e6a2aae92fdc932197e6e7333574455d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Conformance Mark Skall Lynne S. Rosenthal National Institute of Standards and Technology mark. skall@nist. gov lynne. rosenthal@nist. gov
Conformance Mark Skall Lynne S. Rosenthal National Institute of Standards and Technology mark. skall@nist. gov lynne. rosenthal@nist. gov
 Introduction NIST works with industry to develop standards and tests to improve the quality of software and achieve interoperable solutions l Many years experience with l – Formal standards organizations and Consortia – Developing conformance test suites, tools, reference implementations – Developing validation and certification testing programs
Introduction NIST works with industry to develop standards and tests to improve the quality of software and achieve interoperable solutions l Many years experience with l – Formal standards organizations and Consortia – Developing conformance test suites, tools, reference implementations – Developing validation and certification testing programs
 Today’s Objectives l l l Present basic information about conformance and conformance related topics Achieve a common understanding Lead a discussion about how conformance applies to eb. XML Present overview of TA Spec. Conformance Clause Offer our assistance to WG in discussing and developing conformance for their Spec.
Today’s Objectives l l l Present basic information about conformance and conformance related topics Achieve a common understanding Lead a discussion about how conformance applies to eb. XML Present overview of TA Spec. Conformance Clause Offer our assistance to WG in discussing and developing conformance for their Spec.
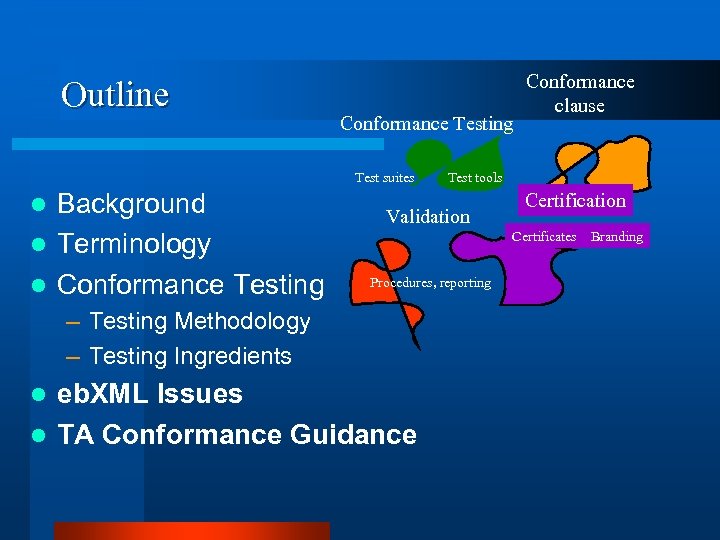 Outline Conformance Testing Test suites Background l Terminology l Conformance Testing l Test tools Validation Certificates Branding Procedures, reporting – Testing Methodology – Testing Ingredients eb. XML Issues l TA Conformance Guidance l Conformance clause
Outline Conformance Testing Test suites Background l Terminology l Conformance Testing l Test tools Validation Certificates Branding Procedures, reporting – Testing Methodology – Testing Ingredients eb. XML Issues l TA Conformance Guidance l Conformance clause
 Background l Standards not enough to ensure interoperability – Standards only meaningful if implemented in a consistent way l Need to ensure that implementations adhere to the standard – What is expected of implementations in order to claim conformance – i. e. , what are the requirements? – How will we know if an implementation conforms? • test suites, test tools l Different ideas of what conformance is – Past experience may have affected view of conformance
Background l Standards not enough to ensure interoperability – Standards only meaningful if implemented in a consistent way l Need to ensure that implementations adhere to the standard – What is expected of implementations in order to claim conformance – i. e. , what are the requirements? – How will we know if an implementation conforms? • test suites, test tools l Different ideas of what conformance is – Past experience may have affected view of conformance
 Terminology Conformance Specification Conformance Clause Conformance Testing test suite, test tools Validation process, reporting Certification certificate, brand
Terminology Conformance Specification Conformance Clause Conformance Testing test suite, test tools Validation process, reporting Certification certificate, brand
 Terminology - Conformance l CONFORMANCE - the fulfillment of a product, process or service of specified requirements (ISO Guide 2) – These requirements are specified in a standard or specification as part of a conformance clause or in the body of the specification l CONFORMANCE CLAUSE - a section of a specification that states all the requirements or criteria that must be satisfied to claim conformance
Terminology - Conformance l CONFORMANCE - the fulfillment of a product, process or service of specified requirements (ISO Guide 2) – These requirements are specified in a standard or specification as part of a conformance clause or in the body of the specification l CONFORMANCE CLAUSE - a section of a specification that states all the requirements or criteria that must be satisfied to claim conformance
 Terminology - Conformance Testing l CONFORMANCE TESTING – a way to verify implementations of a specification to determine whether or not deviations from the specifications exist (through the use of test suites). – tests capture the technical requirements within the specification – testing is bound in scope by the specification – internal structure of product-under-test not accessible (black box testing) l Necessary, but not sufficient, for interoperability Note: referred to as conformity assessment in ISO Guide 2
Terminology - Conformance Testing l CONFORMANCE TESTING – a way to verify implementations of a specification to determine whether or not deviations from the specifications exist (through the use of test suites). – tests capture the technical requirements within the specification – testing is bound in scope by the specification – internal structure of product-under-test not accessible (black box testing) l Necessary, but not sufficient, for interoperability Note: referred to as conformity assessment in ISO Guide 2
 Testing Methodology l Falsification Testing – find errors by means of experimentation – show presence of errors not their absence – prove non-conformance; can never prove conformance l Tests built to check for: – – required functionality has been implemented (basic tests) logical errors by misunderstanding requirements errors from boundary conditions and divergence common programming errors
Testing Methodology l Falsification Testing – find errors by means of experimentation – show presence of errors not their absence – prove non-conformance; can never prove conformance l Tests built to check for: – – required functionality has been implemented (basic tests) logical errors by misunderstanding requirements errors from boundary conditions and divergence common programming errors
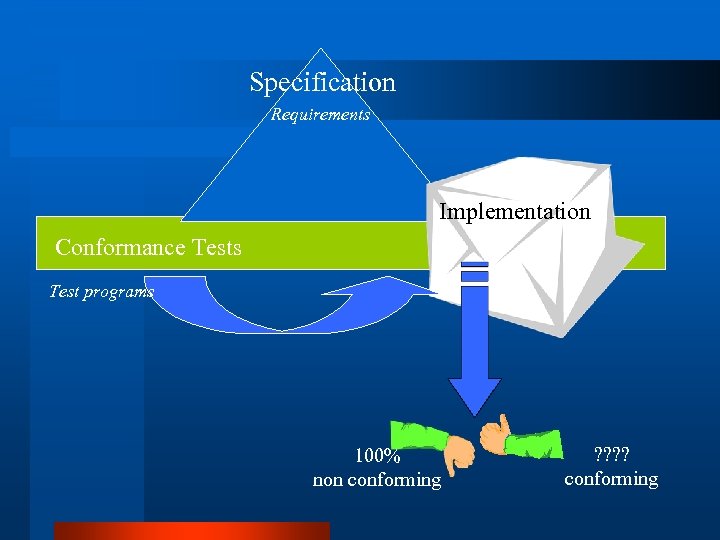 Specification Requirements Implementation Conformance Tests Test programs 100% non conforming ? ? conforming
Specification Requirements Implementation Conformance Tests Test programs 100% non conforming ? ? conforming
 Terminology - Testing Process l VALIDATION - process necessary to perform conformance testing in accordance with a prescribed procedure and official test suite – ensures that testing can be repeatable and reproducible – ensures that conclusions are consistent with facts presented in the evaluation l CERTIFICATION - acknowledgement that a validation was completed and the criteria established by CIO for issuing certificates (brands) was met.
Terminology - Testing Process l VALIDATION - process necessary to perform conformance testing in accordance with a prescribed procedure and official test suite – ensures that testing can be repeatable and reproducible – ensures that conclusions are consistent with facts presented in the evaluation l CERTIFICATION - acknowledgement that a validation was completed and the criteria established by CIO for issuing certificates (brands) was met.
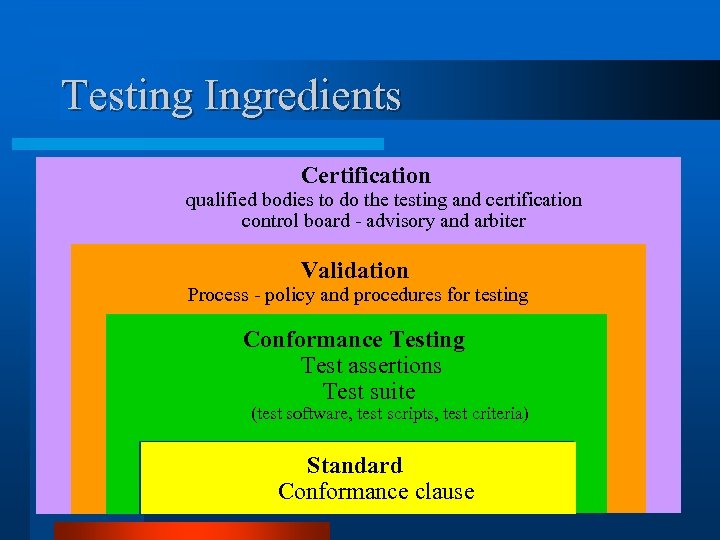 Testing Ingredients Certification qualified bodies to do the testing and certification control board - advisory and arbiter Validation Process - policy and procedures for testing Conformance Testing Test assertions Test suite (test software, test scripts, test criteria) Standard Conformance clause
Testing Ingredients Certification qualified bodies to do the testing and certification control board - advisory and arbiter Validation Process - policy and procedures for testing Conformance Testing Test assertions Test suite (test software, test scripts, test criteria) Standard Conformance clause
 eb. XML Conformance Issues l Conformance Clause should address? 1. What Needs to Conform? 2. Profiles and Levels 3. Extensions 4. Implementation Defined Features 5. Alternate approaches l Scope –what should be addressed? a. Assertions b. Test Suite c. Testing Service d. Certification
eb. XML Conformance Issues l Conformance Clause should address? 1. What Needs to Conform? 2. Profiles and Levels 3. Extensions 4. Implementation Defined Features 5. Alternate approaches l Scope –what should be addressed? a. Assertions b. Test Suite c. Testing Service d. Certification
 eb. XML Issues - Conformance Clause address: 1. What needs to conform – identify the ‘class of products’ that will be developed – what are the conditions that need to be met in order to claim conformance – Examples: registry, messaging service, business service interface, eb. XML message, testing partner agreements
eb. XML Issues - Conformance Clause address: 1. What needs to conform – identify the ‘class of products’ that will be developed – what are the conditions that need to be met in order to claim conformance – Examples: registry, messaging service, business service interface, eb. XML message, testing partner agreements
 eb. XML Issues Conformance Clause address: 2. Profiles and Levels – Are profiles and/or levels needed? – Should a profile have its own levels? – minimal requirements (core) Profile is a subset of the overall specifications that includes all of the functionality necessary to satisfy the requirements of a particular community of users. Levels are nested subsets of the specifications. Level 1 = core that all must implement; subsequent levels include lower level + added functionality
eb. XML Issues Conformance Clause address: 2. Profiles and Levels – Are profiles and/or levels needed? – Should a profile have its own levels? – minimal requirements (core) Profile is a subset of the overall specifications that includes all of the functionality necessary to satisfy the requirements of a particular community of users. Levels are nested subsets of the specifications. Level 1 = core that all must implement; subsequent levels include lower level + added functionality
 eb. XML Issues - Conformance Clause address: 3. Extensions – If allowed: • shall not re-define semantics of existing functions • shall not cause standard-conforming functions to execute incorrectly – Standardized method for extensions? • Define the mechanism for extending the specification, so extended in a standard manner – Register of extensions • document parallel to but distinct from specification • list of recognized, published extensions • may eventually migrate into future versions
eb. XML Issues - Conformance Clause address: 3. Extensions – If allowed: • shall not re-define semantics of existing functions • shall not cause standard-conforming functions to execute incorrectly – Standardized method for extensions? • Define the mechanism for extending the specification, so extended in a standard manner – Register of extensions • document parallel to but distinct from specification • list of recognized, published extensions • may eventually migrate into future versions
 eb. XML Issues - Conformance Clause address: 4. Implementation Defined Features – may want to address implementation dependent ranges, min/max allowed values 5. Alternative Approaches – specification may describe several different ways to accomplish an operation (e. g. , choice of bindings) – specify whether or not all approaches need to be implemented
eb. XML Issues - Conformance Clause address: 4. Implementation Defined Features – may want to address implementation dependent ranges, min/max allowed values 5. Alternative Approaches – specification may describe several different ways to accomplish an operation (e. g. , choice of bindings) – specify whether or not all approaches need to be implemented
 eb. XML Issues - Scope Should eb. XML include or address: a. Assertions (test requirements) - Should assertions be part of the standard? b. Test Suite - Prescribe a test methodology? - How test suite will be delivered/used (e. g. , web based, downloadable)? c. Testing Service - Guidelines for establishing a test service d. Certification - Guidelines for issuing certificates
eb. XML Issues - Scope Should eb. XML include or address: a. Assertions (test requirements) - Should assertions be part of the standard? b. Test Suite - Prescribe a test methodology? - How test suite will be delivered/used (e. g. , web based, downloadable)? c. Testing Service - Guidelines for establishing a test service d. Certification - Guidelines for issuing certificates
 Testing Program - Considerations Testing Program - l How formal should testing be? – Self testing, 3 rd party testing – Branding/certificates l Testing program – – – Who will ‘own’ the testing program Policy and procedures Testing laboratory Issue Certificates Control board Test suite maintenance
Testing Program - Considerations Testing Program - l How formal should testing be? – Self testing, 3 rd party testing – Branding/certificates l Testing program – – – Who will ‘own’ the testing program Policy and procedures Testing laboratory Issue Certificates Control board Test suite maintenance
 TA Conformance Guidance General conformance guidelines for eb. XML l All eb. XML specs shall contain a conformance clause l – Can have levels of eb. XML conformance hierarchical – Explains how conformance requirements can be expressed (mandatory, conditional, optional) l Encourage use of publicly available test suites
TA Conformance Guidance General conformance guidelines for eb. XML l All eb. XML specs shall contain a conformance clause l – Can have levels of eb. XML conformance hierarchical – Explains how conformance requirements can be expressed (mandatory, conditional, optional) l Encourage use of publicly available test suites
 Discussion
Discussion


