b0be2f5a9dde03237fba5174150870f0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84

CONFINED SPACE ENTRY TRAINING Presented by: UM-Flint Environment, Health and Safety Department University of Michigan - Flint 1

Training Outline l l What is a confined space? General overview of UM-Flint’s CSE program Evaluation/Control of Atmospheric Hazards Elimination/Control of Other Hazards Entry Procedures » (General, Hazardous & Hot Work entry permits) l l Evacuation & Rescue Discussion of CS Scenarios & related equip. Working w/ Contractors Video “Life & Death Series CSE” University of Michigan - Flint 2

Training Goal l l Refresh and update employees knowledge of CSE procedures Discuss roles/responsibilities Familiarize new employees with the UMF confined spaces, associated hazards and entry procedures. Provide employees with guidelines to: » Identify confined spaces » Evaluate confined spaces » Enter confined spaces in accordance with MIOSHA regulations and UM guidelines. l Discuss concerns or non-routine entries. University of Michigan - Flint 3

Confined Space Entry Program Prevent Unauthorized Entry l Identify Permit Space Hazards l Develop & Follow Safe Entry Procedures (use entry permit as guide) l Conclude Entry (close out permit) l Coordinate Entry Operations between University departments as well as with non-University agencies i. e. FFD, MPC l Program Evaluation & Review/Revise l University of Michigan - Flint 4

Section 1: What is a Confined Space? l A space that meets ALL THREE of the following criteria: 1. 2. 3. l Has limited means of entry or exit. Is large enough for a person to enter and perform work. Is not designed for continuous human occupancy. Employer must evaluate a space based on the Definition…. NOT on whether or not you may enter the space (per MIOSHA) University of Michigan - Flint 5
Types of Confined Spaces Non-permit required l Permit required l » General permit … c(5) or c(7) entry » Hazardous permit » Hot Work University of Michigan - Flint 6

Non-Permit Required Meets confined space definition, and l Has adequate ventilation, and l Does not contain any hazards that can cause death or harm, and l There is absolutely no potential for a hazardous atmosphere. l University of Michigan - Flint 7

Permit Required l Meets confined space definition and » limited means of entry or exit. » large enough for a person to enter and work. » Is not designed for continuous occupancy. l l Has inadequate ventilation, or Has a hazardous health or safety condition, or » (i. e. engulfment; internal configuration that could trap/asphyxiate; converging wall, sloped/taper floor; entrapment; exposed electrical/mechanical parts, etc. ) l Has a known or potential hazardous atmosphere. University of Michigan - Flint 8

Confined Space Evaluation l l l l Is it a confined space? Is it a permit required confined space? What hazards are present? Source? Can hazards be eliminated? Controlled? What type of permit is required? What procedures/equipment will be used to protect the entrants? Use UM-f Space Evaluation form… University of Michigan - Flint 9
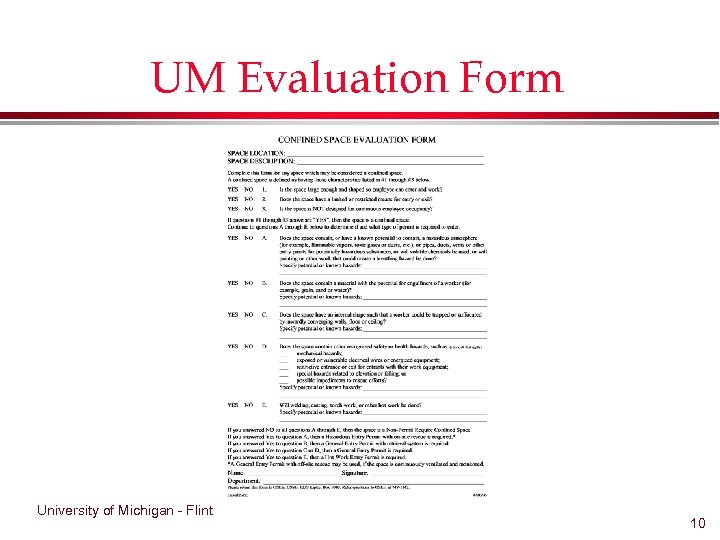
UM Evaluation Form University of Michigan - Flint 10
Types of Permits General Entry Permit l Hazardous Entry Permit l Hot Work Entry Permit l University of Michigan - Flint 11
Confined Space Entry Permit University of Michigan - Flint 12

Confined Space? University of Michigan - Flint 13

Confined Space? University of Michigan - Flint 14

Confined Space? University of Michigan - Flint 15

What Type of Permit? University of Michigan - Flint 16

Confined Space? University of Michigan - Flint 17

Campus Utility Tunnels l UMF utility tunnels are not considered confined spaces because: » Ventilated and lighted » Designed for human occupancy » Not generally hazardous l However, caution must be taken when performing work in tunnels » Buddy system, radio communications/notifications, other regulations do apply… could be upgraded. l AA-OSEH is developing a new Tunnel Safety Program… many of AA’s tunnels are CS. University of Michigan - Flint 18

Section 2: Atmospheric Hazards How Chemicals Enter Body l Acute and Chronic Effects l Exposure Limits l Identifying Atmospheric Hazards l UEL/LEL l Vapor Density l University of Michigan - Flint 19
Routes of Entry Skin Absorption l Inhalation l Ingestion l Injection l University of Michigan - Flint 20
Health Effects l Acute » immediate or short term effect l Chronic » delayed or long term effect University of Michigan - Flint 21

Warning Signs Dizziness/Disorientation l Weakness in knees/abnormal breathing l Blurred vision/profuse sweating l Chest pains/headaches l Loss of coordination/ringing in ears l Skin irritation/irregular heartbeat l Lethargy or excitedness l University of Michigan - Flint 22

What is an Atmospheric Hazard? Oxygen >23. 5% or <19. 5% l Flammables at >10% LEL l Above OSHA/MIOSHA PEL l IDLH l Combustible Dusts l Unknown chemical spill l University of Michigan - Flint 23

Sources of Hazardous Atmospheres Spaces with known hazardous chemicals/substances l Spaces that lack ventilation l Spaces that have the potential to transfer a hazardous atmosphere l Spaces with a work induced hazardous atmosphere l University of Michigan - Flint 24

Permissible Exposure Limits OSHA l 8 Hour TWA l STEL l Ceiling Limit l Contact EHS for monitoring of contaminants not monitored for by standard meters l University of Michigan - Flint 25

Oxygen Deficient Atmosphere <19. 5% l Sources: work induced, rusting, gases that displace oxygen l Simple Asphyxiants: Displace oxygen (carbon dioxide, nitrogen, argon) l Chemical Asphyxiant: Prevent body from using oxygen (carbon monoxide) l University of Michigan - Flint 26

Oxygen Enriched Atmosphere 23. 0% or Greater l Sources: Welding, or oxygen gas lines l Increase fire and explosion hazard l Never use oxygen to ventilate space l University of Michigan - Flint 27

Vapors and Gases Vapor: Gaseous state of material normally found as liquid or solid at normal temperature and pressure l Gas: Material that is found as a formless fluid at normal temperature and pressure l University of Michigan - Flint 28
LEL/LFL and UEL/UFL LEL: Lowest concentration can ignite l UEL: Highest Concentration can ignite l Example: Gasoline LEL 1%, UEL 8% l In between is explosive l Consideration: Atmosphere above the UEL, when ventilated may create an explosive atmosphere l University of Michigan - Flint 29

LEL Safety Factor OSHA: 10% of LEL or Greater l Example: LEL for Methane is 5% l Meter alarm at 10% of 5% (i. e. , 0. 5%) l If exceeded (meter alarms), leave the space and Contact supervisor and EHS. l University of Michigan - Flint 30

Combustible Dusts Metal Powders - Aluminum, Magnesium, Zinc l Wood Products - Dust, Paper l Rubber/Plastic/Spices/Food Products l Rule of Thumb - Obscure Vision 5 Feet or Less –high potential for combustion given the right conditions. l University of Michigan - Flint 31

Toxic or Poisonous Atmospheres l Most Common: » Carbon Monoxide (CO) » Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) » Methane (CH 4) » Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) University of Michigan - Flint 32

Carbon Monoxide (CO) Colorless, odorless & tasteless l Product incomplete combustion l Causes chemical asphyxiation l Slightly lighter than air l MIOSHA PEL 35 PPM, OSHA PEL 50 PPM l University of Michigan - Flint 33

Hydrogen Sulfide (H 2 S) Rotten egg odor l Petroleum/Organic matter decay l Found in sewers or petroleum holding tanks l <10 PPM l University of Michigan - Flint 34
Methane (CH 4) Colorless, odorless & flammable l Petroleum/Organic matter decay l Lighter than air l Meter alarms – 10% of LEL l University of Michigan - Flint 35

Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Colorless, odorless & tasteless l Byproduct of respiration and complete combustion l Heavier than air l University of Michigan - Flint 36

Other Atmospheric Hazards Materials in the space l Work induced hazards (e. g. , welding, painting, solvents) l Review history of space l Contact EHS if other contaminants are suspected l University of Michigan - Flint 37

Vapor Density Heavier than Air: Sinks l Lighter than Air: Rises l Air Vapor density = 1 l <1 Lighter, >1 Heavier l Most contaminants are heavier than air l The few that are lighter, are usually flammable and very toxic l University of Michigan - Flint 38
Section 3: Evaluation & Control of Atmospheric Hazards Air Monitoring Equipment and Procedures l Ventilating, Flushing or Purging l PPE – only after engineer controls l University of Michigan - Flint 39

Air Monitoring Contaminants may not be detected by sight or smell l Two Types of Direct Reading: l » Electronic – Bacharach 4 -gas monitor » Detector Tubes – Drager pump l Always monitor for oxygen, LEL and expected toxics (CO, H 2 S) University of Michigan - Flint 40
BACHARACH Sentinel 44 UM-F’s Four Gas Monitor - Sentinel 44 l % Oxygen, % LEL, Carbon Monoxide (PPM), H 2 S (PPM) l Alarms: l » O 2 - <19. 5% or > 23. 0%, » LEL - > 10%, » CO - >35 ppm » H 2 S - >10 ppm University of Michigan - Flint 41

Air Monitoring Precautions Alarm Goes Off – leave the space, contact EHS and supervisor l Other contaminants known or suspected, contact EHS for monitoring assistance l University of Michigan - Flint 42

Air Monitoring Procedure Ensure monitor has been calibrated l Turn monitor on and let warm up l Verify monitor is functioning properly l Zero sensors in clean ambient airoutside the CS l Keep sensor heads exposed l Test space before opening the hatch l Monitor for oxygen first… l University of Michigan - Flint 43

Air Monitoring - Testing Order University of Michigan - Flint 44

Air Monitoring (continued) Monitor every four feet l Monitor vertically & horizontally l Record results on permit l Before work, periodically during work, and after breaks l Continuously monitor – confidence tone or ”beep” l University of Michigan - Flint 45
Air Monitoring Limitations l l l Sensors must be calibrated and replaced periodically – Contact EHS LEL sensor needs oxygen to work LEL sensor is calibrated for one gas -Methane Sensors can take up to 2 minutes to accurately display concentrations Some gases and RF emissions interfere with sensor accuracy University of Michigan - Flint 46

Flushing/Purging of Space Lock Out/Tag Out Feeds l Can use air, steam, water, etc. l Removes chemical or decomposition hazards l Drain or pump out l Ventilate with fresh air when complete l University of Michigan - Flint 47

Ventilation Natural l Mechanical (General or Local) l » portable/intrinsically safe l Air monitoring determines adequate ventilation University of Michigan - Flint 48
General Ventilating Technique Perform air monitoring l Extend duct into space l Open all access points l Keep duct as short/straight as possible l Ensure intake is at clean air source l Ventilate 15 minutes prior to entry l Continue air monitoring l University of Michigan - Flint 49

Local Exhaust Ventilation Work induced contaminants l Space has acceptable atmosphere prior to work l Place duct opening at point of generation (air is pulled out of space) l University of Michigan - Flint 50

Ventilating Safety Measures l l l l Ventilate with fresh air Never use pure oxygen Use explosion proof equipment if needed Make sure exhaust air is not re-entrained Make sure supply air is reaching all areas of the space Use air monitoring to determine adequate ventilation Don't block exit with equipment University of Michigan - Flint 51

Section 4: Recognition & Control of Other Hazards Engulfment, Entrapment, Configuration l Other Hazards and their Control l University of Michigan - Flint 52

Engulfment Liquid or Solid l Suffocation or Drowning CONTROL l Elimination or Isolation of hazard l On-site remote retrieval rescue equipment such as the Miller tripod w/ harness and or wristlet/anklets) l University of Michigan - Flint 53

Engulfment Hazard! University of Michigan - Flint 54

Entrapment/Configuration Inwardly converging walls l Floor which slopes downward and tapers to a small cross section l Obstacles, blockages or small internal openings CONTROL l On-site remote retrieval rescue equipment such as the Miller tripod w/ harness and or wristlet/anklets) l University of Michigan - Flint 55

Entrapment/Configuration Hazard University of Michigan - Flint 56

Electrical & Mechanical Hazards Use Lock-out/Tag-out Procedures prior to entry l Isolate moving parts l Assure equipment grounding / GFCI’s l University of Michigan - Flint 57

Chemical Hazards Toxics, Flammables, Irritants, Sensitizers, etc. CONTROL: l Read MSDSs l Understand Physical/Health hazards l Remove/ Isolate the source, ventilation l Wear appropriate PPE l University of Michigan - Flint 58

PPE Gloves l Glasses/goggles/face shields l Coveralls or Tyvek suits l Safety Shoes l Hard hats l Respirators l University of Michigan - Flint 59

Gloves Select based on hazard l Latex - general protection l Nitrile/neoprene - chemical resistant l Kevlar - cut/puncture resistant l University of Michigan - Flint 60

Respirators l l Air Purifying Half or full mask. Filters and cartridges are for specific atmospheric hazards. Not for IDLH or oxygen deficient atmospheres. SCBA for IDLH conditions and not permitted for UMF employees’ » Escape packs not used for re-entry l Respiratory Protection Program & Medical Monitoring is required. University of Michigan - Flint 61

Heat Stress & Cold Stress HEAT l Dehydration l Heat Rash l Heat Fatigue l Heat Cramps l Heat Exhaustion l Heat Stroke University of Michigan - Flint COLD l Frost Bite l Hypothermia CONTROLS: l Mechanical Ventilation l Fans, Heaters, Air Conditioners 62

Noise AL: 85 d. BA l PEL: 90 d. BA l Communication is difficult CONTROLS: l Remove or isolate the source l Wear Hearing Protection l Other means of communication l University of Michigan - Flint 63

Slips, Trips & Falls Good housekeeping practices l Fall Protection l Tie off ladders l Hard hats & slip resistant soles l Lower/raise equipment by rope. Don't carry on ladders l Barriers around openings l University of Michigan - Flint 64

Power Tools and Lighting Tools are grounded & insulated l Insulating blankets when arc welding on metal l Equipment grounding/GFCI’s l Provide adequate lighting. Grounding & spark hazards of portable lighting l Tools & lighting should be explosion proof when necessary l University of Michigan - Flint 65

Section 5: Entry Procedures Employee roles l Proper procedures for general, hot work & hazardous entry permits l University of Michigan - Flint 66

Employee Roles l l Attendant (spotter) Authorized Employee (entrant) Entry Supervisor Rescue Personnel » DPS & Flint Fire, or » Contract CSE Rescue team i. e. MPC » IDLH conditions require On site rescue team l EHS – On-site for Hazardous entry University of Michigan - Flint 67

Entry Procedures l l l l l Evaluate the space/ Identify hazards Pre-entry briefing Inform DPS Isolate/control hazards Perform air monitoring Complete, sign and post permit Monitor entrants Exit space and close out permit Debriefing Return completed/closed permit to EHS University of Michigan - Flint 68

Pre-Entry Briefing Use the Evaluation Form and Permit to walk through the evaluation process l Discuss with supervisor to consider previous entries and history of the space l Review of conditions, controls, procedures & contingencies l Determine whether or not on-site rescue team is required… contact EHS. l University of Michigan - Flint 69

Pre-Entry Checklist (just before entry) l l l l l Inform DPS & EHS Atmospheric monitoring Inspect and test equipment prior to use Communication procedures Rescue/emergency procedures Review space use history Verify training Supervisor verify safe entry conditions, etc. Sign & post permit University of Michigan - Flint 70

Non-Permit Required Confined Space Meets definition of confined space, but no health or safety hazard l Two employees (buddy system) l Means of communication l Can be re-classified to a permit required space for work induced hazards… i. e. use of chemicals/solvents, welding, etc. l Examples: ceiling spaces, l University of Michigan - Flint 71

General Permit Required Confined Space Meets definition of a confined space and has a potential or known health or safety hazard l Atmospheric hazard eliminated by ventilation l Two Authorized Employees (One Designated as Entry Supervisor) l University of Michigan - Flint 72

General Entry Permits Pre-entry Briefing l Communication l Continuous Air Monitoring/Ventilation l Trained (Authorized) Employees l Elimination of hazards l PPE l Off-site Rescue l University of Michigan - Flint 73

Hot Work Entry Permit Welding, burning, cutting or torch work l Provisions same as in general permit l If contaminants cannot be controlled by ventilation & air monitoring: Retrieval System and On-site Rescue must be used l University of Michigan - Flint 74

Hazardous Entry Permit Cannot eliminate atmospheric hazard l Provisions of General Permit Plus: l » EHS Representative On Site, » On-site Rescue and Retrieval System Mandatory University of Michigan - Flint 75

Section 6: Evacuation & Rescue When to Evacuate the Space l Rescue Procedures l University of Michigan - Flint 76

When should the Confined Space be evacuated? l Hazardous atmosphere » Alarm on monitor » Overexposure symptoms of entrants Unanticipated health or safety hazard l Damage to PPE or failure of controls l Attendant cannot perform duties l Permit expires l University of Michigan - Flint 77
Rescue If Entrant Becomes Incapacitated l Three Types: l » Remote (retrieval system) » Off-site (Contact DPS 911 & FFD) » On-site (MPC/ Contract on-site rescue team & DPS) l Under No Circumstances is Attendant/Spotter to enter the space University of Michigan - Flint 78

Spotter, Retrieval System, & On-site Rescue Team (MPC) First call DPS on the radio. l If injured due to causes not related to environment/atmosphere-Wait for Fire Dept. l If injured due to environment or atmosphere, then use remote/on-site rescue, if possible. l University of Michigan - Flint 79

Spotter, Retrieval System & Off-Site Rescue Personnel Contact DPS on radio l If injury due to causes not related to the environment/atmosphere-Wait for Fire Dept. l If injured due to environment or atmosphere - use retrieval equipment l If retrieval fails - Wait for Fire Dept. l If unsure - Wait for Fire Dept. l University of Michigan - Flint 80

Spotter & Off-Site Rescue Contact DPS on by radio l Wait for Fire Dept. l University of Michigan - Flint 81

Section 7: Miscellaneous Contractors l UMF Confined Space related documents l Future drills and exercises l University of Michigan - Flint 82

Outside Contractors l l l Inform the contractor of confined spaces Identify spaces they may be entering, and respective hazards Must have own Confined Space Entry Program and employee training current. Coordinate with other workers. Each group entering space issues a separate permit. Work activities cannot conflict. EHS is available to review contractor’s program. University of Michigan - Flint 83

Review UMF CSE Documents Evaluation form l Entry Permit l Contractor Notification l Revised List of UMF Confined Spaces l UMF/UMAA Confined Space program l MI Part 90 Confined Space Entry Regulations l University of Michigan - Flint 84
b0be2f5a9dde03237fba5174150870f0.ppt