Congenital Heart Disease Adult CHD is not








- Размер: 14.9 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 68
Описание презентации Congenital Heart Disease Adult CHD is not по слайдам
 Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital Heart Disease
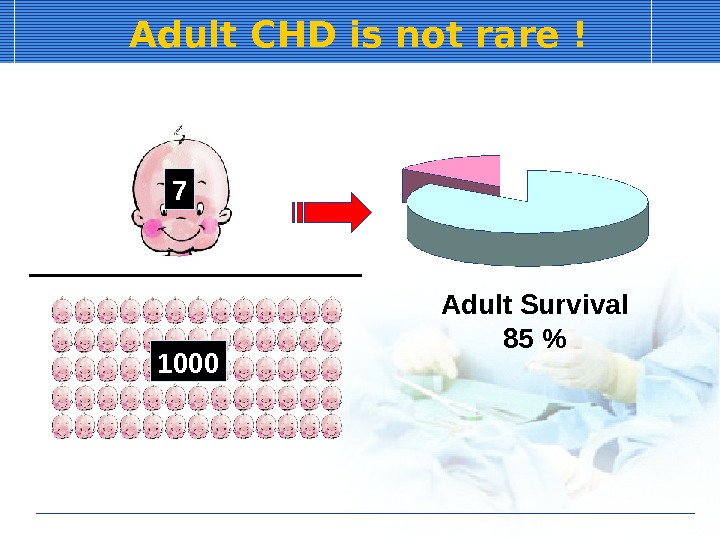
 Adult CHD is not rare ! 7 1000 Adult Survival 85 %
Adult CHD is not rare ! 7 1000 Adult Survival 85 %
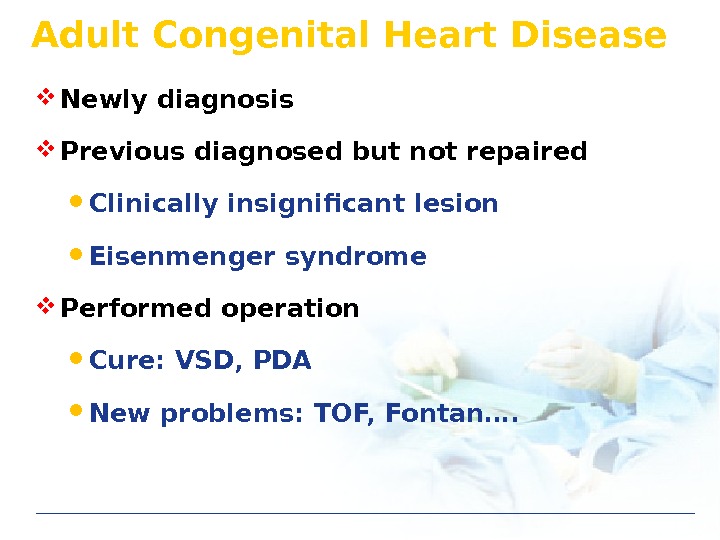
 Adult Congenital Heart Disease Newly diagnosis Previous diagnosed but not repaired Clinically insignificant lesion Eisenmenger syndrome Performed operation Cure: VSD, PDA New problems: TOF, Fontan….
Adult Congenital Heart Disease Newly diagnosis Previous diagnosed but not repaired Clinically insignificant lesion Eisenmenger syndrome Performed operation Cure: VSD, PDA New problems: TOF, Fontan….
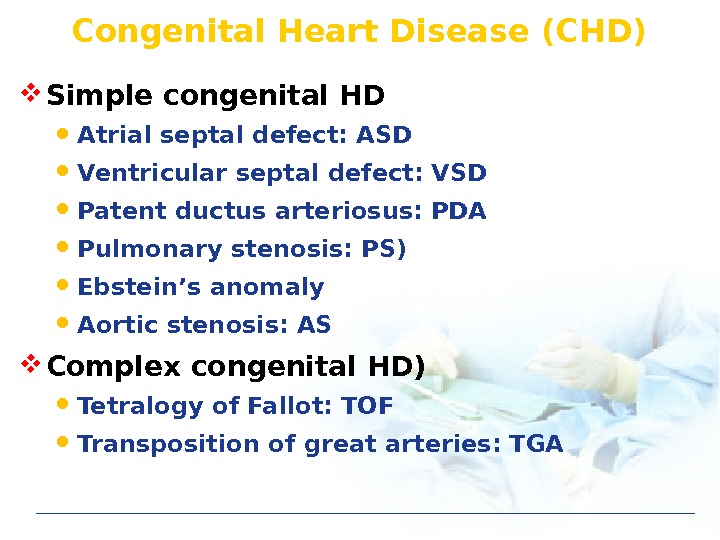
 Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) Simple congenital HD Atrial septal defect: ASD Ventricular septal defect: VSD Patent ductus arteriosus: PDA Pulmonary stenosis: PS) Ebstein’s anomaly Aortic stenosis: AS Complex congenital HD) Tetralogy of Fallot: TOF Transposition of great arteries: TG
Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) Simple congenital HD Atrial septal defect: ASD Ventricular septal defect: VSD Patent ductus arteriosus: PDA Pulmonary stenosis: PS) Ebstein’s anomaly Aortic stenosis: AS Complex congenital HD) Tetralogy of Fallot: TOF Transposition of great arteries: TG
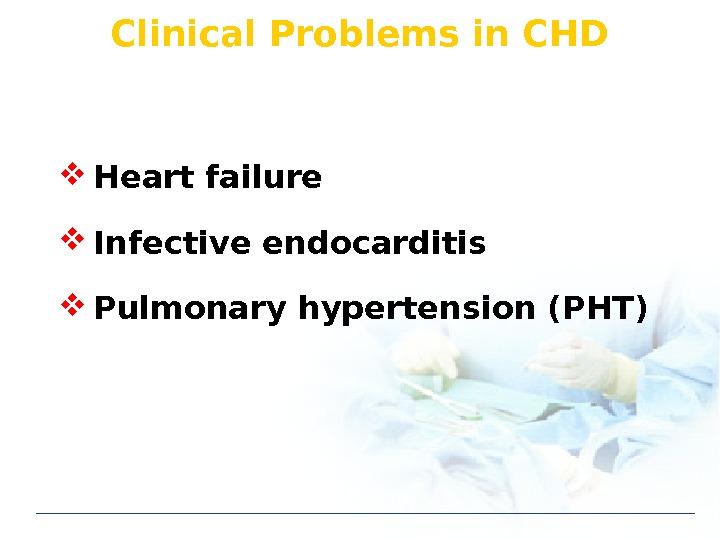
 Clinical Problems in CHD Heart failure Infective endocarditis Pulmonary hypertension (PHT)
Clinical Problems in CHD Heart failure Infective endocarditis Pulmonary hypertension (PHT)
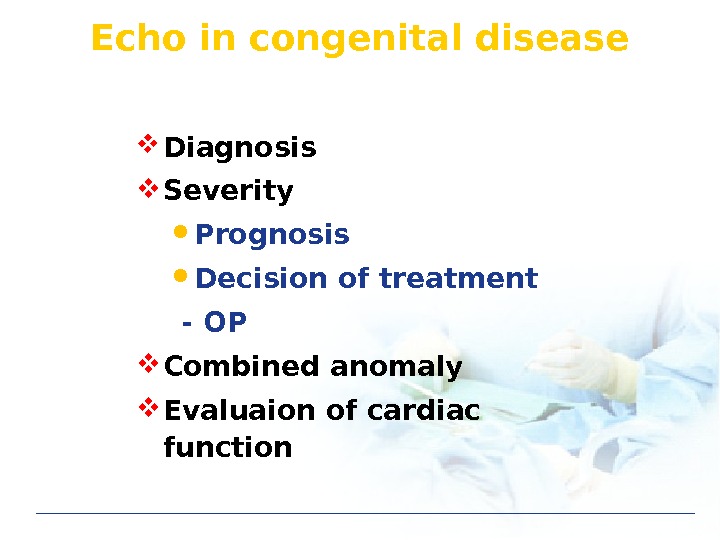
 Echo in congenital disease Diagnosis Severity Prognosis Decision of treatment — OP Combined anomaly Evaluaion of cardiac function
Echo in congenital disease Diagnosis Severity Prognosis Decision of treatment — OP Combined anomaly Evaluaion of cardiac function
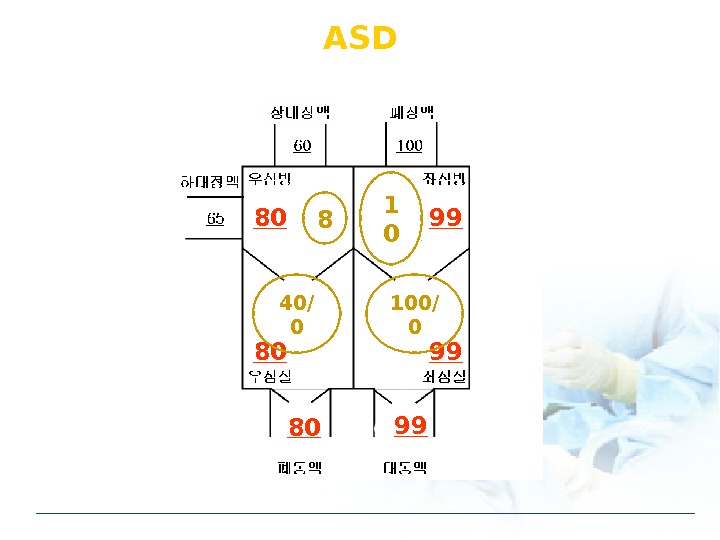
 ASD 80 80 80 99 99 998 1 0 40/ 0 100/
ASD 80 80 80 99 99 998 1 0 40/ 0 100/
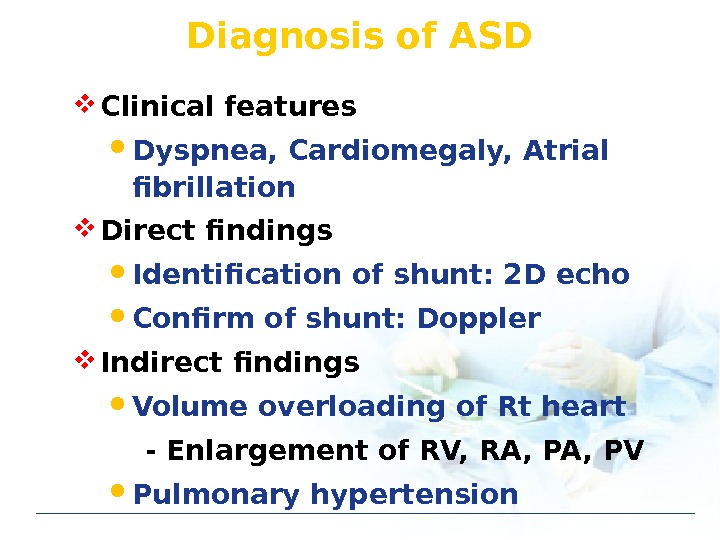
 Diagnosis of ASD Clinical features Dyspnea, Cardiomegaly, Atrial fibrillation Direct findings Identification of shunt: 2 D echo Confirm of shunt: Doppler Indirect findings Volume overloading of Rt heart — Enlargement of RV, RA, PV Pulmonary hypertension
Diagnosis of ASD Clinical features Dyspnea, Cardiomegaly, Atrial fibrillation Direct findings Identification of shunt: 2 D echo Confirm of shunt: Doppler Indirect findings Volume overloading of Rt heart — Enlargement of RV, RA, PV Pulmonary hypertension
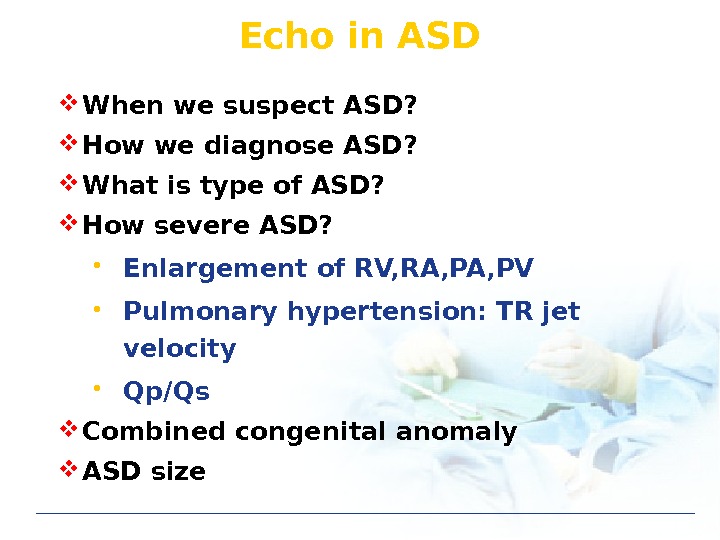
 Echo in ASD When we suspect ASD? How we diagnose ASD? What is type of ASD? How severe ASD? • Enlargement of RV, RA, PV • Pulmonary hypertension: TR jet velocity • Qp/Qs Combined congenital anomaly ASD size
Echo in ASD When we suspect ASD? How we diagnose ASD? What is type of ASD? How severe ASD? • Enlargement of RV, RA, PV • Pulmonary hypertension: TR jet velocity • Qp/Qs Combined congenital anomaly ASD size
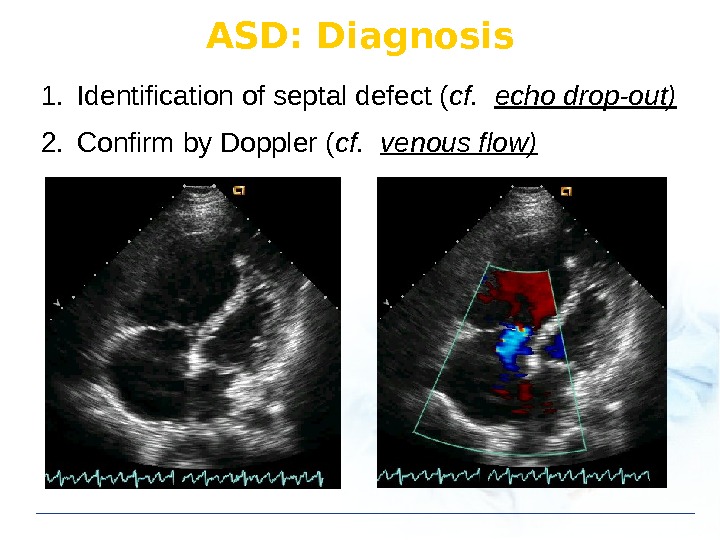
 ASD: Diagnosis 1. Identification of septal defect ( cf. echo drop-out) 2. Confirm by Doppler ( cf. venous flow)
ASD: Diagnosis 1. Identification of septal defect ( cf. echo drop-out) 2. Confirm by Doppler ( cf. venous flow)
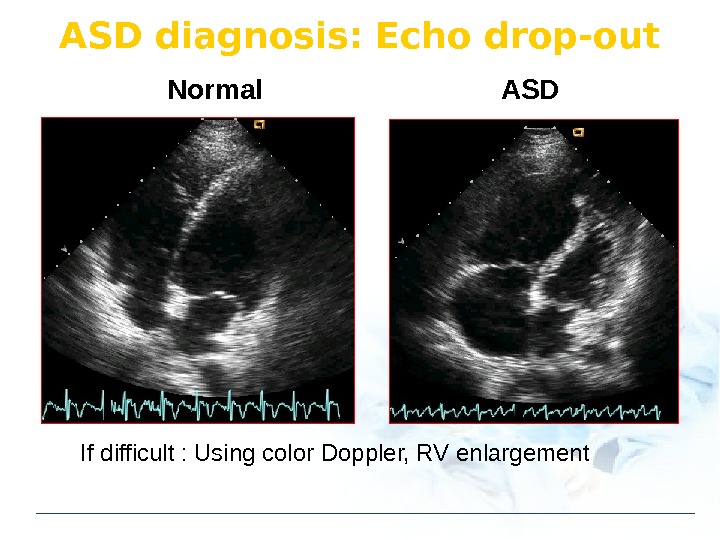
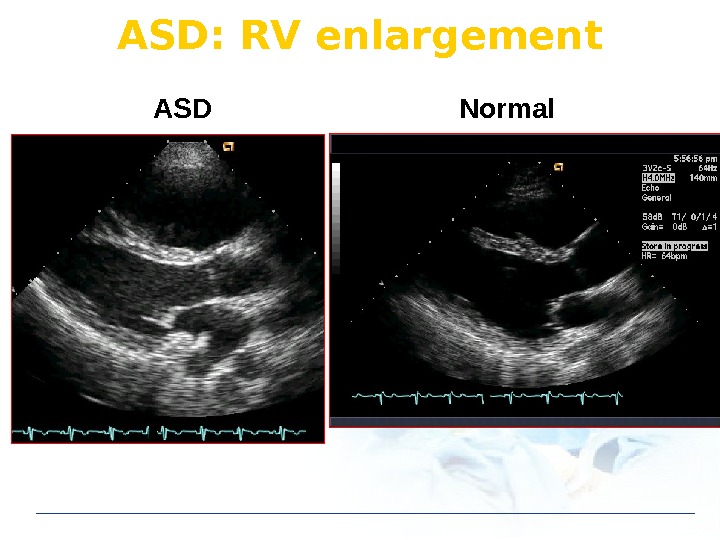
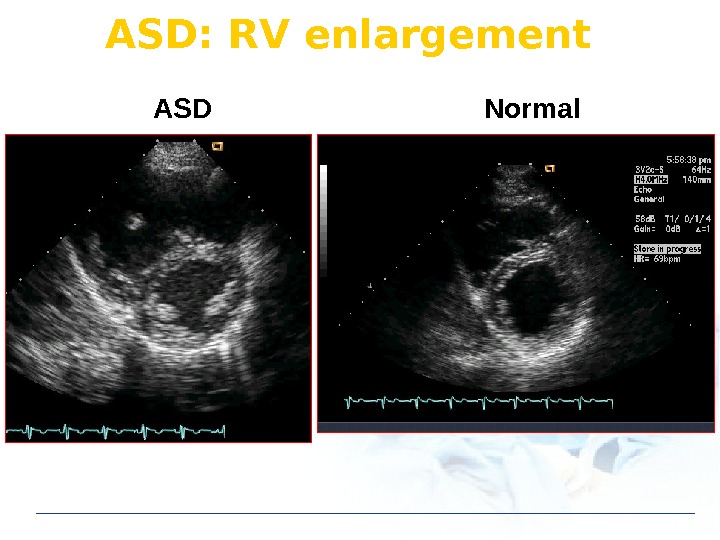
 ASD diagnosis: Echo drop-out Normal ASD If difficult : Using color Doppler, RV enlargement
ASD diagnosis: Echo drop-out Normal ASD If difficult : Using color Doppler, RV enlargement
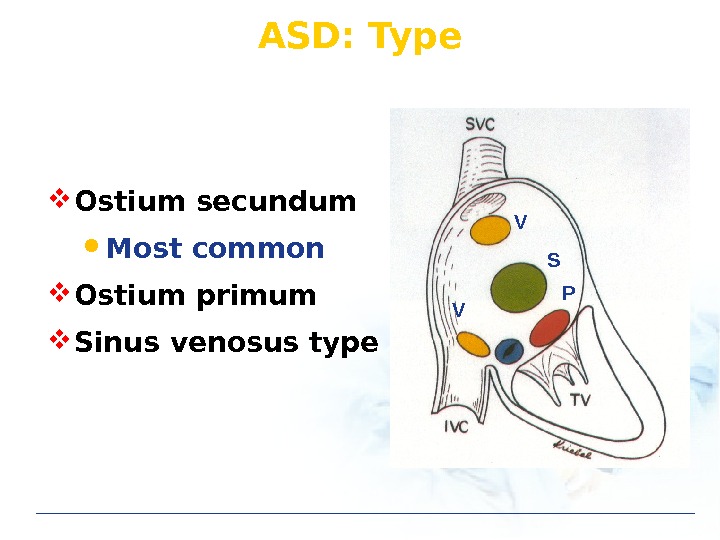
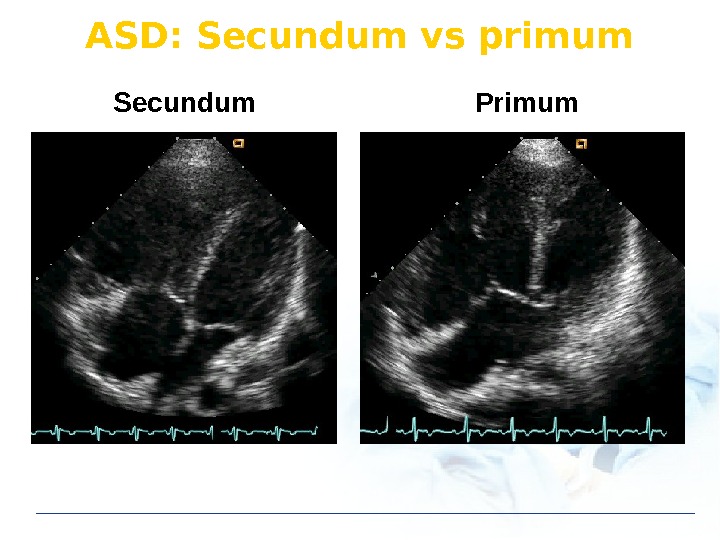
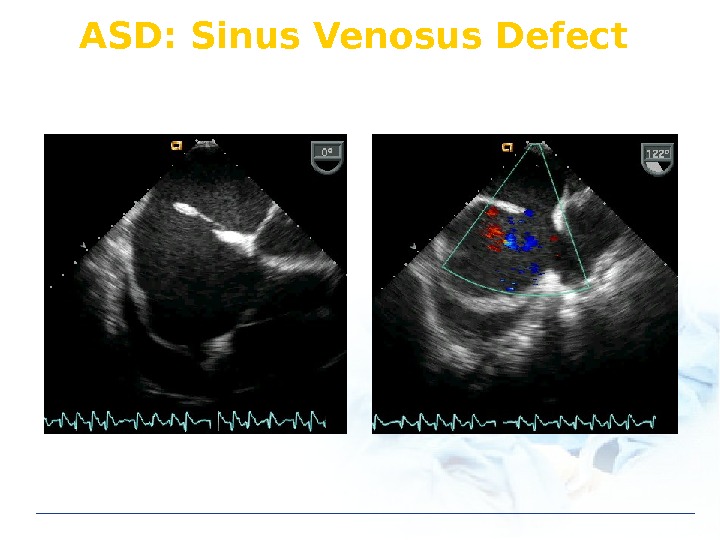
 ASD: Type S PV V Ostium secundum Most common Ostium primum Sinus venosus type
ASD: Type S PV V Ostium secundum Most common Ostium primum Sinus venosus type
 ASD: Secundum vs primum Secundum Primum
ASD: Secundum vs primum Secundum Primum
 ASD: Sinus Venosus Defect
ASD: Sinus Venosus Defect
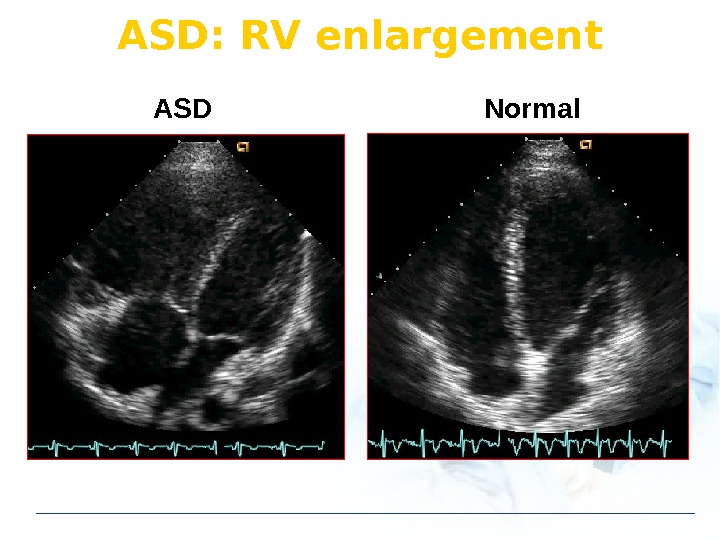
 ASD: RV enlargement ASD Normal
ASD: RV enlargement ASD Normal
 ASD Normal. ASD: RV enlargement
ASD Normal. ASD: RV enlargement
 ASD Normal. ASD: RV enlargement
ASD Normal. ASD: RV enlargement
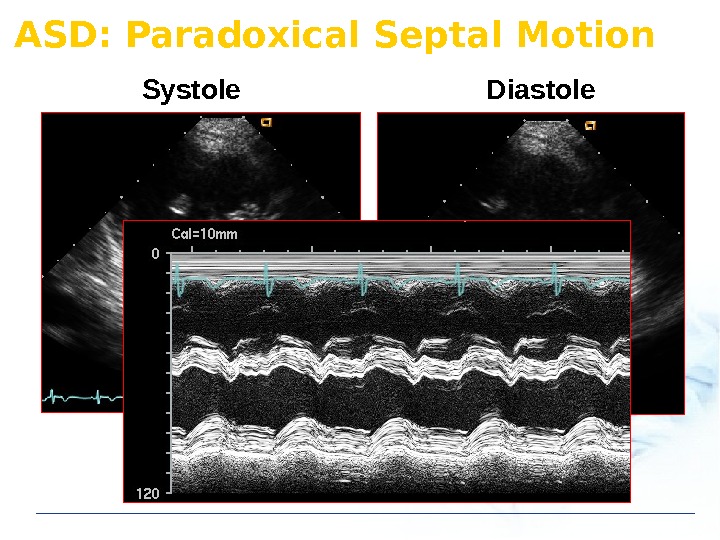
 ASD: Paradoxical Septal Motion Systole Diastole
ASD: Paradoxical Septal Motion Systole Diastole
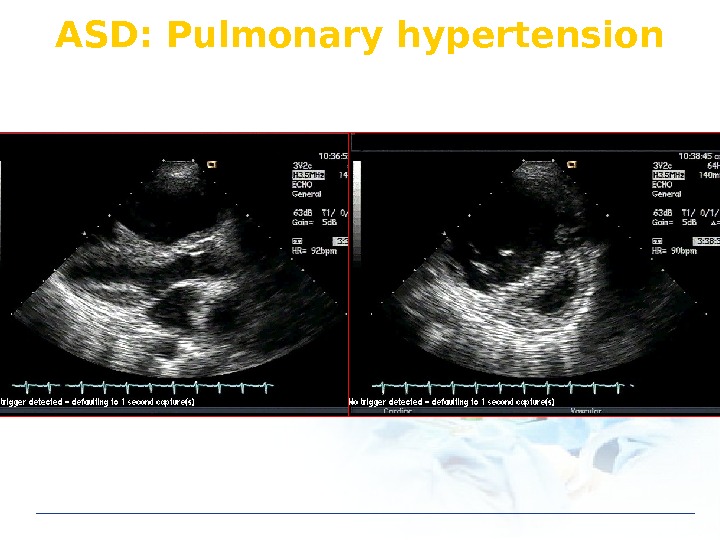
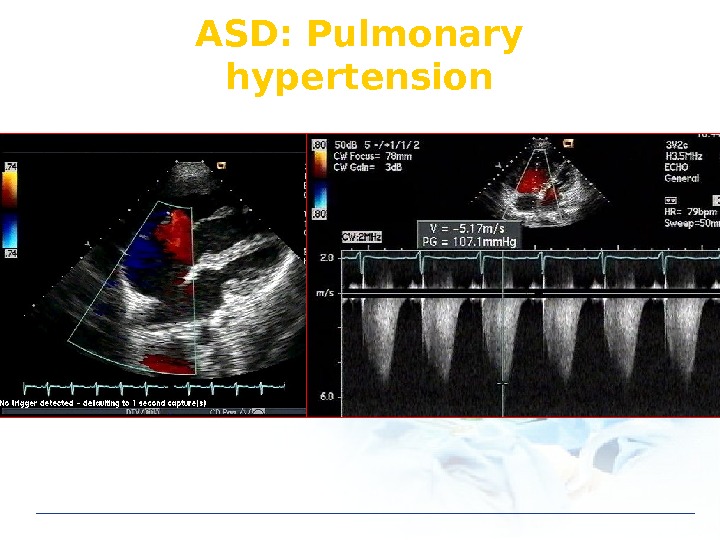
 ASD: Pulmonary hypertension
ASD: Pulmonary hypertension
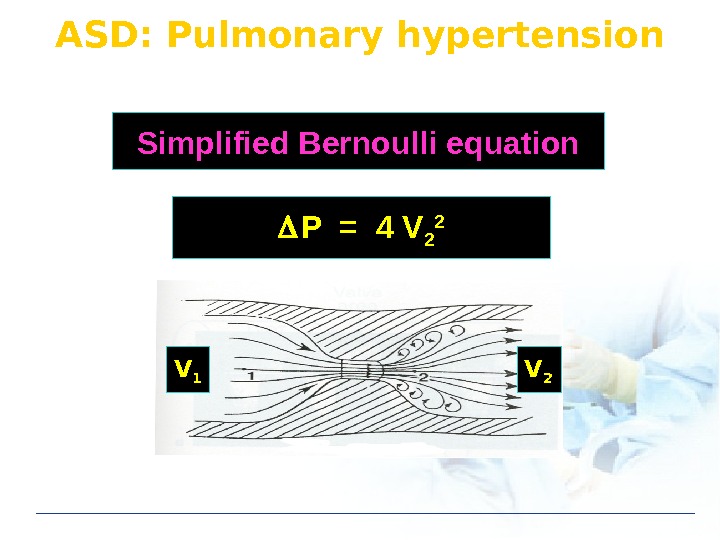
 ASD: Pulmonary hypertension P = 4 V 2 2 Simplified Bernoulli equation V 1 V
ASD: Pulmonary hypertension P = 4 V 2 2 Simplified Bernoulli equation V 1 V
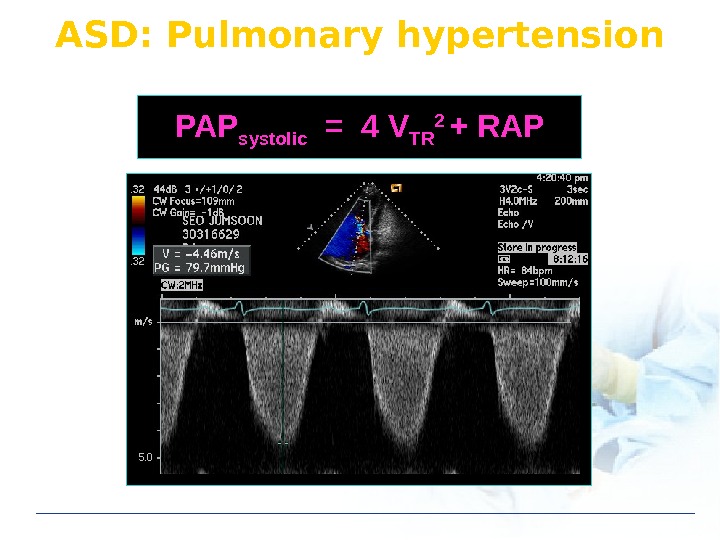
 ASD: Pulmonary hypertension PAP systolic = 4 V TR 2 + RAP
ASD: Pulmonary hypertension PAP systolic = 4 V TR 2 + RAP
 ASD: Pulmonary hypertension
ASD: Pulmonary hypertension
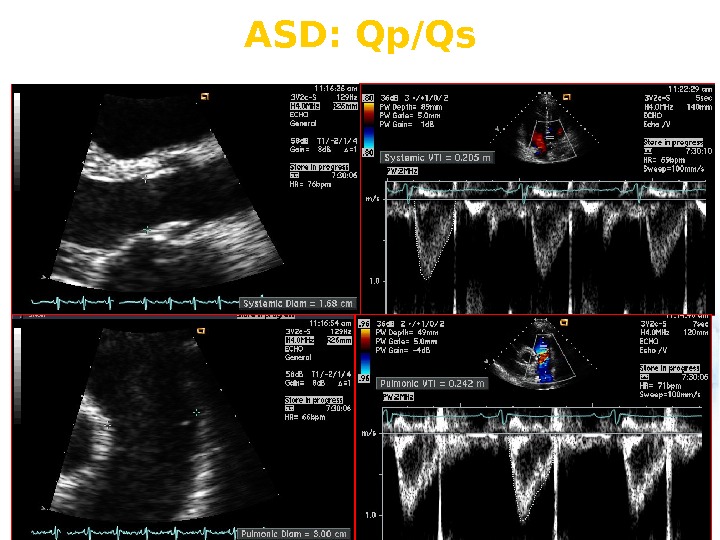
 ASD: Qp/Qs
ASD: Qp/Qs
 ASD: Combined anomaly Secundum ASD mitral valve prolapse Primum ASD cleft mitral valve Sinus venosus defect anomalous pulmonary venous return
ASD: Combined anomaly Secundum ASD mitral valve prolapse Primum ASD cleft mitral valve Sinus venosus defect anomalous pulmonary venous return
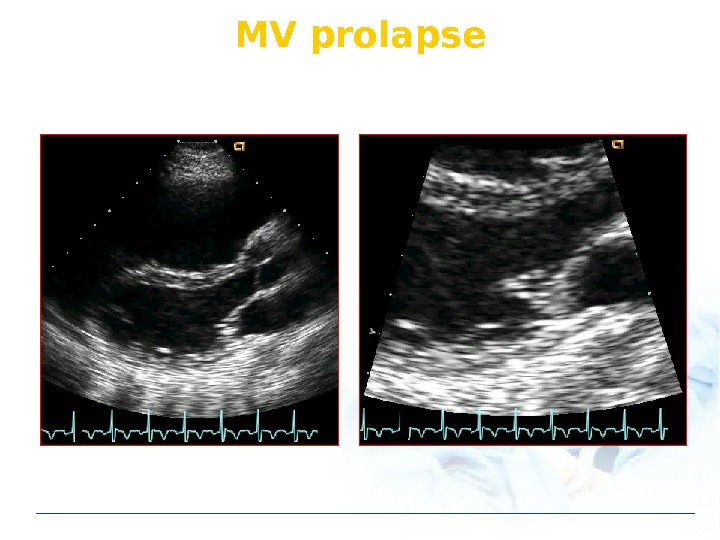
 MV prolapse
MV prolapse
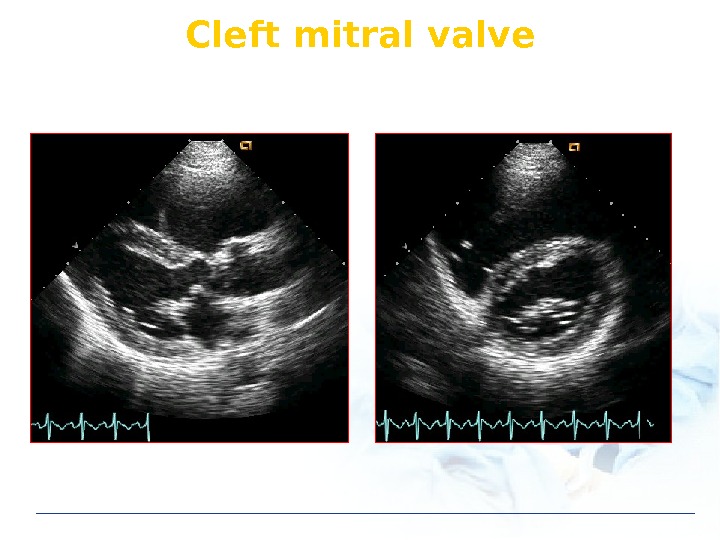
 Cleft mitral valve
Cleft mitral valve
 ASD: Treatment Medical treatment Endocarditis prophylaxis: not recommended Surgical treatment Indication: Qp/Qs 2. 0 Device closure: secundum ASD Contraindication Severe pulmonary hypertension
ASD: Treatment Medical treatment Endocarditis prophylaxis: not recommended Surgical treatment Indication: Qp/Qs 2. 0 Device closure: secundum ASD Contraindication Severe pulmonary hypertension
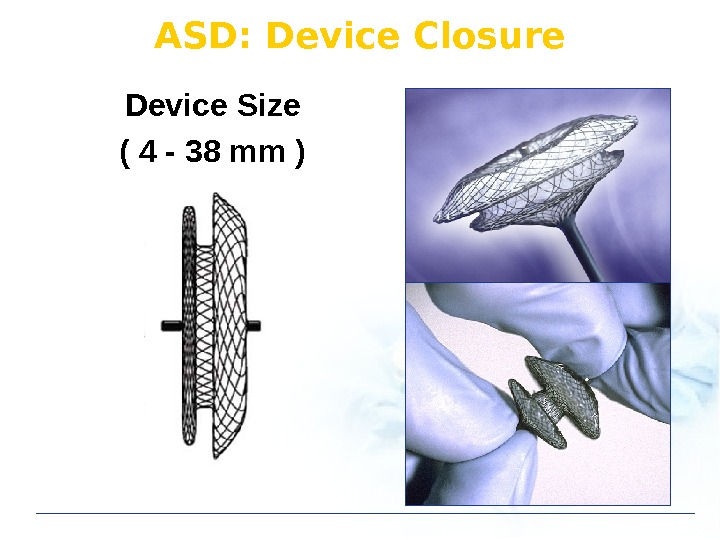
 Device Size ( 4 — 38 mm ) ASD: Device Closure
Device Size ( 4 — 38 mm ) ASD: Device Closure
 Case: 45/Male, Dyspnea
Case: 45/Male, Dyspnea

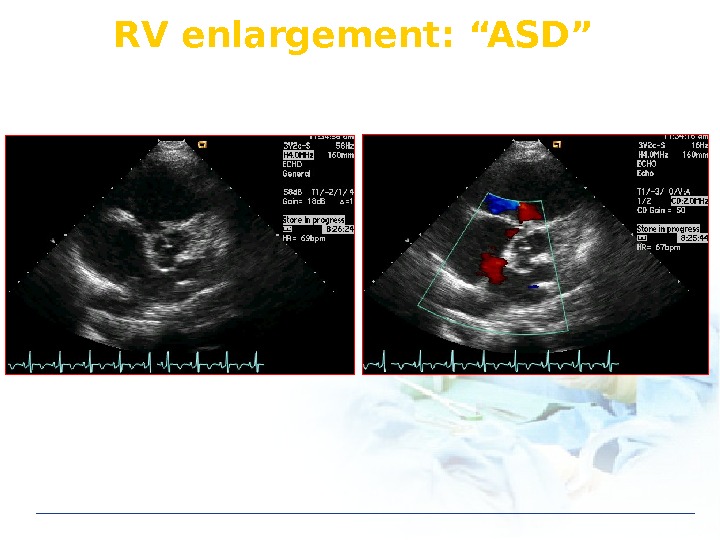
 RV enlargement: “ASD”
RV enlargement: “ASD”
 Echo in ASD Unknown origin RV & RA enlargement TEE in sinus venosus defect
Echo in ASD Unknown origin RV & RA enlargement TEE in sinus venosus defect
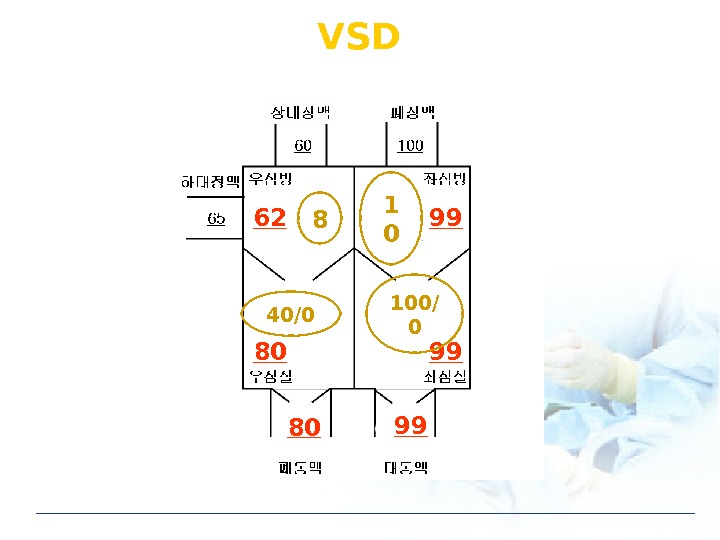
 VSD 62 80 80 99 99 998 1 0 40/0 100/
VSD 62 80 80 99 99 998 1 0 40/0 100/
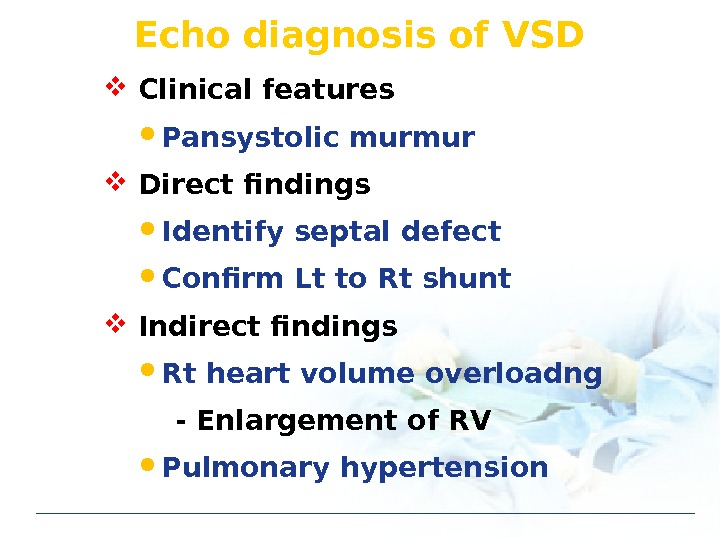
 Echo diagnosis of VSD Clinical features Pansystolic murmur Direct findings Identify septal defect Confirm Lt to Rt shunt Indirect findings Rt heart volume overloadng — Enlargement of RV Pulmonary hypertension
Echo diagnosis of VSD Clinical features Pansystolic murmur Direct findings Identify septal defect Confirm Lt to Rt shunt Indirect findings Rt heart volume overloadng — Enlargement of RV Pulmonary hypertension
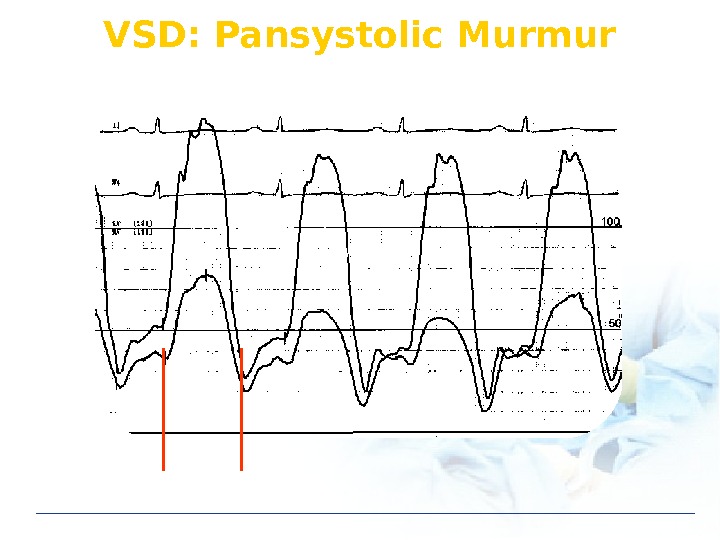
 VSD: Pansystolic Murmur
VSD: Pansystolic Murmur
 Echo in VSD When we suspect VSD? Diagnosis of VSD? What type of VSD? How severe VSD? RV size & function Pulmonary hypertension: TR jet vs VSD jet Qp/Qs Combined anomaly: AV prolapse, AR
Echo in VSD When we suspect VSD? Diagnosis of VSD? What type of VSD? How severe VSD? RV size & function Pulmonary hypertension: TR jet vs VSD jet Qp/Qs Combined anomaly: AV prolapse, AR
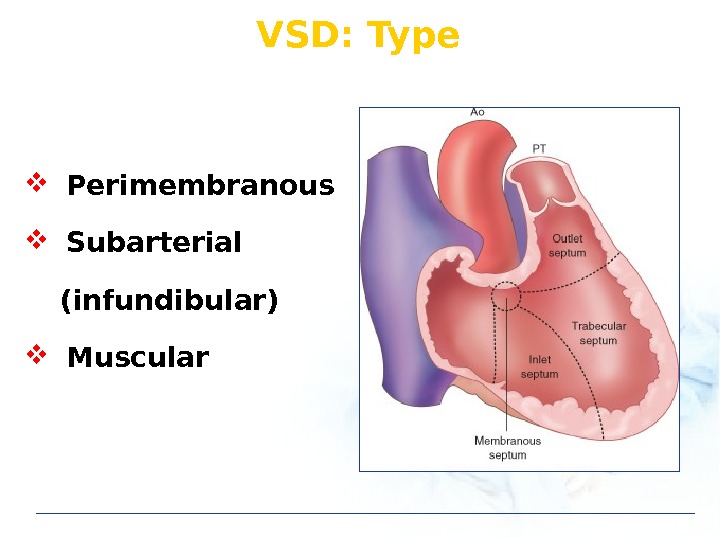
 VSD: Type Perimembranous Subarterial (infundibular) Muscular
VSD: Type Perimembranous Subarterial (infundibular) Muscular
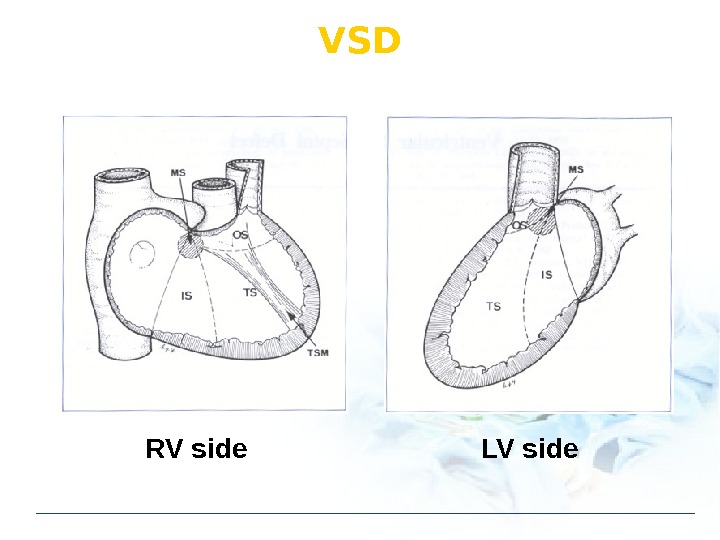
 VSD RV side LV side
VSD RV side LV side
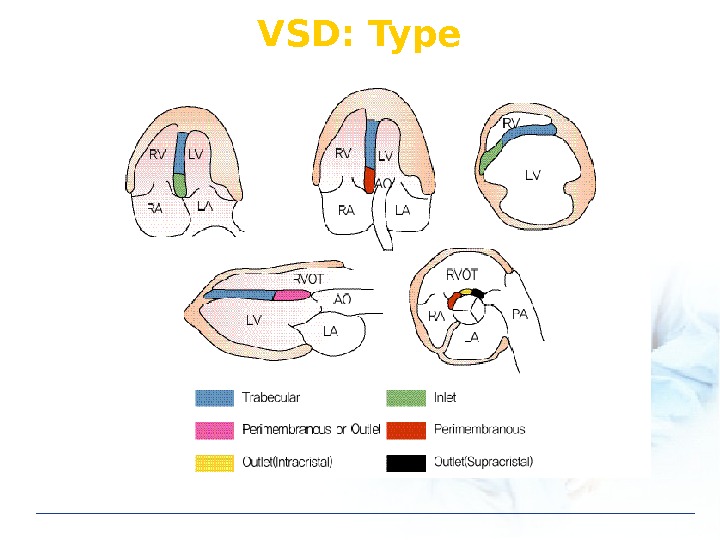
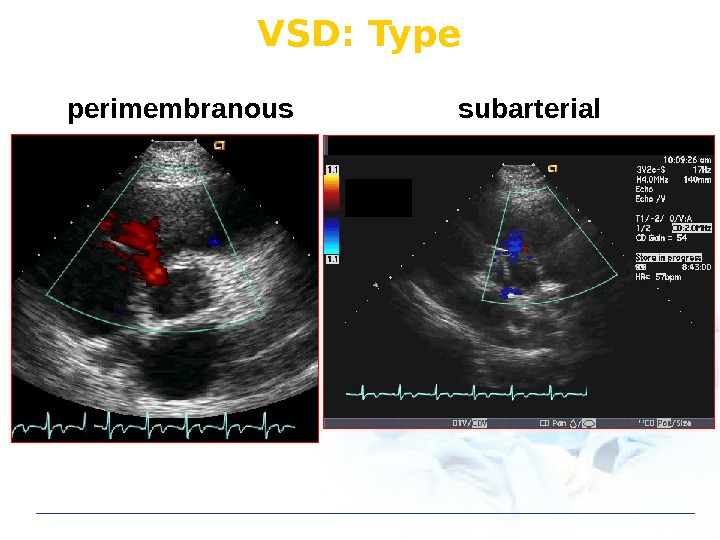
 VSD: Type
VSD: Type
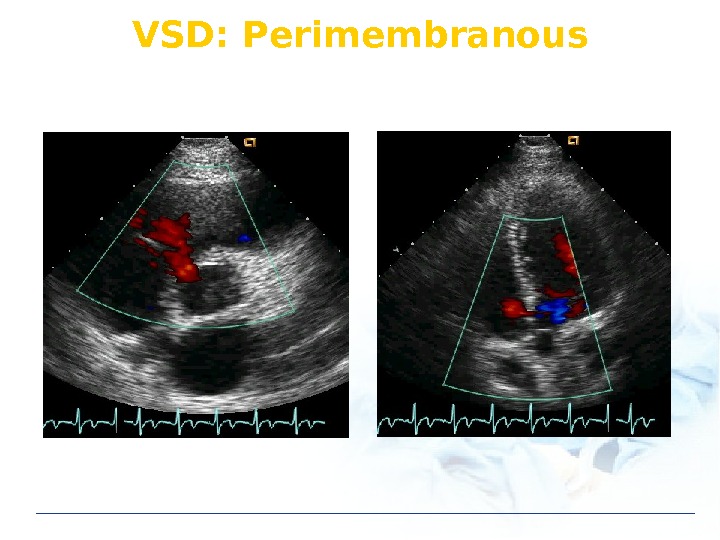
 VSD: Perimembranous
VSD: Perimembranous
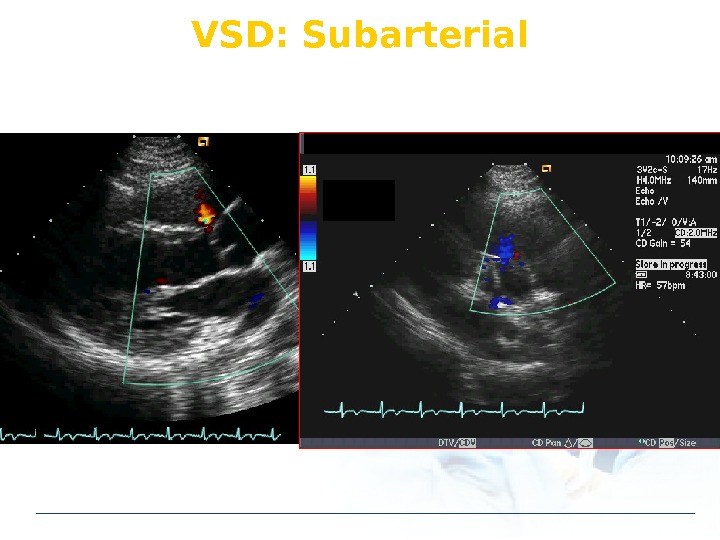
 VSD: Subarterial
VSD: Subarterial
 VSD: Type perimembranous subarterial
VSD: Type perimembranous subarterial
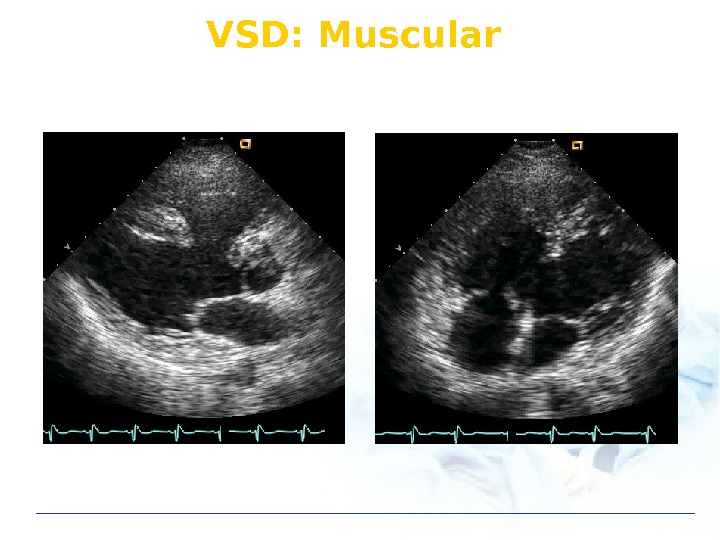
 VSD: Muscular
VSD: Muscular
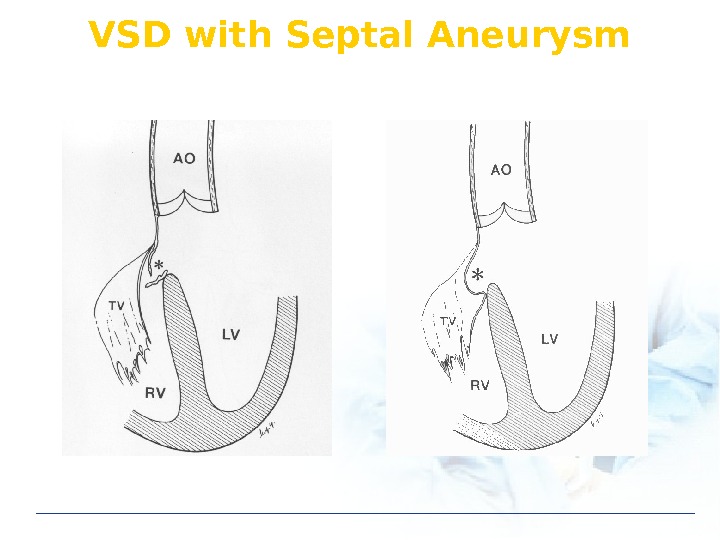
 VSD with Septal Aneurysm
VSD with Septal Aneurysm
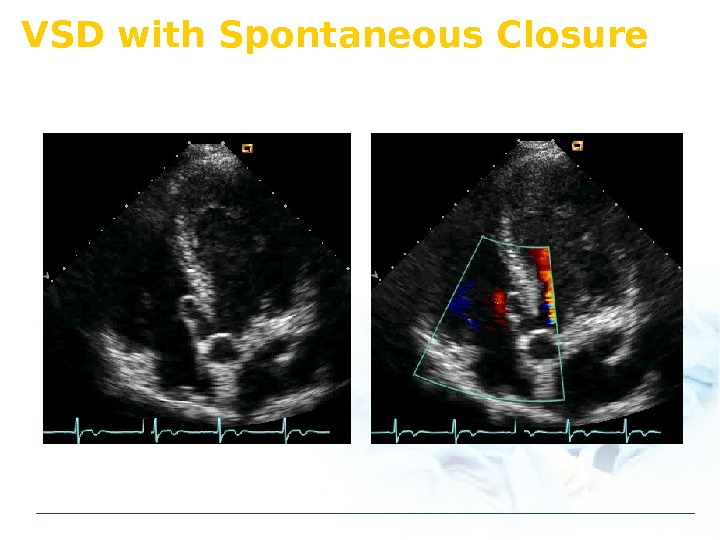
 VSD with Spontaneous Closure
VSD with Spontaneous Closure
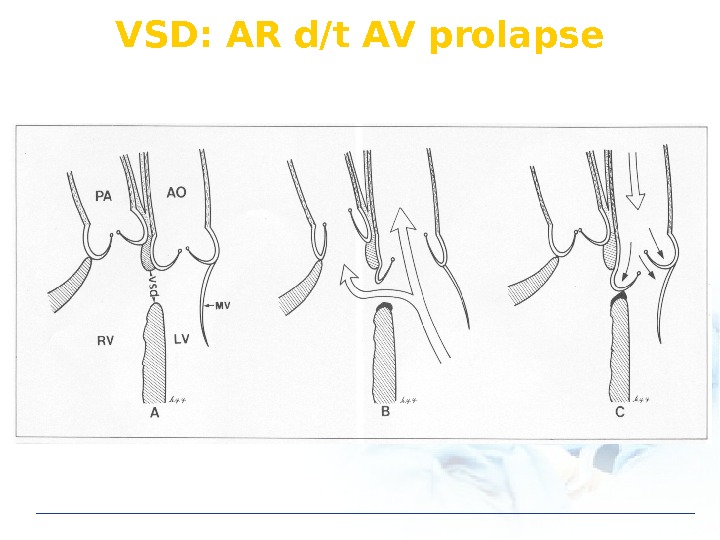
 VSD: AR d/t AV prolapse
VSD: AR d/t AV prolapse
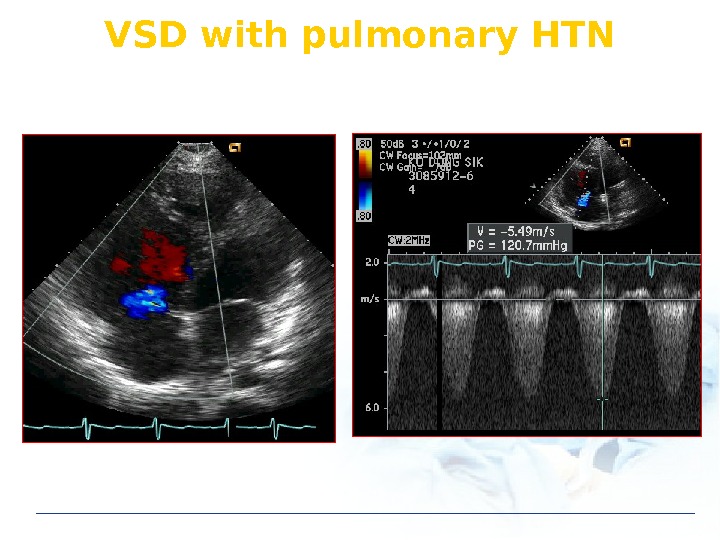
 VSD with pulmonary HTN
VSD with pulmonary HTN
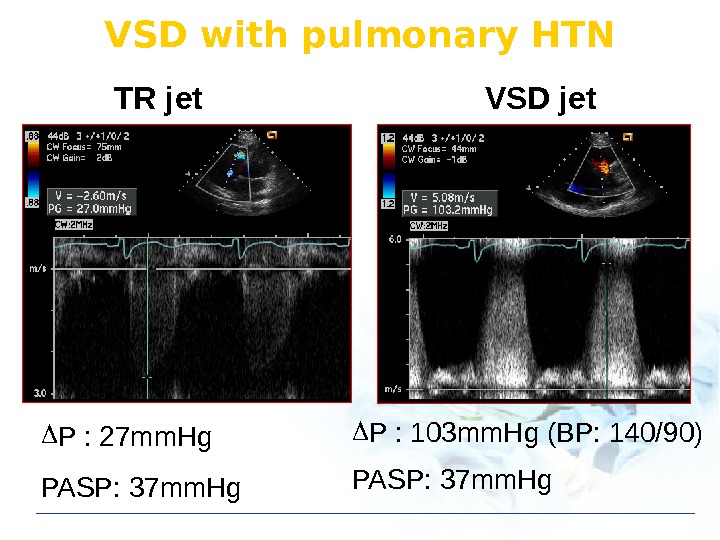
 P : 27 mm. Hg PASP: 37 mm. Hg P : 103 mm. Hg (BP: 140/90) PASP: 37 mm. Hg. TR jet VSD jet. VSD with pulmonary HTN
P : 27 mm. Hg PASP: 37 mm. Hg P : 103 mm. Hg (BP: 140/90) PASP: 37 mm. Hg. TR jet VSD jet. VSD with pulmonary HTN
 VSD: Treatment Medical treatment Endocarditis prophylaxis: not recommended Surgical treatment Indication: Qp/Qs 1. 5 ~ 2. 0 Device closure Contraindication Severe pulmonary hypertension
VSD: Treatment Medical treatment Endocarditis prophylaxis: not recommended Surgical treatment Indication: Qp/Qs 1. 5 ~ 2. 0 Device closure Contraindication Severe pulmonary hypertension
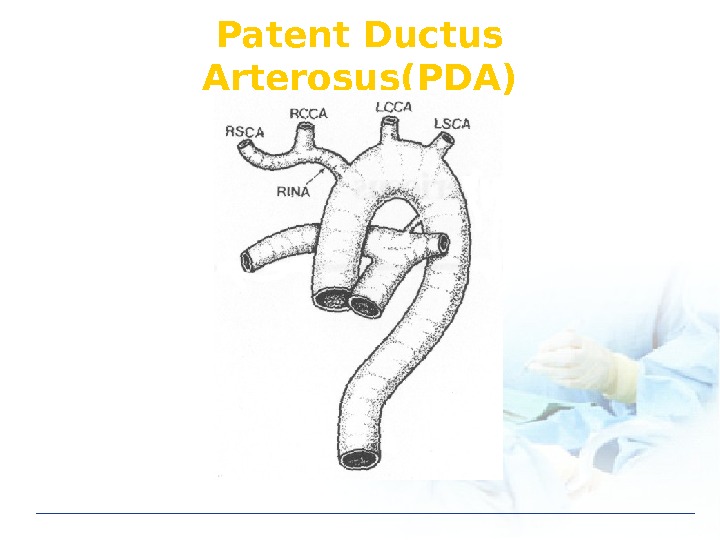
 Patent Ductus Arterosus(PDA)
Patent Ductus Arterosus(PDA)
 P
P
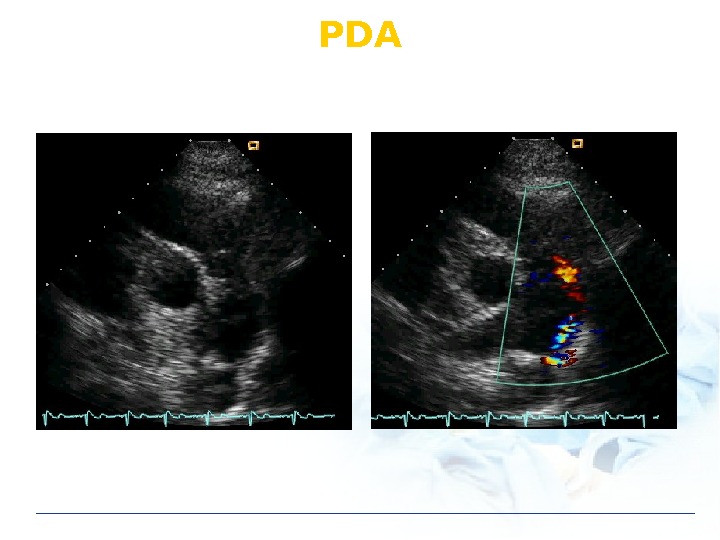
 PDA: Physical Findings Continuous M Wide pulse pressure Differential cyanosis Rt to Lt shunt
PDA: Physical Findings Continuous M Wide pulse pressure Differential cyanosis Rt to Lt shunt
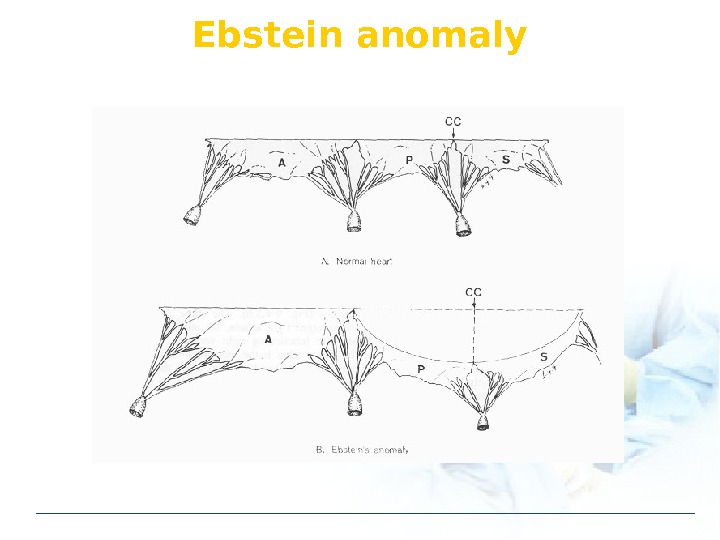
 Ebstein anomaly
Ebstein anomaly
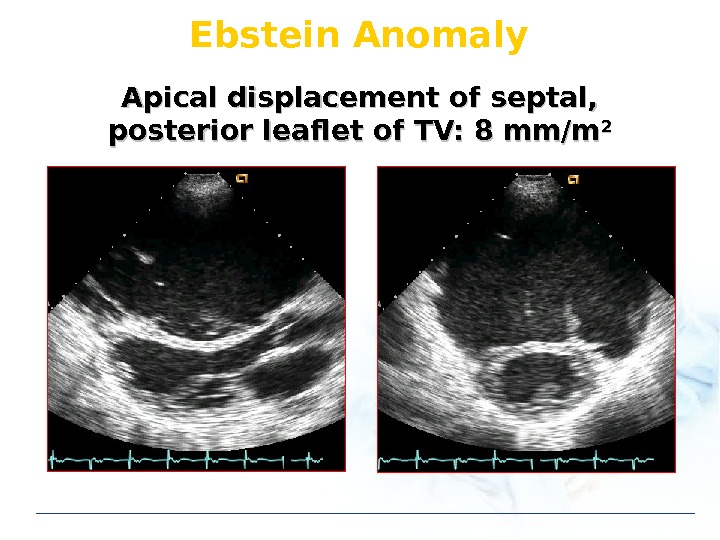
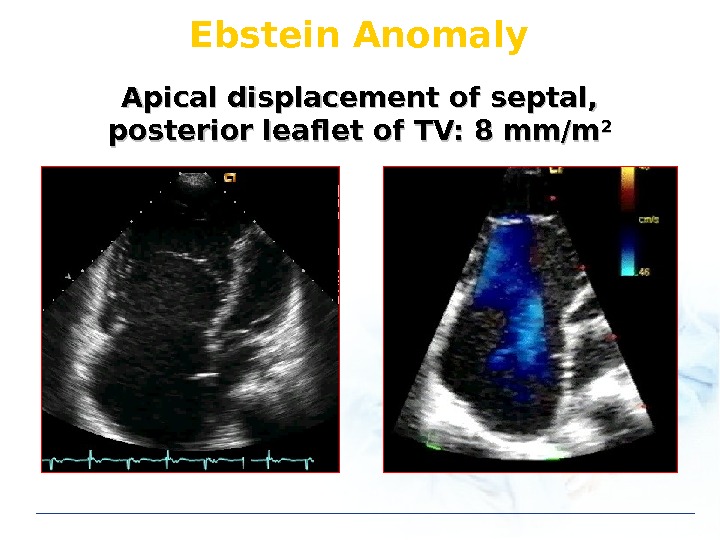
 Ebstein Anomaly Apical displacement of septal, posterior leaflet of TV: 8 mm/m
Ebstein Anomaly Apical displacement of septal, posterior leaflet of TV: 8 mm/m
 Ebstein Anomaly Apical displacement of septal, posterior leaflet of TV: 8 mm/m
Ebstein Anomaly Apical displacement of septal, posterior leaflet of TV: 8 mm/m
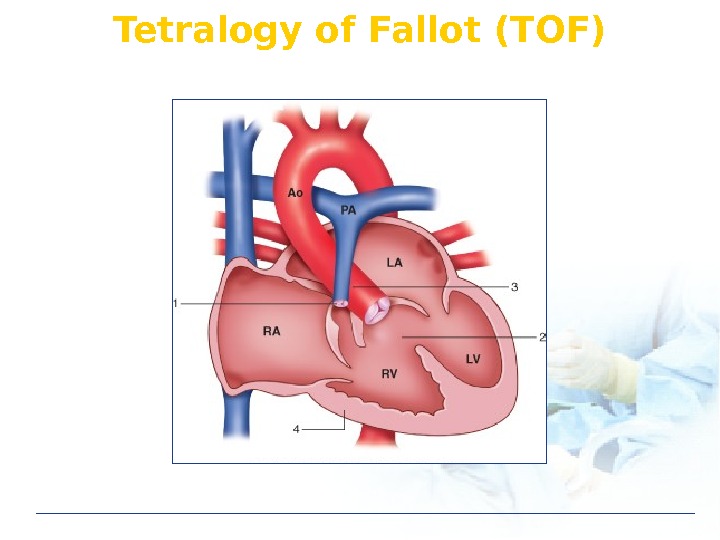
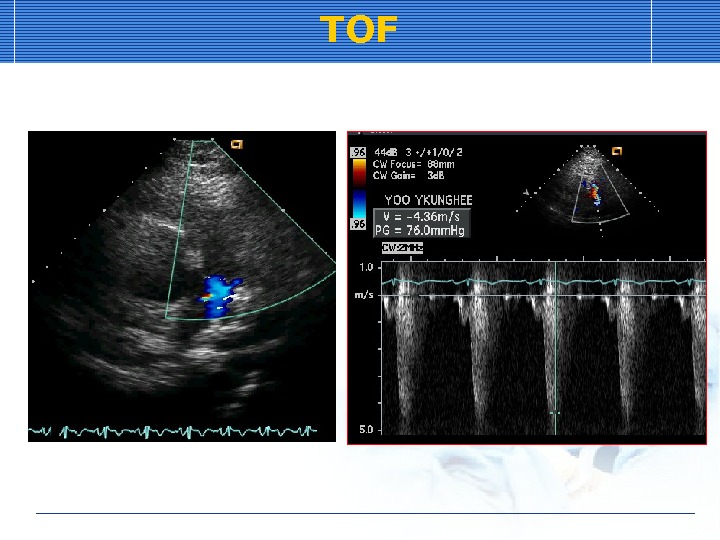
 Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
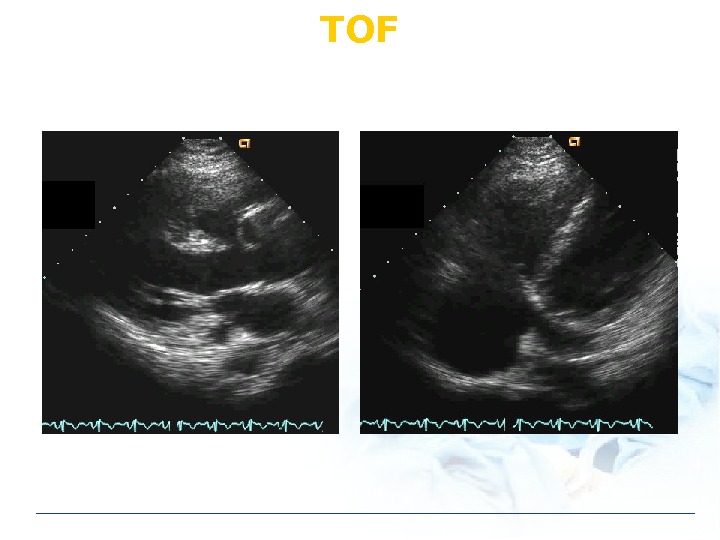
 TOF Ventricular septal defect Pulmonic stenosis Rt ventricular hypertrophy Overriding of aorta
TOF Ventricular septal defect Pulmonic stenosis Rt ventricular hypertrophy Overriding of aorta
 TO
TO
 TO
TO
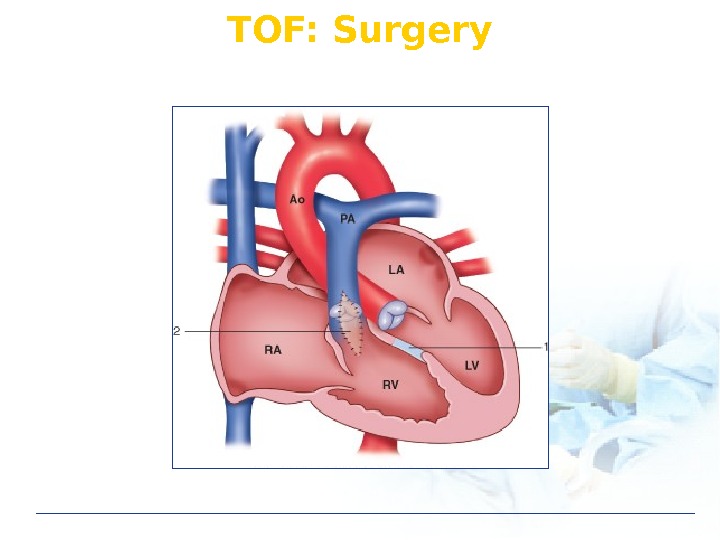
 TOF: Surgery
TOF: Surgery
 Clinical Problems in CHD Heart failure Infective endocarditis Pulmonary hypertension (PHT) Eisenmenger syndrome
Clinical Problems in CHD Heart failure Infective endocarditis Pulmonary hypertension (PHT) Eisenmenger syndrome
 Eisenmenger Syndrome 1897: Vicktor Eisenmenger 32 yo woman with dyspnea, cyanosis Hemoptysis Autopsy: Large VSD 1958: Paul Wood “ Eisenmenger Syndrome”
Eisenmenger Syndrome 1897: Vicktor Eisenmenger 32 yo woman with dyspnea, cyanosis Hemoptysis Autopsy: Large VSD 1958: Paul Wood “ Eisenmenger Syndrome”
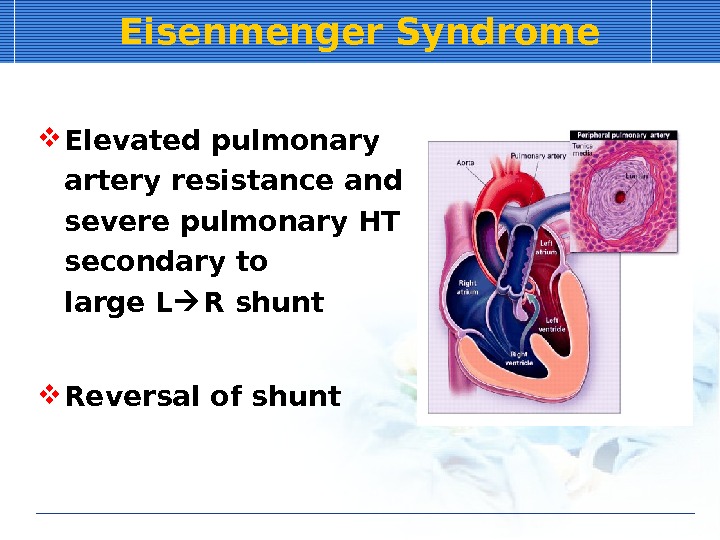
 Eisenmenger Syndrome Elevated pulmonary artery resistance and severe pulmonary HT secondary to large L R shunt Reversal of shunt
Eisenmenger Syndrome Elevated pulmonary artery resistance and severe pulmonary HT secondary to large L R shunt Reversal of shunt
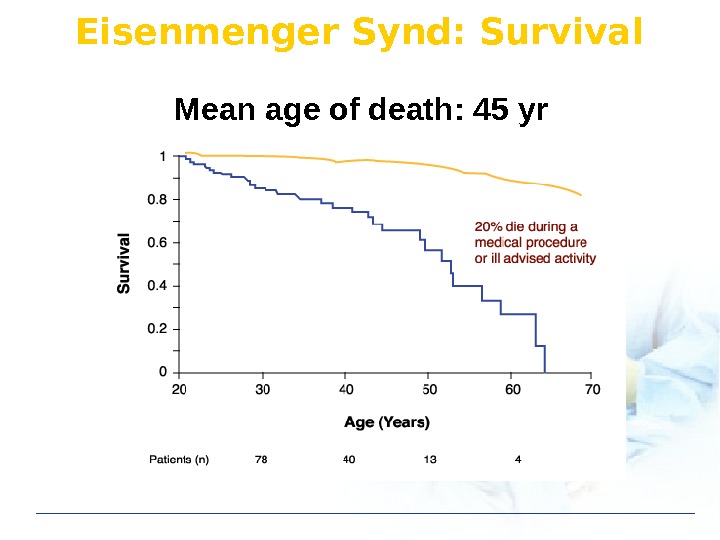
 Eisenmenger Synd: Survival Mean age of death: 45 yr
Eisenmenger Synd: Survival Mean age of death: 45 yr
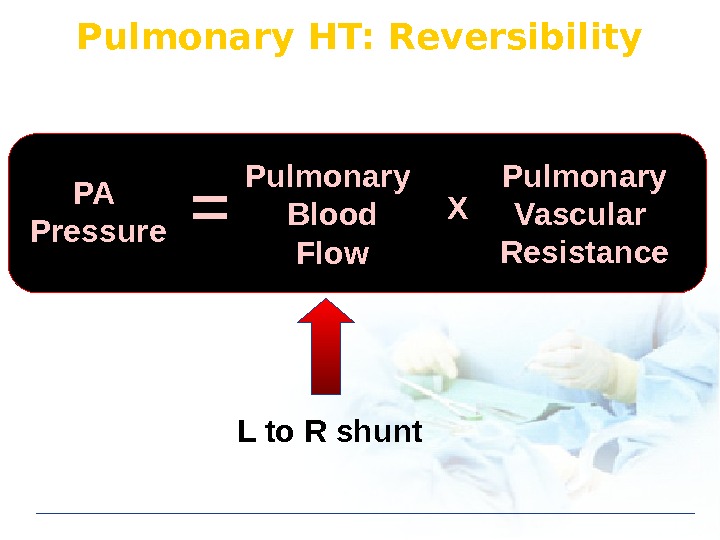
 Pulmonary HT: Reversibility PA Pressure Pulmonary Blood Flow Pulmonary Vascular Resistance. X L to R shunt
Pulmonary HT: Reversibility PA Pressure Pulmonary Blood Flow Pulmonary Vascular Resistance. X L to R shunt
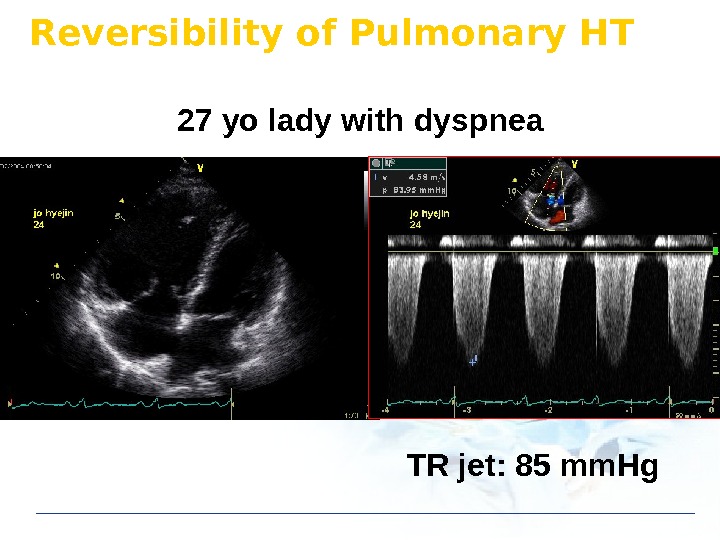
 Reversibility of Pulmonary HT 27 yo lady with dyspnea TR jet: 85 mm. Hg
Reversibility of Pulmonary HT 27 yo lady with dyspnea TR jet: 85 mm. Hg
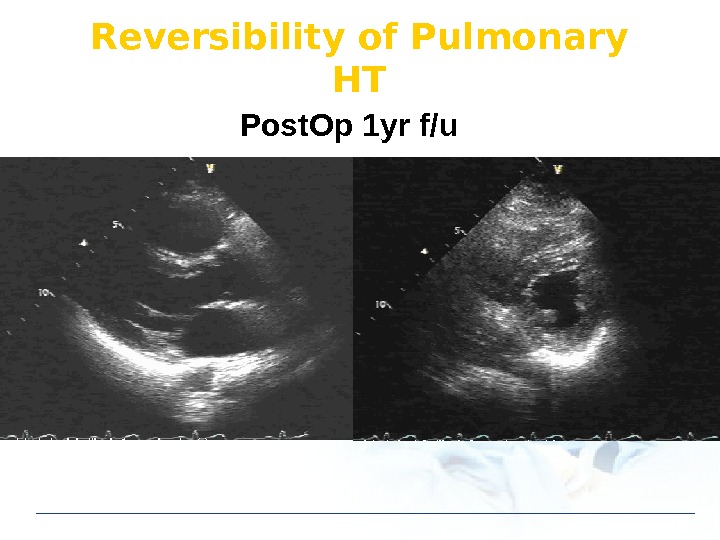
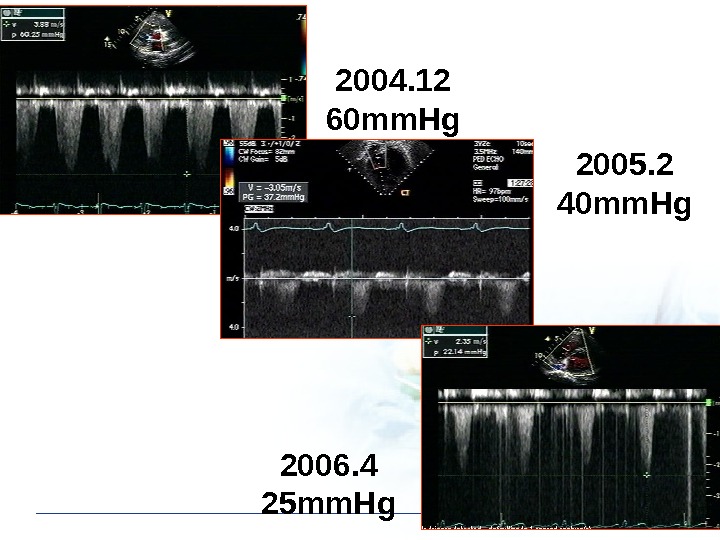
 Reversibility of Pulmonary HT Post. Op 1 yr f/u
Reversibility of Pulmonary HT Post. Op 1 yr f/u
 2004. 12 60 mm. Hg 2005. 2 40 mm. Hg 2006. 4 25 mm. Hg
2004. 12 60 mm. Hg 2005. 2 40 mm. Hg 2006. 4 25 mm. Hg

