Connect. Communicate. Collaborate
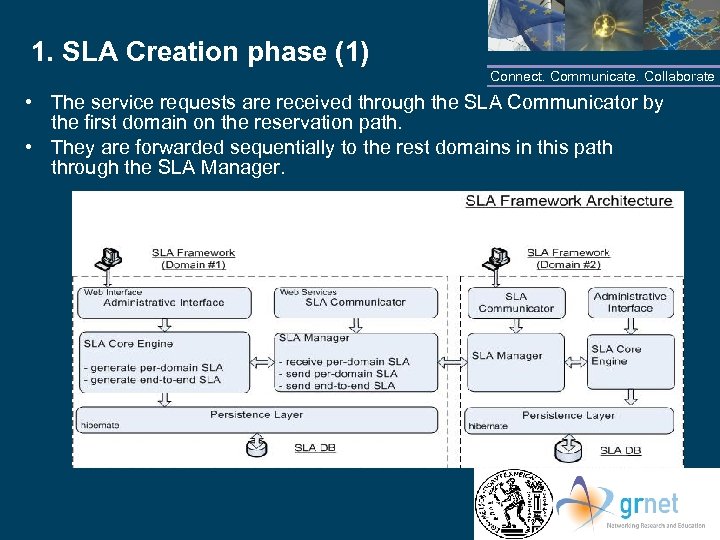
1. SLA Creation phase (1) Connect. Communicate. Collaborate • The service requests are received through the SLA Communicator by the first domain on the reservation path. • They are forwarded sequentially to the rest domains in this path through the SLA Manager. NTUA/GRNET
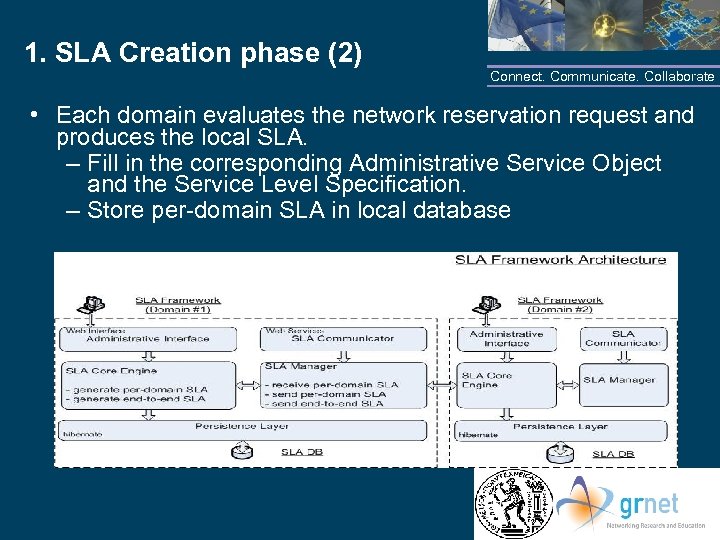
1. SLA Creation phase (2) Connect. Communicate. Collaborate • Each domain evaluates the network reservation request and produces the local SLA. – Fill in the corresponding Administrative Service Object and the Service Level Specification. – Store per-domain SLA in local database NTUA/GRNET
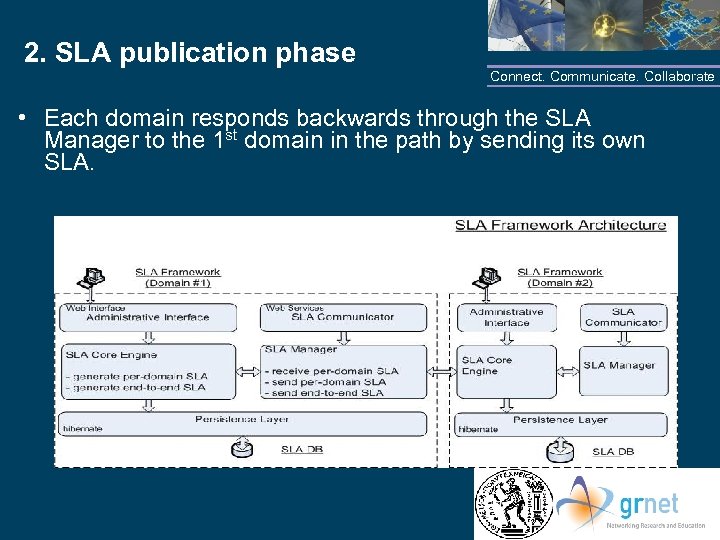
2. SLA publication phase Connect. Communicate. Collaborate • Each domain responds backwards through the SLA Manager to the 1 st domain in the path by sending its own SLA. NTUA/GRNET

3. Delivery phase Connect. Communicate. Collaborate • The first domain on the chain collects the SLAs of all the SLA Frameworks on the chain in order to produce the end-to-end SLA. • The e 2 e SLA is stored in a database among with the per-domain SLAs and other internal data. • The data can be viewed and edited via the administrative functions of the Administrative Interface. • If a domain in the path does not deliver its respective SLA, the first SLA Framework informs the client that an SLA cannot be delivered for the requested IP service, so that the client can make a new request with different level of Qo. S. NTUA/GRNET
Current status Connect. Communicate. Collaborate • Integration and deployment of SLA framework into AMPS(Advanced Multi-domain Provisioning System in GÉANT 2) – Communication of SLA module with other AMPS modules – Triggered by end-user upon service request – Provides e 2 e SLA calculation for user network reservation NTUA/GRNET

SLA Generation Process in AMPS Connect. Communicate. Collaborate 1. Administrative Interface receives notification for SLA creation for a specific AMPS reservation 2. SLA Communicator forwards the request to the singledomain module and SLA Manager to the multi-domain modules 3. Each domain generates local SLA and sends it to the SLA Manager of the previous AMPS 4. First SLA Manager collects the per-domain SLAs, generates e 2 e SLA, stores it to local DB and delivers it to the client NTUA/GRNET

Future work Connect. Communicate. Collaborate • Deploy SLA framework into AMPS in various NRENs • Deploy monitoring tools to: –Take measurements and evaluate the SLA Framework –Monitor the SLA guarantees NTUA/GRNET

Connect. Communicate. Collaborate Thank you! For more info contact: cmarinos@netmode. ntua. gr ? NTUA/GRNET
f1c0be07da308ddb210a569dfb20b340.ppt