a20b498b67ba8dba22be3fbb48832ea3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 Configuring Access to Internal Resources 1
Configuring Access to Internal Resources 1
 What is ISA server publishing? • Publish internal servers to the Internet, so that users on the Internet can access those internal resources • Making internal resources accessible to the Internet increases the security risks for the organization. • ISA Server uses Web and server publishing rules to publish internal network resources to the Internet 2
What is ISA server publishing? • Publish internal servers to the Internet, so that users on the Internet can access those internal resources • Making internal resources accessible to the Internet increases the security risks for the organization. • ISA Server uses Web and server publishing rules to publish internal network resources to the Internet 2
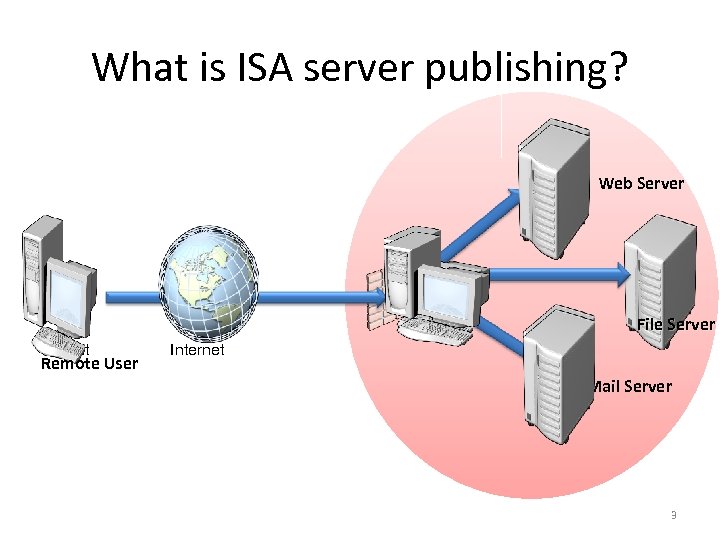 What is ISA server publishing? Web Server File Server Client Remote User Internet Mail Server 3
What is ISA server publishing? Web Server File Server Client Remote User Internet Mail Server 3
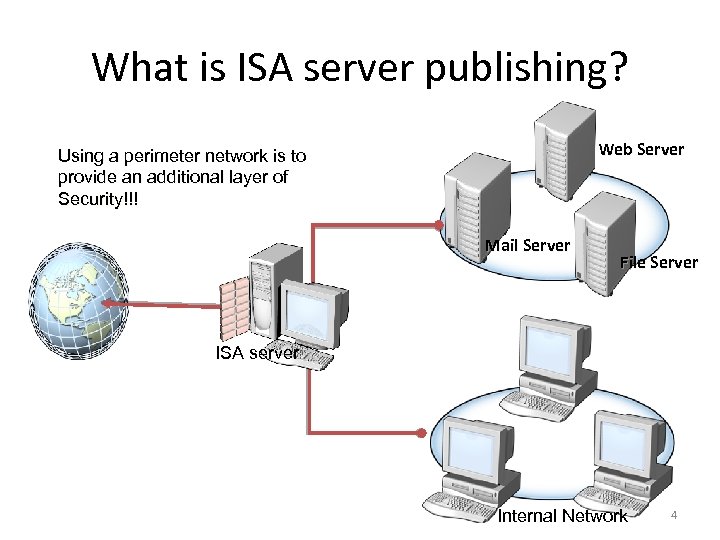 What is ISA server publishing? Web Server Using a perimeter network is to provide an additional layer of Security!!! Mail Server File Server ISA server Internal Network 4
What is ISA server publishing? Web Server Using a perimeter network is to provide an additional layer of Security!!! Mail Server File Server ISA server Internal Network 4
 What Are Web Publishing Rules? • Make Web sites on protected networks available to users on other networks, such as the Internet • A Web publishing rule is a firewall rule that specifies how ISA Server will route incoming requests to internal Web servers • Web Publishing is sometimes referred to as “reverse proxying”. proxying 5
What Are Web Publishing Rules? • Make Web sites on protected networks available to users on other networks, such as the Internet • A Web publishing rule is a firewall rule that specifies how ISA Server will route incoming requests to internal Web servers • Web Publishing is sometimes referred to as “reverse proxying”. proxying 5
 What do Web publishing rules provide? Access to Web servers running HTTP protocol HTTP application-layer filtering Path mapping User authentication Content caching Support for publishing multiple Web sites using a single IP address • Link translation • • • 6
What do Web publishing rules provide? Access to Web servers running HTTP protocol HTTP application-layer filtering Path mapping User authentication Content caching Support for publishing multiple Web sites using a single IP address • Link translation • • • 6
 What Are Server Publishing Rules • Web publishing and secure Web publishing rules can grant access only to Web servers using HTTP or HTTPS. • To grant access to internal resources using any other protocol, you must configure server publishing rules!!! 7
What Are Server Publishing Rules • Web publishing and secure Web publishing rules can grant access only to Web servers using HTTP or HTTPS. • To grant access to internal resources using any other protocol, you must configure server publishing rules!!! 7
 • • What do Server publishing rules provide? Access to multiple protocols Application-layer filtering for specified protocols Support for encryption IP address logging for the client computer 8
• • What do Server publishing rules provide? Access to multiple protocols Application-layer filtering for specified protocols Support for encryption IP address logging for the client computer 8
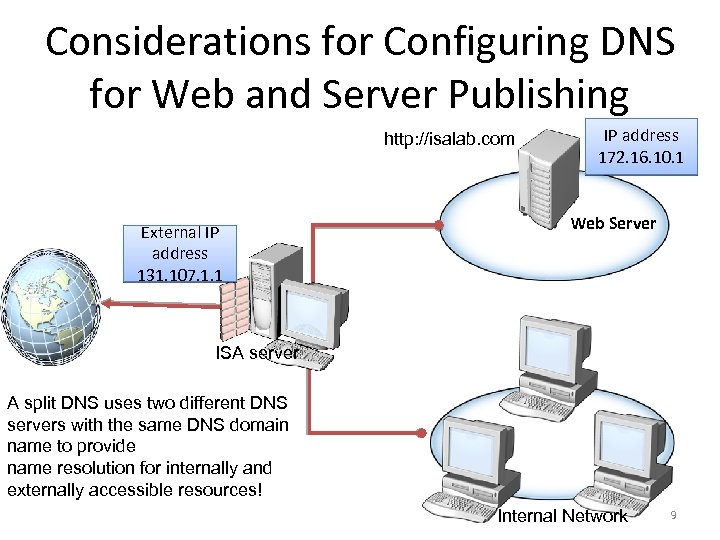 Considerations for Configuring DNS for Web and Server Publishing http: //isalab. com External IP address 131. 107. 1. 1 IP address 172. 16. 10. 1 Web Server ISA server A split DNS uses two different DNS servers with the same DNS domain name to provide name resolution for internally and externally accessible resources! Internal Network 9
Considerations for Configuring DNS for Web and Server Publishing http: //isalab. com External IP address 131. 107. 1. 1 IP address 172. 16. 10. 1 Web Server ISA server A split DNS uses two different DNS servers with the same DNS domain name to provide name resolution for internally and externally accessible resources! Internal Network 9
 Configuring Web Publishing Rules • Web Listener • Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • SSL Web Publishing Rules 10
Configuring Web Publishing Rules • Web Listener • Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • SSL Web Publishing Rules 10
 Web Listener • Web listeners are used by Web and secure Web publishing rules • A Web listener is an ISA Server configuration object that defines how the ISA Server computer listens for HTTP requests and SSL requests • All incoming Web requests must be received by a Web listener • A Web listener may be used in multiple Web publishing rules 11
Web Listener • Web listeners are used by Web and secure Web publishing rules • A Web listener is an ISA Server configuration object that defines how the ISA Server computer listens for HTTP requests and SSL requests • All incoming Web requests must be received by a Web listener • A Web listener may be used in multiple Web publishing rules 11
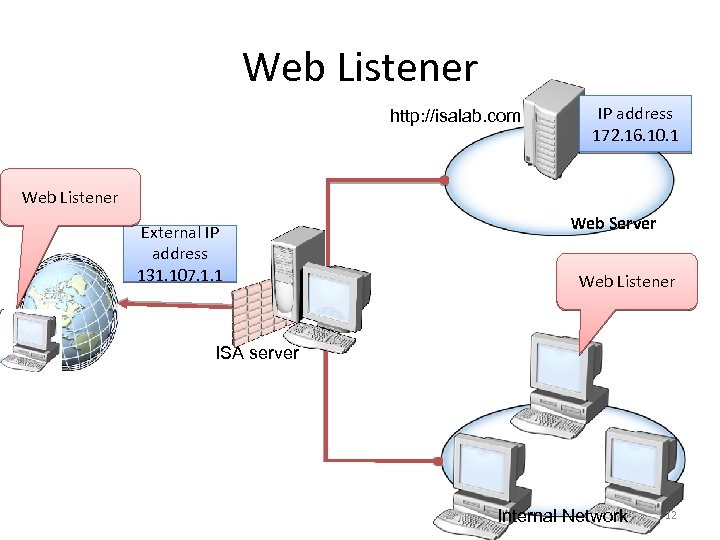 Web Listener http: //isalab. com IP address 172. 16. 10. 1 Web Listener External IP address 131. 107. 1. 1 Web Server Web Listener ISA server Internal Network 12
Web Listener http: //isalab. com IP address 172. 16. 10. 1 Web Listener External IP address 131. 107. 1. 1 Web Server Web Listener ISA server Internal Network 12
 How to Configure Web Listeners • • Network Port numbers Client authentication methods Client Connection Settings 13
How to Configure Web Listeners • • Network Port numbers Client authentication methods Client Connection Settings 13
 Network If you have multiple network adapters or multiple IP addresses 14
Network If you have multiple network adapters or multiple IP addresses 14
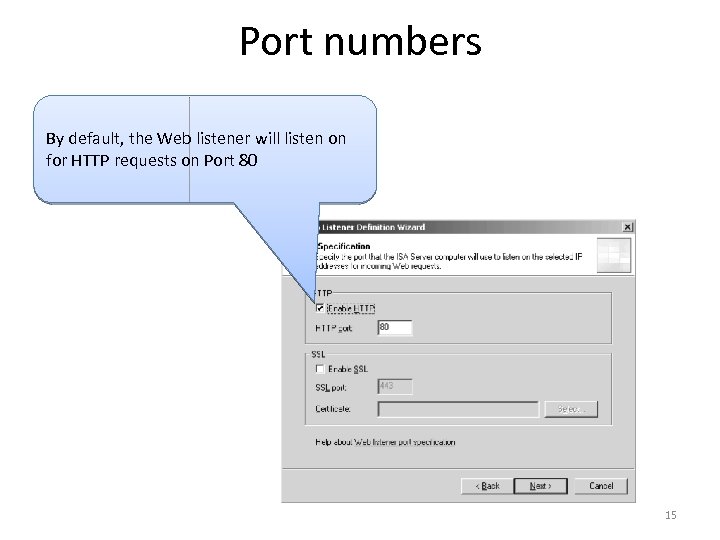 Port numbers By default, the Web listener will listen on for HTTP requests on Port 80 15
Port numbers By default, the Web listener will listen on for HTTP requests on Port 80 15
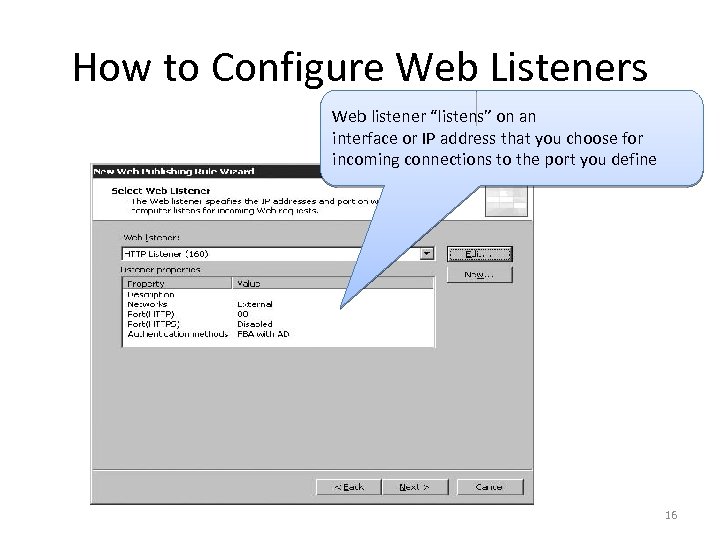 How to Configure Web Listeners Web listener “listens” on an interface or IP address that you choose for incoming connections to the port you define 16
How to Configure Web Listeners Web listener “listens” on an interface or IP address that you choose for incoming connections to the port you define 16
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules 17
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules 17
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules Rule Action Page 18
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules Rule Action Page 18
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • Publishing Type Page – Publish a single Web site or load balancer – Publish a server farm of load balanced Web Servers – Publish multiple web sites 19
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • Publishing Type Page – Publish a single Web site or load balancer – Publish a server farm of load balanced Web Servers – Publish multiple web sites 19
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Server Connection Security Page: 20
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Server Connection Security Page: 20
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Internal Publishing Details Page: – Internal Site Name – Computer name or IP address 21
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Internal Publishing Details Page: – Internal Site Name – Computer name or IP address 21
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Internal Publishing Details Page: – Path Name – Forward the original host header instead of the actual one 22
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Internal Publishing Details Page: – Path Name – Forward the original host header instead of the actual one 22
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Public Name Details Page – Accept requests for – Public Name – Path (optional 23
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Public Name Details Page – Accept requests for – Public Name – Path (optional 23
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Select Web Listener Page and Creating an HTTP Web Listener: – Edit – New 24
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Select Web Listener Page and Creating an HTTP Web Listener: – Edit – New 24
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Authentication Settings Page 25
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Authentication Settings Page 25
 • • • Web Listener Authentication Methods Basic Digest Integrated RADIUS OTP Secur. ID OWA Forms-based Forms-Based Authentication SSL Certificate 26
• • • Web Listener Authentication Methods Basic Digest Integrated RADIUS OTP Secur. ID OWA Forms-based Forms-Based Authentication SSL Certificate 26
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Single Sign on Settings Page 27
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Single Sign on Settings Page 27
 Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Authentication Delegation Page 28
Configuring Non-SSL Web Publishing Rules • The Authentication Delegation Page 28
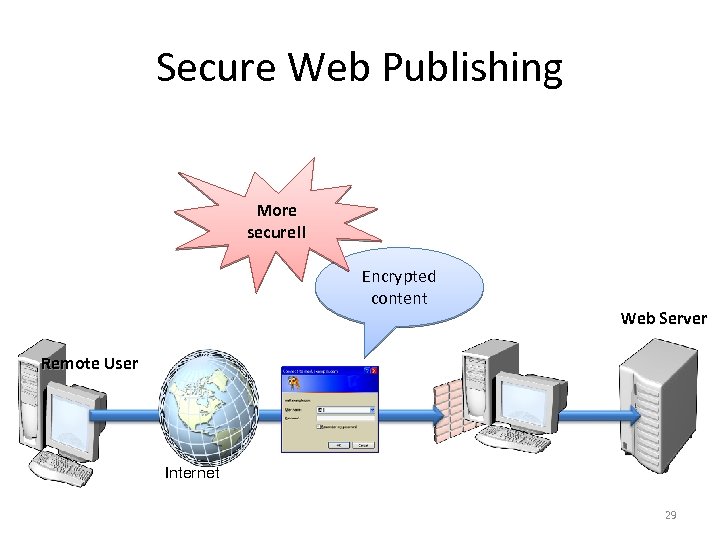 Secure Web Publishing More secure!! Encrypted content Web Server Remote User Client Internet 29
Secure Web Publishing More secure!! Encrypted content Web Server Remote User Client Internet 29
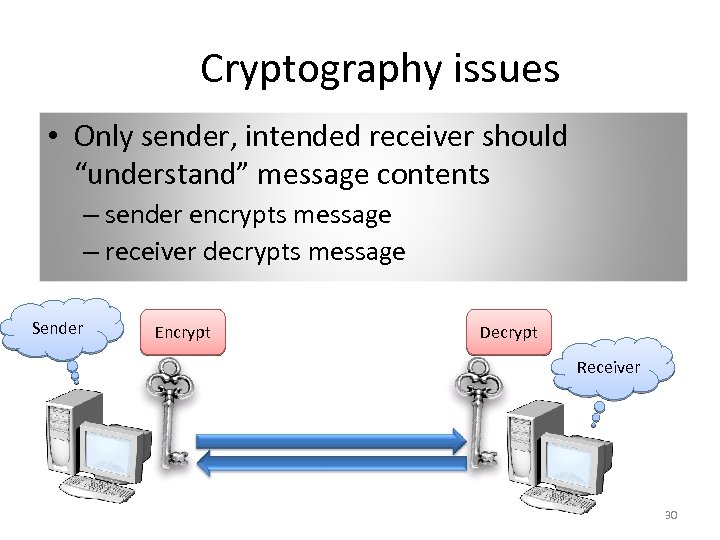 Cryptography issues • Only sender, intended receiver should “understand” message contents – sender encrypts message – receiver decrypts message Sender Encrypt Decrypt Receiver 30
Cryptography issues • Only sender, intended receiver should “understand” message contents – sender encrypts message – receiver decrypts message Sender Encrypt Decrypt Receiver 30
 Types of Cryptography • Crypto often uses keys: – Algorithm is known to everyone – Only “keys” are secret • Public key cryptography – Involves the use of two keys • Symmetric key cryptography – Involves the use one key • Hash functions – Involves the use of no keys – Nothing secret: How can this be useful? 31
Types of Cryptography • Crypto often uses keys: – Algorithm is known to everyone – Only “keys” are secret • Public key cryptography – Involves the use of two keys • Symmetric key cryptography – Involves the use one key • Hash functions – Involves the use of no keys – Nothing secret: How can this be useful? 31
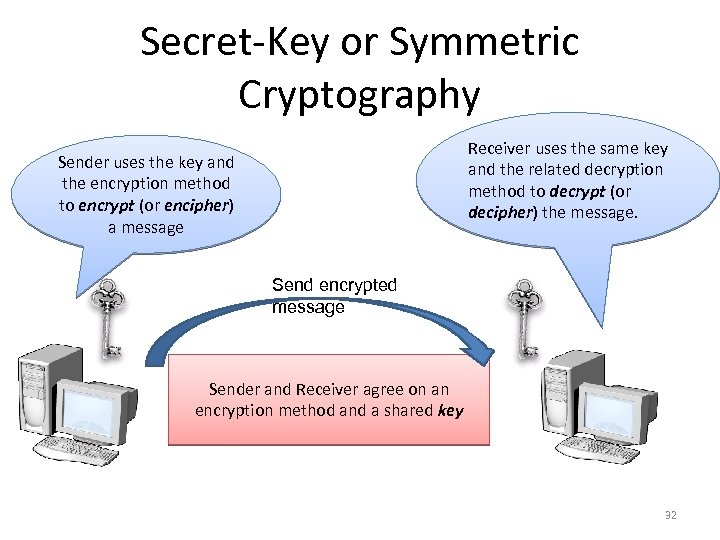 Secret-Key or Symmetric Cryptography Receiver uses the same key and the related decryption method to decrypt (or decipher) the message. Sender uses the key and the encryption method to encrypt (or encipher) a message Send encrypted message Sender and Receiver agree on an encryption method and a shared key 32
Secret-Key or Symmetric Cryptography Receiver uses the same key and the related decryption method to decrypt (or decipher) the message. Sender uses the key and the encryption method to encrypt (or encipher) a message Send encrypted message Sender and Receiver agree on an encryption method and a shared key 32
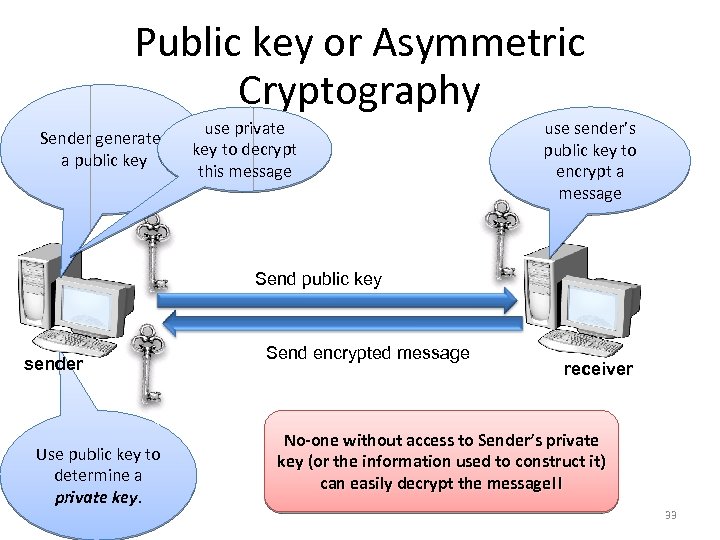 Public key or Asymmetric Cryptography Sender generates a public key use private key to decrypt this message use sender’s public key to encrypt a message Send public key sender Use public key to determine a private key. Send encrypted message receiver No-one without access to Sender’s private key (or the information used to construct it) can easily decrypt the message!! 33
Public key or Asymmetric Cryptography Sender generates a public key use private key to decrypt this message use sender’s public key to encrypt a message Send public key sender Use public key to determine a private key. Send encrypted message receiver No-one without access to Sender’s private key (or the information used to construct it) can easily decrypt the message!! 33
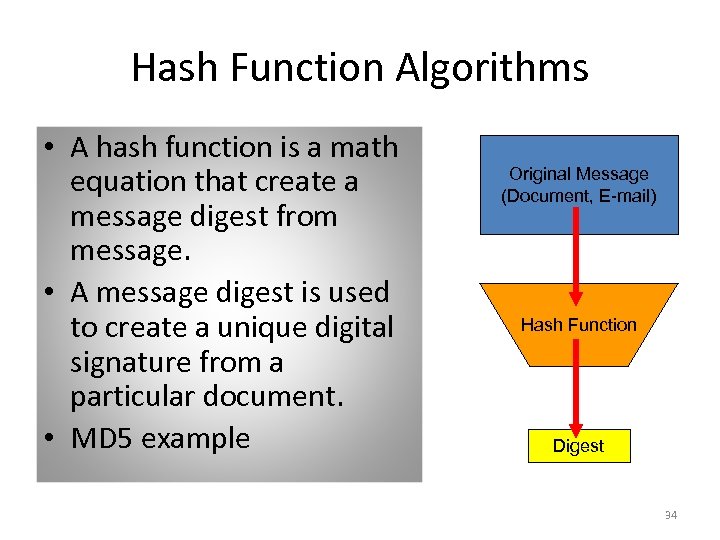 Hash Function Algorithms • A hash function is a math equation that create a message digest from message. • A message digest is used to create a unique digital signature from a particular document. • MD 5 example Original Message (Document, E-mail) Hash Function Digest 34
Hash Function Algorithms • A hash function is a math equation that create a message digest from message. • A message digest is used to create a unique digital signature from a particular document. • MD 5 example Original Message (Document, E-mail) Hash Function Digest 34
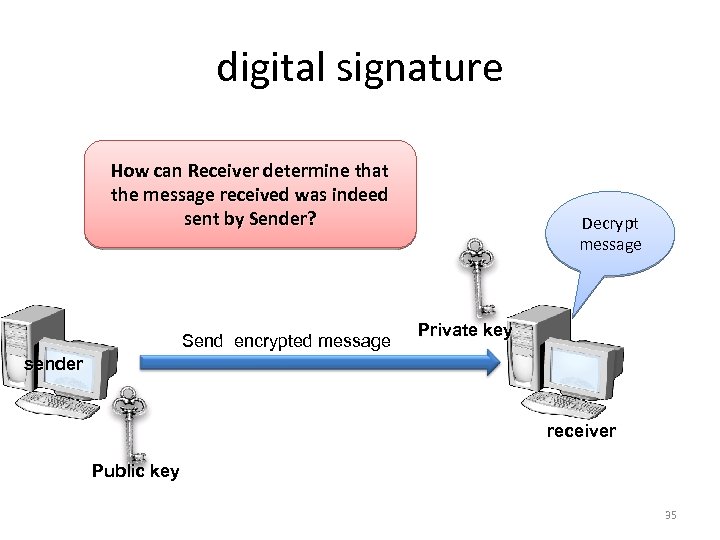 digital signature How can Receiver determine that the message received was indeed sent by Sender? Send encrypted message Decrypt message Private key sender receiver Public key 35
digital signature How can Receiver determine that the message received was indeed sent by Sender? Send encrypted message Decrypt message Private key sender receiver Public key 35
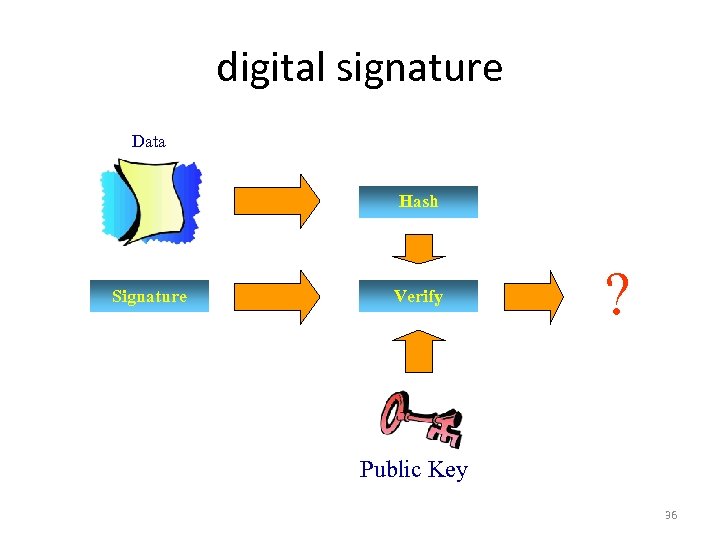 digital signature Data Hash Signature Verify ? Public Key 36
digital signature Data Hash Signature Verify ? Public Key 36
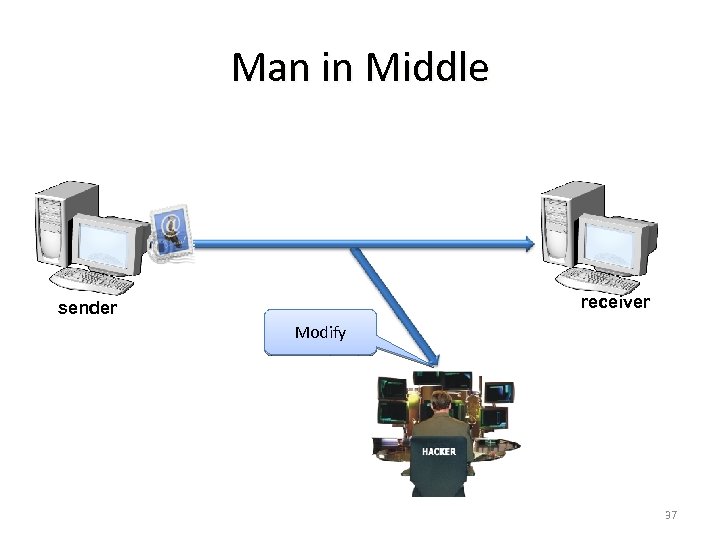 Man in Middle receiver sender Modify 37
Man in Middle receiver sender Modify 37
 Digital certificate • A digital certificate (DC) is a digital file that certifies the identity of an individual or institution, or even a router seeking access to computer- based information. It is issued by a Certification Authority (CA), and serves the same purpose as a driver’s license or a passport 38
Digital certificate • A digital certificate (DC) is a digital file that certifies the identity of an individual or institution, or even a router seeking access to computer- based information. It is issued by a Certification Authority (CA), and serves the same purpose as a driver’s license or a passport 38
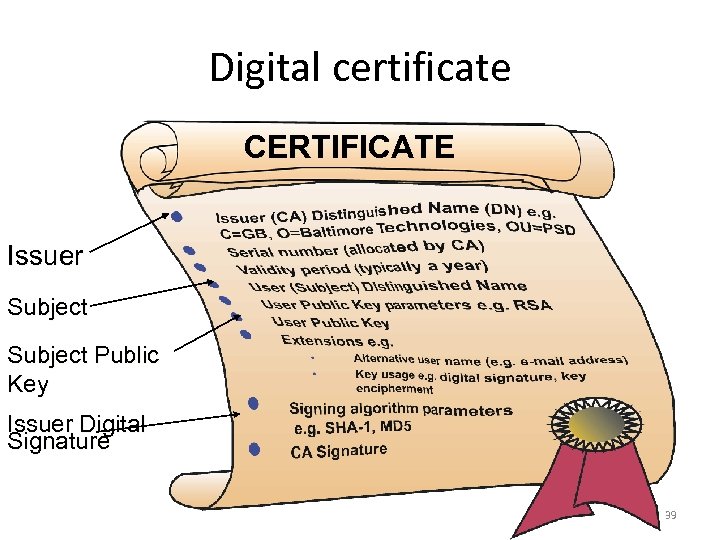 Digital certificate CERTIFICATE Issuer Subject Public Key Issuer Digital Signature 39
Digital certificate CERTIFICATE Issuer Subject Public Key Issuer Digital Signature 39
 Certification Authorities • A trusted agent who certifies public keys for general use (Corporation or Bank). – User has to decide which CAs can be trusted. • The model for key certification based on friends and friends of friends is called “Web of Trust”. – The public key is passing from friend to friend. – Works well in small or high connected worlds. – What if you receive a public key from someone you don’t know? 40
Certification Authorities • A trusted agent who certifies public keys for general use (Corporation or Bank). – User has to decide which CAs can be trusted. • The model for key certification based on friends and friends of friends is called “Web of Trust”. – The public key is passing from friend to friend. – Works well in small or high connected worlds. – What if you receive a public key from someone you don’t know? 40
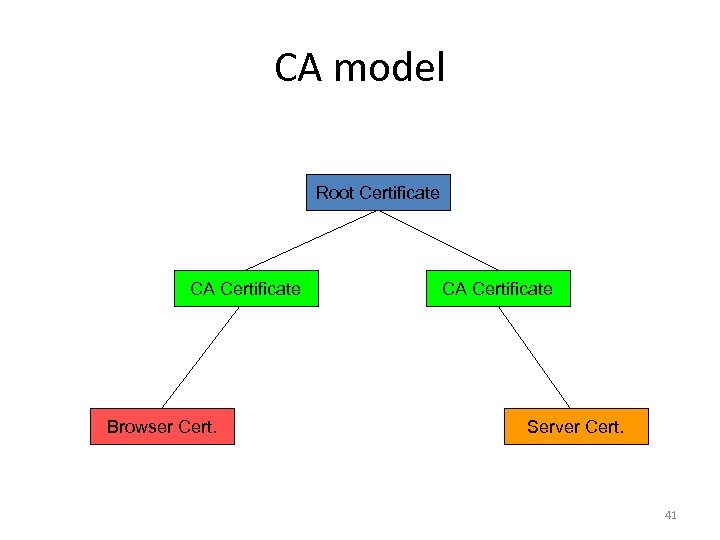 CA model Root Certificate CA Certificate Browser Cert. CA Certificate Server Cert. 41
CA model Root Certificate CA Certificate Browser Cert. CA Certificate Server Cert. 41
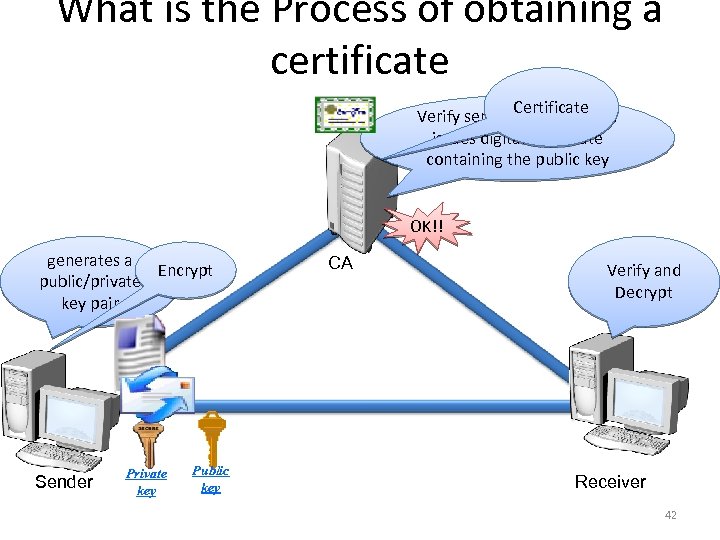 What is the Process of obtaining a certificate Certificate Verify sender’s identity and issues digital certificate containing the public key OK!! generates a Encrypt public/private key pair Sender Private key Public key CA Verify and Decrypt Receiver 42
What is the Process of obtaining a certificate Certificate Verify sender’s identity and issues digital certificate containing the public key OK!! generates a Encrypt public/private key pair Sender Private key Public key CA Verify and Decrypt Receiver 42
 Secure Sockets Layer • Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is used to validate the identities of two computers involved in a connection across a public network, and to ensure that the data sent between the two computers is encrypted • SSL uses digital certificates and public and private keys 43
Secure Sockets Layer • Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is used to validate the identities of two computers involved in a connection across a public network, and to ensure that the data sent between the two computers is encrypted • SSL uses digital certificates and public and private keys 43
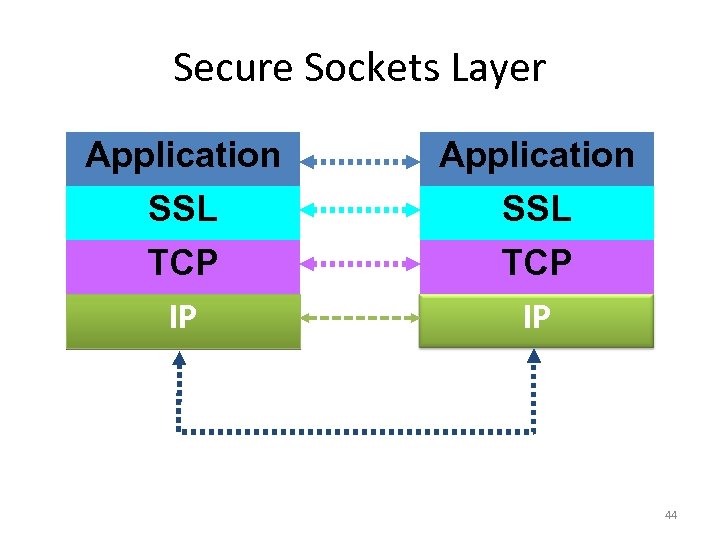 Secure Sockets Layer Application SSL TCP IP 44
Secure Sockets Layer Application SSL TCP IP 44
 Advantages of SSL • Independent of application layer • Includes support for negotiated encryption techniques. – easy to add new techniques. • Possible to switch encryption algorithms in the middle of a session 45
Advantages of SSL • Independent of application layer • Includes support for negotiated encryption techniques. – easy to add new techniques. • Possible to switch encryption algorithms in the middle of a session 45
 HTTPS Usage • HTTPS is HTTP running over SSL. – used for most secure web transactions. – HTTPS server usually runs on port 443. – Include notion of verification of server via a certificate. – Central trusted source of certificates 46
HTTPS Usage • HTTPS is HTTP running over SSL. – used for most secure web transactions. – HTTPS server usually runs on port 443. – Include notion of verification of server via a certificate. – Central trusted source of certificates 46
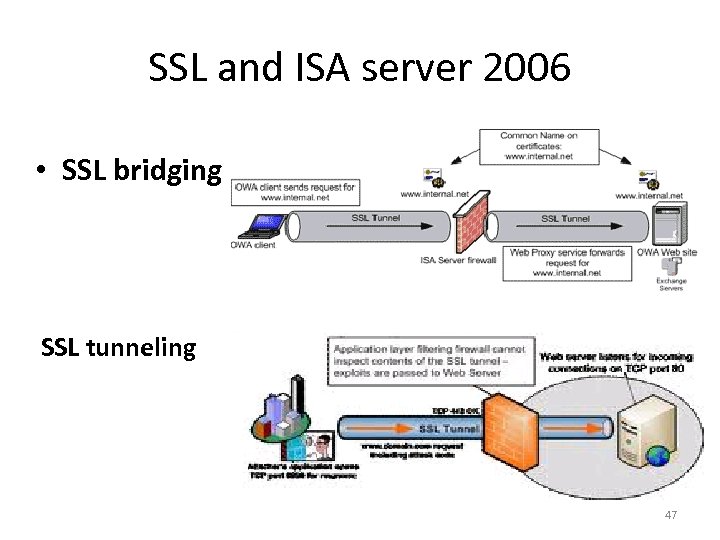 SSL and ISA server 2006 • SSL bridging SSL tunneling 47
SSL and ISA server 2006 • SSL bridging SSL tunneling 47
 Configuring SSL-to-SSL Bridging for Secured Websites • Working with Third. Party Certificate Authorities • Installing a Local Certificate Authority and Using Certificates • Modifying a Rule to Allow for End-to-End SSL Bridging 48
Configuring SSL-to-SSL Bridging for Secured Websites • Working with Third. Party Certificate Authorities • Installing a Local Certificate Authority and Using Certificates • Modifying a Rule to Allow for End-to-End SSL Bridging 48
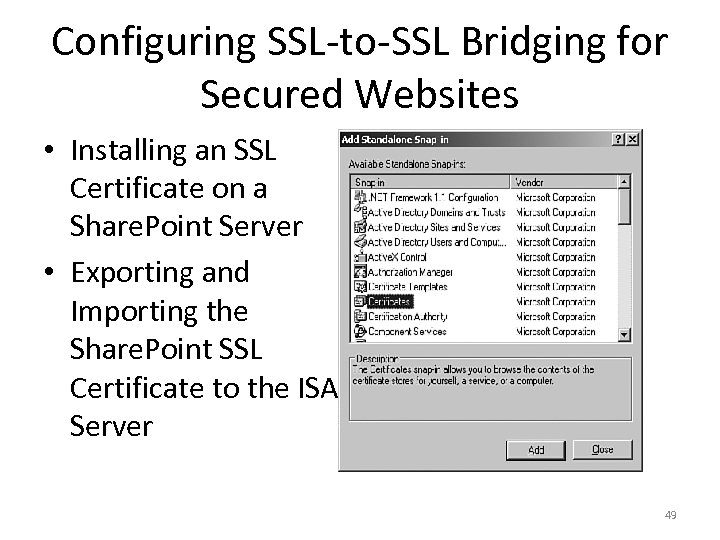 Configuring SSL-to-SSL Bridging for Secured Websites • Installing an SSL Certificate on a Share. Point Server • Exporting and Importing the Share. Point SSL Certificate to the ISA Server 49
Configuring SSL-to-SSL Bridging for Secured Websites • Installing an SSL Certificate on a Share. Point Server • Exporting and Importing the Share. Point SSL Certificate to the ISA Server 49
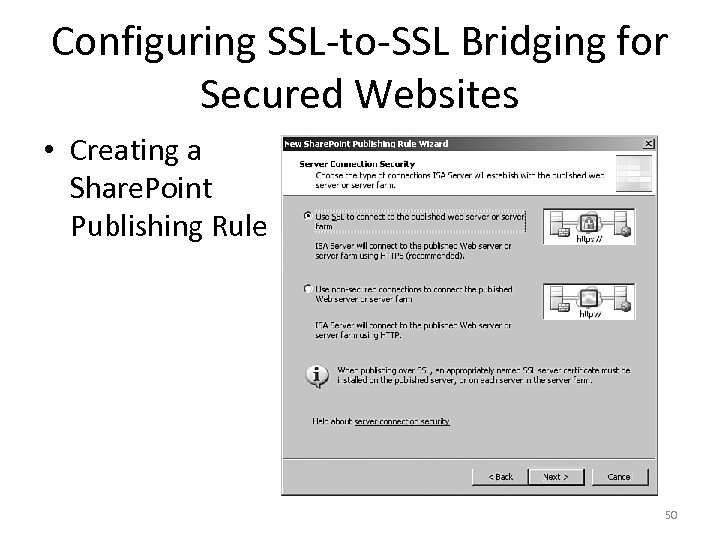 Configuring SSL-to-SSL Bridging for Secured Websites • Creating a Share. Point Publishing Rule 50
Configuring SSL-to-SSL Bridging for Secured Websites • Creating a Share. Point Publishing Rule 50
 Configuring SSL-to-SSL Bridging for Secured Websites • Choosing a certificate for the listener 51
Configuring SSL-to-SSL Bridging for Secured Websites • Choosing a certificate for the listener 51
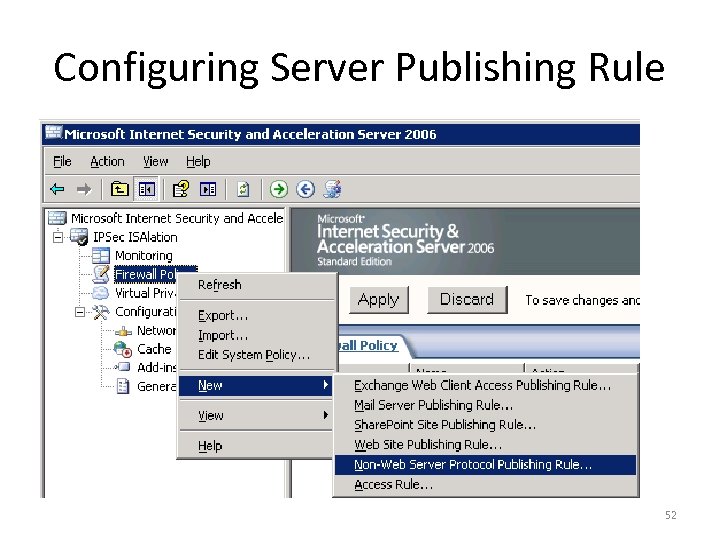 Configuring Server Publishing Rule 52
Configuring Server Publishing Rule 52


