b17b7b56aaf755efc5c985618c882605.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

 Congress Gets Organized! n The First Day in the House n All members are sworn in n House elects the Speaker n. Member of the majority party – selected in private meetings before session
Congress Gets Organized! n The First Day in the House n All members are sworn in n House elects the Speaker n. Member of the majority party – selected in private meetings before session

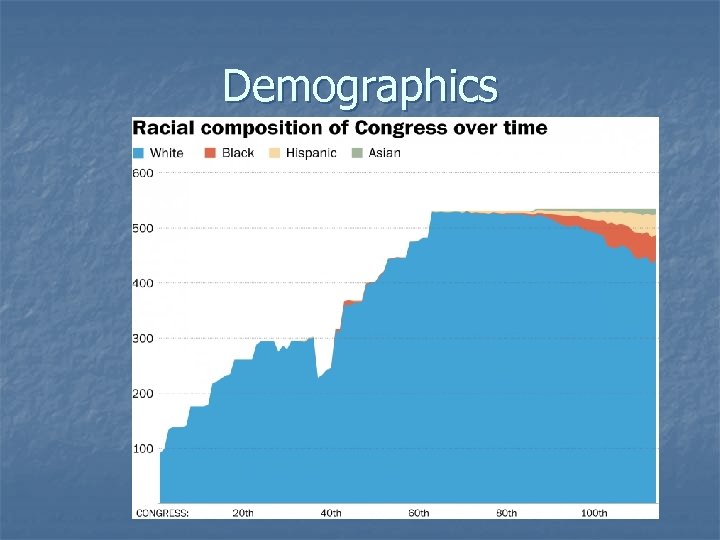 Demographics
Demographics
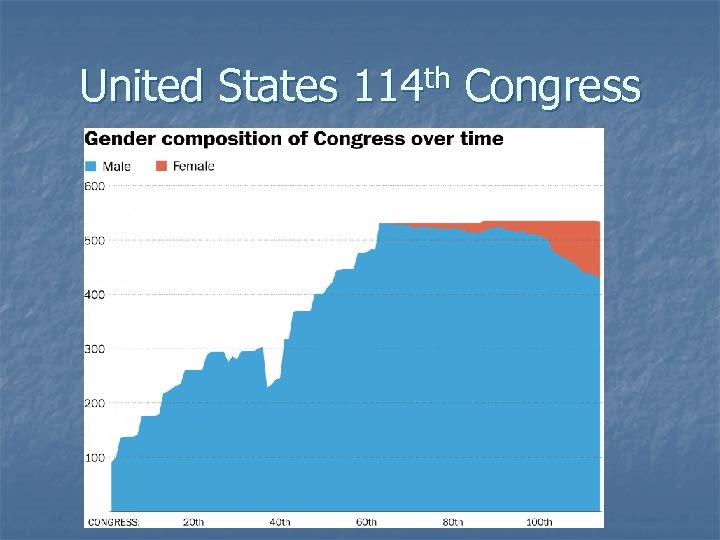 United States 114 th Congress
United States 114 th Congress
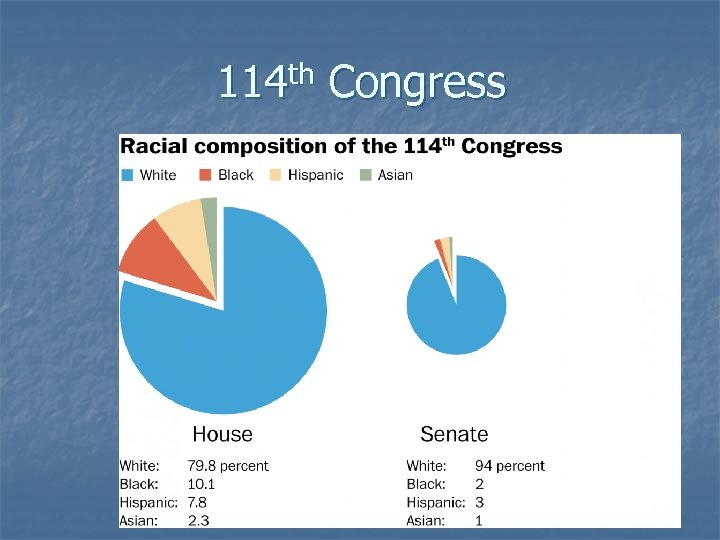 th 114 Congress
th 114 Congress
 Congress Gets Organized! n The First Day in the House n Members are put into committees n. Majority party gets a majority in every committee n. Seniority Rules
Congress Gets Organized! n The First Day in the House n Members are put into committees n. Majority party gets a majority in every committee n. Seniority Rules
 Congress Gets Organized! n First Day in the Senate n 1/3 of the members are sworn n Vacant committee seats are filled
Congress Gets Organized! n First Day in the Senate n 1/3 of the members are sworn n Vacant committee seats are filled
 House Leadership n Speaker of the House n Paul Ryan (RWisconsin) n Presides over House session
House Leadership n Speaker of the House n Paul Ryan (RWisconsin) n Presides over House session
 House Leadership n Speaker of the House -Presides over sessions n Refers bills to relevant committee n Assigns members to a committee n Usually does not vote but must to break a tie
House Leadership n Speaker of the House -Presides over sessions n Refers bills to relevant committee n Assigns members to a committee n Usually does not vote but must to break a tie
 House Leadership n House Leader Majority n Kevin Mc. Carthy (R- CA) n Tries to carry out the decisions of their parties’ caucuses (party meeting) and steer floor action to their parties benefit
House Leadership n House Leader Majority n Kevin Mc. Carthy (R- CA) n Tries to carry out the decisions of their parties’ caucuses (party meeting) and steer floor action to their parties benefit
 House Leadership n House Majority Whip n Steve Scalise (R-LA) n Helps plan party strategy and round up votes
House Leadership n House Majority Whip n Steve Scalise (R-LA) n Helps plan party strategy and round up votes
 House Leadership n Link between leadership and “rank and file” n Check who plans to vote and how n Persuade “defectors” to vote with the party
House Leadership n Link between leadership and “rank and file” n Check who plans to vote and how n Persuade “defectors” to vote with the party
 House Leadership n House Minority Leader n Nancy Pelosi (D-CA) n Plans minority party strategy to take power back n Expected to become Speaker if they win
House Leadership n House Minority Leader n Nancy Pelosi (D-CA) n Plans minority party strategy to take power back n Expected to become Speaker if they win
 House Leadership n House Minority Whip n Steny Hoyer (D -MD) n Strategy & advice n helps round up votes for their party
House Leadership n House Minority Whip n Steny Hoyer (D -MD) n Strategy & advice n helps round up votes for their party
 Senate Leadership n President of the Senate n = Vice President of the U. S. n Joe Biden- (D) Delaware
Senate Leadership n President of the Senate n = Vice President of the U. S. n Joe Biden- (D) Delaware
 Senate Leadership n Presides over the Senate n Powerless and thankless job n Can only vote to break a tie
Senate Leadership n Presides over the Senate n Powerless and thankless job n Can only vote to break a tie
 Senate Leadership n President Pro. Tempore of the Senate n Orrin Hatch (RUT) n Presides in place of the VP
Senate Leadership n President Pro. Tempore of the Senate n Orrin Hatch (RUT) n Presides in place of the VP
 Senate Leadership n President Pro. Tempore of the Senate n Longest serving member of the majority party n Also doesn’t want to do it, passes the job off on junior members
Senate Leadership n President Pro. Tempore of the Senate n Longest serving member of the majority party n Also doesn’t want to do it, passes the job off on junior members
 Senate Leadership n Senate Majority Leader n Mitch Mc. Connell (R-KY)
Senate Leadership n Senate Majority Leader n Mitch Mc. Connell (R-KY)
 Senate Leadership n Senate Majority Leader n Mitch Mc. Connell (RKY) n Plans party strategy
Senate Leadership n Senate Majority Leader n Mitch Mc. Connell (RKY) n Plans party strategy
 Senate Leadership n Places bills on the calendar for voting n May speak first on any bill
Senate Leadership n Places bills on the calendar for voting n May speak first on any bill
 Senate Leadership n Senate Minority Leader n Harry Reid n (D-NV) n Announced his retirement…
Senate Leadership n Senate Minority Leader n Harry Reid n (D-NV) n Announced his retirement…

 Senate Leadership n Senate Minority Whip n Richard “Dick” Durbin (D-IL) n Organizes votes, advise Min. Leader
Senate Leadership n Senate Minority Whip n Richard “Dick” Durbin (D-IL) n Organizes votes, advise Min. Leader
 Senate Leadership n Senate Majority Whip n John Cornyn n (R-TX) n Strategy, advice organize votes, order of business
Senate Leadership n Senate Majority Whip n John Cornyn n (R-TX) n Strategy, advice organize votes, order of business
 Committees n Committee – “expert” groups who decide what bills will go to the whole House or Senate for vote n Most work in Congress is done in committees
Committees n Committee – “expert” groups who decide what bills will go to the whole House or Senate for vote n Most work in Congress is done in committees
 Types of Committees n Standing Committee – permanent committees that remain from session to session n Examples: n Foreign Relations, Armed Services, Agriculture, Judiciary
Types of Committees n Standing Committee – permanent committees that remain from session to session n Examples: n Foreign Relations, Armed Services, Agriculture, Judiciary
 Types of Committees n Select or Special Committees – Temporary committee to investigate wrongdoing or research a special matter n Examples: n n Senate Watergate Committee Select Committee on Aging
Types of Committees n Select or Special Committees – Temporary committee to investigate wrongdoing or research a special matter n Examples: n n Senate Watergate Committee Select Committee on Aging
 Types of Committees n Joint Committees – have members of both the House and Senate n Conference Committees –is a type of joint committee that meets to find a compromise to different versions of bills between House and Senate
Types of Committees n Joint Committees – have members of both the House and Senate n Conference Committees –is a type of joint committee that meets to find a compromise to different versions of bills between House and Senate
 Bills and Resolutions What is the deal with bills and resolutions? Bill – A proposed law presented to the House or Senate for consideration
Bills and Resolutions What is the deal with bills and resolutions? Bill – A proposed law presented to the House or Senate for consideration
 Bills and Resolutions What is the deal with bills and resolutions? Resolution – possibly legally binding, but not always
Bills and Resolutions What is the deal with bills and resolutions? Resolution – possibly legally binding, but not always
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n For a brief overview, let’s watch a short documentary on the process
How a Bill Becomes a Law n For a brief overview, let’s watch a short documentary on the process
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 1 – The House n Bill is introduced and given a # H. R. #) n. Can only be introduced by a member of the House n. Bill is read to the entire chamber
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 1 – The House n Bill is introduced and given a # H. R. #) n. Can only be introduced by a member of the House n. Bill is read to the entire chamber
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 2 – The House n Referred to a standing committee n. Full committee decides whether to consider it, or “pigeonhole” it…. or die in committee (put away never to be acted on) n. Discharge Petition- a way to save a pigeonholed bill, needs a majority vote of all house members to send to it to the floor for consideration, happens rarely.
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 2 – The House n Referred to a standing committee n. Full committee decides whether to consider it, or “pigeonhole” it…. or die in committee (put away never to be acted on) n. Discharge Petition- a way to save a pigeonholed bill, needs a majority vote of all house members to send to it to the floor for consideration, happens rarely.
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 3 – The House n Referred to subcommittee n. Chairman of the committee decides which subcommittee n. Subcommittee does the vast majority of research and work on the bill n 90% of bills die in steps 2 and 3
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 3 – The House n Referred to subcommittee n. Chairman of the committee decides which subcommittee n. Subcommittee does the vast majority of research and work on the bill n 90% of bills die in steps 2 and 3
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 4 – The House n Committee/Subcommittee Hearings n. Government officials, experts invited to speak in favor or against bills n. Congressmen may take “junkets, ” or trips to locations for further research n. Meanwhile, they “markup, ” or make changes to the bill
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 4 – The House n Committee/Subcommittee Hearings n. Government officials, experts invited to speak in favor or against bills n. Congressmen may take “junkets, ” or trips to locations for further research n. Meanwhile, they “markup, ” or make changes to the bill

 How a Bill Becomes a Law Step 5 – The House n Sent back to full committee Oh, no!!Committee can either n n. Send the bill to step 6 with a “do pass” recommendation n. Or refuse to report the bill, thus killing it n
How a Bill Becomes a Law Step 5 – The House n Sent back to full committee Oh, no!!Committee can either n n. Send the bill to step 6 with a “do pass” recommendation n. Or refuse to report the bill, thus killing it n
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n If the rest of Congress disagrees with a committee’s decision to kill a bill, there is one option* n *Discharge Petition – majority of the House votes to pull a dead bill out of committee
How a Bill Becomes a Law n If the rest of Congress disagrees with a committee’s decision to kill a bill, there is one option* n *Discharge Petition – majority of the House votes to pull a dead bill out of committee
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 6 – The House n Referred to Rules Committee Oh, no!! n. Places bill on the calendar n. Sets the rules for time limits and number of amendments allowed n. If they refuse to put rules on it…
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 6 – The House n Referred to Rules Committee Oh, no!! n. Places bill on the calendar n. Sets the rules for time limits and number of amendments allowed n. If they refuse to put rules on it…
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 7 – The House n Bill is read a second time n Whole House debates n There is a time limit in the House for how long a Representative may speak
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 7 – The House n Bill is read a second time n Whole House debates n There is a time limit in the House for how long a Representative may speak
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 8 – The House n Whole House Votes n. Majority vote passes, sends bill to the Senate
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 8 – The House n Whole House Votes n. Majority vote passes, sends bill to the Senate
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 9 – The Senate n Introduced in the Senate n Step 10 – The Senate n Referred to a standing committee n. Senate Majority Leader chooses which committee
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 9 – The Senate n Introduced in the Senate n Step 10 – The Senate n Referred to a standing committee n. Senate Majority Leader chooses which committee
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 11 -12 – The Senate n Same as House – referred to subcommittee, back to committee, then out to floor for debate
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 11 -12 – The Senate n Same as House – referred to subcommittee, back to committee, then out to floor for debate
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 13 – The Senate n Whole Senate Debates n. No Rules Committee, so no limits on time or amendments n. Filibuster – talking at length to stall action on a bill, can only be ended by cloture (60 votes) n. Riders – amendments that have nothing to do with a bill
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 13 – The Senate n Whole Senate Debates n. No Rules Committee, so no limits on time or amendments n. Filibuster – talking at length to stall action on a bill, can only be ended by cloture (60 votes) n. Riders – amendments that have nothing to do with a bill
 This leads to…
This leads to…
 Taxpayers Paid For… $167, 000 for Horn Fly Research (AL) n $1 million for Mormon Cricket suppression (UT) n $2 million for the “First Tee” program, teaching inner-city kids to play golf n $270, 000 for potato storage (WI) n $270, 000 to combat “Goth Culture” (MO) n
Taxpayers Paid For… $167, 000 for Horn Fly Research (AL) n $1 million for Mormon Cricket suppression (UT) n $2 million for the “First Tee” program, teaching inner-city kids to play golf n $270, 000 for potato storage (WI) n $270, 000 to combat “Goth Culture” (MO) n
 Pork Barrel Spending n How congressmen “bring home the bacon” n Shows constituents that their congressman gets “things” for their district or state n Helps congressman win reelection!
Pork Barrel Spending n How congressmen “bring home the bacon” n Shows constituents that their congressman gets “things” for their district or state n Helps congressman win reelection!
 How a Bill Becomes a Law Step 14 – The Senate n Senate votes n Step 15 – Conference Committee n Members of both houses’ subcommittees that worked on the bill compromise n Both houses then vote again on the compromise bill n
How a Bill Becomes a Law Step 14 – The Senate n Senate votes n Step 15 – Conference Committee n Members of both houses’ subcommittees that worked on the bill compromise n Both houses then vote again on the compromise bill n
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 16 – The President n President has 4 options: n. Sign the bill, make it law n. Veto the bill, explain why n. Goes back to Congress, who can override with 2/3 vote in both houses
How a Bill Becomes a Law n Step 16 – The President n President has 4 options: n. Sign the bill, make it law n. Veto the bill, explain why n. Goes back to Congress, who can override with 2/3 vote in both houses
 How a Bill Becomes a Law n. Wait 10 days and let it become law without his signature n. Pocket Veto - If Congress ends its session before 10 days are up, bill dies without a veto
How a Bill Becomes a Law n. Wait 10 days and let it become law without his signature n. Pocket Veto - If Congress ends its session before 10 days are up, bill dies without a veto


