e0a02c6780004804f8e8a6e47c4e1238.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 CONFIDENTIAL Outsourcing – Then , Now & Tomorrow May 2008 The information contained within this document is proprietary to Copal Partners and it reserves the right to all information provided. The recipient agrees not to distribute, share or use any part of the material without express written permission of Copal Partners. The recipient would treat this material as Confidential Information. www. copalpartners. com 1
CONFIDENTIAL Outsourcing – Then , Now & Tomorrow May 2008 The information contained within this document is proprietary to Copal Partners and it reserves the right to all information provided. The recipient agrees not to distribute, share or use any part of the material without express written permission of Copal Partners. The recipient would treat this material as Confidential Information. www. copalpartners. com 1
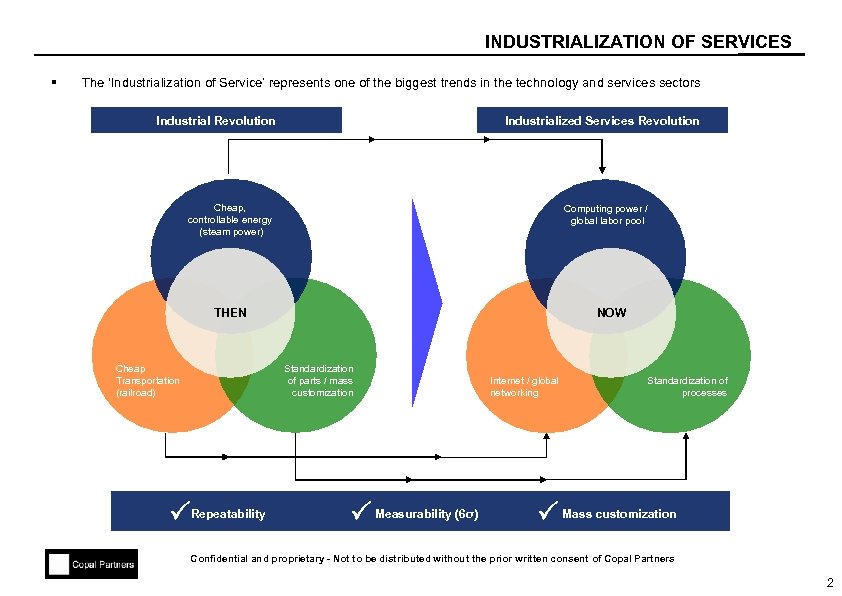 INDUSTRIALIZATION OF SERVICES § The ‘Industrialization of Service’ represents one of the biggest trends in the technology and services sectors Industrial Revolution Industrialized Services Revolution Cheap, controllable energy (steam power) Computing power / global labor pool THEN Cheap Transportation (railroad) NOW Standardization of parts / mass customization Repeatability Measurability (6σ) Internet / global networking Standardization of processes Mass customization Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 2
INDUSTRIALIZATION OF SERVICES § The ‘Industrialization of Service’ represents one of the biggest trends in the technology and services sectors Industrial Revolution Industrialized Services Revolution Cheap, controllable energy (steam power) Computing power / global labor pool THEN Cheap Transportation (railroad) NOW Standardization of parts / mass customization Repeatability Measurability (6σ) Internet / global networking Standardization of processes Mass customization Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 2
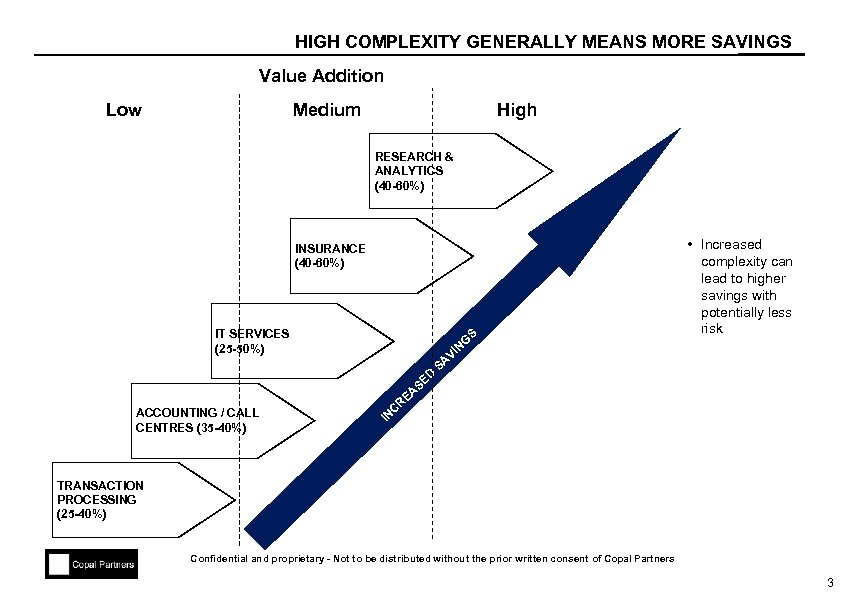 HIGH COMPLEXITY GENERALLY MEANS MORE SAVINGS Value Addition Low Medium High RESEARCH & ANALYTICS (40 -60%) INSURANCE (40 -60%) IT SERVICES (25 -50%) S G IN V D ACCOUNTING / CALL CENTRES (35 -40%) • Increased complexity can lead to higher savings with potentially less risk SE R C IN EA SA TRANSACTION PROCESSING (25 -40%) Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 3
HIGH COMPLEXITY GENERALLY MEANS MORE SAVINGS Value Addition Low Medium High RESEARCH & ANALYTICS (40 -60%) INSURANCE (40 -60%) IT SERVICES (25 -50%) S G IN V D ACCOUNTING / CALL CENTRES (35 -40%) • Increased complexity can lead to higher savings with potentially less risk SE R C IN EA SA TRANSACTION PROCESSING (25 -40%) Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 3
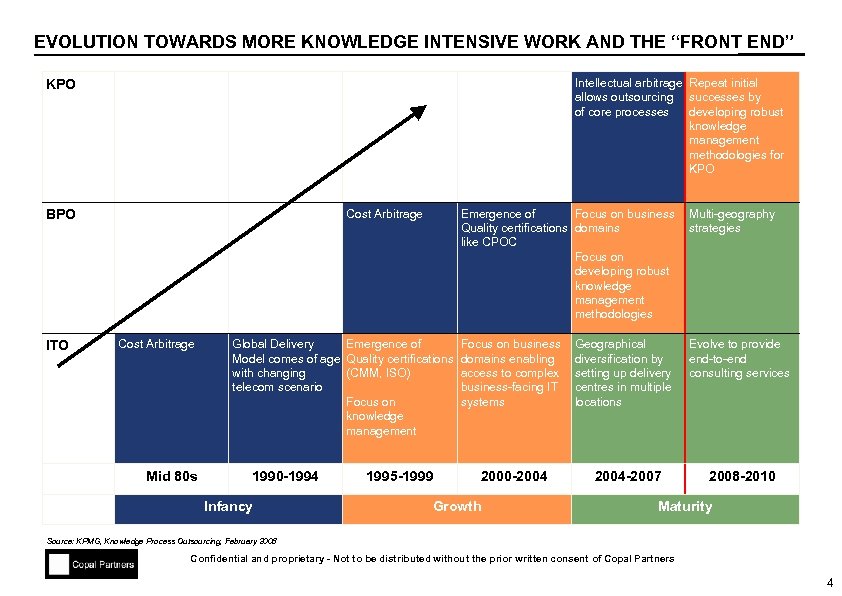 EVOLUTION TOWARDS MORE KNOWLEDGE INTENSIVE WORK AND THE “FRONT END” Intellectual arbitrage Repeat initial allows outsourcing successes by of core processes developing robust knowledge management methodologies for KPO Cost Arbitrage BPO ITO Cost Arbitrage Mid 80 s Emergence of Focus on business Quality certifications domains like CPOC Focus on developing robust knowledge management methodologies Global Delivery Emergence of Model comes of age Quality certifications with changing (CMM, ISO) telecom scenario Focus on knowledge management 1990 -1994 Infancy 1995 -1999 Multi-geography strategies Focus on business domains enabling access to complex business-facing IT systems Evolve to provide end-to-end consulting services 2000 -2004 Growth Geographical diversification by setting up delivery centres in multiple locations 2004 -2007 2008 -2010 Maturity Source: KPMG, Knowledge Process Outsourcing, February 2008 Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 4
EVOLUTION TOWARDS MORE KNOWLEDGE INTENSIVE WORK AND THE “FRONT END” Intellectual arbitrage Repeat initial allows outsourcing successes by of core processes developing robust knowledge management methodologies for KPO Cost Arbitrage BPO ITO Cost Arbitrage Mid 80 s Emergence of Focus on business Quality certifications domains like CPOC Focus on developing robust knowledge management methodologies Global Delivery Emergence of Model comes of age Quality certifications with changing (CMM, ISO) telecom scenario Focus on knowledge management 1990 -1994 Infancy 1995 -1999 Multi-geography strategies Focus on business domains enabling access to complex business-facing IT systems Evolve to provide end-to-end consulting services 2000 -2004 Growth Geographical diversification by setting up delivery centres in multiple locations 2004 -2007 2008 -2010 Maturity Source: KPMG, Knowledge Process Outsourcing, February 2008 Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 4
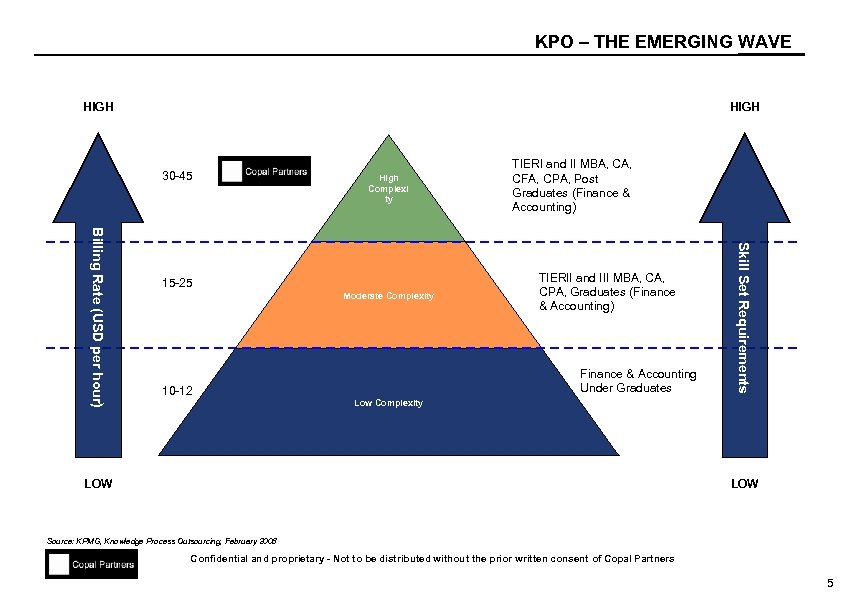 KPO – THE EMERGING WAVE HIGH 30 -45 High Complexi ty Moderate Complexity TIERII and III MBA, CPA, Graduates (Finance & Accounting) Finance & Accounting Under Graduates 10 -12 Skill Set Requirements Billing Rate (USD per hour) 15 -25 TIERI and II MBA, CFA, CPA, Post Graduates (Finance & Accounting) Low Complexity LOW Source: KPMG, Knowledge Process Outsourcing, February 2008 Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 5
KPO – THE EMERGING WAVE HIGH 30 -45 High Complexi ty Moderate Complexity TIERII and III MBA, CPA, Graduates (Finance & Accounting) Finance & Accounting Under Graduates 10 -12 Skill Set Requirements Billing Rate (USD per hour) 15 -25 TIERI and II MBA, CFA, CPA, Post Graduates (Finance & Accounting) Low Complexity LOW Source: KPMG, Knowledge Process Outsourcing, February 2008 Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 5
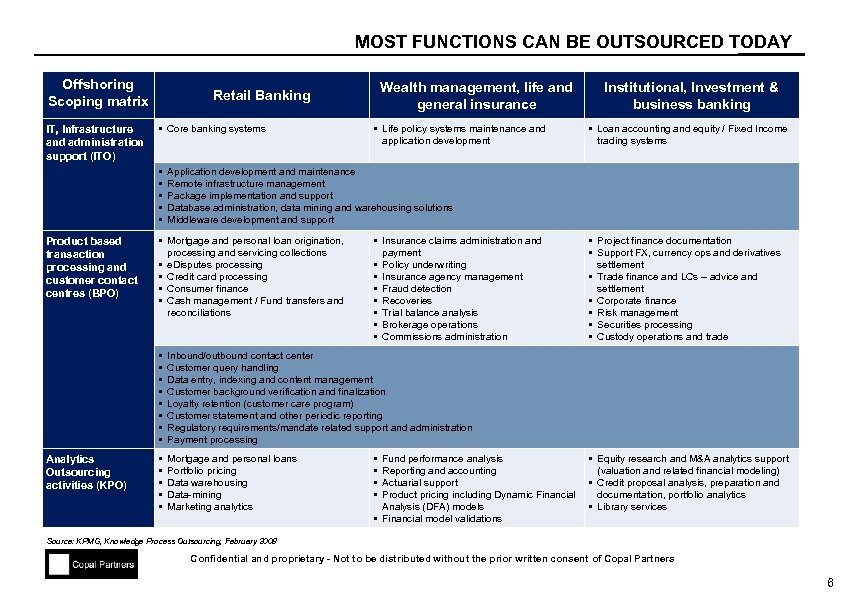 MOST FUNCTIONS CAN BE OUTSOURCED TODAY Offshoring Scoping matrix IT, Infrastructure and administration support (ITO) § Core banking systems § § § Product based transaction processing and customer contact centres (BPO) Wealth management, life and general insurance Retail Banking § Life policy systems maintenance and application development § Loan accounting and equity / Fixed Income trading systems Application development and maintenance Remote infrastructure management Package implementation and support Database administration, data mining and warehousing solutions Middleware development and support § Mortgage and personal loan origination, processing and servicing collections § e. Disputes processing § Credit card processing § Consumer finance § Cash management / Fund transfers and reconciliations § Insurance claims administration and payment § Policy underwriting § Insurance agency management § Fraud detection § Recoveries § Trial balance analysis § Brokerage operations § Commissions administration § § § § Analytics Outsourcing activities (KPO) Institutional, Investment & business banking Inbound/outbound contact center Customer query handling Data entry, indexing and content management Customer background verification and finalization Loyalty retention (customer care program) Customer statement and other periodic reporting Regulatory requirements/mandate related support and administration Payment processing § § § Mortgage and personal loans Portfolio pricing Data warehousing Data-mining Marketing analytics § Project finance documentation § Support FX, currency ops and derivatives settlement § Trade finance and LCs – advice and settlement § Corporate finance § Risk management § Securities processing § Custody operations and trade § § Fund performance analysis Reporting and accounting Actuarial support Product pricing including Dynamic Financial Analysis (DFA) models § Financial model validations § Equity research and M&A analytics support (valuation and related financial modeling) § Credit proposal analysis, preparation and documentation, portfolio analytics § Library services Source: KPMG, Knowledge Process Outsourcing, February 2008 Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 6
MOST FUNCTIONS CAN BE OUTSOURCED TODAY Offshoring Scoping matrix IT, Infrastructure and administration support (ITO) § Core banking systems § § § Product based transaction processing and customer contact centres (BPO) Wealth management, life and general insurance Retail Banking § Life policy systems maintenance and application development § Loan accounting and equity / Fixed Income trading systems Application development and maintenance Remote infrastructure management Package implementation and support Database administration, data mining and warehousing solutions Middleware development and support § Mortgage and personal loan origination, processing and servicing collections § e. Disputes processing § Credit card processing § Consumer finance § Cash management / Fund transfers and reconciliations § Insurance claims administration and payment § Policy underwriting § Insurance agency management § Fraud detection § Recoveries § Trial balance analysis § Brokerage operations § Commissions administration § § § § Analytics Outsourcing activities (KPO) Institutional, Investment & business banking Inbound/outbound contact center Customer query handling Data entry, indexing and content management Customer background verification and finalization Loyalty retention (customer care program) Customer statement and other periodic reporting Regulatory requirements/mandate related support and administration Payment processing § § § Mortgage and personal loans Portfolio pricing Data warehousing Data-mining Marketing analytics § Project finance documentation § Support FX, currency ops and derivatives settlement § Trade finance and LCs – advice and settlement § Corporate finance § Risk management § Securities processing § Custody operations and trade § § Fund performance analysis Reporting and accounting Actuarial support Product pricing including Dynamic Financial Analysis (DFA) models § Financial model validations § Equity research and M&A analytics support (valuation and related financial modeling) § Credit proposal analysis, preparation and documentation, portfolio analytics § Library services Source: KPMG, Knowledge Process Outsourcing, February 2008 Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 6
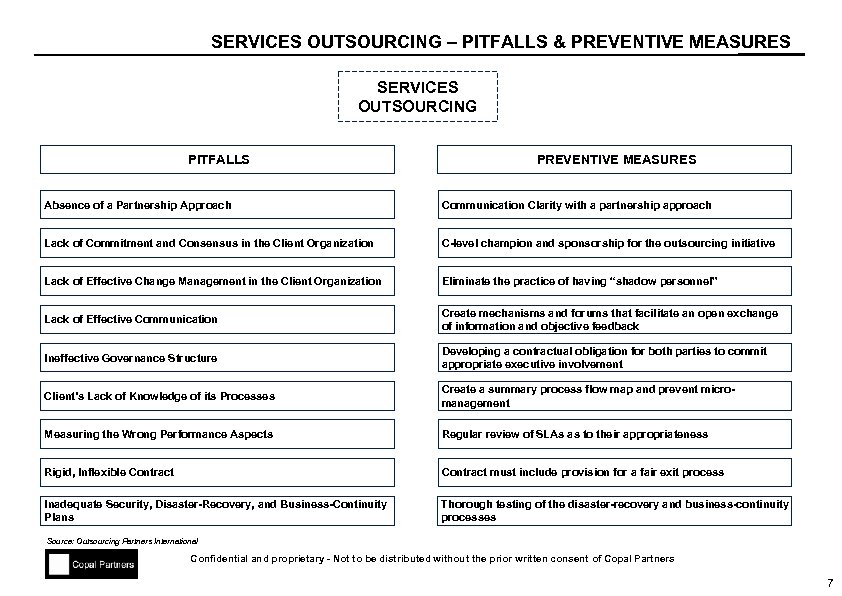 SERVICES OUTSOURCING – PITFALLS & PREVENTIVE MEASURES SERVICES OUTSOURCING PITFALLS PREVENTIVE MEASURES Absence of a Partnership Approach Communication Clarity with a partnership approach Lack of Commitment and Consensus in the Client Organization C-level champion and sponsorship for the outsourcing initiative Lack of Effective Change Management in the Client Organization Eliminate the practice of having “shadow personnel” Lack of Effective Communication Create mechanisms and forums that facilitate an open exchange of information and objective feedback Ineffective Governance Structure Developing a contractual obligation for both parties to commit appropriate executive involvement Client’s Lack of Knowledge of its Processes Create a summary process flow map and prevent micromanagement Measuring the Wrong Performance Aspects Regular review of SLAs as to their appropriateness Rigid, Inflexible Contract must include provision for a fair exit process Inadequate Security, Disaster-Recovery, and Business-Continuity Plans Thorough testing of the disaster-recovery and business-continuity processes Source: Outsourcing Partners International Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 7
SERVICES OUTSOURCING – PITFALLS & PREVENTIVE MEASURES SERVICES OUTSOURCING PITFALLS PREVENTIVE MEASURES Absence of a Partnership Approach Communication Clarity with a partnership approach Lack of Commitment and Consensus in the Client Organization C-level champion and sponsorship for the outsourcing initiative Lack of Effective Change Management in the Client Organization Eliminate the practice of having “shadow personnel” Lack of Effective Communication Create mechanisms and forums that facilitate an open exchange of information and objective feedback Ineffective Governance Structure Developing a contractual obligation for both parties to commit appropriate executive involvement Client’s Lack of Knowledge of its Processes Create a summary process flow map and prevent micromanagement Measuring the Wrong Performance Aspects Regular review of SLAs as to their appropriateness Rigid, Inflexible Contract must include provision for a fair exit process Inadequate Security, Disaster-Recovery, and Business-Continuity Plans Thorough testing of the disaster-recovery and business-continuity processes Source: Outsourcing Partners International Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 7
 SERVICES OUTSOURCING – CONTRACTUAL ISSUES Transferring analytics business processes to an external provider is a complex process that involves transitioning high-value data and knowledge about a company's internal plans and objectives. For this reason, contractual issues relating to extensive due diligence on privacy laws pertaining to that country, security & confidentiality aspects, and planning & documentation of knowledge–transfer processes become absolutely critical Competitive Pricing Change Control § One of the biggest challenges in an outsourcing contract is to ensure that the customer continues to obtain the level of service it requires at a competitive price § Given the dynamic nature of business requirements and the time taken to negotiate an outsourcing contract, a signed contract may not reflect all of the customer’s original requirements & additional ones – Given the length of some outsourcing contracts, what starts out as a competitively priced contract may not remain the same. Contracts must therefore be drafted to effectively manage this risk – Therefore, outsourcing contracts need to comprise of a control mechanism which would contain procedures for proposing and accepting changes, as well as an escalation process for resolving disputes Data Protection § Data protection and related issues of security have always been areas of concern for companies considering outsourcing – Solutions to this issue include negotiations of any gaps between the solution offered by the supplier and what the customer believes is appropriate security for its needs Termination § Both parties in an Outsourcing contract need to draft an effective exit strategy to avoid the possibility of being tied into an unfavorable outsourcing deal. Reasons why a party might want to terminate an outsourcing contract include: – Material breach by the other party – Insolvency, winding up or change of control of the other party – Right for the buyer to terminate for convenience, where there is no fault on the part of the supplier Source: Gartner 2007, Copal Analysis Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 8
SERVICES OUTSOURCING – CONTRACTUAL ISSUES Transferring analytics business processes to an external provider is a complex process that involves transitioning high-value data and knowledge about a company's internal plans and objectives. For this reason, contractual issues relating to extensive due diligence on privacy laws pertaining to that country, security & confidentiality aspects, and planning & documentation of knowledge–transfer processes become absolutely critical Competitive Pricing Change Control § One of the biggest challenges in an outsourcing contract is to ensure that the customer continues to obtain the level of service it requires at a competitive price § Given the dynamic nature of business requirements and the time taken to negotiate an outsourcing contract, a signed contract may not reflect all of the customer’s original requirements & additional ones – Given the length of some outsourcing contracts, what starts out as a competitively priced contract may not remain the same. Contracts must therefore be drafted to effectively manage this risk – Therefore, outsourcing contracts need to comprise of a control mechanism which would contain procedures for proposing and accepting changes, as well as an escalation process for resolving disputes Data Protection § Data protection and related issues of security have always been areas of concern for companies considering outsourcing – Solutions to this issue include negotiations of any gaps between the solution offered by the supplier and what the customer believes is appropriate security for its needs Termination § Both parties in an Outsourcing contract need to draft an effective exit strategy to avoid the possibility of being tied into an unfavorable outsourcing deal. Reasons why a party might want to terminate an outsourcing contract include: – Material breach by the other party – Insolvency, winding up or change of control of the other party – Right for the buyer to terminate for convenience, where there is no fault on the part of the supplier Source: Gartner 2007, Copal Analysis Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 8
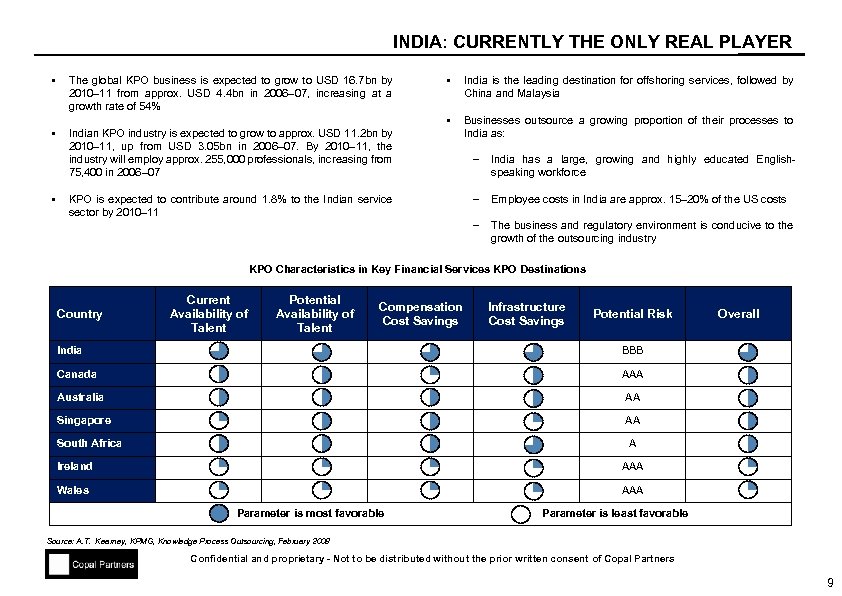 INDIA: CURRENTLY THE ONLY REAL PLAYER § § § India is the leading destination for offshoring services, followed by China and Malaysia § The global KPO business is expected to grow to USD 16. 7 bn by 2010– 11 from approx. USD 4. 4 bn in 2006– 07, increasing at a growth rate of 54% Businesses outsource a growing proportion of their processes to India as: Indian KPO industry is expected to grow to approx. USD 11. 2 bn by 2010– 11, up from USD 3. 05 bn in 2006– 07. By 2010– 11, the industry will employ approx. 255, 000 professionals, increasing from 75, 400 in 2006– 07 KPO is expected to contribute around 1. 8% to the Indian service sector by 2010– 11 India has a large, growing and highly educated Englishspeaking workforce – Employee costs in India are approx. 15– 20% of the US costs – § – The business and regulatory environment is conducive to the growth of the outsourcing industry KPO Characteristics in Key Financial Services KPO Destinations Country Current Availability of Talent Potential Availability of Talent Compensation Cost Savings Infrastructure Cost Savings Potential Risk India BBB Canada Overall AAA Australia AA Singapore AA South Africa A Ireland AAA Wales AAA Parameter is most favorable Parameter is least favorable Source: A. T. Kearney, KPMG, Knowledge Process Outsourcing, February 2008 Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 9
INDIA: CURRENTLY THE ONLY REAL PLAYER § § § India is the leading destination for offshoring services, followed by China and Malaysia § The global KPO business is expected to grow to USD 16. 7 bn by 2010– 11 from approx. USD 4. 4 bn in 2006– 07, increasing at a growth rate of 54% Businesses outsource a growing proportion of their processes to India as: Indian KPO industry is expected to grow to approx. USD 11. 2 bn by 2010– 11, up from USD 3. 05 bn in 2006– 07. By 2010– 11, the industry will employ approx. 255, 000 professionals, increasing from 75, 400 in 2006– 07 KPO is expected to contribute around 1. 8% to the Indian service sector by 2010– 11 India has a large, growing and highly educated Englishspeaking workforce – Employee costs in India are approx. 15– 20% of the US costs – § – The business and regulatory environment is conducive to the growth of the outsourcing industry KPO Characteristics in Key Financial Services KPO Destinations Country Current Availability of Talent Potential Availability of Talent Compensation Cost Savings Infrastructure Cost Savings Potential Risk India BBB Canada Overall AAA Australia AA Singapore AA South Africa A Ireland AAA Wales AAA Parameter is most favorable Parameter is least favorable Source: A. T. Kearney, KPMG, Knowledge Process Outsourcing, February 2008 Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 9
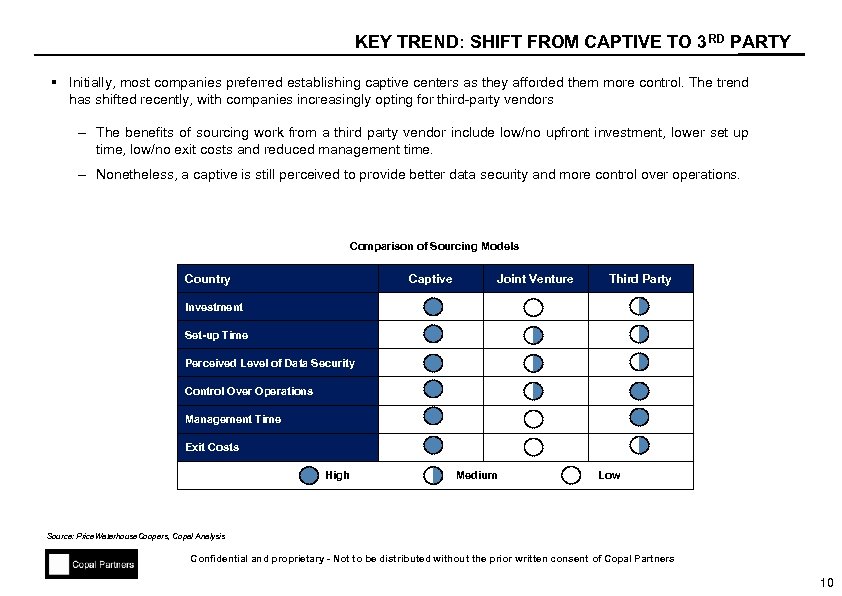 KEY TREND: SHIFT FROM CAPTIVE TO 3 RD PARTY § Initially, most companies preferred establishing captive centers as they afforded them more control. The trend has shifted recently, with companies increasingly opting for third-party vendors – The benefits of sourcing work from a third party vendor include low/no upfront investment, lower set up time, low/no exit costs and reduced management time. – Nonetheless, a captive is still perceived to provide better data security and more control over operations. Comparison of Sourcing Models Country Captive Joint Venture Third Party Investment Set-up Time Perceived Level of Data Security Control Over Operations Management Time Exit Costs High Medium Low Source: Price. Waterhouse. Coopers, Copal Analysis Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 10
KEY TREND: SHIFT FROM CAPTIVE TO 3 RD PARTY § Initially, most companies preferred establishing captive centers as they afforded them more control. The trend has shifted recently, with companies increasingly opting for third-party vendors – The benefits of sourcing work from a third party vendor include low/no upfront investment, lower set up time, low/no exit costs and reduced management time. – Nonetheless, a captive is still perceived to provide better data security and more control over operations. Comparison of Sourcing Models Country Captive Joint Venture Third Party Investment Set-up Time Perceived Level of Data Security Control Over Operations Management Time Exit Costs High Medium Low Source: Price. Waterhouse. Coopers, Copal Analysis Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 10
 KEY TREND: SHIFT FROM CAPTIVE TO 3 RD PARTY (cont) § There has been gradual shift in the sourcing model from establishment of captive units to joint ventures or third party outsourcing § HCL Technologies, a member of the USD 740 mn HCL Group, formed a joint venture with Deutsche Bank AG by acquiring a 51% stake in the holding company of Deutsche Software, Deutsche Bank's IT services subsidiary in India § The call center operations of AOL were recently acquired by Aegis BPO, the business process outsourcing company of the USD 50 bn Essar Group in India. Aegis BPO will take over customer service and technical support, both voice-based and non-voice, for AOL s customers § The Genpact transition is the subject of considerable interest in the outsourcing world. The company moved to a third party operation from a captive model. Genpact began in 1997 as the India-based business process services operation for GE Capital. In 2004, GE Capital divested 60 per cent of its stake in its BPO arm to General Atlantic and Oak Hill Capital Partners at an estimated price of USD 500 mn Source: Gartner 2007, Copal Analysis Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 11
KEY TREND: SHIFT FROM CAPTIVE TO 3 RD PARTY (cont) § There has been gradual shift in the sourcing model from establishment of captive units to joint ventures or third party outsourcing § HCL Technologies, a member of the USD 740 mn HCL Group, formed a joint venture with Deutsche Bank AG by acquiring a 51% stake in the holding company of Deutsche Software, Deutsche Bank's IT services subsidiary in India § The call center operations of AOL were recently acquired by Aegis BPO, the business process outsourcing company of the USD 50 bn Essar Group in India. Aegis BPO will take over customer service and technical support, both voice-based and non-voice, for AOL s customers § The Genpact transition is the subject of considerable interest in the outsourcing world. The company moved to a third party operation from a captive model. Genpact began in 1997 as the India-based business process services operation for GE Capital. In 2004, GE Capital divested 60 per cent of its stake in its BPO arm to General Atlantic and Oak Hill Capital Partners at an estimated price of USD 500 mn Source: Gartner 2007, Copal Analysis Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 11
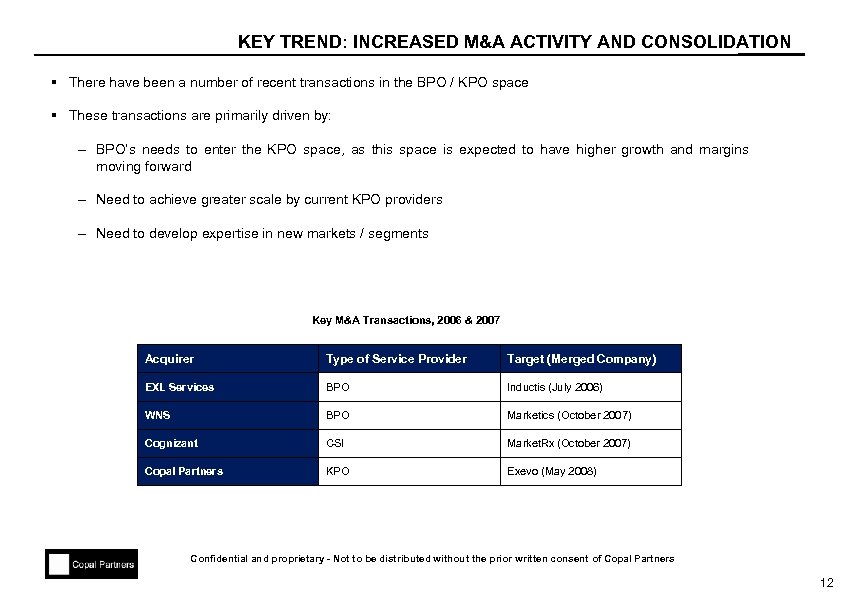 KEY TREND: INCREASED M&A ACTIVITY AND CONSOLIDATION § There have been a number of recent transactions in the BPO / KPO space § These transactions are primarily driven by: – BPO’s needs to enter the KPO space, as this space is expected to have higher growth and margins moving forward – Need to achieve greater scale by current KPO providers – Need to develop expertise in new markets / segments Key M&A Transactions, 2006 & 2007 Acquirer Type of Service Provider Target (Merged Company) EXL Services BPO Inductis (July 2006) WNS BPO Marketics (October 2007) Cognizant CSI Market. Rx (October 2007) Copal Partners KPO Exevo (May 2008) Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 12
KEY TREND: INCREASED M&A ACTIVITY AND CONSOLIDATION § There have been a number of recent transactions in the BPO / KPO space § These transactions are primarily driven by: – BPO’s needs to enter the KPO space, as this space is expected to have higher growth and margins moving forward – Need to achieve greater scale by current KPO providers – Need to develop expertise in new markets / segments Key M&A Transactions, 2006 & 2007 Acquirer Type of Service Provider Target (Merged Company) EXL Services BPO Inductis (July 2006) WNS BPO Marketics (October 2007) Cognizant CSI Market. Rx (October 2007) Copal Partners KPO Exevo (May 2008) Confidential and proprietary - Not to be distributed without the prior written consent of Copal Partners 12


