20a8ff4d9b01f468b65b8f20eb7aca92.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Congress 6


Roots of the Legislative Branch of Government ¤ Bicameral legislature n House n Representatives based on population n Two-year term ¤ Senate n Two from each state n Six-year term 6. 1

Eligibility and Apportionment 6. 1 ¤ Members of the House n Twenty-five years old and a citizen for at least seven years ¤ Senators n Thirty years old and a citizen for at least nine years ¤ Census n Conducted every ten years

Key Powers ¤ Make laws n Both House and Senate must pass bills ¤ Raise and spend revenue ¤ Impeachment ¤ Other powers “as necessary and proper” to carry out the functions of Congress 6. 1

TABLE 6. 1: What are the key differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate? 6. 1

Members of Congress ¤ Congressional Demographics ¤ Running for and Staying in Office n Incumbency n Redistricting 6. 2

Congressional Demographics ¤ Better educated than general population n Two-thirds of members hold advanced degrees ¤ Wealthier than general population n Senate “Millionaires Club” ¤ Recent increases in minority representation 6. 2

TABLE 6. 3: What are the advantages to incumbency? 6. 2

How Congress Is Organized 6. 3 ¤ Leadership in the House of Representatives ¤ Leadership in the Senate ¤ The Committee System

FIGURE 6. 2 How are the House of Representatives and the Senate Organized? 6. 3

Leadership in the House of Representatives ¤ Speaker of the House n Most powerful position in the House ¤ Leadership Teams n Majority Leader n Minority Leader n Whips 6. 3

Leadership in the Senate ¤ Presiding Officer ¤ Majority Leader ¤ Leadership Teams 6. 3

The Committee System ¤ Types of committees n n Standing Committees Joint Committees Conference Committees Select (or Special) Committees ¤ Committee chairs ¤ Committee membership 6. 3
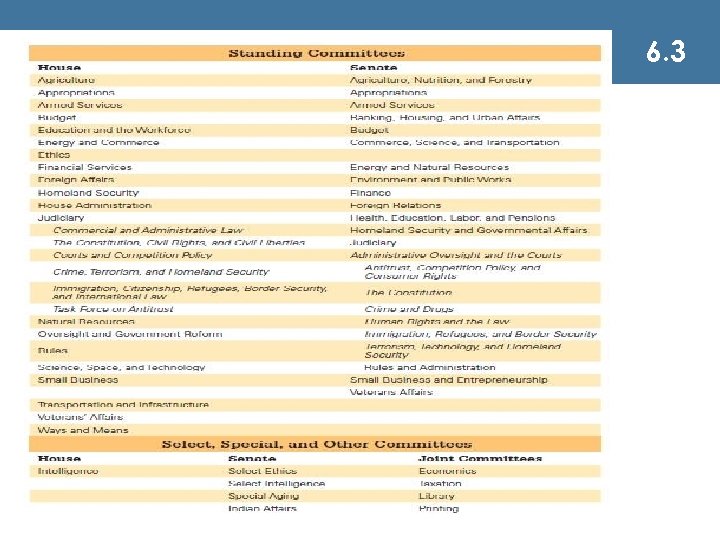
TABLE 6. 4: What were the committees of the 112 th Congress? 6. 3

Functions of Congress ¤ The Law-making Function ¤ The Budgetary Function ¤ The Oversight Function 6. 4

The Law-making Function ¤ Committee Referral § § Bill is introduced and sent to committee If accepted, bill goes through changes, then sent to floor ¤ Floor Debate ¤ Holds or filibusters in Senate ¤ Final Approval § § Approved bill sent to president Veto power of president 6. 4
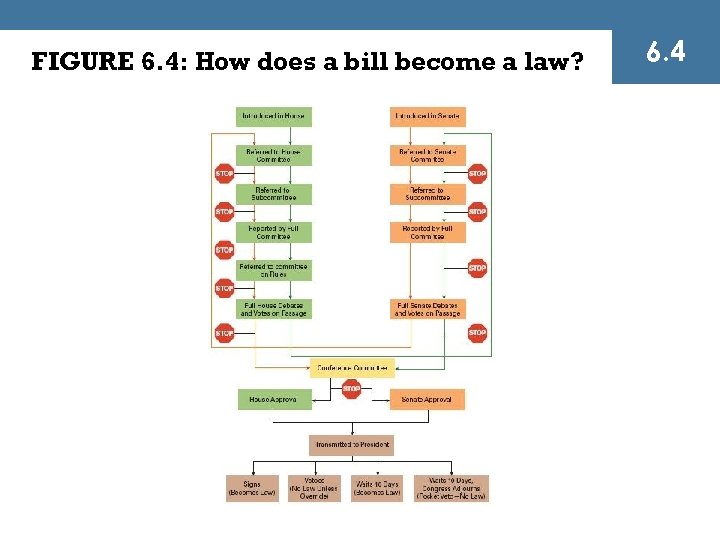
FIGURE 6. 4: How does a bill become a law? 6. 4

The Budgetary Function ¤ Congressional Budget Act of 1974 n Establishes levels of spending n Reconciliation process to limit debates ¤ Pork and Programmatic Requests 6. 4

TABLE 6. 5: What is the timeline for the congressional budgetary process? 6. 4

The Oversight Function ¤ ¤ The War Powers Resolution Congressional Review Confirmation of Presidential Appointees Impeachment 6. 4

War Powers Resolution ¤ Passed over President Nixon’s veto ¤ Requires Congressional approval to commit troops ¤ Limits power of president as commander in chief 6. 4

Congressional Review Confirmation of Presidential Appointees ¤ Congressional review (Act 1996) allows Congress to overrule regulations for federal agencies (within 60 days). Needs presidential signature. ¤ Senate confirms Supreme Court, federal district court, and Cabinet nominations 6. 4

Impeachment ¤ Power to remove official from office ¤ House votes to impeach ¤ Senate conducts trial 6. 4

How Members Make Decisions Political Parties Constituents Colleagues and Caucuses Interest Groups, Lobbyists and Political Action Committees ¤ Staff and Support Agencies ¤ ¤ 6. 5

Political Parties 6. 5 ¤ Influence of political parties on the passage of legislation ¤ Divided government n Different political parties control presidency and Congress ¤ Unified government n Same political party controls presidency and Congress

Constituents ¤ People who live, work and vote in a member’s district ¤ Wedge issues 6. 5

Colleagues and Caucuses ¤ Logrolling n Supporting another member’s legislation in exchange for future support ¤ Special-interest caucuses n Informal groups based on shared interest 6. 5

Interest Groups, Lobbyists and Political Action Committees ¤ Research and data n Provide information to justify members’ positions on legislation n Persuade constituents to contact or pressure members ¤ Fundraising n PACS 6. 5

Staff and Support Agencies ¤ Congressional staffers ¤ Agency staffers ¤ Committee staffers 6. 5

Smith—Troubled Institution The filibuster

20a8ff4d9b01f468b65b8f20eb7aca92.ppt