543e68c049f1408f5630504d8fe130e0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89
 Congenital and Perinatal Infection
Congenital and Perinatal Infection
 Congenital Infections: Presentation • • Intrauterine growth retardation Microcephaly Hydrocephalus Intracranial calcifications Thrombocytopenia Blueberry muffin skin rash Hepatosplenomegaly, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia • Chorioretinitis • Cataracts
Congenital Infections: Presentation • • Intrauterine growth retardation Microcephaly Hydrocephalus Intracranial calcifications Thrombocytopenia Blueberry muffin skin rash Hepatosplenomegaly, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia • Chorioretinitis • Cataracts
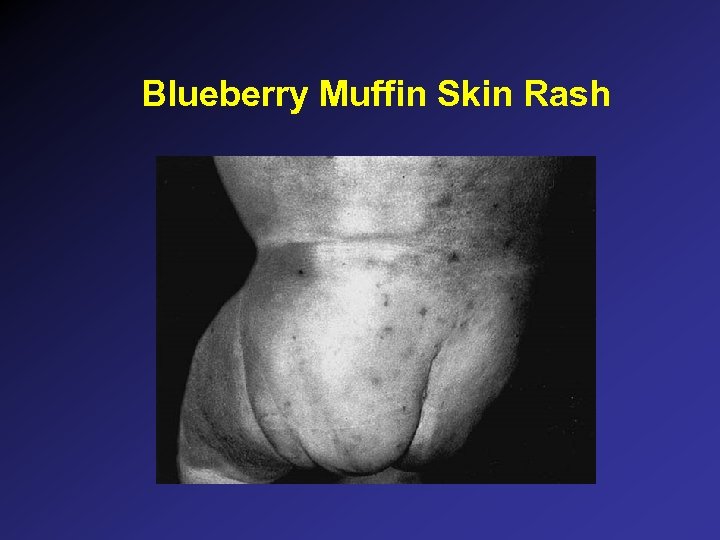 Blueberry Muffin Skin Rash
Blueberry Muffin Skin Rash
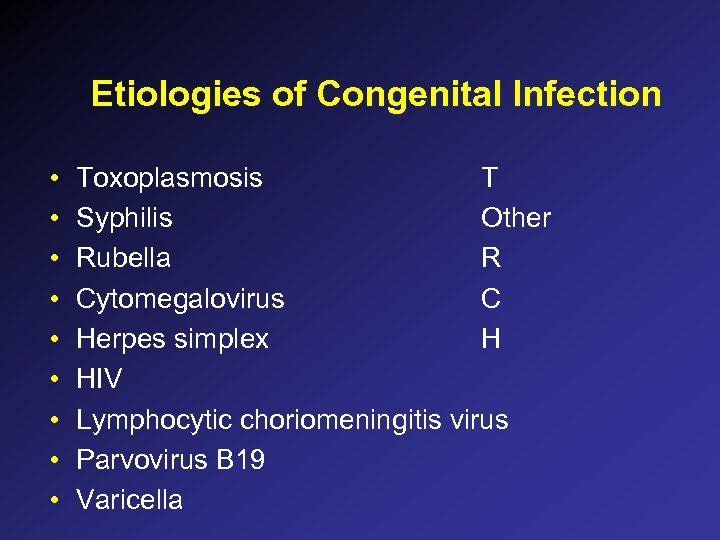 Etiologies of Congenital Infection • • • Toxoplasmosis T Syphilis Other Rubella R Cytomegalovirus C Herpes simplex H HIV Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus Parvovirus B 19 Varicella
Etiologies of Congenital Infection • • • Toxoplasmosis T Syphilis Other Rubella R Cytomegalovirus C Herpes simplex H HIV Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus Parvovirus B 19 Varicella
 Diagnosis of Congenital Infection: General Tests • • CBC Total/direct bilirubin, liver enzymes Total Ig. M Bone radiographs CSF exam Eye exam CNS imaging
Diagnosis of Congenital Infection: General Tests • • CBC Total/direct bilirubin, liver enzymes Total Ig. M Bone radiographs CSF exam Eye exam CNS imaging
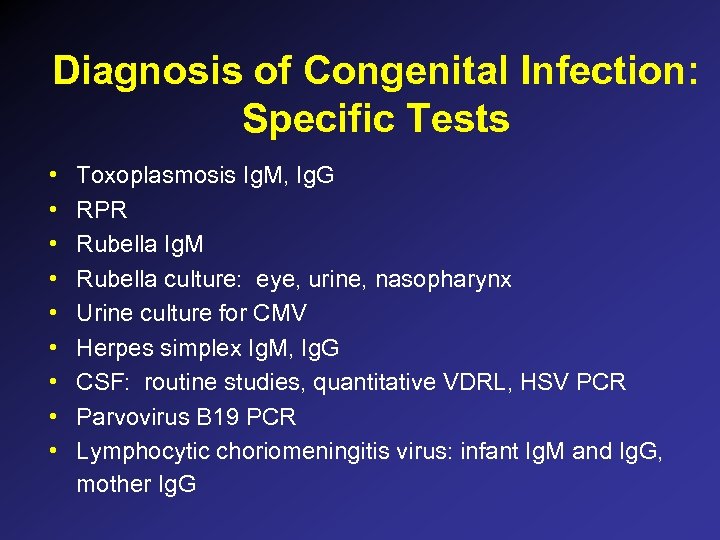 Diagnosis of Congenital Infection: Specific Tests • • • Toxoplasmosis Ig. M, Ig. G RPR Rubella Ig. M Rubella culture: eye, urine, nasopharynx Urine culture for CMV Herpes simplex Ig. M, Ig. G CSF: routine studies, quantitative VDRL, HSV PCR Parvovirus B 19 PCR Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: infant Ig. M and Ig. G, mother Ig. G
Diagnosis of Congenital Infection: Specific Tests • • • Toxoplasmosis Ig. M, Ig. G RPR Rubella Ig. M Rubella culture: eye, urine, nasopharynx Urine culture for CMV Herpes simplex Ig. M, Ig. G CSF: routine studies, quantitative VDRL, HSV PCR Parvovirus B 19 PCR Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: infant Ig. M and Ig. G, mother Ig. G
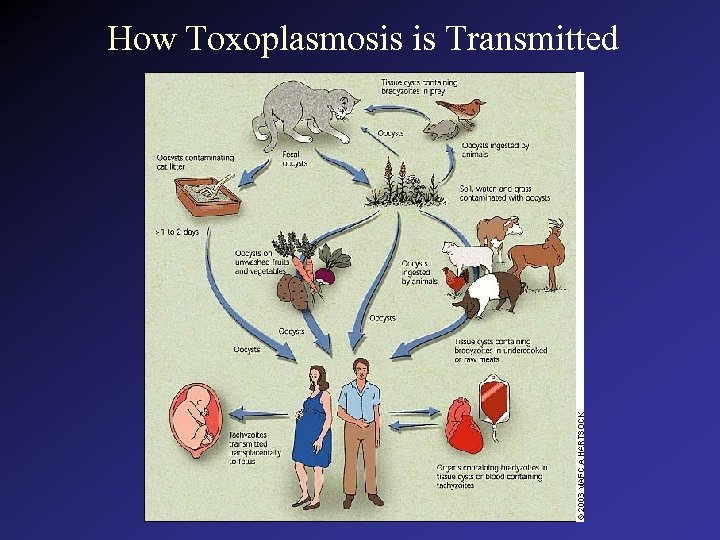 How Toxoplasmosis is Transmitted
How Toxoplasmosis is Transmitted
 Toxoplasmosis • Toxoplasma gondii, protozoan, cats are host • 70 -90% asymptomatic • Symptoms: maculopapular rash, thrombocytopenia, lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, jaundice, hydrocephalus, microcephaly, chorioretinitis, seizures, deafness • Diagnosis: Ig. M, Ig. G, intracranial calcifications • Treatment: pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine
Toxoplasmosis • Toxoplasma gondii, protozoan, cats are host • 70 -90% asymptomatic • Symptoms: maculopapular rash, thrombocytopenia, lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, jaundice, hydrocephalus, microcephaly, chorioretinitis, seizures, deafness • Diagnosis: Ig. M, Ig. G, intracranial calcifications • Treatment: pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine
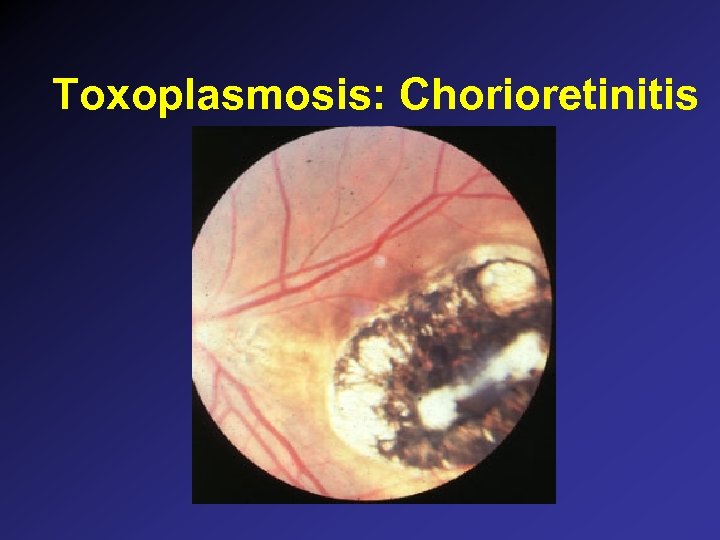 Toxoplasmosis: Chorioretinitis
Toxoplasmosis: Chorioretinitis
 Congenital Syphilis: Symptoms • • Asymptomatic 50% Fever, lymphadenopathy, irritability, failure to thrive Jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly Mucocutaneous: palmar/plantar bullae, maculopapular rash trunk/limbs, mucosal lesions, condylomata lata Anemia (BM arrest, hemolysis), thrombocytopenia, low/high WBCs Meningitis “Snuffles” (serous rhinitis) Bone changes: osteochondritis of humerus, tibia
Congenital Syphilis: Symptoms • • Asymptomatic 50% Fever, lymphadenopathy, irritability, failure to thrive Jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly Mucocutaneous: palmar/plantar bullae, maculopapular rash trunk/limbs, mucosal lesions, condylomata lata Anemia (BM arrest, hemolysis), thrombocytopenia, low/high WBCs Meningitis “Snuffles” (serous rhinitis) Bone changes: osteochondritis of humerus, tibia
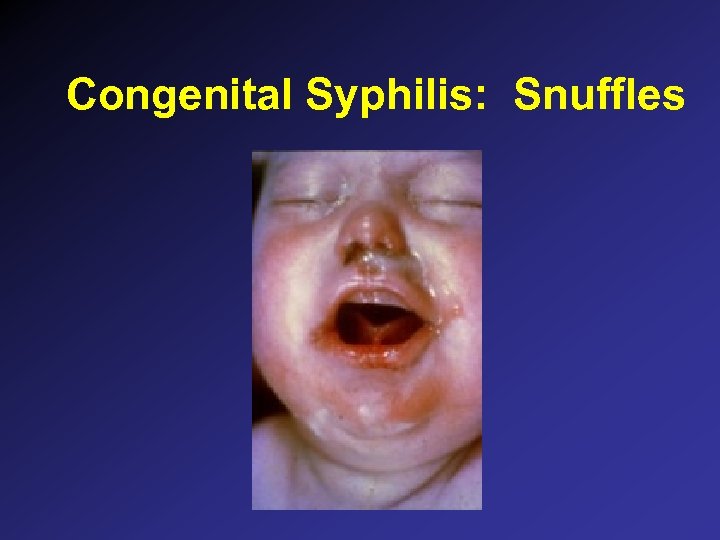 Congenital Syphilis: Snuffles
Congenital Syphilis: Snuffles
 Congenital Syphilis: Diagnostic Studies • • • Quantitative RPR CSF exam: cell count, protein, VDRL CBC, platelets, liver enzymes Long bone radiographs Demonstration of spirochetes: tissue/fluid HIV testing
Congenital Syphilis: Diagnostic Studies • • • Quantitative RPR CSF exam: cell count, protein, VDRL CBC, platelets, liver enzymes Long bone radiographs Demonstration of spirochetes: tissue/fluid HIV testing
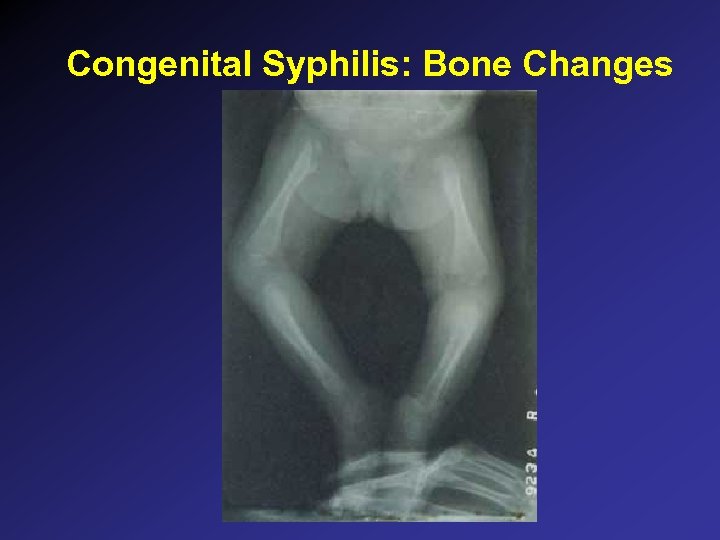 Congenital Syphilis: Bone Changes
Congenital Syphilis: Bone Changes
 Congenital Syphilis: Treatment and Follow-up of the Newborn • Choice of regimens for confirmed or probable congenital syphilis: – Penicillin G 100 -150, 000 unit/kg/day x 10 -14 days (50, 000 unit/kg/dose IV BID x 7 days, then TID for a total of 10 days) – Procaine penicillin G 50, 000 unit/kg/day IM once daily x 10 days (may not adequately treat CNS) – ampicillin is not a suitable alternative • RPR at 3, 6, 12 months • Complicated cases should be referred to specialist
Congenital Syphilis: Treatment and Follow-up of the Newborn • Choice of regimens for confirmed or probable congenital syphilis: – Penicillin G 100 -150, 000 unit/kg/day x 10 -14 days (50, 000 unit/kg/dose IV BID x 7 days, then TID for a total of 10 days) – Procaine penicillin G 50, 000 unit/kg/day IM once daily x 10 days (may not adequately treat CNS) – ampicillin is not a suitable alternative • RPR at 3, 6, 12 months • Complicated cases should be referred to specialist
 Congenital Rubella: Clinical Findings • • Asymptomatic: 50% at birth Sensorineural hearing loss Mental retardation PDA, peripheral pulmonic stenosis Ocular: cataracts, chorioretinitis, glaucoma Microcephaly Blueberry muffin rash Metaphyseal radiolucencies
Congenital Rubella: Clinical Findings • • Asymptomatic: 50% at birth Sensorineural hearing loss Mental retardation PDA, peripheral pulmonic stenosis Ocular: cataracts, chorioretinitis, glaucoma Microcephaly Blueberry muffin rash Metaphyseal radiolucencies
 Congenital Rubella: Vertical Transmission • Transplacental passage of virus • Greatest risk for congenital defects and hearing loss early in the pregnancy • Non-immune pregnant women – do not immunize during pregnancy – no cases of malformation due to rubella vaccine in women immunized during pregnancy – avoid exposure to rubella – post-partum vaccine
Congenital Rubella: Vertical Transmission • Transplacental passage of virus • Greatest risk for congenital defects and hearing loss early in the pregnancy • Non-immune pregnant women – do not immunize during pregnancy – no cases of malformation due to rubella vaccine in women immunized during pregnancy – avoid exposure to rubella – post-partum vaccine
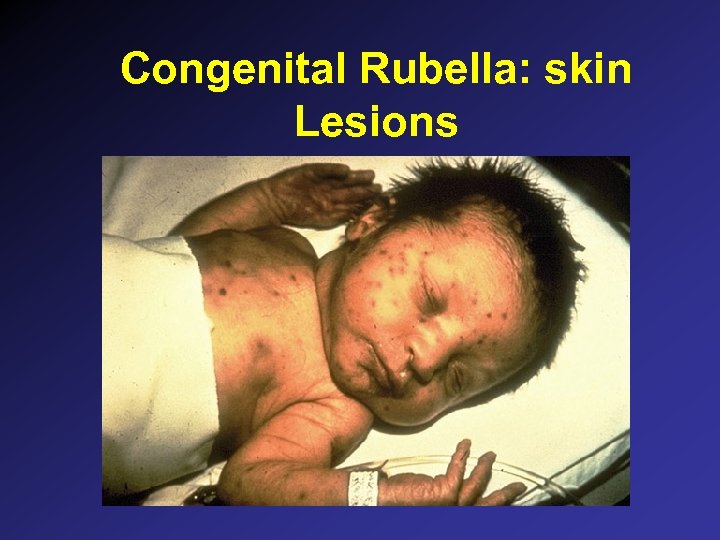 Congenital Rubella: skin Lesions
Congenital Rubella: skin Lesions
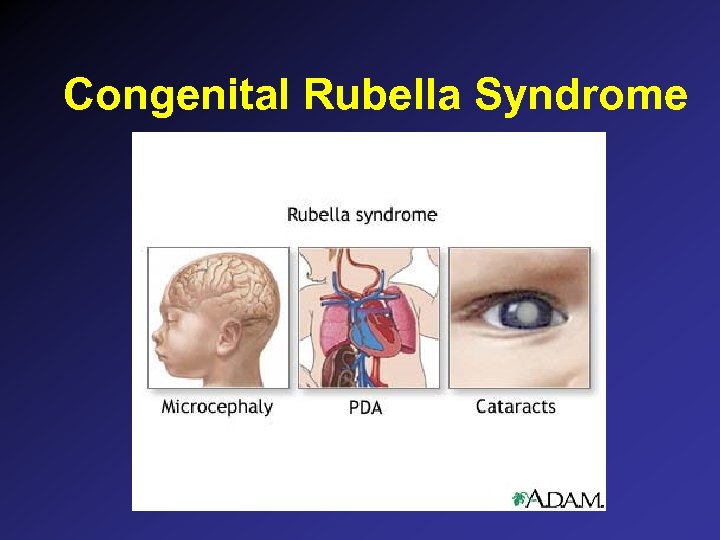 Congenital Rubella Syndrome
Congenital Rubella Syndrome
 Congenital Rubella: Diagnosis and Treatment • Diagnosis: – Rubella specific Ig. M – culture: nasopharynx, blood, urine, CSF, throat • Treatment: supportive
Congenital Rubella: Diagnosis and Treatment • Diagnosis: – Rubella specific Ig. M – culture: nasopharynx, blood, urine, CSF, throat • Treatment: supportive
 Cytomegalovirus: Transmission • Vertical transmission – transplacental and perinatal acquisition – maternal primary and reactivated CMV • Incidence: – 2. 5% – most are asymptomatic - 95%
Cytomegalovirus: Transmission • Vertical transmission – transplacental and perinatal acquisition – maternal primary and reactivated CMV • Incidence: – 2. 5% – most are asymptomatic - 95%
 Cytomegalovirus: Clinical Findings In Symptomatic Infants • Microcephaly, intracranial calcifications • Thrombocytopenia, petechiae, purpura • Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, elevated liver enzymes, liver failure • Interstitial pneumonitis • Hearing loss • Mental retardation • Neurologic impairment, cerebral palsy • Chorioretinitis • Intestinal pseudo-obstruction like illness
Cytomegalovirus: Clinical Findings In Symptomatic Infants • Microcephaly, intracranial calcifications • Thrombocytopenia, petechiae, purpura • Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, elevated liver enzymes, liver failure • Interstitial pneumonitis • Hearing loss • Mental retardation • Neurologic impairment, cerebral palsy • Chorioretinitis • Intestinal pseudo-obstruction like illness
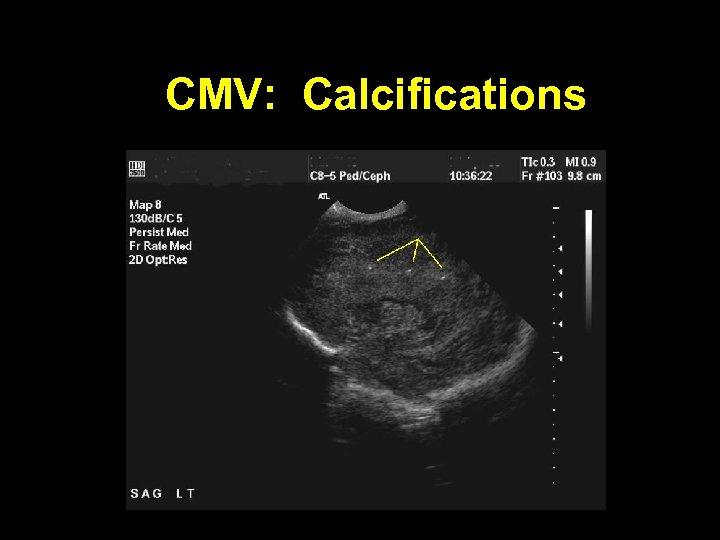 CMV: Calcifications
CMV: Calcifications
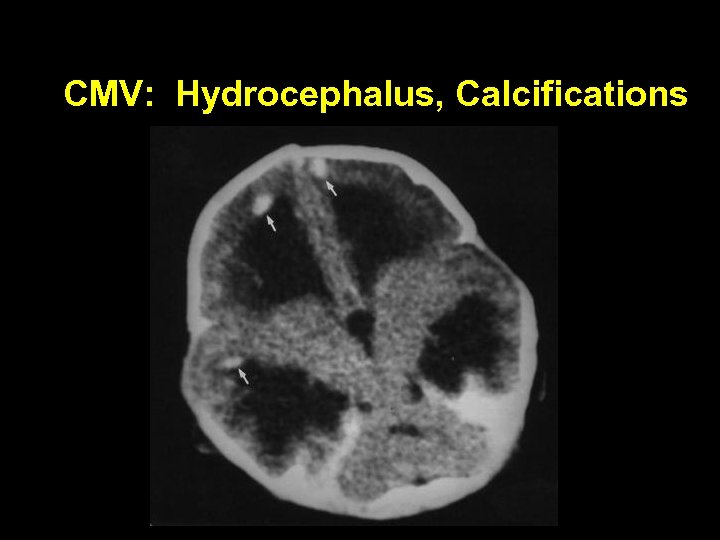 CMV: Hydrocephalus, Calcifications
CMV: Hydrocephalus, Calcifications
 Cytomegalovirus: Diagnosis • CMV titers: – Ig. M, Ig. G – Acute and convalescent • Urine culture for CMV – Excretion may be intermittent • CNS imaging • Eye exam
Cytomegalovirus: Diagnosis • CMV titers: – Ig. M, Ig. G – Acute and convalescent • Urine culture for CMV – Excretion may be intermittent • CNS imaging • Eye exam
 Cytomegalovirus: Treatment • Supportive – Platelet transfusion • Anti-viral treatment – Ganciclovir may reduce sequelae, but of limited efficacy • CMV hyperimmune globulin • Infectious disease consultation
Cytomegalovirus: Treatment • Supportive – Platelet transfusion • Anti-viral treatment – Ganciclovir may reduce sequelae, but of limited efficacy • CMV hyperimmune globulin • Infectious disease consultation
 Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus • Arenavirus, shed by rodents • Symptoms in adults: influenza like illness - fever, malaise, myalgia, retro-orbital headache, photophobia • Congenital infection: hydrocephalus, chorioretinitis, intracranial calcifications, microcephaly, mental retardation, neurologic sequelae, visual loss • Diagnosis: culture, acute and convalescent titers • Treatment: supportive
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus • Arenavirus, shed by rodents • Symptoms in adults: influenza like illness - fever, malaise, myalgia, retro-orbital headache, photophobia • Congenital infection: hydrocephalus, chorioretinitis, intracranial calcifications, microcephaly, mental retardation, neurologic sequelae, visual loss • Diagnosis: culture, acute and convalescent titers • Treatment: supportive
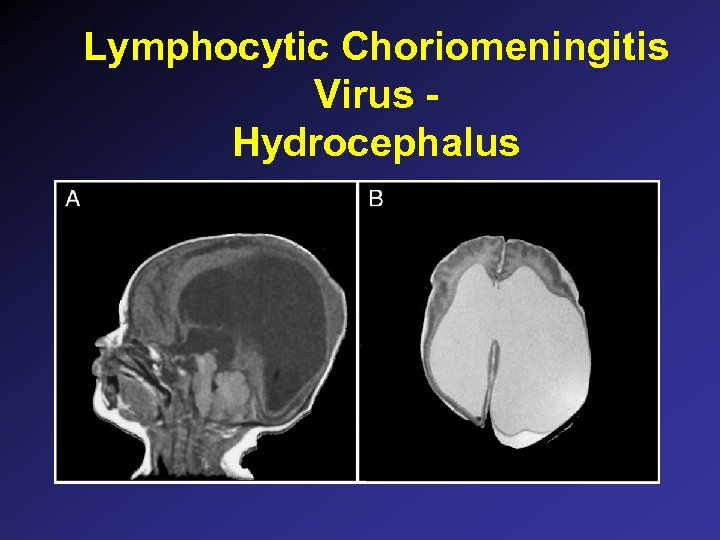 Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Hydrocephalus
Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Hydrocephalus
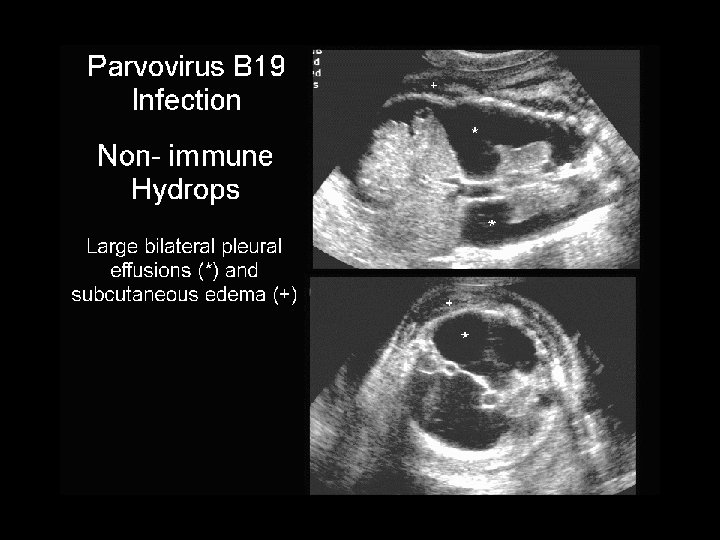
 Parvovirus B 19 • Associated with multiple disorders: – Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) – Aplastic crisis (hemolytic disorders, sickle cell) – Chronic anemia in immunosuppressed – Acute arthritis • Fetal hydrops and death due to anemia – (? )Efficacy of intrauterine transfusion – Spontaneous recovery of fetal hydrops can occur
Parvovirus B 19 • Associated with multiple disorders: – Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) – Aplastic crisis (hemolytic disorders, sickle cell) – Chronic anemia in immunosuppressed – Acute arthritis • Fetal hydrops and death due to anemia – (? )Efficacy of intrauterine transfusion – Spontaneous recovery of fetal hydrops can occur
 Varicella • Maternal varicella before 20 weeks: congenital anomalies reported to be 1 -2% – Cicatricial skin lesions – Limb hypoplasia – CNS, ocular, neurologic • Maternal varicella in last 5 days of pregnancy to 2 days post partum: – VZIG 125 units IM indicated in exposed infants – Skin lesions, pneumonitis, dissemination reported – Add acyclovir if signs or symptoms develop
Varicella • Maternal varicella before 20 weeks: congenital anomalies reported to be 1 -2% – Cicatricial skin lesions – Limb hypoplasia – CNS, ocular, neurologic • Maternal varicella in last 5 days of pregnancy to 2 days post partum: – VZIG 125 units IM indicated in exposed infants – Skin lesions, pneumonitis, dissemination reported – Add acyclovir if signs or symptoms develop
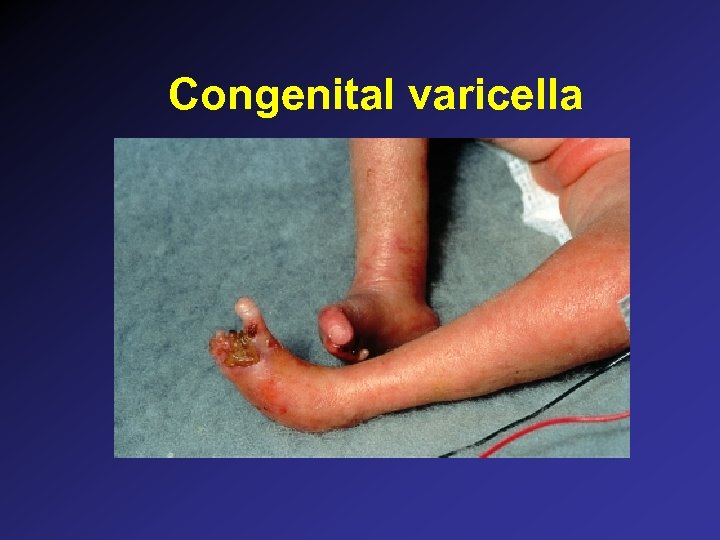 Congenital varicella
Congenital varicella
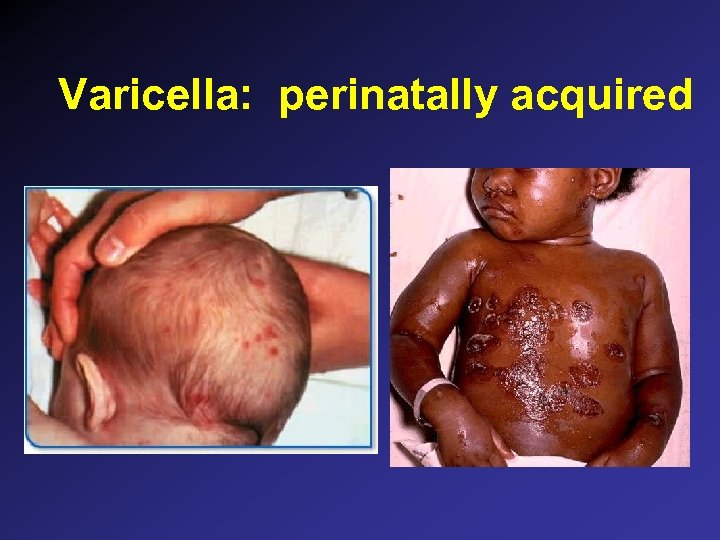 Varicella: perinatally acquired
Varicella: perinatally acquired
 Perinatally Acquired Infection: Basic Principles • Maternal colonization or infection: – Amniotic fluid – Blood – Genital tract secretions – Breast milk – Direct skin contact, environment • Timing and duration of exposure • Interventions, prophylaxis
Perinatally Acquired Infection: Basic Principles • Maternal colonization or infection: – Amniotic fluid – Blood – Genital tract secretions – Breast milk – Direct skin contact, environment • Timing and duration of exposure • Interventions, prophylaxis
 Herpes Simplex: Epidemiology • Vertical transmission most common – – – perinatal exposure with ROM and delivery 50% risk if infant exposed to primary maternal HSV <1 -5% risk if infant exposed to recurrent maternal HSV increased risk in premature infants (reduced Ig. G) C-section reduces risk if ROM < 4 -6 hour • Horizontal transmission reported – nursery outbreaks • Time of onset: 2 days - several weeks
Herpes Simplex: Epidemiology • Vertical transmission most common – – – perinatal exposure with ROM and delivery 50% risk if infant exposed to primary maternal HSV <1 -5% risk if infant exposed to recurrent maternal HSV increased risk in premature infants (reduced Ig. G) C-section reduces risk if ROM < 4 -6 hour • Horizontal transmission reported – nursery outbreaks • Time of onset: 2 days - several weeks
 Herpes Simplex: Clinical Presentation • • Fever skin vesicles encephalitis seizures respiratory distress, pneumonia hepatitis septic shock like syndrome
Herpes Simplex: Clinical Presentation • • Fever skin vesicles encephalitis seizures respiratory distress, pneumonia hepatitis septic shock like syndrome
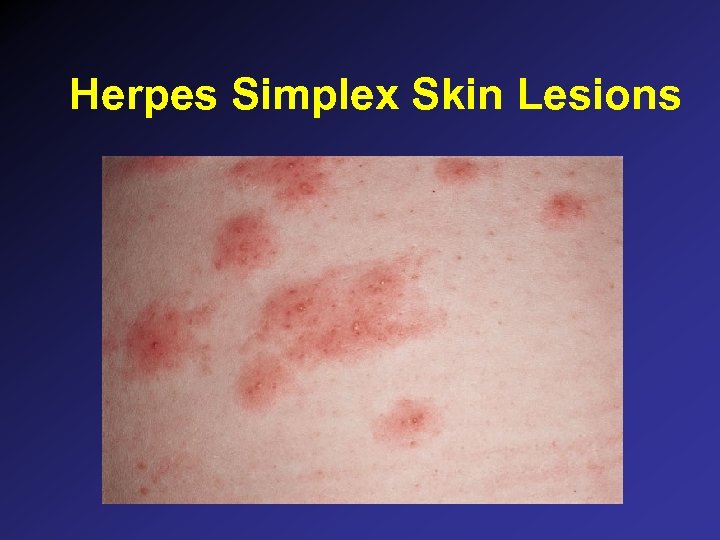 Herpes Simplex Skin Lesions
Herpes Simplex Skin Lesions
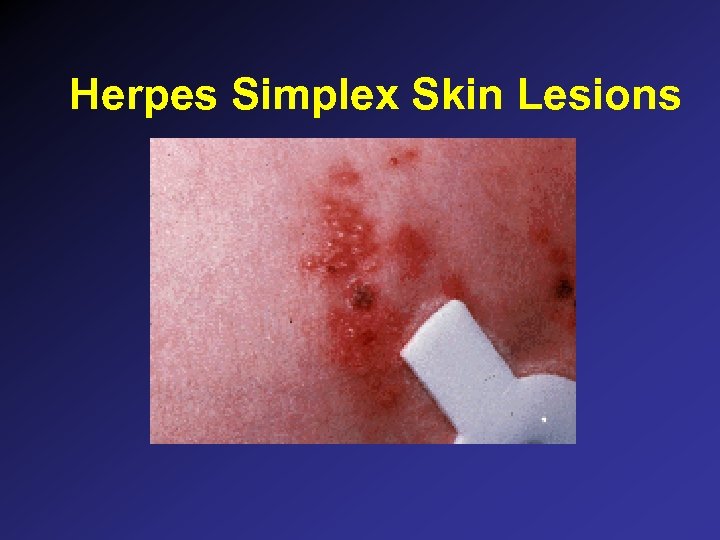 Herpes Simplex Skin Lesions
Herpes Simplex Skin Lesions
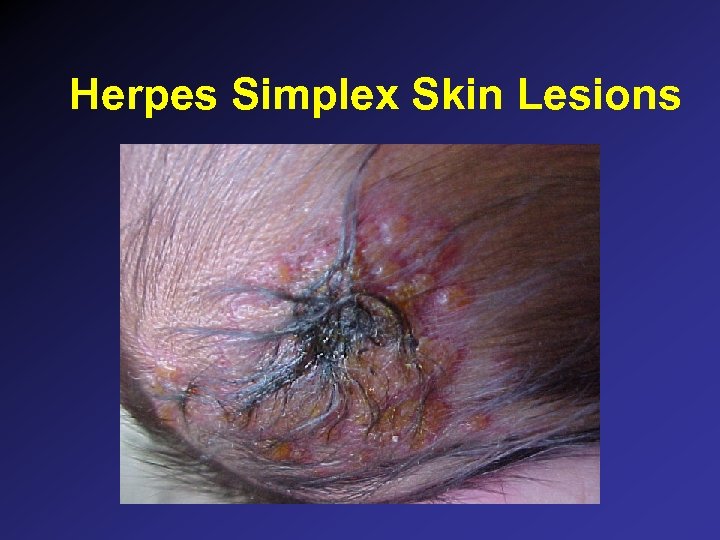 Herpes Simplex Skin Lesions
Herpes Simplex Skin Lesions
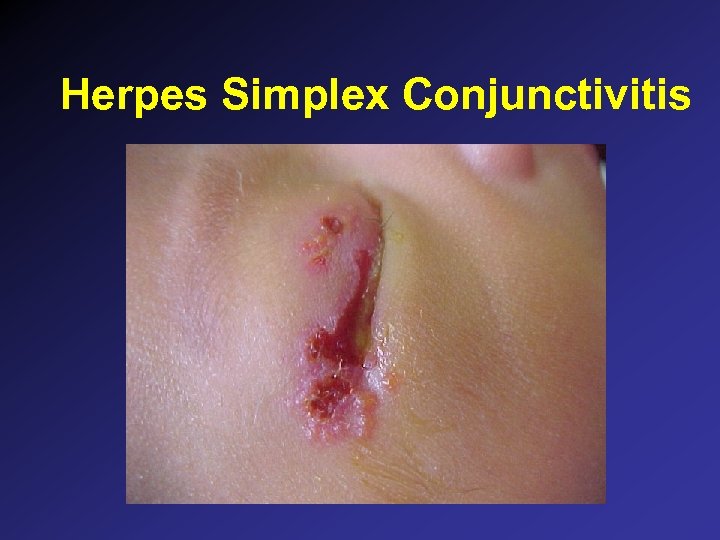 Herpes Simplex Conjunctivitis
Herpes Simplex Conjunctivitis
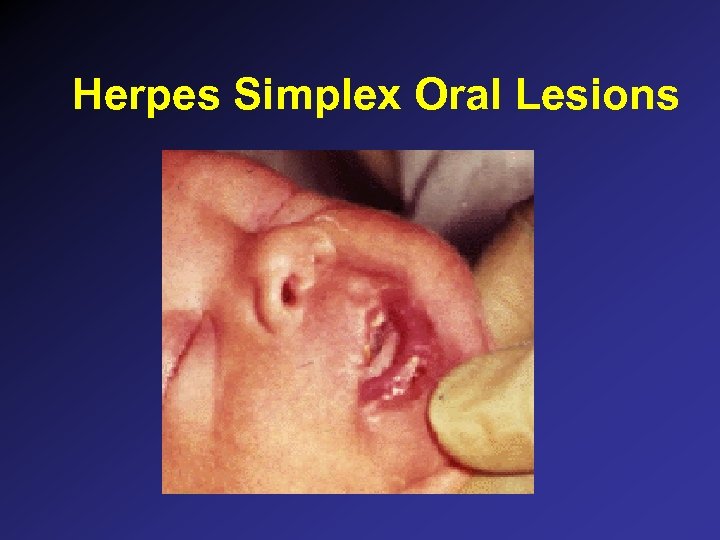 Herpes Simplex Oral Lesions
Herpes Simplex Oral Lesions
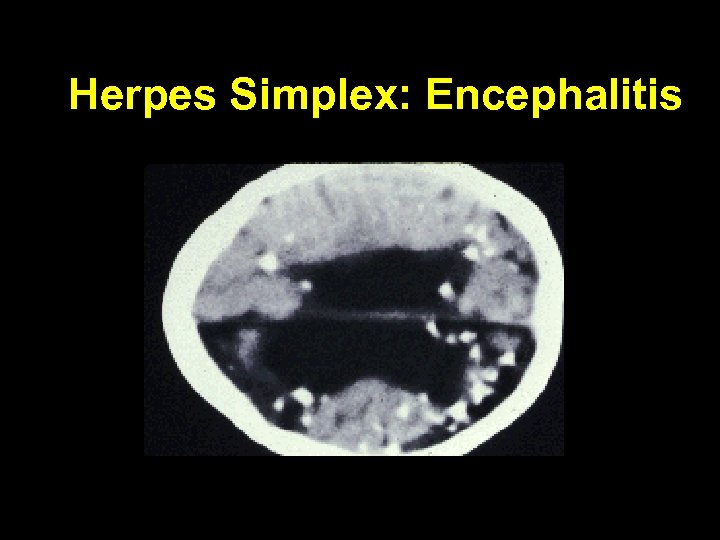 Herpes Simplex: Encephalitis
Herpes Simplex: Encephalitis
 Neonatal Herpes Simplex: Treatment • Acyclovir 60 mg/kg/day divided q 8 hr x 14 days (21 days for systemic or CNS) • Ocular HSV: add ophthalmic trifluridine, iododeoxyuridine, or vidarabine • Supportive: control seizures, respiratory and cardiovascular support • Reduce cutaneous or ocular spread • High mortality rate for CNS or systemic HSV, even with treatment
Neonatal Herpes Simplex: Treatment • Acyclovir 60 mg/kg/day divided q 8 hr x 14 days (21 days for systemic or CNS) • Ocular HSV: add ophthalmic trifluridine, iododeoxyuridine, or vidarabine • Supportive: control seizures, respiratory and cardiovascular support • Reduce cutaneous or ocular spread • High mortality rate for CNS or systemic HSV, even with treatment
 Management of HSV Exposure • Recurrent maternal HSV – risk is very low; observation only • Primary maternal disease – risk is high – viral throat culture at 24 -48 hr of age – empiric therapy is controversial • Premature infant - risk may be greater
Management of HSV Exposure • Recurrent maternal HSV – risk is very low; observation only • Primary maternal disease – risk is high – viral throat culture at 24 -48 hr of age – empiric therapy is controversial • Premature infant - risk may be greater
 HIV • Transmission is vertical – In utero, intrapartum (most common), and postnatal (breastfeeding) • Risk factors
HIV • Transmission is vertical – In utero, intrapartum (most common), and postnatal (breastfeeding) • Risk factors
 Zidovudine (AZT) for reduction of perinatal HIV transmission • pregnancy: begin 200 mg PO 3 x/day at 14 -34 wk, continue throughout pregnancy • intrapartum: 2 mg/kg x 1 h, then 1 mg/kg/h IV until delivery • newborn: 2 mg/kg 4 x/day PO begining at 8 -12 h of age until 6 weeks of age • referral to pediatric HIV center
Zidovudine (AZT) for reduction of perinatal HIV transmission • pregnancy: begin 200 mg PO 3 x/day at 14 -34 wk, continue throughout pregnancy • intrapartum: 2 mg/kg x 1 h, then 1 mg/kg/h IV until delivery • newborn: 2 mg/kg 4 x/day PO begining at 8 -12 h of age until 6 weeks of age • referral to pediatric HIV center
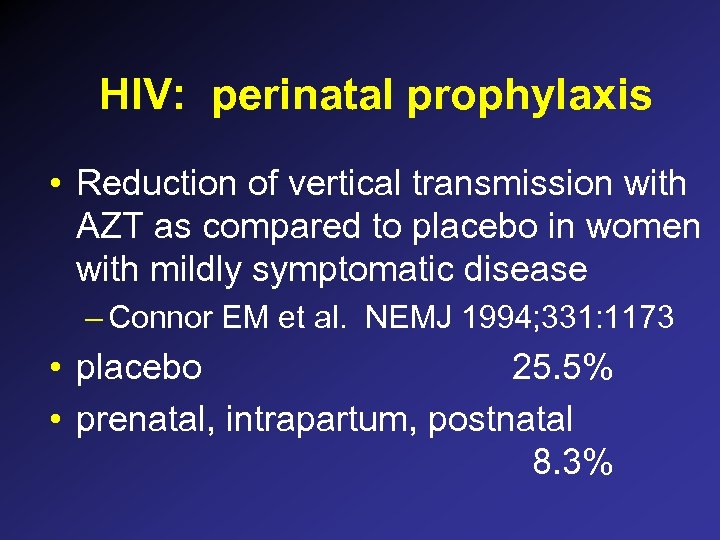 HIV: perinatal prophylaxis • Reduction of vertical transmission with AZT as compared to placebo in women with mildly symptomatic disease – Connor EM et al. NEMJ 1994; 331: 1173 • placebo 25. 5% • prenatal, intrapartum, postnatal 8. 3%
HIV: perinatal prophylaxis • Reduction of vertical transmission with AZT as compared to placebo in women with mildly symptomatic disease – Connor EM et al. NEMJ 1994; 331: 1173 • placebo 25. 5% • prenatal, intrapartum, postnatal 8. 3%
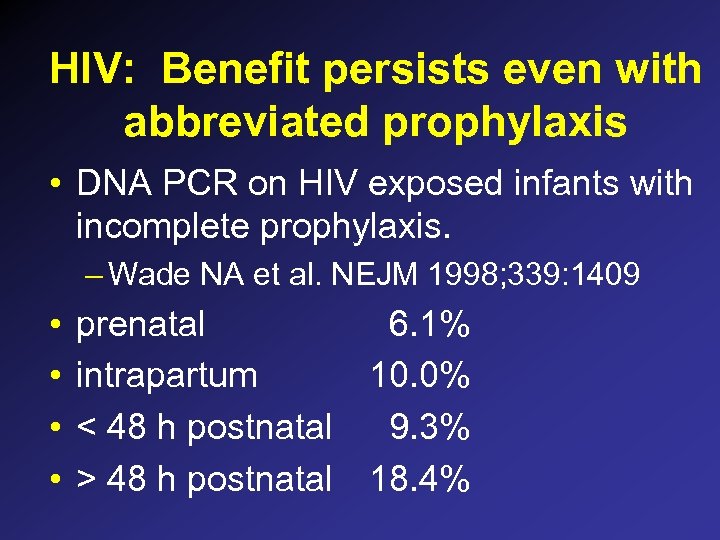 HIV: Benefit persists even with abbreviated prophylaxis • DNA PCR on HIV exposed infants with incomplete prophylaxis. – Wade NA et al. NEJM 1998; 339: 1409 • • prenatal 6. 1% intrapartum 10. 0% < 48 h postnatal 9. 3% > 48 h postnatal 18. 4%
HIV: Benefit persists even with abbreviated prophylaxis • DNA PCR on HIV exposed infants with incomplete prophylaxis. – Wade NA et al. NEJM 1998; 339: 1409 • • prenatal 6. 1% intrapartum 10. 0% < 48 h postnatal 9. 3% > 48 h postnatal 18. 4%
 HIV: mode of delivery • Metanalysis of 15 NA/European studies • 8533 mother-child pairs • adjusted for antiretroviral Rx, maternal stage of disease and birth weight • elective C-section: prior to labor or ROM • International Perinatal HIV Group – NEJM 1999; 340: 977
HIV: mode of delivery • Metanalysis of 15 NA/European studies • 8533 mother-child pairs • adjusted for antiretroviral Rx, maternal stage of disease and birth weight • elective C-section: prior to labor or ROM • International Perinatal HIV Group – NEJM 1999; 340: 977
 HIV: mode of delivery • • • other mode (vag, non-elective C/S) elective C-section other mode, complete retroviral Rx elective C/S, complete retroviral Rx International Perinatal HIV Group – NEJM 1999; 340: 977 16. 7% 8. 4% 7. 3% 2. 0%
HIV: mode of delivery • • • other mode (vag, non-elective C/S) elective C-section other mode, complete retroviral Rx elective C/S, complete retroviral Rx International Perinatal HIV Group – NEJM 1999; 340: 977 16. 7% 8. 4% 7. 3% 2. 0%
 Hepatitis B • Vertical transmission – Blood exposure during labor and delivery – In utero transmission: < 2% of cases • Maternal HBs. Ag+ HBe. Ag+ 70 -80% • Maternal HBs. Ag+ HBe. Ag 5 -20% • Chronic carrier, hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatitis B • Vertical transmission – Blood exposure during labor and delivery – In utero transmission: < 2% of cases • Maternal HBs. Ag+ HBe. Ag+ 70 -80% • Maternal HBs. Ag+ HBe. Ag 5 -20% • Chronic carrier, hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma
 Infant born to HBs. Ag + mother: management • • Avoid skin to skin until infant bathed Hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hr HBIG given at separate site Complete standard HBV schedule – Preterm < 2 kg: 1 st dose not counted, total 4 doses • HBs. Ag and anti-HBs. Ag at 9 -15 months of age • Breast feeding not precluded: controversial
Infant born to HBs. Ag + mother: management • • Avoid skin to skin until infant bathed Hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hr HBIG given at separate site Complete standard HBV schedule – Preterm < 2 kg: 1 st dose not counted, total 4 doses • HBs. Ag and anti-HBs. Ag at 9 -15 months of age • Breast feeding not precluded: controversial
 Infant born to HBs. Ag unknown mother: management • • Avoid skin to skin until infant bathed HBV within 12 hours If mother HBs. Ag +, HBIG within 7 days Premature infant < 2 kg: give both HBV and HBIG within 12 hours, if unable to determine maternal status by 12 hours. • Complete standard HBV schedule – Preterm < 2 kg: 1 st dose not counted, total 4 doses
Infant born to HBs. Ag unknown mother: management • • Avoid skin to skin until infant bathed HBV within 12 hours If mother HBs. Ag +, HBIG within 7 days Premature infant < 2 kg: give both HBV and HBIG within 12 hours, if unable to determine maternal status by 12 hours. • Complete standard HBV schedule – Preterm < 2 kg: 1 st dose not counted, total 4 doses
 Hepatitis C • Prevalence in adults in U. S. - 1. 8% • Vertical transmission - 5% of infants born to mothers with hepatitis C • No specific preventive measures • Breast feeding is allowed – Transmission not proven – Cracked or bleeding nipples: may be risk • Test infant at 18 months: anti-HCV – Earlier testing with HCV RNA PCR
Hepatitis C • Prevalence in adults in U. S. - 1. 8% • Vertical transmission - 5% of infants born to mothers with hepatitis C • No specific preventive measures • Breast feeding is allowed – Transmission not proven – Cracked or bleeding nipples: may be risk • Test infant at 18 months: anti-HCV – Earlier testing with HCV RNA PCR
 Enterovirus • • • Commonly occurs in summer and fall seasons History of maternal illness late in pregnancy Perinatal vertical transmission from mother to infant Outbreaks reported in NICU’s Presents in the first 2 weeks Neonatal symptoms: fever, lethargy, poor feeding, respiratory distress • Clinical syndromes: aseptic meningitis, “sepsis, ” cardiomyopathy, hepatitis, pneumonia, pulmonary hypertension
Enterovirus • • • Commonly occurs in summer and fall seasons History of maternal illness late in pregnancy Perinatal vertical transmission from mother to infant Outbreaks reported in NICU’s Presents in the first 2 weeks Neonatal symptoms: fever, lethargy, poor feeding, respiratory distress • Clinical syndromes: aseptic meningitis, “sepsis, ” cardiomyopathy, hepatitis, pneumonia, pulmonary hypertension
 Etiology of Early Onset Sepsis • Group B Strep (GBS): 67% • Non-GBS organisms – E Coli: 25% – Others: 8% • Enterococcus, staph aureus, strep pneumonia, candida.
Etiology of Early Onset Sepsis • Group B Strep (GBS): 67% • Non-GBS organisms – E Coli: 25% – Others: 8% • Enterococcus, staph aureus, strep pneumonia, candida.
 Epidemiology of Group B Strep • Maternal Colonization: 15 -40% • 50 -75% of newborns born to colonized mothers become colonized during birth • Attack Rate (# infected nb/# colonized mothers): 1 -2% • Neonatal Early Onset Disease: – 1 -4 per 1000
Epidemiology of Group B Strep • Maternal Colonization: 15 -40% • 50 -75% of newborns born to colonized mothers become colonized during birth • Attack Rate (# infected nb/# colonized mothers): 1 -2% • Neonatal Early Onset Disease: – 1 -4 per 1000
 Risk Factors for Neonatal Infection in Colonized Mothers • • Prolonged rupture of membranes > 18 hr Premature birth esp < 34 weeks Intrapartum fever African-American Race Maternal age < 20 yr Previous birth of GBS infected infant Heavy maternal colonization, e. g. bacteruria Low levels of anti-GBS capsular antibody
Risk Factors for Neonatal Infection in Colonized Mothers • • Prolonged rupture of membranes > 18 hr Premature birth esp < 34 weeks Intrapartum fever African-American Race Maternal age < 20 yr Previous birth of GBS infected infant Heavy maternal colonization, e. g. bacteruria Low levels of anti-GBS capsular antibody
 Maternal GBS Disease • • UTI amnionitis endometritis wound infection
Maternal GBS Disease • • UTI amnionitis endometritis wound infection
 Neonatal GBS Disease • Early Onset Disease – symptomatic infection occurring during 1 st week – results from vertical transmission during labor or delivery – constitutes 80% of neonatal GBS infection – pneumonia and overwhelming sepsis more common
Neonatal GBS Disease • Early Onset Disease – symptomatic infection occurring during 1 st week – results from vertical transmission during labor or delivery – constitutes 80% of neonatal GBS infection – pneumonia and overwhelming sepsis more common
 Prevention of early onset group B strep • GBS is sensitive to Ampicillin and Penicillin • Failure of prenatal administration of Amp/PCN to eradicate colonization • Failure of immediate postnatal treatment with Penicillin – Lack of treatment efficacy in several studies – increased morbidity from Penicillin resistant organisms in one study
Prevention of early onset group B strep • GBS is sensitive to Ampicillin and Penicillin • Failure of prenatal administration of Amp/PCN to eradicate colonization • Failure of immediate postnatal treatment with Penicillin – Lack of treatment efficacy in several studies – increased morbidity from Penicillin resistant organisms in one study
 Prevention of early onset group B strep • Only success at maternal treatment is intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis – Boyer and Gottof, 1986 • • • Reduces maternal colonization Reduces neonatal colonization Reduces attack rate of GBS by 80 -95% – Allen et al, meta-analysis, 1993: 30 fold decrease in neonatal infection
Prevention of early onset group B strep • Only success at maternal treatment is intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis – Boyer and Gottof, 1986 • • • Reduces maternal colonization Reduces neonatal colonization Reduces attack rate of GBS by 80 -95% – Allen et al, meta-analysis, 1993: 30 fold decrease in neonatal infection
 Strategies to Reduce GBS Disease • AAP, 1992 – 26 -28 week cultures of all pregnant women – intrapartum prophylaxis for: • • • positive cultures ROM > 12 hr onset of labor or ROM < 37 wks intrapartum fever previous birth of an infant with GBS disease – Will treat approx 3. 4% of all mothers, to prevent 50% of Early Onset GBS disease
Strategies to Reduce GBS Disease • AAP, 1992 – 26 -28 week cultures of all pregnant women – intrapartum prophylaxis for: • • • positive cultures ROM > 12 hr onset of labor or ROM < 37 wks intrapartum fever previous birth of an infant with GBS disease – Will treat approx 3. 4% of all mothers, to prevent 50% of Early Onset GBS disease
 Strategies to Reduce GBS Disease • ACOG – Prophylaxis for: • • • preterm labor < 37 wks PROM < 37 wks ROM > 18 hr previous child with GBS disease maternal fever during labor – Note: cultures not included in decision – Will treat approximately 18. 3% of mothers and prevent 68. 8% of early onset GBS disease
Strategies to Reduce GBS Disease • ACOG – Prophylaxis for: • • • preterm labor < 37 wks PROM < 37 wks ROM > 18 hr previous child with GBS disease maternal fever during labor – Note: cultures not included in decision – Will treat approximately 18. 3% of mothers and prevent 68. 8% of early onset GBS disease
 Risks of Maternal Treatment Why not treat all mothers? • Fatal anaphylaxis to Ampicillin: 1 per 100, 000 • Pseudomembraneous enterocolitis (Clostridium dificile) • incidence of other less severe maternal reactions • risk of antibiotic resistance among GBS or other organisms
Risks of Maternal Treatment Why not treat all mothers? • Fatal anaphylaxis to Ampicillin: 1 per 100, 000 • Pseudomembraneous enterocolitis (Clostridium dificile) • incidence of other less severe maternal reactions • risk of antibiotic resistance among GBS or other organisms
 Failures of GBS Prophylaxis • Late administration of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis (< 4 hr before birth) • Inadequate dosing • Failure to recognize mothers at risk
Failures of GBS Prophylaxis • Late administration of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis (< 4 hr before birth) • Inadequate dosing • Failure to recognize mothers at risk
 Prophylaxis Failures • Importance of hospital guidelines • Surveillance study, 1997 – 165 hospitals surveyed – 96 (58%) had established departmental guidelines for maternal prophylaxis – Lower early onset GBS incidence in hospitals with guidelines • . 58/1000 vs 1. 29/1000 (p=. 006) Factor SE, et al, OB GYN 2000; 95: 377 -82)
Prophylaxis Failures • Importance of hospital guidelines • Surveillance study, 1997 – 165 hospitals surveyed – 96 (58%) had established departmental guidelines for maternal prophylaxis – Lower early onset GBS incidence in hospitals with guidelines • . 58/1000 vs 1. 29/1000 (p=. 006) Factor SE, et al, OB GYN 2000; 95: 377 -82)
 Failures of Intrapartum Prophylaxis • CDC study 1998 -1999; 629, 912 births • 312 infants with GBS early onset sepsis (0. 5/1000 births) – 62% had no maternal risk factors – 52% of women were screened for GBS • Relative Risk of neonatal GBS in screened vs risk based approach was 0. 48 (0. 38 -0. 61) Schrag SJ, et al, NEJM 2002; 347: 233 -9.
Failures of Intrapartum Prophylaxis • CDC study 1998 -1999; 629, 912 births • 312 infants with GBS early onset sepsis (0. 5/1000 births) – 62% had no maternal risk factors – 52% of women were screened for GBS • Relative Risk of neonatal GBS in screened vs risk based approach was 0. 48 (0. 38 -0. 61) Schrag SJ, et al, NEJM 2002; 347: 233 -9.
 Failure of Intrapartum Prophylaxis • Reasons for failure of risk-based approach: – Incidence of GBS colonization in mothers who have no risk factors on presentation – Failure of identification of risk factors when present
Failure of Intrapartum Prophylaxis • Reasons for failure of risk-based approach: – Incidence of GBS colonization in mothers who have no risk factors on presentation – Failure of identification of risk factors when present
 CDC Guidelines Updated 2002 • All pregnant women should be cultured at 35 -37 weeks gestation • Penicillin prophylaxis preferred, due to narrow spectrum • Prophylaxis recommended for – Positive cervical culture for GBS – GBS bacteruria during gestation – Previous infant born with invasive GBS disease – Risk factors in absence of culture results • • • Gestation < 37 wks Fever ROM > 18 hr • Prophylaxis not needed for Cesarean sections for culture positive mothers with intact membranes
CDC Guidelines Updated 2002 • All pregnant women should be cultured at 35 -37 weeks gestation • Penicillin prophylaxis preferred, due to narrow spectrum • Prophylaxis recommended for – Positive cervical culture for GBS – GBS bacteruria during gestation – Previous infant born with invasive GBS disease – Risk factors in absence of culture results • • • Gestation < 37 wks Fever ROM > 18 hr • Prophylaxis not needed for Cesarean sections for culture positive mothers with intact membranes
 Change in Epidemiology of Early Onset Sepsis • Does widespread use of Intrapartum Antibiotic Prophylaxis lead to emergence of resistant organisms?
Change in Epidemiology of Early Onset Sepsis • Does widespread use of Intrapartum Antibiotic Prophylaxis lead to emergence of resistant organisms?
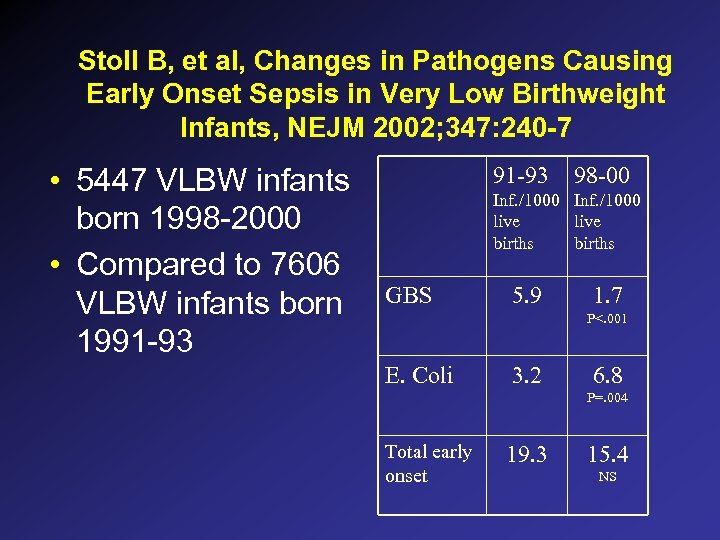 Stoll B, et al, Changes in Pathogens Causing Early Onset Sepsis in Very Low Birthweight Infants, NEJM 2002; 347: 240 -7 • 5447 VLBW infants born 1998 -2000 • Compared to 7606 VLBW infants born 1991 -93 98 -00 Inf. /1000 live births GBS 5. 9 1. 7 P<. 001 E. Coli 3. 2 6. 8 P=. 004 Total early onset 19. 3 15. 4 NS
Stoll B, et al, Changes in Pathogens Causing Early Onset Sepsis in Very Low Birthweight Infants, NEJM 2002; 347: 240 -7 • 5447 VLBW infants born 1998 -2000 • Compared to 7606 VLBW infants born 1991 -93 98 -00 Inf. /1000 live births GBS 5. 9 1. 7 P<. 001 E. Coli 3. 2 6. 8 P=. 004 Total early onset 19. 3 15. 4 NS
 Explanations for Ampicillin Resistance • Selection of resistant organisms from maternal GU tract – Especially in preterm infants • Change in NICU resistance patterns • Change in resistance patterns of ambulatory patients • Change in general resistance patterns
Explanations for Ampicillin Resistance • Selection of resistant organisms from maternal GU tract – Especially in preterm infants • Change in NICU resistance patterns • Change in resistance patterns of ambulatory patients • Change in general resistance patterns
 Hyde T, et al, Trends in Incidence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Early-onset Sepsis: Population Based Surveillance in San Francisco and Atlanta, Ped 2002; 110: 690 -5. • CDC Emerging Infection Program Network, 1998 -2000 – All hospitals with a delivery service in 3 county area of San Francisco (39, 768) – All 10 birthing hospitals in the 8 county Atlanta area (42, 960)
Hyde T, et al, Trends in Incidence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Early-onset Sepsis: Population Based Surveillance in San Francisco and Atlanta, Ped 2002; 110: 690 -5. • CDC Emerging Infection Program Network, 1998 -2000 – All hospitals with a delivery service in 3 county area of San Francisco (39, 768) – All 10 birthing hospitals in the 8 county Atlanta area (42, 960)
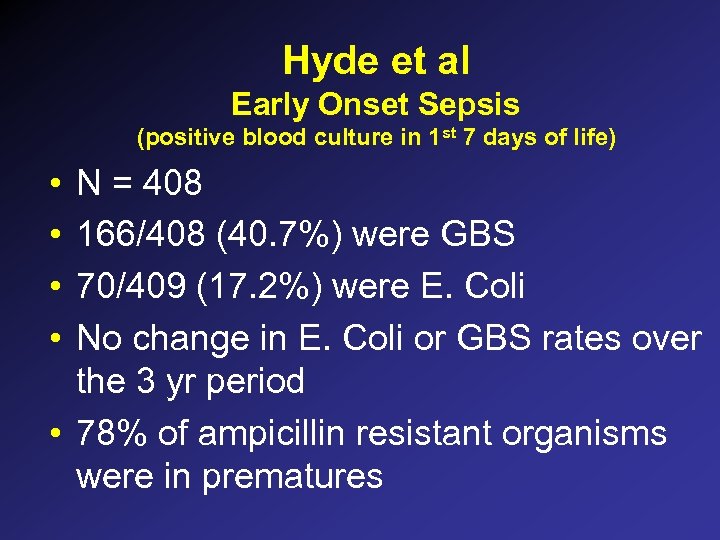 Hyde et al Early Onset Sepsis (positive blood culture in 1 st 7 days of life) • • N = 408 166/408 (40. 7%) were GBS 70/409 (17. 2%) were E. Coli No change in E. Coli or GBS rates over the 3 yr period • 78% of ampicillin resistant organisms were in prematures
Hyde et al Early Onset Sepsis (positive blood culture in 1 st 7 days of life) • • N = 408 166/408 (40. 7%) were GBS 70/409 (17. 2%) were E. Coli No change in E. Coli or GBS rates over the 3 yr period • 78% of ampicillin resistant organisms were in prematures
 Changing Epidemiology of Early Onset Sepsis • Term deliveries – 3. 9 million per year – Incidence of early onset sepsis: 1/1000 live births – 3, 900 term infants per year • Antibiotic resistance does not appear to be a problem in term infants
Changing Epidemiology of Early Onset Sepsis • Term deliveries – 3. 9 million per year – Incidence of early onset sepsis: 1/1000 live births – 3, 900 term infants per year • Antibiotic resistance does not appear to be a problem in term infants
 Changing Epidemiology of Early Onset Sepsis • VLBW Infants – 48, 000 births/yr < 1500 gm – Incidence of Early Onset Sepsis: 15/1000 (Stoll data) – 720 preterm infants/yr • Antibiotic resistance is a problem in VLBW infants – Due to GBS prophylaxis vs background changes in microbial resistance patterns? • Strategies to prevent GBS must address the majority of susceptible infants (5 out of every 6 susceptible infants is term) • Strategies must reflect the potential for resistance in preterm infants
Changing Epidemiology of Early Onset Sepsis • VLBW Infants – 48, 000 births/yr < 1500 gm – Incidence of Early Onset Sepsis: 15/1000 (Stoll data) – 720 preterm infants/yr • Antibiotic resistance is a problem in VLBW infants – Due to GBS prophylaxis vs background changes in microbial resistance patterns? • Strategies to prevent GBS must address the majority of susceptible infants (5 out of every 6 susceptible infants is term) • Strategies must reflect the potential for resistance in preterm infants
 Management of Newborn Whose Mother Received Prophylaxis • Diagnostic evaluation and empiric antibiotics if: – signs and symptoms of sepsis – < 35 weeks gestation • Limited Evaluation and 48 hr observation if: – Duration of prophylaxis < 4 hr before delivery – Asymptomatic infant • No evaluation, but 48 hr observation if: > 4 hr antibiotics prophylaxis Diagnostic Eval: CBC, Diff, Bld Cult, plus CXR, LP etc, as indicated Limited Eval: CBC, diff and Bld Cult.
Management of Newborn Whose Mother Received Prophylaxis • Diagnostic evaluation and empiric antibiotics if: – signs and symptoms of sepsis – < 35 weeks gestation • Limited Evaluation and 48 hr observation if: – Duration of prophylaxis < 4 hr before delivery – Asymptomatic infant • No evaluation, but 48 hr observation if: > 4 hr antibiotics prophylaxis Diagnostic Eval: CBC, Diff, Bld Cult, plus CXR, LP etc, as indicated Limited Eval: CBC, diff and Bld Cult.

 Is an LP necessary in evaluation for sepsis in the newborn? • Pro – Risk of meningitis in absence of positive blood cultures or CNS symptoms – Wiswell et al: • • • 5 yr review of U. S. Army Hospitals; 169, 849 births Incidence of meningitis: 0. 25/1000 live births 8/43 (19%) were term infants with no CNS symptoms and negative blood cultures Wiswell TE et al, Ped 1995; 95: 803 -6
Is an LP necessary in evaluation for sepsis in the newborn? • Pro – Risk of meningitis in absence of positive blood cultures or CNS symptoms – Wiswell et al: • • • 5 yr review of U. S. Army Hospitals; 169, 849 births Incidence of meningitis: 0. 25/1000 live births 8/43 (19%) were term infants with no CNS symptoms and negative blood cultures Wiswell TE et al, Ped 1995; 95: 803 -6
 Is an LP necessary in evaluation for sepsis in the newborn? • Con: – Metanalysis of 6 papers excluding Wiswell et al • • • 4913 LP’s successfully performed 19 cases of culture positive meningitis (259 LP’s per case of meningitis) 16/19 cases had positive blood cultures Thus, 1638 successful LP’s are needed to diagnose one case of meningitis in the absence of a positive blood culture Better blood culture technique lessens the need for LP’s
Is an LP necessary in evaluation for sepsis in the newborn? • Con: – Metanalysis of 6 papers excluding Wiswell et al • • • 4913 LP’s successfully performed 19 cases of culture positive meningitis (259 LP’s per case of meningitis) 16/19 cases had positive blood cultures Thus, 1638 successful LP’s are needed to diagnose one case of meningitis in the absence of a positive blood culture Better blood culture technique lessens the need for LP’s
 Blood Culture Technique • Appropriate prep: – 30 seconds vs 10 seconds x 2 • Appropriate volume: – At least 1 ml • Obtain from peripheral stick and central line if line is in more than 12 hr
Blood Culture Technique • Appropriate prep: – 30 seconds vs 10 seconds x 2 • Appropriate volume: – At least 1 ml • Obtain from peripheral stick and central line if line is in more than 12 hr
 Duration of Antibiotics • Are negative blood cultures conclusive when the mother has received IAP? • Ancillary tests – CBC: • • Neutropenia I: T ratio – CRP
Duration of Antibiotics • Are negative blood cultures conclusive when the mother has received IAP? • Ancillary tests – CBC: • • Neutropenia I: T ratio – CRP
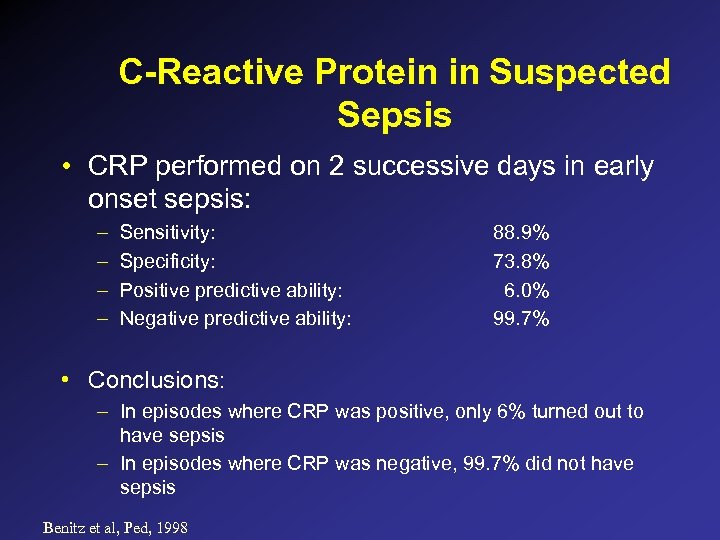 C-Reactive Protein in Suspected Sepsis • CRP performed on 2 successive days in early onset sepsis: – – Sensitivity: Specificity: Positive predictive ability: Negative predictive ability: 88. 9% 73. 8% 6. 0% 99. 7% • Conclusions: – In episodes where CRP was positive, only 6% turned out to have sepsis – In episodes where CRP was negative, 99. 7% did not have sepsis Benitz et al, Ped, 1998
C-Reactive Protein in Suspected Sepsis • CRP performed on 2 successive days in early onset sepsis: – – Sensitivity: Specificity: Positive predictive ability: Negative predictive ability: 88. 9% 73. 8% 6. 0% 99. 7% • Conclusions: – In episodes where CRP was positive, only 6% turned out to have sepsis – In episodes where CRP was negative, 99. 7% did not have sepsis Benitz et al, Ped, 1998
 Decision to stop antibiotics • Negative blood cultures at 48 -72 hr • Symptoms of mild severity (tachypnea, brief O 2 dependency, poor feeding) – D/C antibiotics and observe 24 -48 hr • If moderate-severe symptoms – decision to D/C or continue antibiotics depends on other factors: – Presence of chorioamniotis? – Elevated CRP? – Neutropenia or elevated I: T ratio?
Decision to stop antibiotics • Negative blood cultures at 48 -72 hr • Symptoms of mild severity (tachypnea, brief O 2 dependency, poor feeding) – D/C antibiotics and observe 24 -48 hr • If moderate-severe symptoms – decision to D/C or continue antibiotics depends on other factors: – Presence of chorioamniotis? – Elevated CRP? – Neutropenia or elevated I: T ratio?
 Nosocomial infection in the NICU: Common organisms • Coagulase negative staphylococcus • Coagulase positive staphylococcus • Gram negatives: E coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia, Pseudomonas • Candida albicans, parapsilosis
Nosocomial infection in the NICU: Common organisms • Coagulase negative staphylococcus • Coagulase positive staphylococcus • Gram negatives: E coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia, Pseudomonas • Candida albicans, parapsilosis
 Risk factors for nosocomial infection • Central lines – Duration of insertion – Type of catheter: Broviac, silastic • • Ventilation, endotracheal intubation Exposure to antibiotics Surgical procedures: intestinal Use of intravenous lipids
Risk factors for nosocomial infection • Central lines – Duration of insertion – Type of catheter: Broviac, silastic • • Ventilation, endotracheal intubation Exposure to antibiotics Surgical procedures: intestinal Use of intravenous lipids
 Strategies to reduce nosocomial infection • Remove central lines ASAP • Limit entries into central lines – Medications via PIV – Limit number of ports into central line – Use ports rather than stopcocks • Good handwashing • Respiratory care, suctioning techniques • Limit use of IV lipids
Strategies to reduce nosocomial infection • Remove central lines ASAP • Limit entries into central lines – Medications via PIV – Limit number of ports into central line – Use ports rather than stopcocks • Good handwashing • Respiratory care, suctioning techniques • Limit use of IV lipids
 Empiric treatment of suspected nosocomial sepsis • • Ampicillin and gentamicin Ampicillin and cefotaxime Vancomycin and gentamicin Vancomycin and cefotaxime
Empiric treatment of suspected nosocomial sepsis • • Ampicillin and gentamicin Ampicillin and cefotaxime Vancomycin and gentamicin Vancomycin and cefotaxime


