b0e453d2cb1a4a3a4961195fef9a6760.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Congress Chapter 7
Congress Chapter 7
 Congress n We will cover: n Intentions of Framers/Changes n The Constitution and the Legislative Branch n Functions n How Congress is Organized-differences between two houses/powers n Committees n Members n Apportionment
Congress n We will cover: n Intentions of Framers/Changes n The Constitution and the Legislative Branch n Functions n How Congress is Organized-differences between two houses/powers n Committees n Members n Apportionment
 Constitution and the Legislative Branch n Article I creates a bicameral legislative branch of government n The upper house is the Senate and states receive two representatives n The lower house is the House of Representatives which is apportioned by population n The Senate has a six-year term with 1/3 of the seats up for reelections every two years n House members serve two-year terms
Constitution and the Legislative Branch n Article I creates a bicameral legislative branch of government n The upper house is the Senate and states receive two representatives n The lower house is the House of Representatives which is apportioned by population n The Senate has a six-year term with 1/3 of the seats up for reelections every two years n House members serve two-year terms
 Continuity and Change n Framers of US Constitution placed Congress at the center of the government n In early years, Congress held the bulk of power n Face of Congress is changing as women and minorities have achieved seats n Presidency has become quite powerful, particularly since FDR n Congress now generally responds to executive branch legislative proposals. Confidence in Congress
Continuity and Change n Framers of US Constitution placed Congress at the center of the government n In early years, Congress held the bulk of power n Face of Congress is changing as women and minorities have achieved seats n Presidency has become quite powerful, particularly since FDR n Congress now generally responds to executive branch legislative proposals. Confidence in Congress
 Table 7. 3: What is a typical day like for a member of Congress?
Table 7. 3: What is a typical day like for a member of Congress?
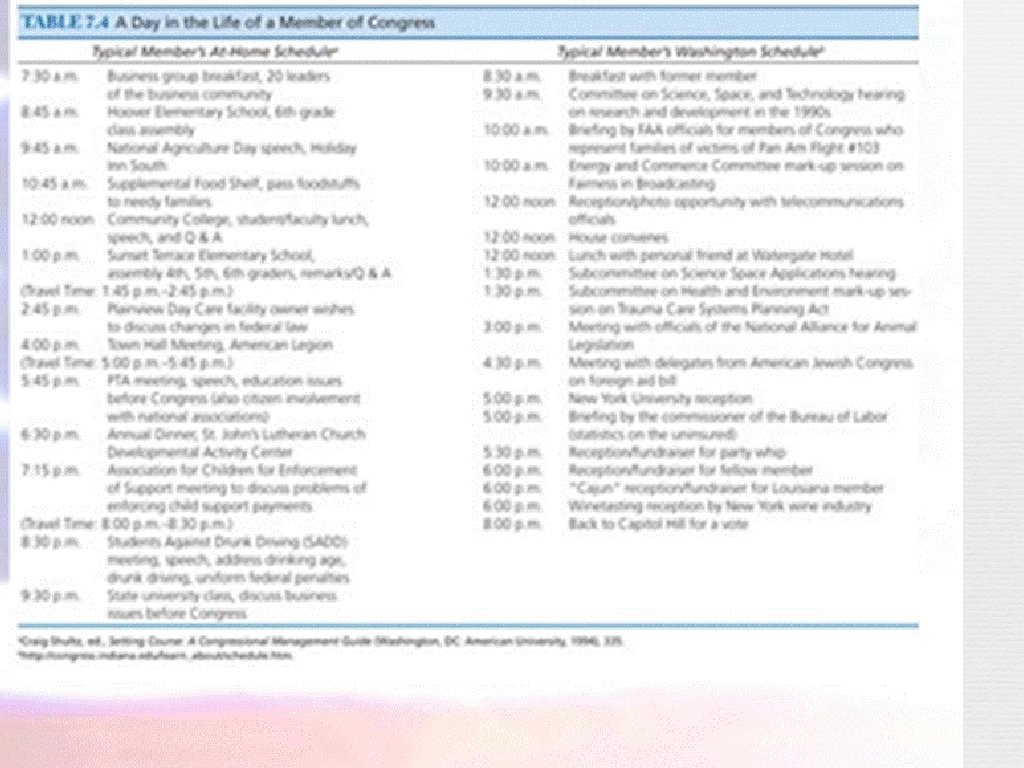
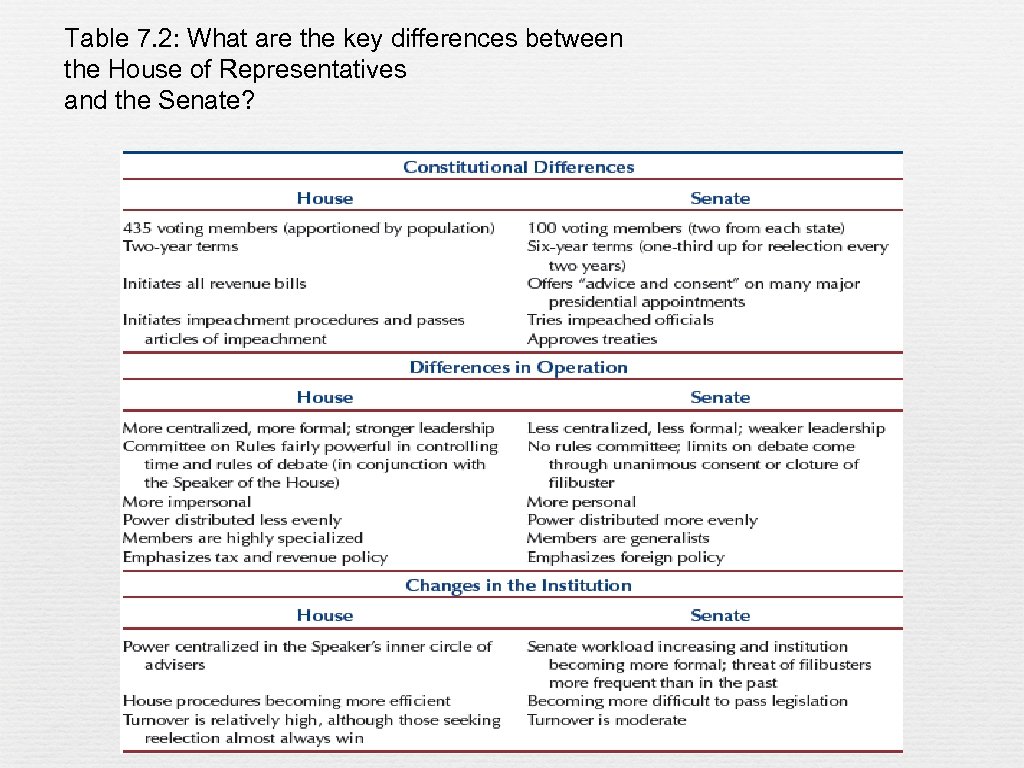 Table 7. 2: What are the key differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate?
Table 7. 2: What are the key differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate?
 Table 7. 1: What are the powers of Congress?
Table 7. 1: What are the powers of Congress?
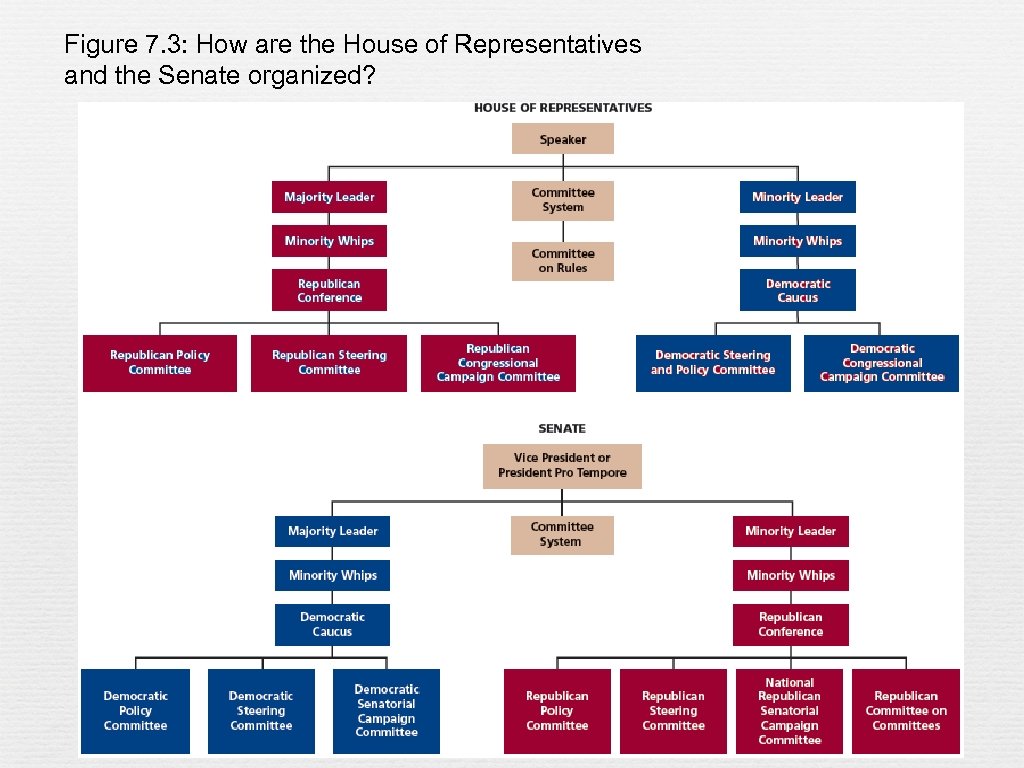 Figure 7. 3: How are the House of Representatives and the Senate organized?
Figure 7. 3: How are the House of Representatives and the Senate organized?
 Functions n Lawmaking-Budget n Representation (trustee delegate-politico) n Oversight n Constituent Service n Other
Functions n Lawmaking-Budget n Representation (trustee delegate-politico) n Oversight n Constituent Service n Other
 The Representational Role Of Members Of Congress n How should an elected official represent his/her constituents? n Trustee - representatives use their own best judgment n Delegate - representatives vote the way their constituents want them to n Politico - representatives act as trustee or delegate depending on the issue
The Representational Role Of Members Of Congress n How should an elected official represent his/her constituents? n Trustee - representatives use their own best judgment n Delegate - representatives vote the way their constituents want them to n Politico - representatives act as trustee or delegate depending on the issue
 How Members Make Decisions n Political parties n Divided/unified government n Constituents n Colleagues and caucuses n Logrolling n Interest groups, lobbyists, and political action committees n Staff and support agencies
How Members Make Decisions n Political parties n Divided/unified government n Constituents n Colleagues and caucuses n Logrolling n Interest groups, lobbyists, and political action committees n Staff and support agencies
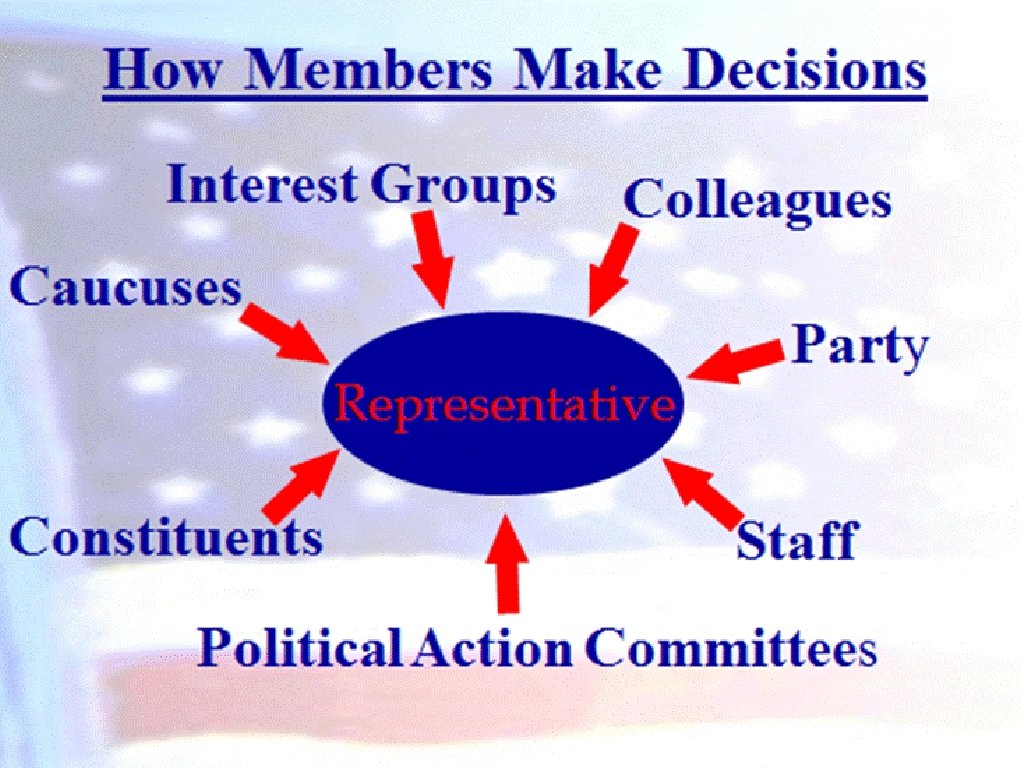
 The Law-Making Function of Congress n Only a member of the House or Senate may introduce a bill buy anyone can write a bill n Over 9, 000 bills are proposed (every 2 year session) and fewer than 5 -10% are enacted n Most bills originate in the Executive Branch n A bill must survive three stages to become a law committees, the floor, and the conference committee. A bill can die at any stage.
The Law-Making Function of Congress n Only a member of the House or Senate may introduce a bill buy anyone can write a bill n Over 9, 000 bills are proposed (every 2 year session) and fewer than 5 -10% are enacted n Most bills originate in the Executive Branch n A bill must survive three stages to become a law committees, the floor, and the conference committee. A bill can die at any stage.
 The Budgetary Function n Congressional Budget Act of 1974 n n n Reconciliation Timeline on budget process Pork and Earmarks
The Budgetary Function n Congressional Budget Act of 1974 n n n Reconciliation Timeline on budget process Pork and Earmarks
 The Oversight Function n War Powers Act (1973) n Congressional review n Confirmation of Presidential appointments n n Senatorial courtesy Impeachment
The Oversight Function n War Powers Act (1973) n Congressional review n Confirmation of Presidential appointments n n Senatorial courtesy Impeachment
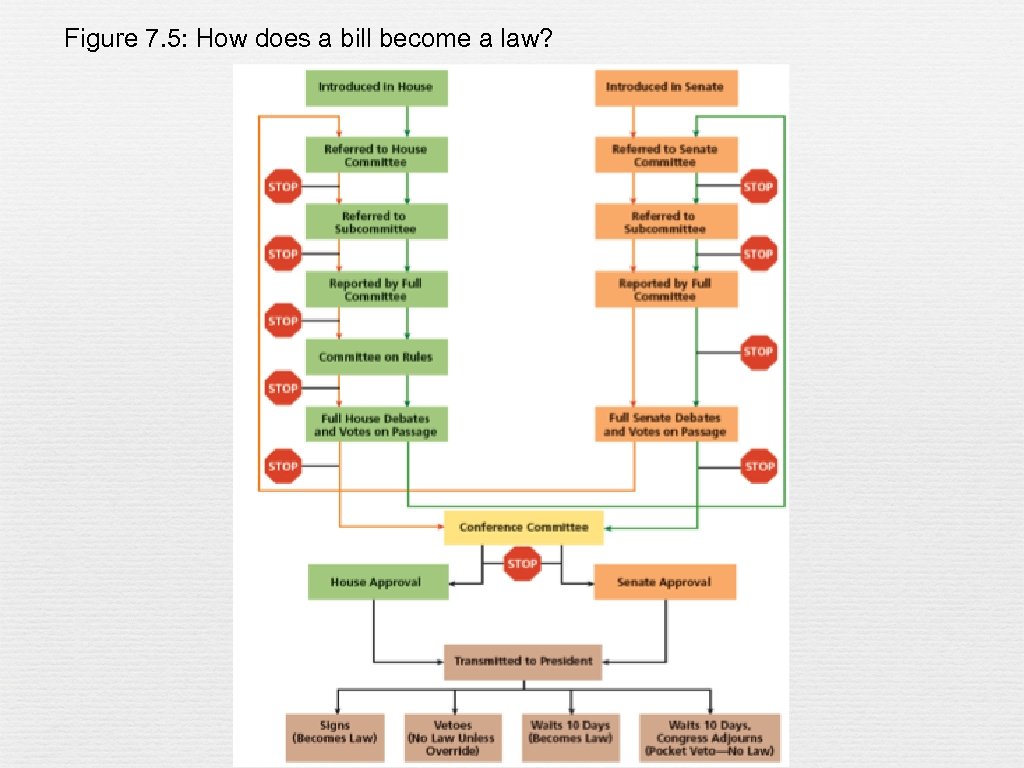 Figure 7. 5: How does a bill become a law?
Figure 7. 5: How does a bill become a law?
 Congress and the President n Especially since the 1930 s, the president has seemed to be more powerful than Congress n However, Congress retains several key powers vis-a-vis the president n funding powers n oversight n impeachment/removal
Congress and the President n Especially since the 1930 s, the president has seemed to be more powerful than Congress n However, Congress retains several key powers vis-a-vis the president n funding powers n oversight n impeachment/removal
 Congress and the Judiciary n Courts can overturn laws if unconstitutional n Congress reviews judicial nominees n Role of senatorial courtesy n Congress also sets court’s jurisdiction
Congress and the Judiciary n Courts can overturn laws if unconstitutional n Congress reviews judicial nominees n Role of senatorial courtesy n Congress also sets court’s jurisdiction
 Role of Parties in Organizing Congress n Parties and their strength have important implications in Congress n Committees are controlled by the majority n Committees set the agenda
Role of Parties in Organizing Congress n Parties and their strength have important implications in Congress n Committees are controlled by the majority n Committees set the agenda
 Table 7. 5: What were the committees of the 111 th Congress?
Table 7. 5: What were the committees of the 111 th Congress?
 Different Types of Congressional Committees n Standing Committee - continues from one Congress to the next n Joint Committee - set up to expedite business between the two houses n Conference Committee - special joint committees that resolve differences in bills passed by either house n Ad hoc, special, or select committees - temporary committees designed for a specific purpose
Different Types of Congressional Committees n Standing Committee - continues from one Congress to the next n Joint Committee - set up to expedite business between the two houses n Conference Committee - special joint committees that resolve differences in bills passed by either house n Ad hoc, special, or select committees - temporary committees designed for a specific purpose
 Committee Membership n Members often seek assignments to committees based on n Their own interests or expertise n A committee’s ability to help their prospects for reelection n Pork: legislation that allows representatives to bring home the “bacon” to their districts in the form of public works programs, military bases, or other programs designed to benefit their districts directly n Access to large campaign contributors
Committee Membership n Members often seek assignments to committees based on n Their own interests or expertise n A committee’s ability to help their prospects for reelection n Pork: legislation that allows representatives to bring home the “bacon” to their districts in the form of public works programs, military bases, or other programs designed to benefit their districts directly n Access to large campaign contributors
 Committee Chairs n These individuals have tremendous power and prestige n Authorized to select all subcommittee chairs n Call meetings n Recommend majority members to sit on conference committees n Can kill a bill by not scheduling hearings on it n Have staff at their disposal n Seniority vs loyalty to the party in the House n Seniority still important in the Senate n Both Chambers have term limits for chairs
Committee Chairs n These individuals have tremendous power and prestige n Authorized to select all subcommittee chairs n Call meetings n Recommend majority members to sit on conference committees n Can kill a bill by not scheduling hearings on it n Have staff at their disposal n Seniority vs loyalty to the party in the House n Seniority still important in the Senate n Both Chambers have term limits for chairs
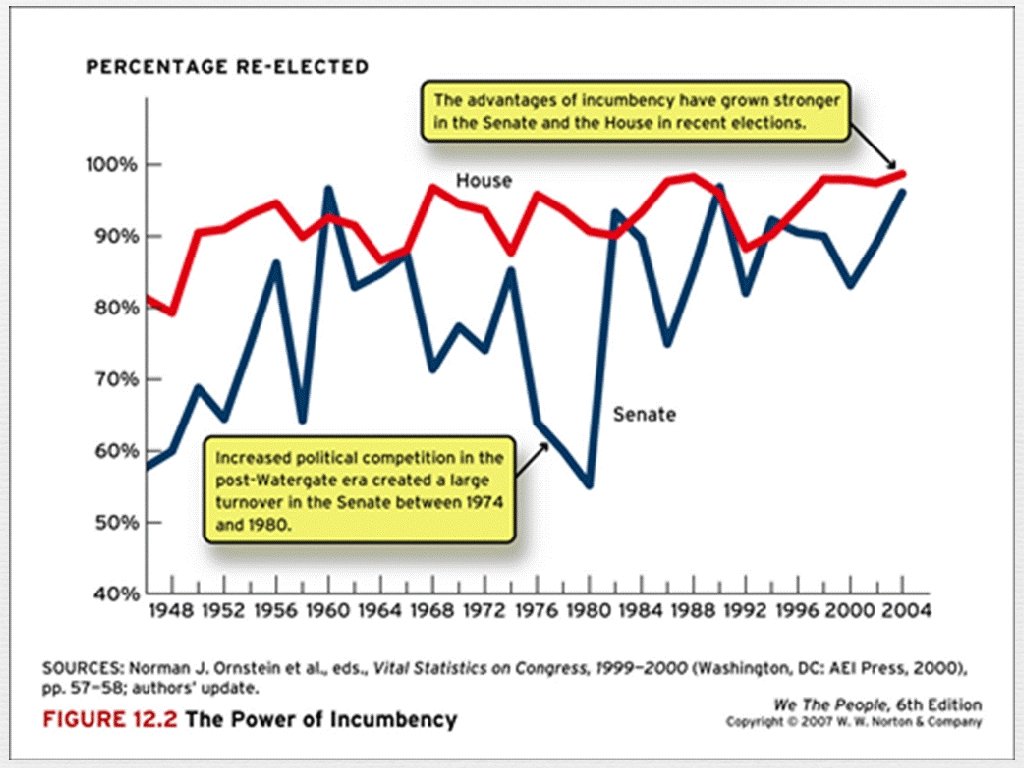
 Running for Office and Stying in Office n Incumbency Being in office helps a person stay in office n n n access to free media n inside track on fund-raising n n name recognition district is drawn to favor incumbent 1980 -1990, an average of 95% of incumbents who sought reelection won their primary and general elections races
Running for Office and Stying in Office n Incumbency Being in office helps a person stay in office n n n access to free media n inside track on fund-raising n n name recognition district is drawn to favor incumbent 1980 -1990, an average of 95% of incumbents who sought reelection won their primary and general elections races
 Table 7. 4: What are the advantages of incumbency?
Table 7. 4: What are the advantages of incumbency?
 Members of Congress n Congress is older, better educated, whiter, and richer than most of us n However, great strides have been made, Currently, both California senators are women n Can a man represent a woman? n Can a white person adequately represent the views of a black person?
Members of Congress n Congress is older, better educated, whiter, and richer than most of us n However, great strides have been made, Currently, both California senators are women n Can a man represent a woman? n Can a white person adequately represent the views of a black person?
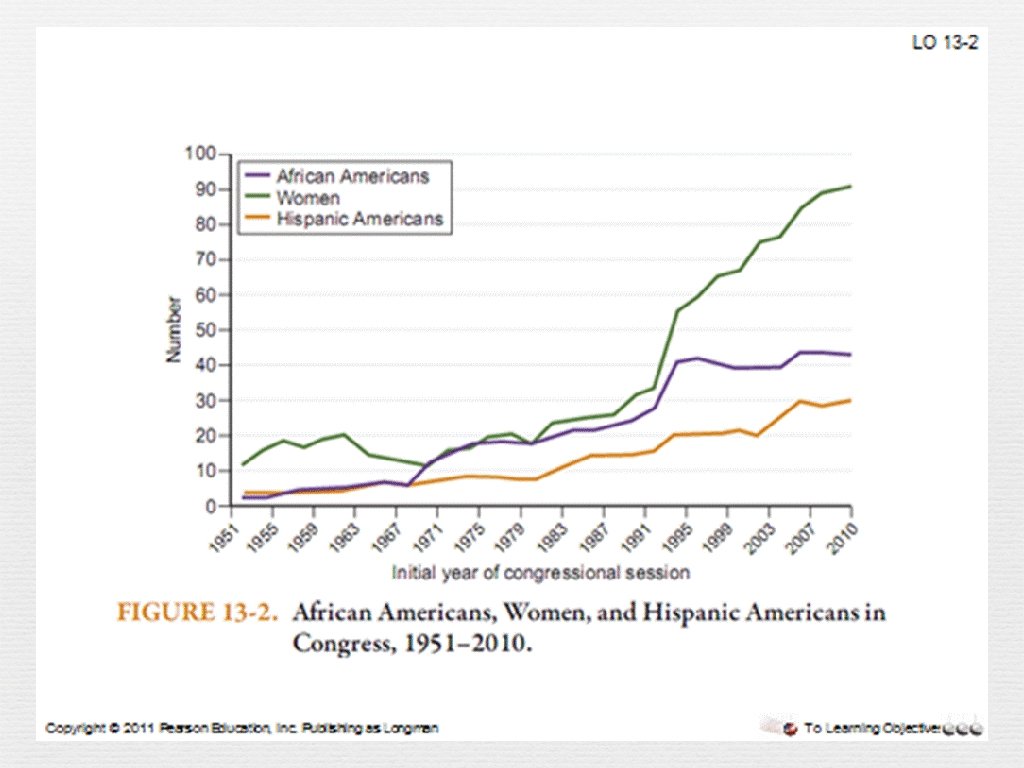
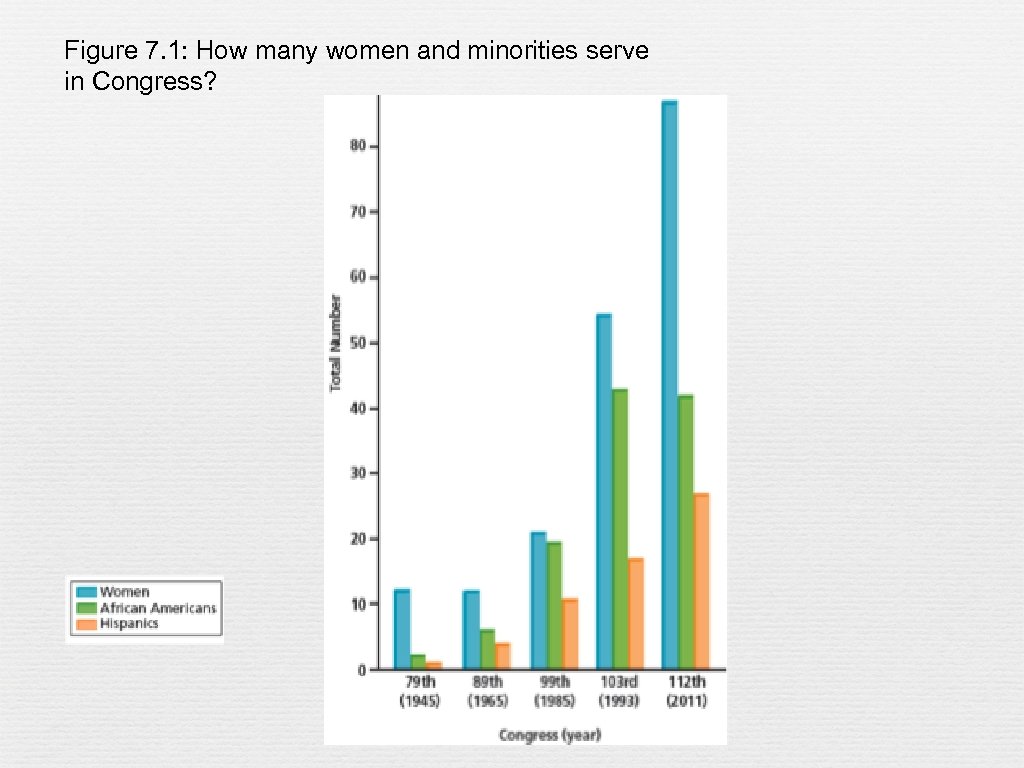 Figure 7. 1: How many women and minorities serve in Congress?
Figure 7. 1: How many women and minorities serve in Congress?
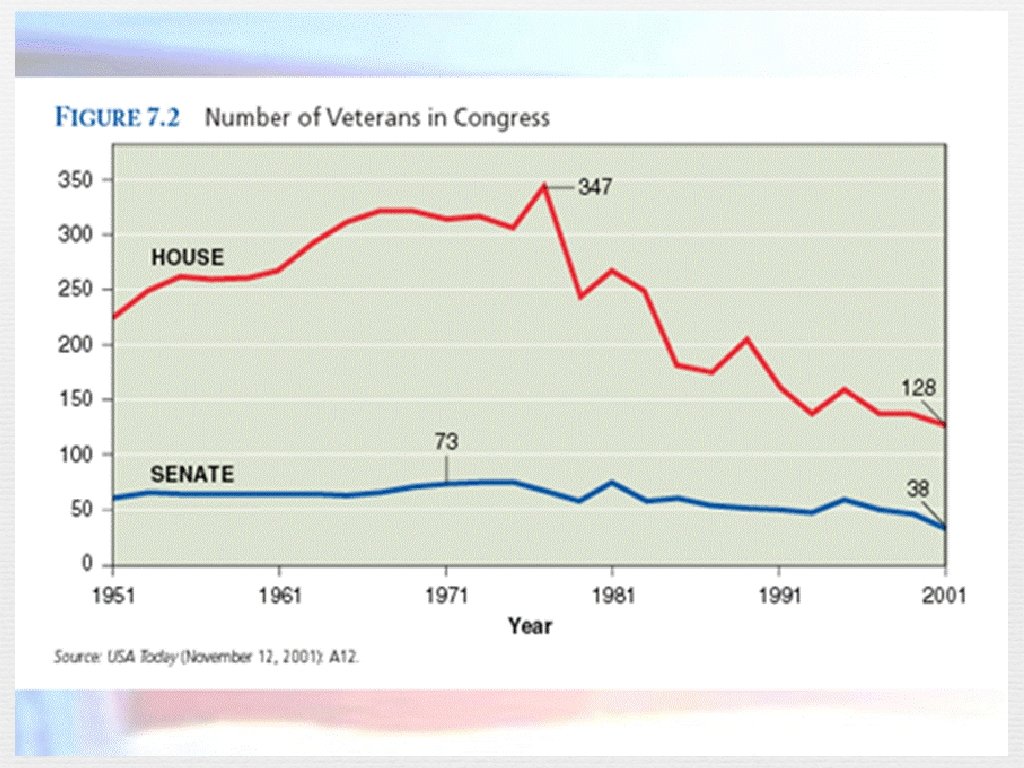
 Apportionment and Redistricting n The Constitution requires that all Americans be counted every ten years by a census n Census determines the representation in the House of Representatives n Redistricting (the redrawing of congressional districts to reflect changes in seats allocated to the states from population shifts)is done by states legislatures and, of course, always has political overtones n When the process is outrageously political, it is called gerrymandering and is often struck down by the courts
Apportionment and Redistricting n The Constitution requires that all Americans be counted every ten years by a census n Census determines the representation in the House of Representatives n Redistricting (the redrawing of congressional districts to reflect changes in seats allocated to the states from population shifts)is done by states legislatures and, of course, always has political overtones n When the process is outrageously political, it is called gerrymandering and is often struck down by the courts
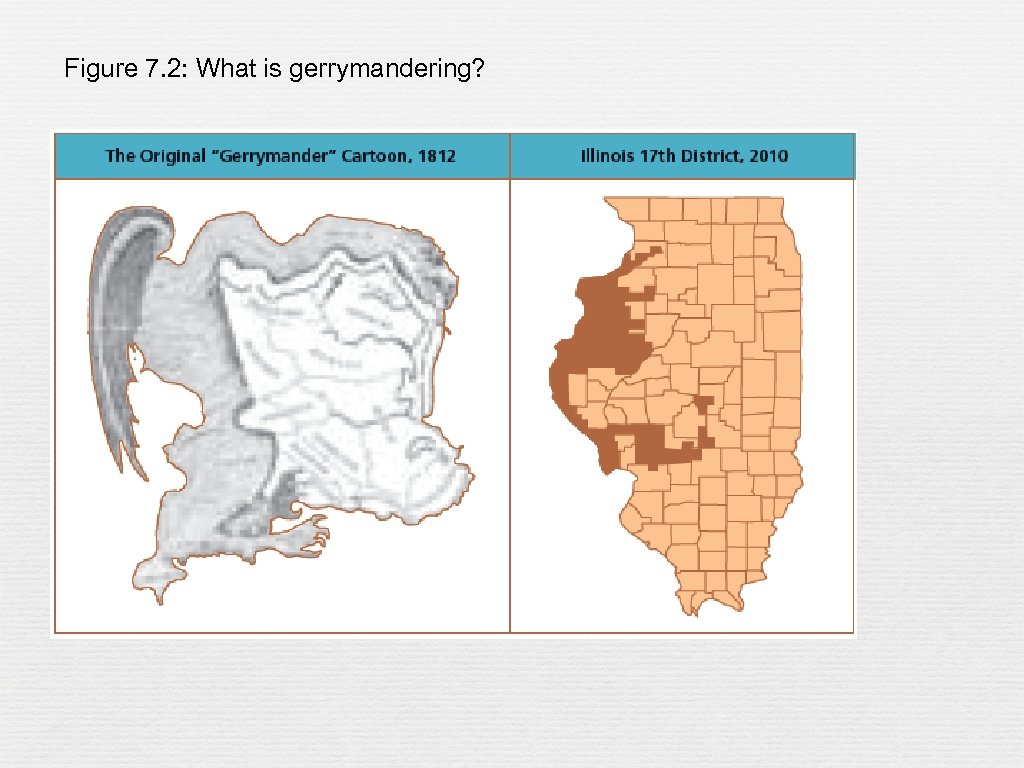 Figure 7. 2: What is gerrymandering?
Figure 7. 2: What is gerrymandering?
 Table 7. 6: What are the congressional support agencies?
Table 7. 6: What are the congressional support agencies?
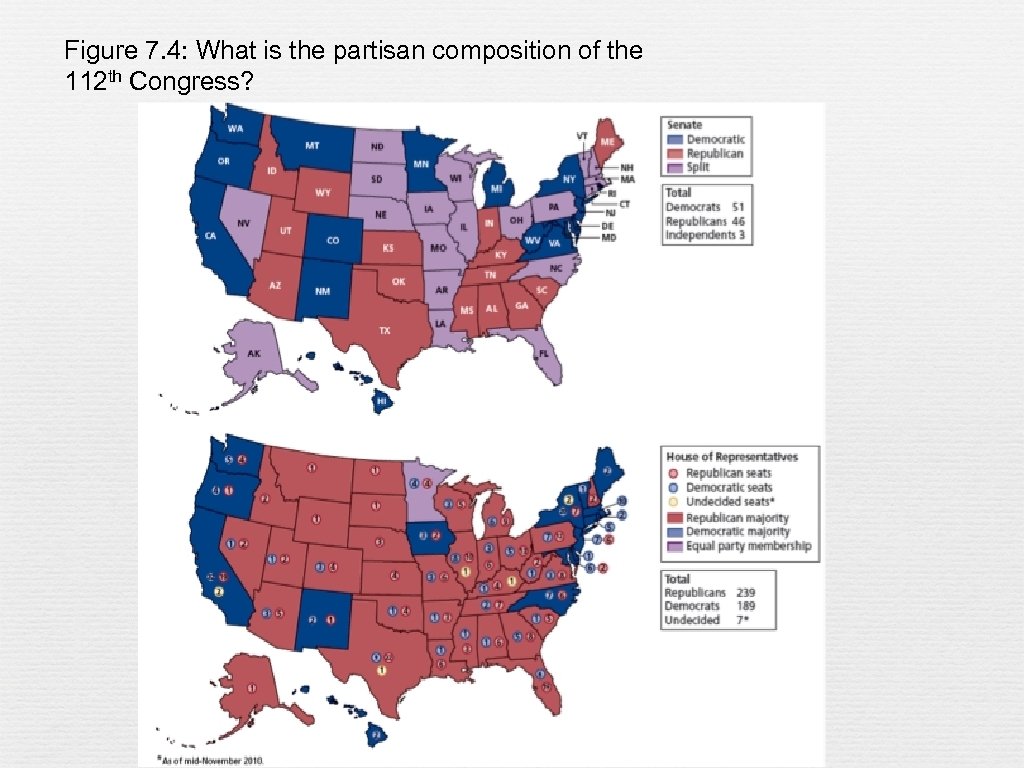 Figure 7. 4: What is the partisan composition of the 112 th Congress?
Figure 7. 4: What is the partisan composition of the 112 th Congress?


